Android Project 1: Intro
Intro to Java / Kotlin
Every Class is going to be a Story!
Evolution

Java / Kotlin
Converted to ⬇️
Binary (0s and 1s)
Early days of Programming till 1950s
0100 1001 0001 0000This instruction tells the computer to add the contents of memory location 1 to the contents of memory location 0 and store the result in memory location 2.
ADD 1,0,20100 1001 0001 0000This instruction tells the computer to add the contents of memory location 1 to the contents of memory location 0 and store the result in memory location 2.
Machine Language
Assembly Language
| Year | Event |
|---|---|
| 1946 | The first electronic digital computer, the Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer (ENIAC), is built. It is programmed using machine language. |
| 1950s | Assembly language is developed. |
| 1960s | High-level programming languages are developed, such as FORTRAN and COBOL. These languages are easier to use than assembly language, but they are not as efficient. |
| 1970s | The microprocessor is invented. This makes it possible to build smaller and more affordable computers. |
| 1980s | Personal computers become popular. Assembly language is still used for some low-level programming tasks, but high-level languages are becoming more common. |
| 1990s | The internet becomes popular. This leads to the development of new programming languages, such as Java and Python. |
| 2000s | Cloud computing and mobile computing become popular. This leads to the development of new programming languages, such as Swift and Kotlin. |
| 2020s | The development of artificial intelligence and machine learning is driving the development of new programming languages. |
Trend
More Code to Less Code
Hello World
class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello, World!");
}
}https://www.programiz.com/java-programming/online-compiler/
object Driver {
@JvmStatic
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
println("Hello World")
}
}
Important Concepts
Important Concepts
Primitive Data Types
Int
Char
String
Primitive Data Types
Int
Char
String
Array
Problem:
Harder to store data in just Primitive Data Types
Solution
1. Creating Objects using Primite Data Types
Object {
name: "Harnoor"
age: 25
DOB: "12/12/2000"
}
Objects
Hold data
Employee empl1 = new Employee("Harry", 25,1947))
Employee empl1 = new Employee("Harry", 25,1947))
Static keyword Significance
These variables are shared among all instances (objects) of the class
Static keyword Significance
example: static final double PI = 3.14159; in Kotlin-> val PI: Double = 3.14159
1. saves memory
2. Usage -> Class.staticname
3. one value and consisten
Python vs Java
# hello.py
print("Hello, World!")
python3 hello.py
Python vs Java
# hello.py
print("Hello, World!")
# hello.py
print("Hello, World!")
java ->
javac file.java
java file
builds the compile code (Whole unit gets run vs line by line)
Kotlin vs Java
Which is faster?
Java or Kotlin?
Answer: We need both as both compile to JVM and Kotlin and Java are used interchangeable
Java / Kotlin
⬇️
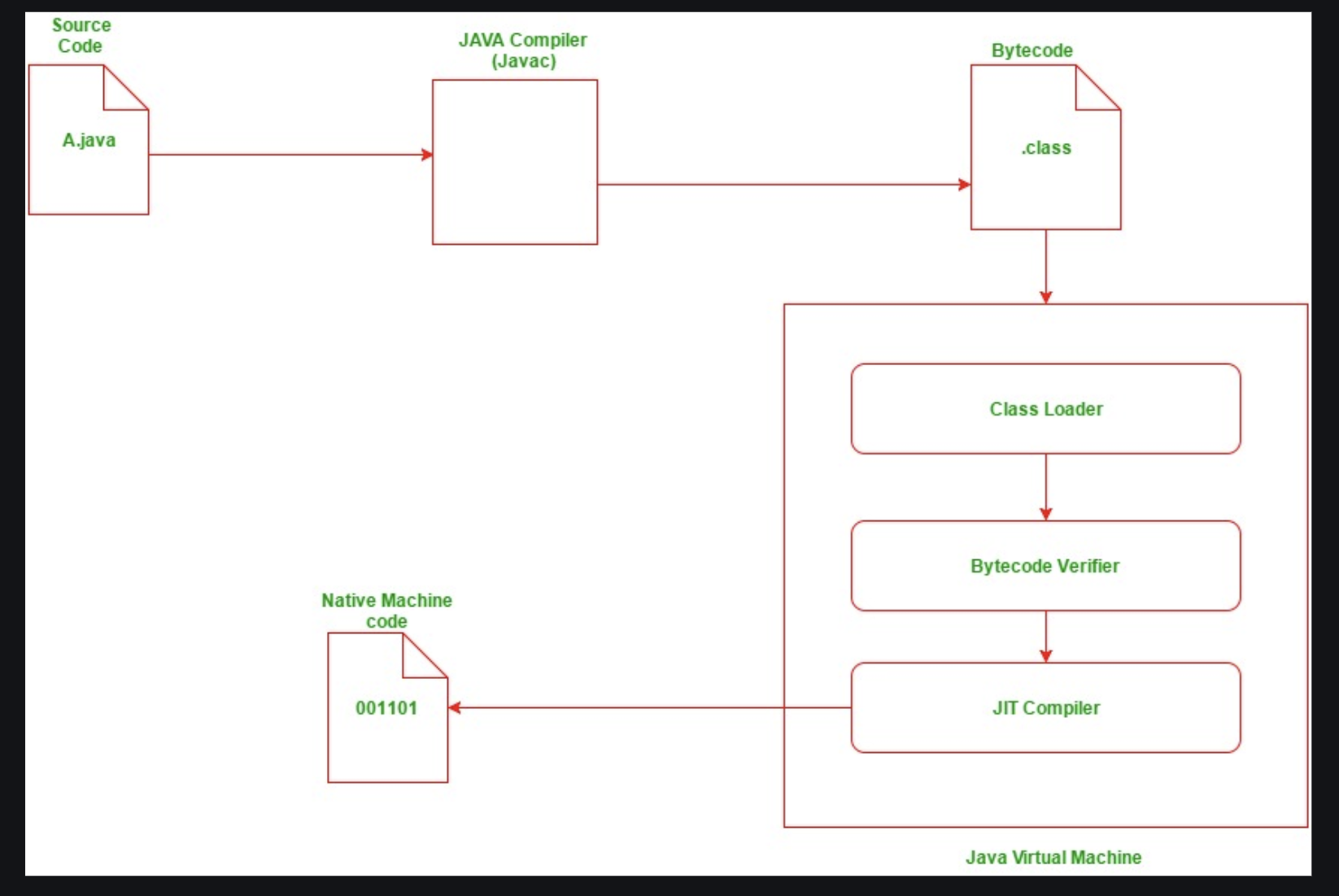
JVM
Byte Code: 0s or 1s
Slow Down Harnoor
Reminding myself
Why Object in Kotlin?
