Introduction to NodeJS/ExpressJS
Chandan Jhunjhunwal
Session -1
13/01/2017

Basics
- V8 Engine
- Sync vs Async functions
- Understanding call stacks
- Web APIs and Task queues
- http://latentflip.com/loupe/
- https://jsfiddle.net/dkdk5y8a/1/
- Why setTimeout(fn(), 0)?
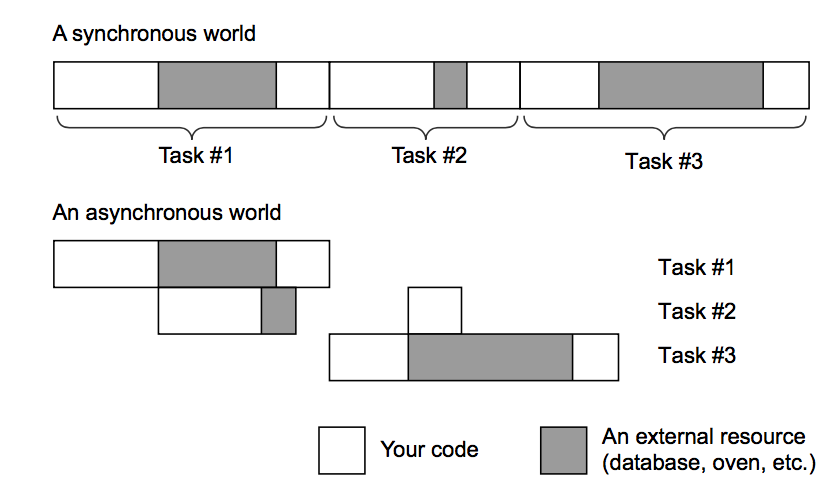
Async Call
NodeJS
- NPM
- NVM
- package.json
- Built in modules
- Third party modules
- Your own module
var url = require("url");
var parsedURL = url.parse("http://www.example.com/profile?name=barry");
console.log(parsedURL.protocol); // "http:"
console.log(parsedURL.host); // "www.example.com"
console.log(parsedURL.query); // "name=barry"Built in module
Mustache.render("Hello, {{first}} {{last}}!", {
first: "Nicolas",
last: "Cage"
});
Mustache.render("Hello, {{first}} {{last}}!", {
first: "Sheryl",
last: "Sandberg"
});Third Party Module
var MAX = 100;
function randomInteger() {
return Math.floor((Math.random() * MAX));
}
module.exports = randomInteger;Your module
1. Find number of 'X' (case insensitive) in a text file from disc
using file system 'fs' module.
2. Write console.log at the end of file, check what's gets
printed firstAsync Calls
var http = require("http");
function requestHandler(request, response) {
console.log("In comes a request to: " + request.url);
response.end("Hello, world!");
}
var server = http.createServer(requestHandler);
server.listen(3000);http server
Node vs Express
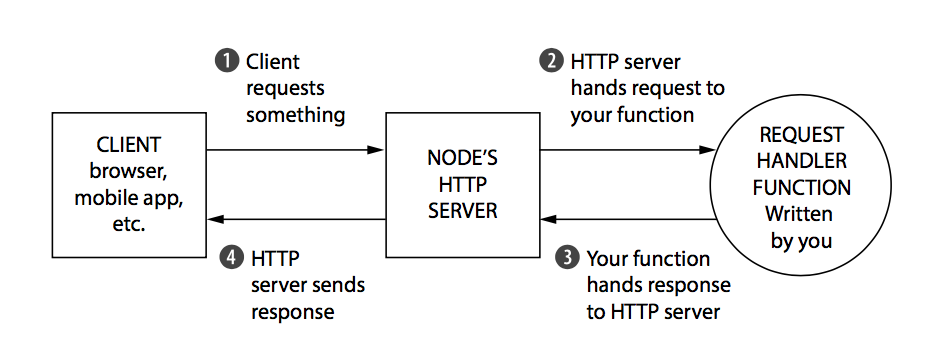
Node JS
ExpressJS
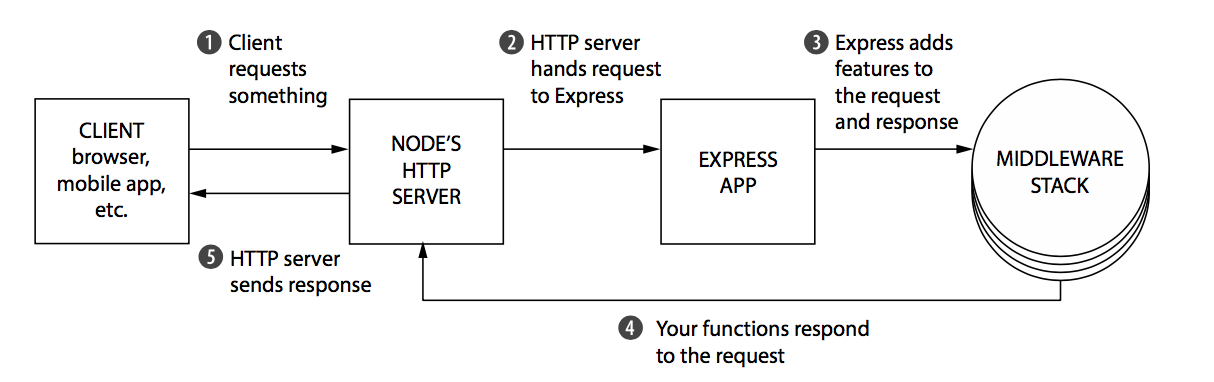
// Node http server
var http = require("http");
requestHandler = function(req, res){
if(req.url === '/'){
res.end('Home page')
}
else {
res.end("Don't go out of home");
}
}
var server = http.createServer(requestHandler);
server.listen(3000)
// Express Server
var express = require('express');
var funApp = express();
funApp.get('/', function(req, res){
console.log("request received at" + req.url);
response.send("Hello world!");
})
fundApp.listen(3000, function(){
console.log('Application Started...');
})References
- Stackoverflow
- Event Loop: JSConf EU 2014(Philip Roberts talk)
- ExpressJS in Action