When I think about ‘dynamics’/‘dynamical systems’ this is what I mean:
spatiotemporal data is everywhere
Human brain
Medicine (Disease Spread)
Science (Fluids, Climate)
Robotics (Video generation)
Stock Markets
Simulate: Dynamical Representations
Neural Wave Machines (Keller, 2023),
Artificial Kuramoto Oscillatory Networks (Miyato, 2024)
Explain: Discover Potential Differential Equations
Symbolic Regression, LLMs(?)
Acceleration: Replace Simulator
Scaling/Generalisation: Remove Dependency on Grid/Mesh
Operator Based Models
PINNs, Neural Fields
Flexible (data driven): Parameterise the vector field as a NN
Neural ODE (~Flow Matching)
Optical Flow
Gaussian Processes
spatiotemporal data is everywhere
scale of problem
Decoding
Network
Encoder/Decoder Architecture
Encoding
Network
Modelling in
Latent Space
Modulated
Neural ODEs
I.A. Auzina, Ç. Yıldız, S. Magliacane, M. Bethge and E. Gavves




Modulated NODEs
I.A. Auzina, Ç. Yıldız, S. Magliacane, M. Bethge and E. Gavves
Key Idea:
length, mass
length of limbs
influence dynamics
influence reconstruction
color of a ball
color of clothes
does setting apart dynamic states from
underlying static factors of variation improve existing model performance?
Modulated NODEs
Key Idea:
does setting apart dynamic states from
underlying static factors of variation improve existing model performance?
I.A. Auzina, Ç. Yıldız, S. Magliacane, M. Bethge and E. Gavves


Latent Space
Encoding
Network
Decoding
Network
Forward
Simulation
(ODE)
Dynamics Modulator
Modulator Prediction
Network
Modulator Prediction
Network
Static Modulator
Latent NODE
(Chen et al., 2018)
ours
MoNODE (2023)

Parameters of an ODE

Style of a digit
influence dynamics
influence reconstruction
Modulated NODEs
Generative Model
implicit, point-estimates
ELBO (Chen, 2018)
I.A. Auzina, Ç. Yıldız, S. Magliacane, M. Bethge and E. Gavves

Modulated NODEs
I.A. Auzina, Ç. Yıldız, S. Magliacane, M. Bethge and E. Gavves

A general framework
Latent NODE
(Chen et al., 2018)
Second Order NODE
(Norcliffe et al., 2020)
Latent Second Order NODE
(Yildiz et al., 2019)
Heavy Ball NODE
(Xia et al., 2021)
Modulated NODEs
Define the modulators and evaluate the framework
I.A. Auzina, Ç. Yıldız, S. Magliacane, M. Bethge and E. Gavves
each trajectory a different parametrization
Predator-Prey
Part I. Dynamics Modulator
Part II. Static Modulator
each trajectory a different 'style'
Rotating MNIST

Part III. Both Modulator Variables
CMU Human Mocap
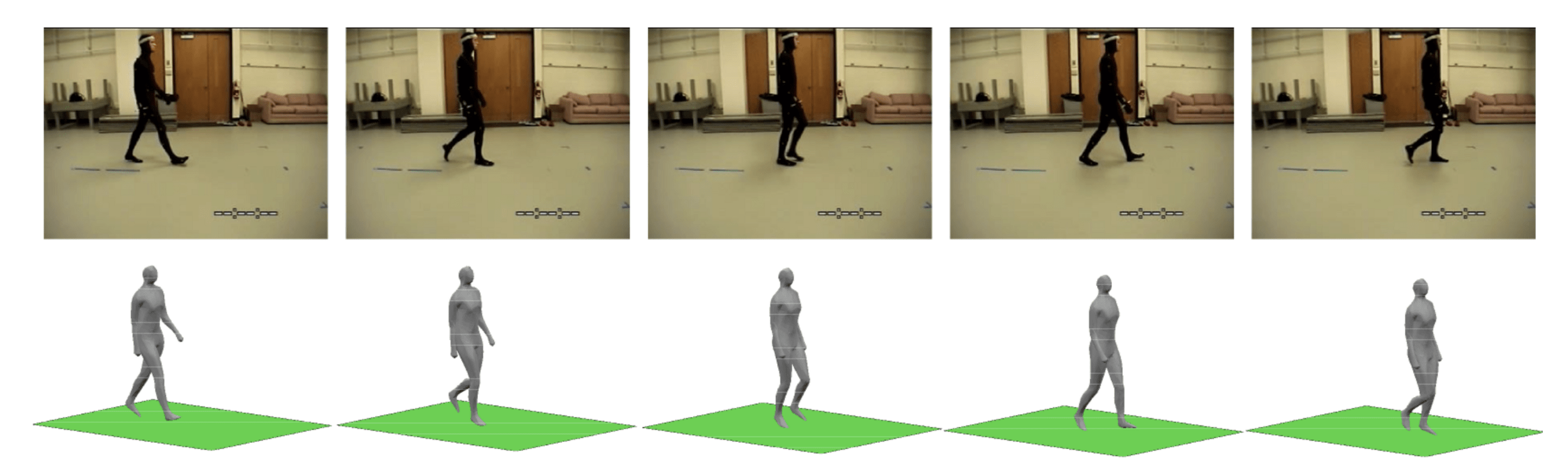
(Wandt et al., 2015)
Modulated NODEs
A general framework
that improves forecasting and generalization (on average by 55.25% (MSE) across all experiments)
Sinusoidal Data
Latent NODE
(Chen et al., 2018)


