Promise
팀 러버덕 by Hoon
callback cons
Callback Hell
doSomething(function(result) {
doSomethingElse(result, function(newResult) {
doThirdThing(newResult, function(finalResult) {
console.log('Got the final result: ' + finalResult);
}, failureCallback);
}, failureCallback);
}, failureCallback);callback cons
Difficulties in handling errors
try {
setTimeout(() => { throw new Error('Error!'); }, 1000);
} catch (e) {
console.log('에러를 캐치하지 못한다..');
console.log(e);
}Promise
Promise 생성자함수를 활용한다
const result = new Promise((res, rej) => {
/** 비동기 작업 실행 */
...
if( /** 작업 성공시 */ ) {
res('result')
} else {
rej('error!')
}
})Promise
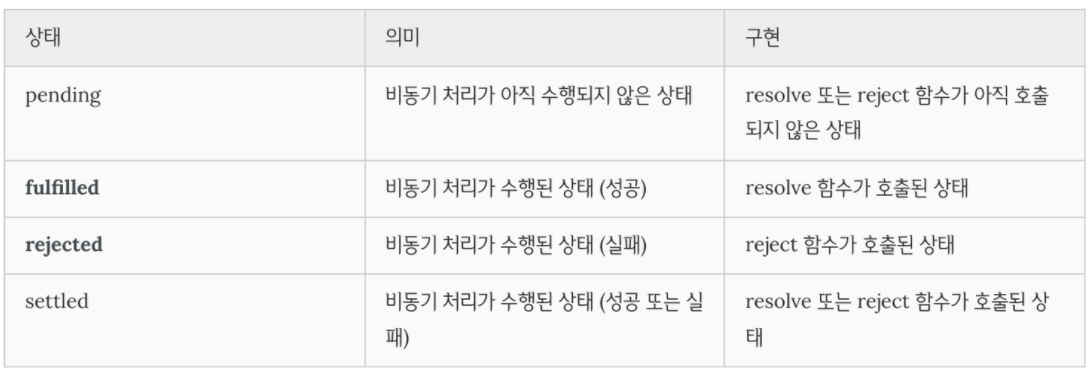
프로미스의 경우, 비동기 처리가 성공했는지 실패했는지 등의 상태정보를 제공해줍니다
Promise chaining
프로미스의 경우, 비동기 처리가 성공했는지 실패했는지 등의 상태정보를 제공해줍니다

Promise chaining
doSomething()
.then(result => doSomethingElse(result))
.then(newResult => doThirdThing(newResult))
.then(finalResult => {
console.log(`Got the final result: ${finalResult}`);
})
.catch(failureCallback);기존 API를 프로미스를 이용해 구현
setTimeout(() => saySomething("10 seconds passed"), 10*1000);
const wait = ms => new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, ms));
wait(10*1000)
.then(() => saySomething("10 seconds"))
.catch(failureCallback);Composition
Promise
.all([func1(), func2(), func3()])
.then(([result1, result2, result3]) => {
/* use result1, result2 and result3 */
});
[func1, func2, func3].reduce((p, f) =>
p.then(f), Promise.resolve()
).then(result3 => { /* use result3 */ });Timing
Promise.resolve().then(() => console.log(2));
console.log(1); // 1, 2Fetch
라이브 코딩