Object-Oriented Design Patterns
What is OOP
Classes , Objects and code reuse
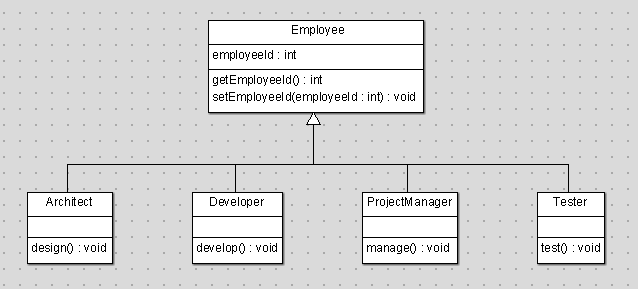
OOP Principles
- Encapsulation
- Inheritance , Composition and Delegation
- Polymorphism
Encapsulation
Encapsulation is used to hide the values or state of a structured data object inside a class, preventing unauthorized parties to direct access them
class Program {
public class Account {
private decimal accountBalance = 500.00m;
public decimal CheckBalance() {
return accountBalance;
}
}
static void Main() {
Account myAccount = new Account();
decimal myBalance = myAccount.CheckBalance();
}
}Inheritance and Composition
Inheritance, a mechanism for code reuse
in C# and Java:
- All classes inherit from the base class Object (System.Object and java.lang.Object)
- Multiple class inheritance is not possible
Interfaces provide definitions of methods and values which the objects agree upon in order to co-operate.
Inheritance and Composition
Inheritance, a mechanism for code reuse
in C# and Java:
- All classes inherit from the base class Object (System.Object and java.lang.Object)
- Multiple class inheritance is not possible
abstract class Animal {
private string biologicalFamily;
abstract String biologicalFamily();
}
class Cat extends Animal {
private string biologicalFamily = "felidae";
public String getBiologicalFamily()
{
return biologicalFamily;
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
private string biologicalFamily = "canidae";
public String biologicalFamily()
{
return biologicalFamily;
}
}
void printBiologicalFamily(Animal a) {
println("This animal is a " + a.biologicalFamily());
}
void main() {
printBiologicalFamily(new Cat());
printBiologicalFamily(new Dog());
}Inheritance and Composition
Composition : objects of one class contain objects of another class
class Address {
private string line1;
private string line2;
private string postCode;
private string coutrycode;
...
}
class Employee {
private string firstname;
private string surname;
private Address adrc;
...
}Polymorphism
- Ad hoc Polymorphism or function overloading
static void MakeAtLeast<T>(T[] list, T lowest) where T : IComparable<T>
{
for (int i = 0; i < list.Length; i++)
if (list[i].CompareTo(lowest) < 0)
list[i] = lowest;
}static void FindEmployee(String employeeName)
{
//search the employee list by name
}
static void FindEmployee(Int employeeID)
{
//search the employee list by ID
}- Parametric Polymorphism or generic programming
Polymorphism
- Subtype polymorphism
abstract class Shape {
abstract String draw();
}
class Circle extends Shape {
String draw() {
return "I am a circle.";
}
}
class Square extends Shape {
String draw() {
return "This is a square.";
}
}
void letsDraw(Shape aShape) {
println(aShape.draw());
}What is a design pattern?