ours Mo-xNODE
Heavy Ball NODE
(Xia et al., 2021)


I.A. Auzina, Ç. Yıldız, S. Magliacane, M. Bethge and E. Gavves
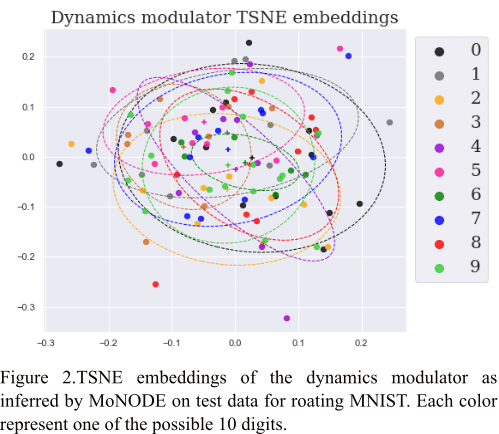
Part I. Dynamics Modulator
Modulated NODEs
A general framework
that is easier to train



ours: Mo-xNODE
NODE (Chen et al., 2018)
SONODE (Norcliffe et al., 2020)
HBNODE (Xia et al., 2021)
I.A. Auzina, Ç. Yıldız, S. Magliacane, M. Bethge and E. Gavves
Sinusoidal Data
Part I. Dynamics Modulator
Modulated NODEs
A general framework
that disentangles underlying FoVs
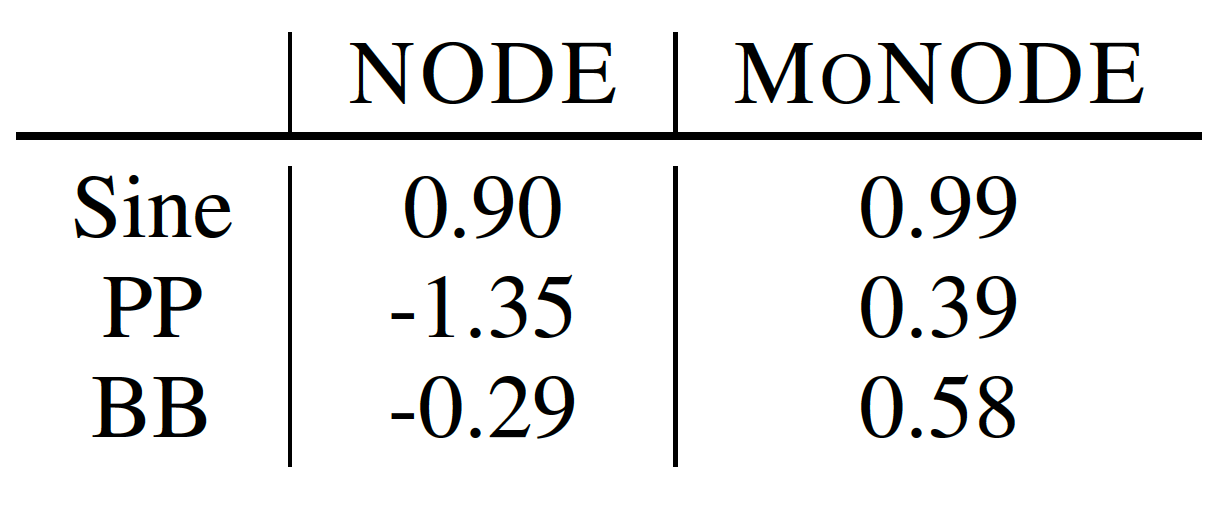
