COMP6771
Advanced C++ Programming
Week 2.2
STL Iterators
- Iterator is an abstract notion of a pointer
- Iterators are types that abstract container data as a sequence of objects (i.e. linear)
- Iterators will allow us to connect a wide range of containers with a wide range of algorithms via a common interface
STL: Iterators

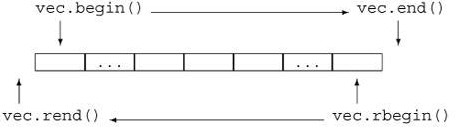
- a.begin(): abstractly "points" to the first element
-
a.end(): abstractly "points" to one past the last element
- a.end() is not an invalid iterator value
- If iter abstractly points to the k-th element, then:
- *p is the object it abstractly points to
- ++p abstractly points to the (k + 1)-st element
STL: Iterators
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
int main() {
std::vector<std::string> names;
for (auto iter = names.begin(); iter != names.end(); ++iter) {
std::cout << *iter << "\n";
}
for (std::vector<std::string>::iterator iter = names.begin(); iter != names.end(); ++iter) {
std::cout << *iter << "\n";
}
}demo204-iter1.cpp
Iterators, Constness, Reverse
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
int main() {
std::vector<int> ages;
ages.push_back(18);
ages.push_back(19);
ages.push_back(20);
// type of iter would be std::vector<int>::iterator
for (auto iter = ages.begin(); iter != ages.end(); ++iter) {
(*iter)++; // OK
}
// type of iter would be std::vector<int>::const_iterator
for (auto iter = ages.cbegin(); iter != ages.cend(); ++iter) {
//(*iter)++; // NOT OK
}
// type of iter would be std::vector<int>::reverse_iterator
for (auto iter = ages.rbegin(); iter != ages.rend(); ++iter) {
std::cout << *iter << "\n"; // prints 20, 19, 18
}
// Can also use crbegin and crend
}
demo205-iter2.cpp
Stream Iterators
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <iterator>
int main() {
std::ifstream in("data.in");
std::istream_iterator<int>begin(in);
std::istream_iterator<int> end;
std::cout << *begin++ << "\n"; // read the first int
++begin; // skip the 2nd int
std::cout << *begin++ << "\n"; // read the third int
while (begin != end) {
std::cout << *begin++ << "\n"; // read and print the rest
}
}demo206-iter3.cpp
Feedback