Christopher Alexander says, "Each pattern describes a problem which occurs over and over again in our environment, and then describes the core of the solution
to that problem, in such a way that you can use this solution a million times over, without ever doing it the same way twice"
DP Classificaton : purpose and scope
| Creational | Structural | Behavioral | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Class | Factory Method | Adapter | Interpreter Template Method |
| Object | Abstract Factory Builder Prototype Singleton |
Adapter Bridge Composite Decorator Facade Flyweight Proxy |
Chain of Responsibility Command Iterator Mediator Memento Observer State Strategy Visitor |
The Factory Method
AKA Virtual Constructor
Define an interface for creating an object, but let subclasses decide which class
to instantiate. Factory Method lets a class defer instantiation to subclasses
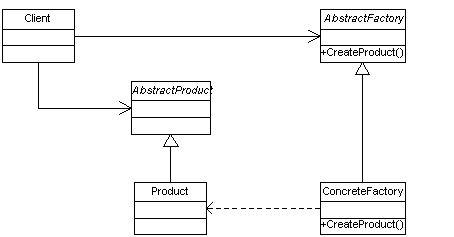
Intent
The Framework dilemma : The framework must instantiate classes, but it only knows about abstract classes, which it cannot instantiate
The Factory Method's solution encapsulates the knowledge of which Document subclass to create and moves this knowledge out of the framework
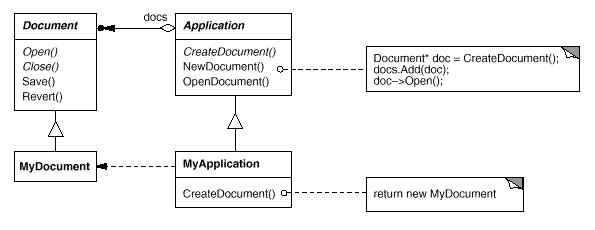
Motivation
Use the Factory Method pattern when
• a class can't anticipate the class of objects it must create.
• a class wants its subclasses to specify the objects it creates.
• classes delegate responsibility to one of several helper subclasses, and
you want to localize the knowledge of which helper subclass is the delegate
Applicability
Structure
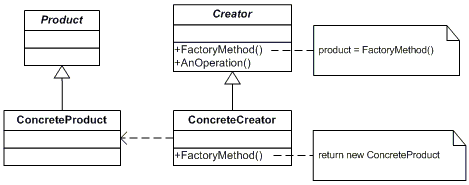
Participants
Product (Document) : defines the interface of objects the factory method creates.
ConcreteProduct (MyDocument) : implements the Product interface.
Creator (Application) : declares the factory method, which returns an object of type Product. Creator may also define a default implementation of the factory method that returns a default ConcreteProduct object. May call the factory method to create a Product object.
ConcreteCreator (MyApplication) : overrides the factory method to return an instance of a ConcreteProduct.
Collaborations and Consequences
- Creator relies on its subclasses to define the factory method so that it returns an instance of the appropriate ConcreteProduct.
- Factory methods eliminate the need to bind application-specific classes into your code
- A potential disadvantage of factory methods is that clients might have to subclass the Creator class just to create a particular ConcreteProduct object
- Factory Method gives subclasses a hook for providing an extended version of an object
Factory Method Implementation
public class VehicleFactory {
public CarFactory() {
Vehicle car1 = makeVehicle();
Vehicle car2 = makeVehicle();
this.addCar(car1);
this.addCar(car2);
}
protected Vehicle makeVehicle() {
//This is a default implementation of the makeVehicle factory method
return new Car();
}
}
public class MotorcycleFactory extends VehicleFactory {
@Override
protected Vehicle makeVehicle() {
return new Motorcycle();
}
}
public interface Vehicle{}
public class Car implements Vehicle{}
public class Motorcycle implments Vehicle{}interface VehicleFactory {
public function makeVehicle();
}
interface Vehicle {
public function getType();
}
/* Concrete implementations of the factory and car */
class CarFactory implements VehicleFactory {
public function makeVehicle() {
return new Car();
}
}
class MotorcycleFactory implements VehicleFactory {
public function makeVehicle() {
return new Motorcycle();
}
}
class Car implements Vehicle {
public function getType() {
return '4 wheels car';
}
}
class Motorcycle implements Vehicle {
public function getType() {
return '2 wheels Motorcycle';
}
}/* Client */
if(SelectedType == "Car"){
$factory = new CarFactory();
// returns an object of type Car
$car = $factory->makeVehicle();
print $car->getType();
}Links
- http://www.newthinktank.com/2012/09/factory-design-pattern-tutorial/
- http://www.dofactory.com/net/factory-method-design-pattern
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Factory_method_pattern
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Software_design_pattern#Classification_and_list