Table 2. R^2 scores to predict the unknown FoV from inferred latents. Higher is better.
~
dynamics
modulator
PP parameters
I.A. Auzina, Ç. Yıldız, S. Magliacane, M. Bethge and E. Gavves
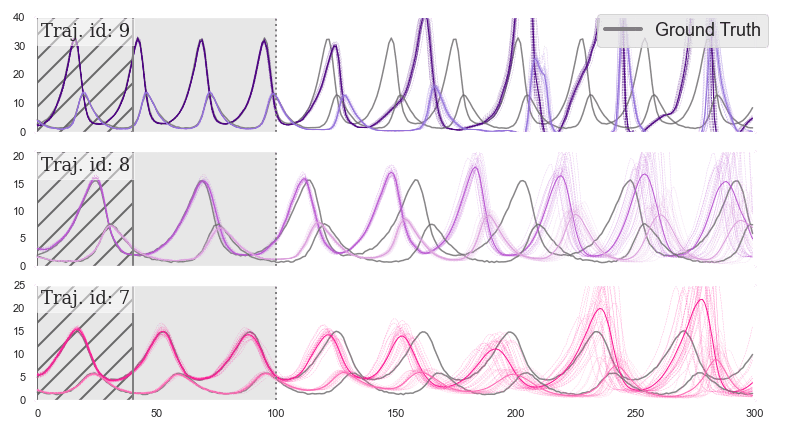
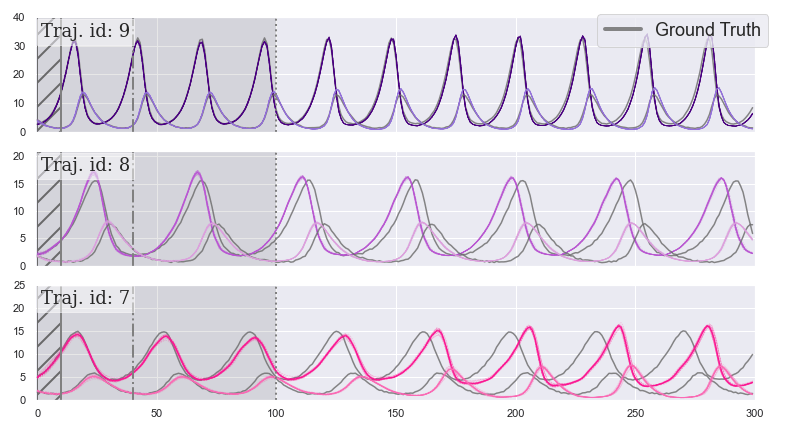
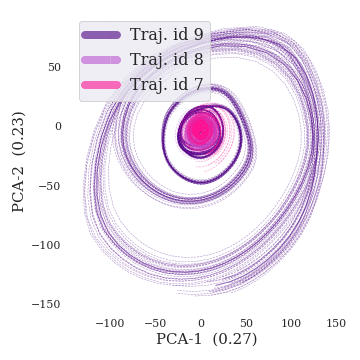
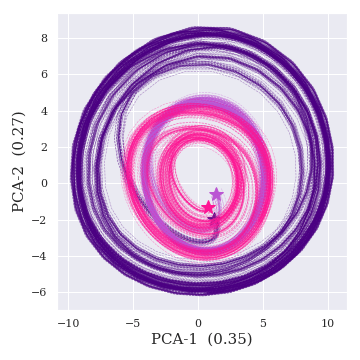
HBNODE
HBNODE
Mo-HBNODE
Mo-HBNODE
Part I. Dynamics Modulator
Modulated NODEs
A general framework
that disentangles underlying FoVs
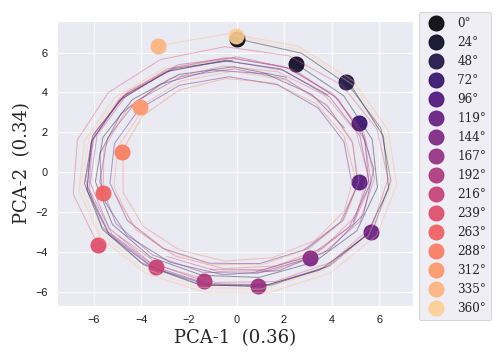
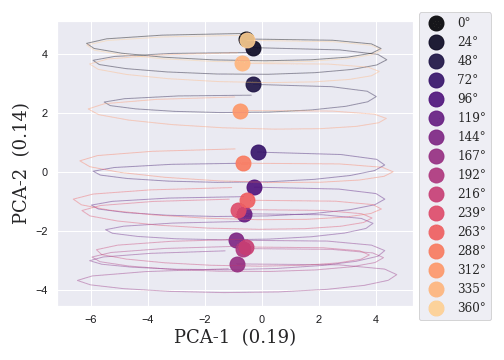
NODE
MoNODE