Class can have one driver
- Object -> executed when program starts
- No Constructor
- Static-Like Behavior
Keywords in Java
for, while, class, private etc
cannot be used as variable / class / object Names
Inheritance
- Don't reinvent the wheel
- Parent -> Child class
- Child is become meta class (meta means more than before)
- So easy to add features
Encapsulation
Encapsulation
code looks clean when can be accessed by
object.function()
as you know the operations possible easily
Polymorphism
Object having multiple forms
Employee employee1 = new Contractor("John", "Contractor", 123);
Employee employee2 = new Intern("Smith", "Full Time", 456);
Employee employee3 = new FullTime("Sara", "Intern", 789);
Declarative vs Imperative
SQL vs Java
SELECT * FROM customers WHERE state = 'CA';
public String getCustomers() {
return "Customer1"
}Java Objects
Employee employee1 = new Employee("Harnoor",25,"12/12/2000")
Problem:
public static void printEmployeeSalary(Employee employee){
if (employee.employeeType.equals("Contractor")) {
System.out.println("Contractor Salary: $100,000");
} else if (employee.employeeType.equals("Full Time")) {
System.out.println("Full Time Salary: $150,000");
} else if (employee.employeeType.equals("Intern")) {
System.out.println("Intern Salary: $50,000");
}
}Let's Implement together 2 mins break
Solution of Messy If statements / Switch
Object Oriened Programming:
1. Inheritance
2. Polymorphism
3. Abstraction
Refer: Week 1 repo
github.com/iHarnoor/Week1Android
Homework Discussion
Reviewing PR
Android Revision (week2)
Constraint Layout
ImageView
Button Click
Compile-Time vs Run-Time Error
Which is Better?
lateinit var vs null object
| Initialization | Property is uninitialized until explicitly initialized using lateinit. | Property is initialized to null by default. |
| Nullable Property | No need for a ? after the property type, as it's not nullable. | Property is implicitly nullable (requires ? after the property type). |
| Null Safety | Risky if not properly initialized; accessing an uninitialized lateinit property will result in a runtime exception. | Safe by default, as properties are initialized to null. Null checks or safe calls (?.) are required when accessing. |
| Initialization Responsibility | Developer must ensure that the property is initialized before use. | No obligation to explicitly initialize the property; it can remain null. |
| Use Cases | - Used when you can guarantee that the property will be initialized before being accessed. - To avoid nullable types and null checks, especially for properties that are expected to always have a value. | - Used when there's a possibility that the property might not be initialized immediately or can be left as null intentionally. - When you need to handle null values explicitly. |
without Lamda
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Adder adder = new Adder();
int result = adder.add(5, 7);
System.out.println("Result of adding 5 and 7 is: " + result);
}
}
class Adder {
public int add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
}
fun main() {
val add: (Int, Int) -> Int = { a, b -> a + b }
val result = add(5, 7)
println("Result of adding 5 and 7 is: $result")
}
with Lamda in Kotlin
ImageView and set Image in Android
1. Which is faster to share Image: Base64 or Downloading?
2. Why use Glide?
Using Library: Glide
1. Never reinvent wheel
2. Use Documentations
3. Gradle import
https://github.com/bumptech/glide
Add Permission
Add internet permisson
I Root cause (1 of 1)
java.lang.SecurityException: Permission denied (missing INTERNET permission?)
at java.net.Inet6AddressImpl.lookupHostByName(Inet6AddressImpl.java:150)
at java.net.Inet6AddressImpl.lookupAllHostAddr(Inet6AddressImpl.java:103)
at java.net.InetAddress.getAllByName(InetAddress.java:1152)
at com.android.okhttp.Dns$1.lookup(Dns.java:41)
at com.android.okhttp.internal.http.RouteSelector.resetNextInetSocketAddress(RouteSelector.java:178)
at com.android.okhttp.internal.http.RouteSelector.nextProxy(Ro