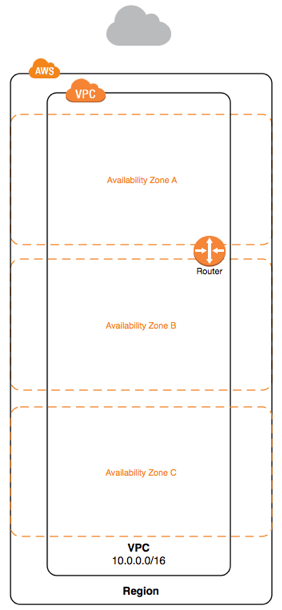
VPC
Virtual Private Cloud
AWS Architecture Overview
What is a VPC
- Logically, a VPC is your datacentre in the cloud
- Complete control over network i.e. ip addresses and subnets
- A VPC spans availability zones but not Regions
- VPCs can contain multiple subnets
- EC2 instances are launched inside a VPC
- They can be 'peered' with other VPCs to allow for communication without going over the internet. Transitive peering is not allowed
- ie. A -> B | B -> C | A !-> C
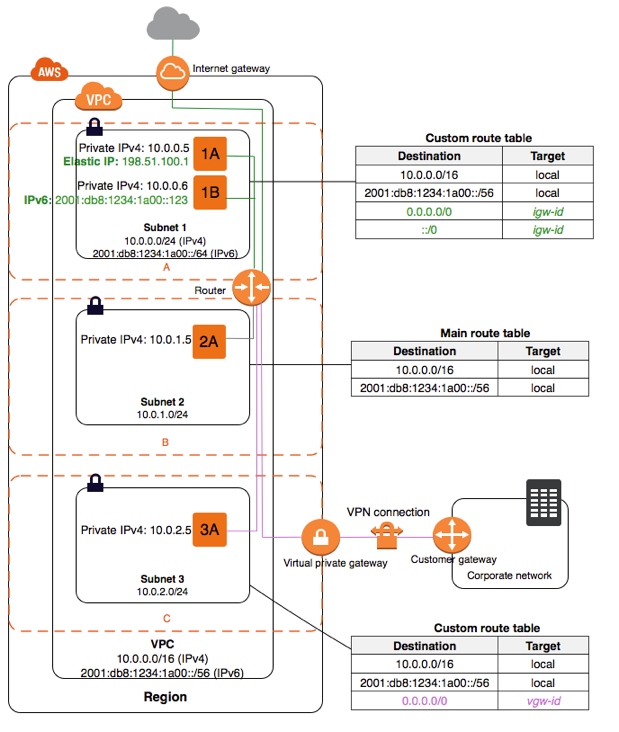
Internet Gateway
- Allows for communication between the VPC and the internet
- Used as a target by route tables
- The scope of traffic through an internet gateway can be configured to certain IP addresses or allow all
Subnet
- A subnet is a part of a larger network, in this case, a VPC
- Subnets cannot span availability zones
- If a subnet doesn't have a route to the VPCs internet gateway, then it is a private subnet.
- If a subnets traffic is routed to an internet gateway, then its a public subnet
- In order for instances in the public subnet to accept traffic, they must also be assigned an elastic IP address
- If a subnet has its traffic routed to a virtual private gateway, then it is a VPN only subnet
VPC and Subnet Sizing
- The size of a VPC cant be changed after its been created, it can contain between 16 to 65,536 IP addresses
- The CIDR block of a subnet can be the same as the VPC (for single subnet in the VPC) or smaller, for a subsection (for multiple subnets)
NAT
- If we have configured security for our private subnet correctly, we will have no outbound or inbound access to / from the internet
- This makes installing software / configuring packages impossible
- NAT allows us to safely access the internet from our instances in our private subnet
- NAT hides the source of traffic, making all outbound requests appear as if they're coming from the NAT itself
NAT Instance
- EC2 Instance managed by the user
- Must run in a public subnet
- Internet traffic from the private subnet is routed through this instance via routing tables
- Remember to disable source / destination check
NAT Gateway
- Service provided by AWS
- Internet traffic is routed through the gateway via routing tables
- No maintenance is required by the user, all managed my EC2
Access
Security Groups
- Applied at an Instance level
- Whitelist only (allow)
- Stateful (return traffic automatically allowed)
- All rules are evaluated
- Applies to an instance in a security group if that security group is applied
Network ACLs
- Operates at a subnet level
- Black & White list (Allow & deny rules)
- Stateful (return traffic must be explicitly allowed)
- Automatically applied to all instances in a subnet
Elastic Load Balancers
- Application load balancer
- Layer 7 load balancer
- Makes decisions at the application layer (http[s])
- Supports path based routing
- Can route to different ports on the same EC2 instance
- Classic load balancer
- Layer 4 load balancer
- Makes decisions at the TCP / SSL layer
Bastion Server
- A hardened server allowing SSH or RDP connections from the outside world
- Used as a jumpbox to access private resources. Our private resources can be configured to allow access from only our bastion server
- Typically very secure in terms of who it will allow incoming connections from