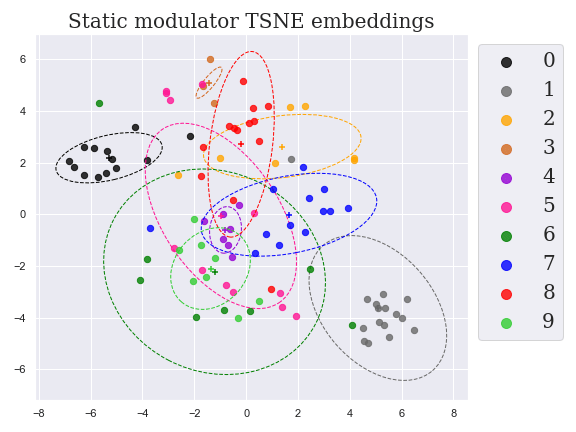
Part II. Static Modulator
and correspond to their 'descriptive' roles
Modulated NODEs
that improves performance
on real world data
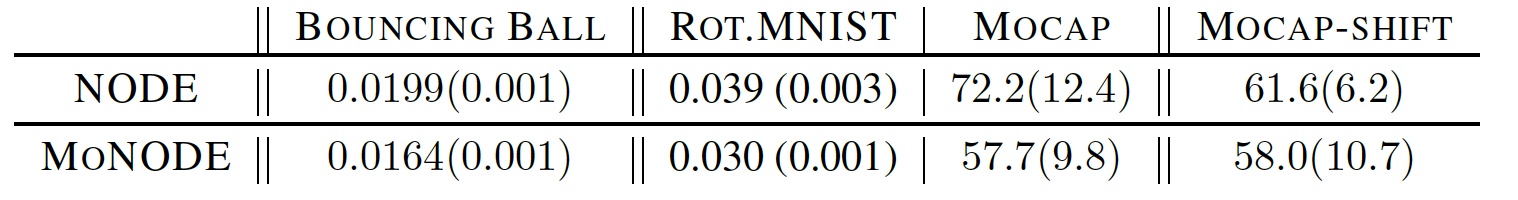
Table 3. Test MSE and standard deviation. Lower is better.
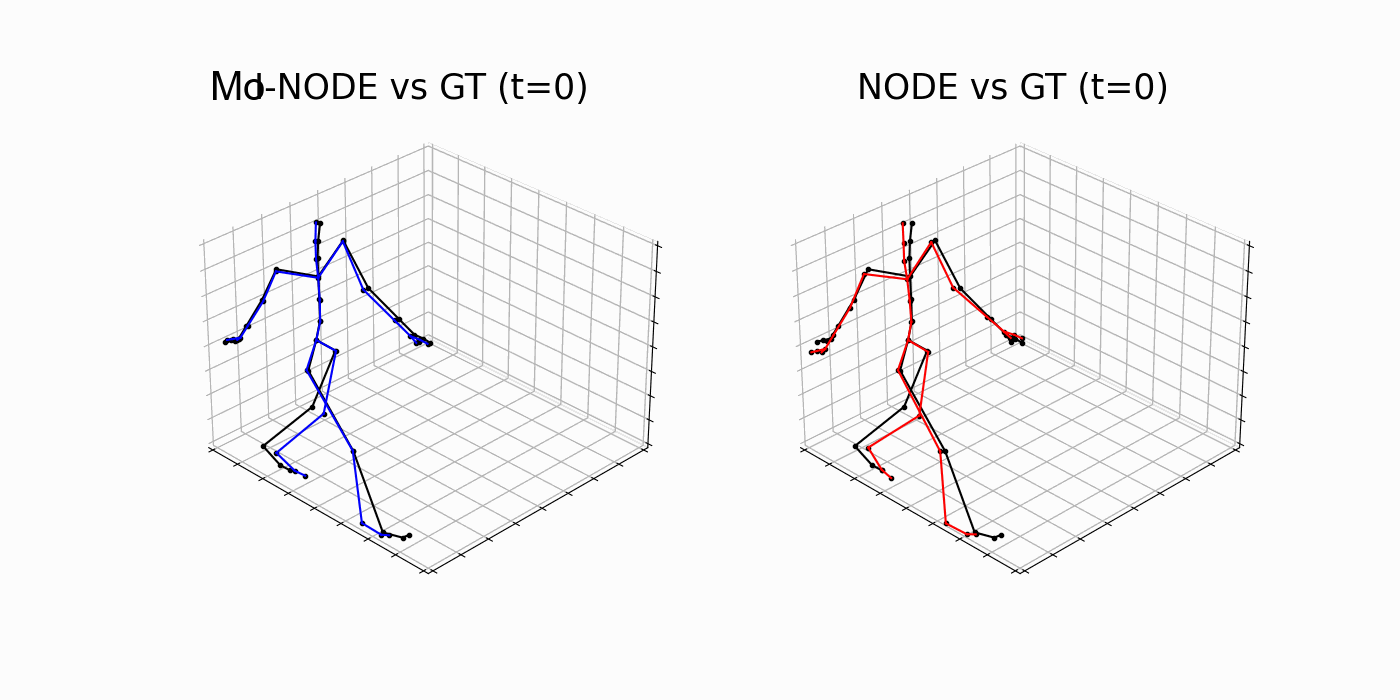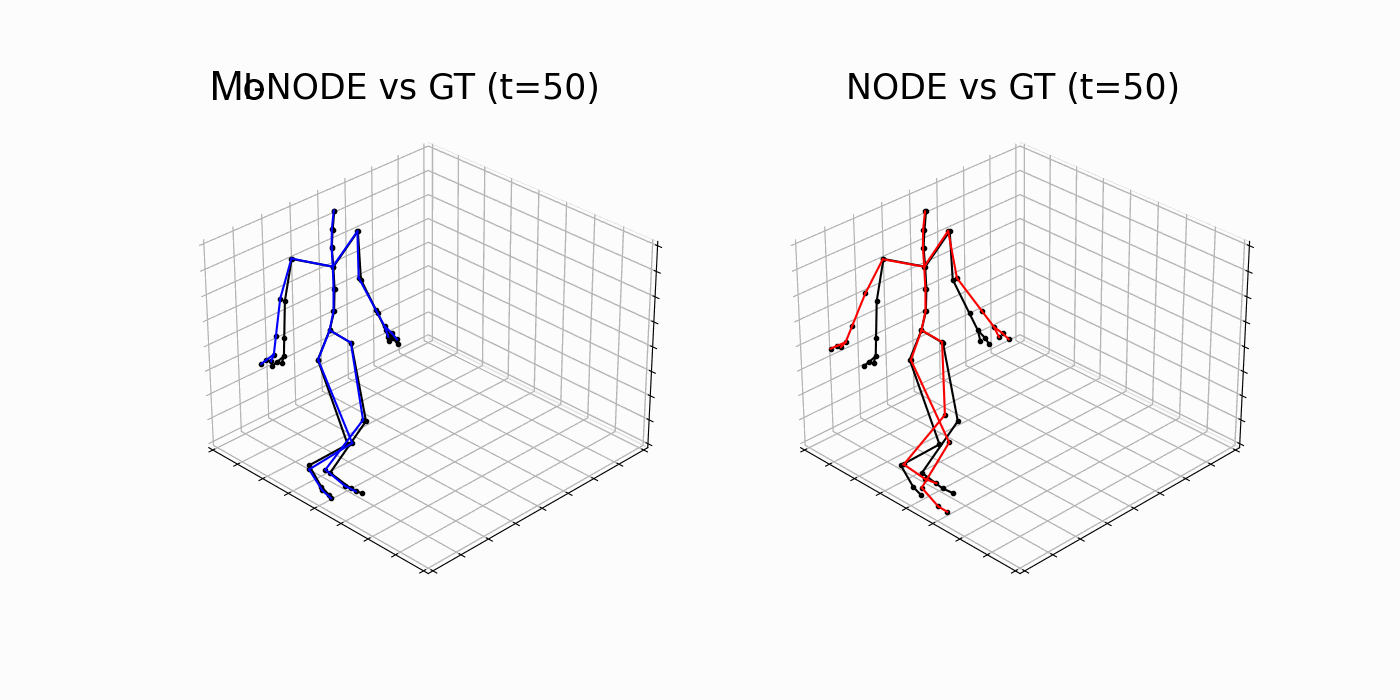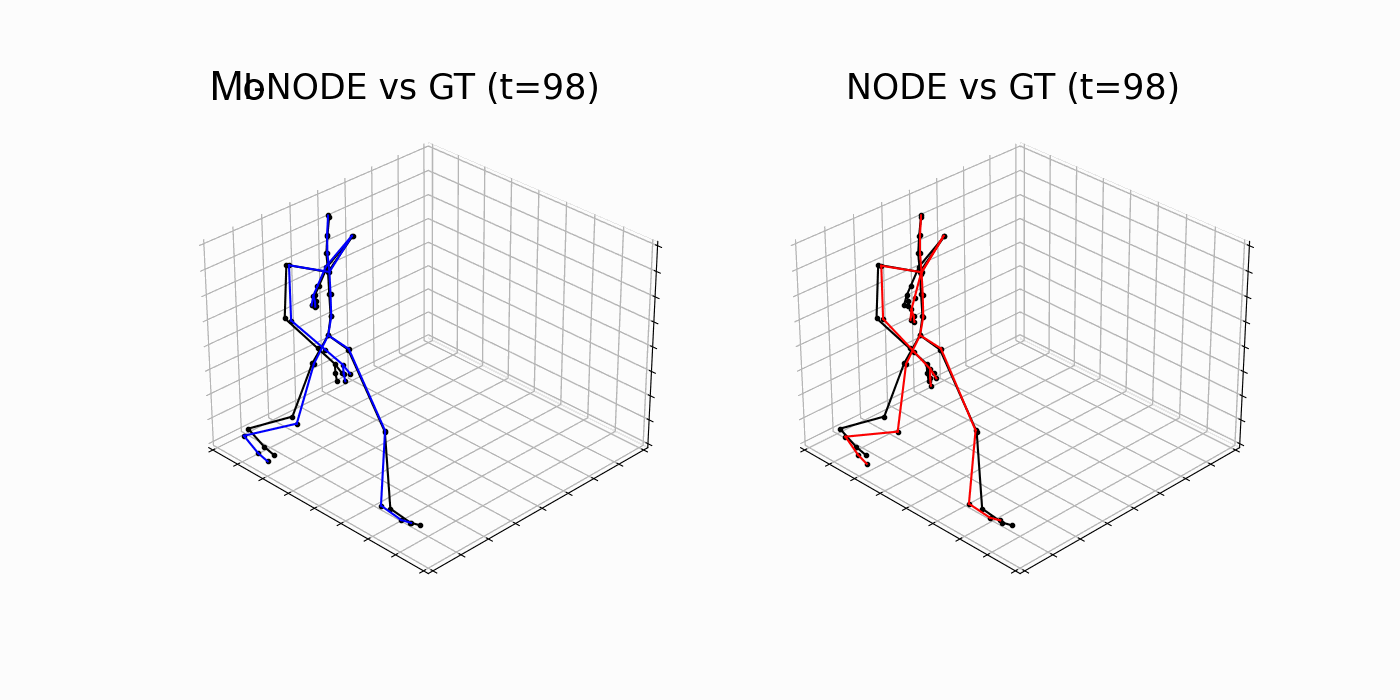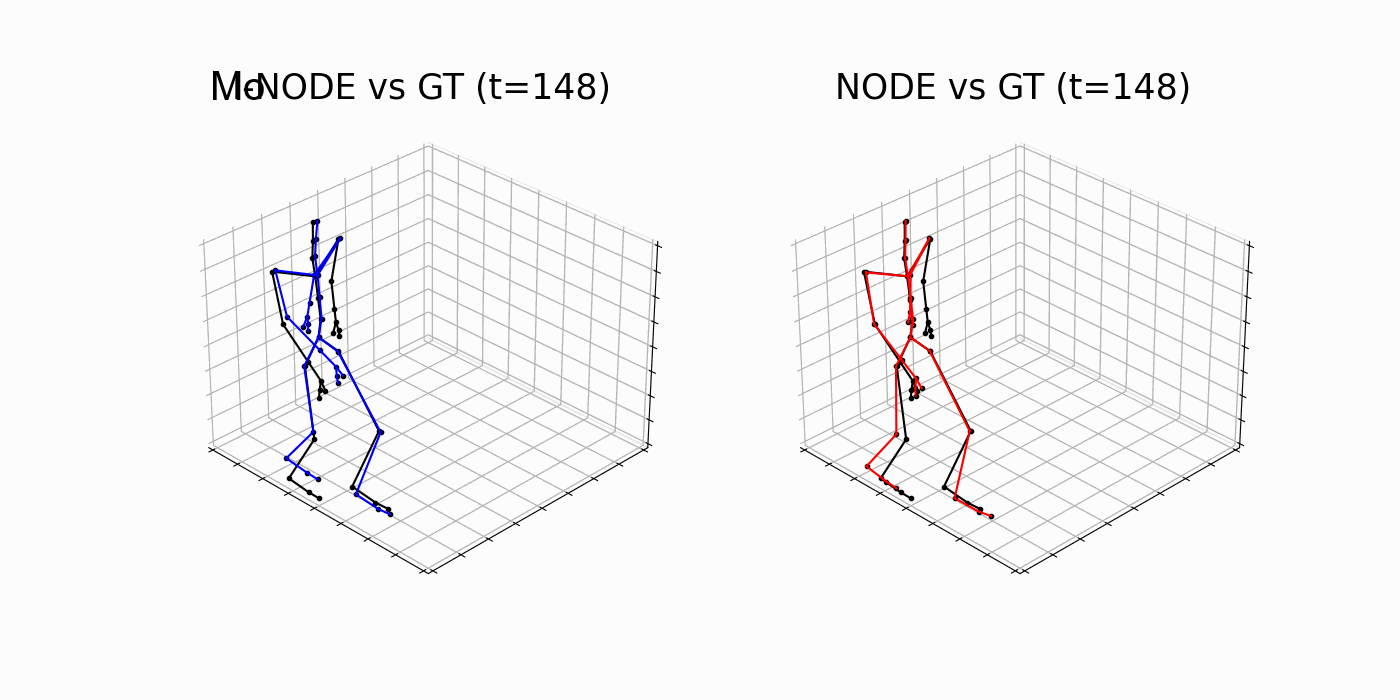
MoNODE
NODE
I.A. Auzina, Ç. Yıldız, S. Magliacane, M. Bethge and E. Gavves
Part III. Both Modulator Variables
Modulated NODEs
I.A. Auzina, Ç. Yıldız, S. Magliacane, M. Bethge and E. Gavves


Latent Space
Encoding
Network
Decoding
Network
Forward
Simulation
(ODE)
Dynamics Modulator
Modulator Prediction
Network
Modulator Prediction
Network
Static Modulator
influence dynamics
influence reconstruction
Modeling dynamic's variation through time-invariant modulator variables is beneficial:
results in an ODE state that is consistent with the true dynamics and
modulator variables that correlate with the true unknown factors of variation
key take-away:
Thank you for your attention
I.A. Auzina, Ç. Yıldız, S. Magliacane, M. Bethge and E. Gavves
Modulated NODEs




All experiments and models publicly available at: