Distributed Node #6
Chat service

Agenda
A bit about WebSockets
NodeJS libraries
NestJS

Let's start

Client 2
Server
Client 3
Client 1
Client 4




Standard situation
WS in TCP/IP protocol stack
WS
HTTP
DNS
FTP
TCP
UDP
IP
ICMP
ARP
DHCP
Ethernet
Wi-Fi
DSL
Application
Transport
Network
Data Link and Physical
Collect the data from the application software and format it for further processing
Packetize the data. Add sequecing and error correction info to each packet
Add source and destination IP address to each packet
Add source and destination MAC address to each packet and pass to NIC drivers
First, let's check other ways


Client
Server
GET / poll
GET / poll
XHR polling


Client
Server
Connection
Events
SSE
EventSource protocol
What is WebSockets?
The WebSocket protocol, described in the specification RFC 6455 provides a way to exchange data between browser and server via a persistent connection. The data can be passed in both directions as “packets”, without breaking the connection and additional HTTP-requests.
WebSocket is especially great for services that require continuous data exchange, e.g. online games, real-time trading systems and so on.

// To open a websocket connection, we need to create new
// WebSocket using the special protocol ws in the url:
let socket = new WebSocket("ws://chat.com");
// There’s also encrypted wss:// protocol.
// It’s like HTTPS for websockets.
Opening a websocket
When new WebSocket(url) is created, it starts connecting immediately.
During the connection, the browser (using headers) asks the server: “Do you support Websocket?” And if the server replies “yes”, then the talk continues in WebSocket protocol, which is not HTTP at all.



Client
Server
"Hey, server, let's talk WebSocket?"
HTTP-request
HTTP-response
"Okay!"
WebSocket protocol
If the server agrees to switch to WebSocket, it should send code 101 response
Handshake (HTTP upgrade)
Bi-directional messages
Visual representation
Opening connection
GET /chat
Host: ourchat.net
Origin: https://javascript.info
Connection: Upgrade
Upgrade: websocket
Sec-WebSocket-Key: Iv8io/9s+lYFgZWcXczP8Q==
Sec-WebSocket-Version: 13
- Origin – the origin of the client page, e.g. https://chat.com. WebSocket objects are cross-origin by nature. There are no special headers or other limitations. Old servers are unable to handle WebSocket anyway, so there are no compatibility issues. But Origin header is important, as it allows the server to decide whether or not to talk WebSocket with this website.
- Connection: Upgrade – signals that the client would like to change the protocol.
- Upgrade: websocket – the requested protocol is “websocket”.
- Sec-WebSocket-Key – a random browser-generated key for security.
- Sec-WebSocket-Version – WebSocket protocol version, 13 is the current one.
new WebSocket("wss://ourchat.net/chat");Opening connection
If the server agrees to switch to WebSocket, it should send code 101 response:
101 Switching Protocols
Upgrade: websocket
Connection: Upgrade
Sec-WebSocket-Accept: hsBlbuDTkk24srzEOTBUlZAlC2g=Data transfer
WebSocket communication consists of “frames” – data fragments, that can be sent from either side and can be of several kinds:
- “text frames” – contain text data that parties send to each other.
- “binary data frames” – contain binary data that parties send to each other.
- “ping/pong frames” are used to check the connection, sent from the server, the browser responds to these automatically.
- there’s also a “connection close frame” and a few other service frames.

WS events
Once the socket is created, we should listen to events on it. There are totally 4 events:
- open – connection established,
- message – data received,
- error – websocket error,
- close – connection closed.
…And if we’d like to send something, then socket.send(data) will do that.

Summary
-
RFC 6455 "The WebSocket Protocol", 2011
-
Support in all browsers
-
Working phases:
-
opening handshake
-
data transferring (bi-directional messages)
-
-
The 2-ways permanent connection between client and server
-
permanent TCP connection
-
Ports 80(ws)/443(wss)
-
Prefix URI ws/wss (ws://ourchat.net/chat)
-

Time for NodeJS + WebSockets

Which JS library to choose? 🤔
- Socket.io - supports WS, XHR pooling, and flash transport protocols with automatic detection
- WS - It used by the socket.io as a dependency for a WebSocket transport protocol
- sockjs
- websocket node
- socketcluster
- Feathers
- faye-websocket-node
- websocket as promised
...there are plenty of them
Socket.IO is the most feature-rich! But you may not need it on the simple project.
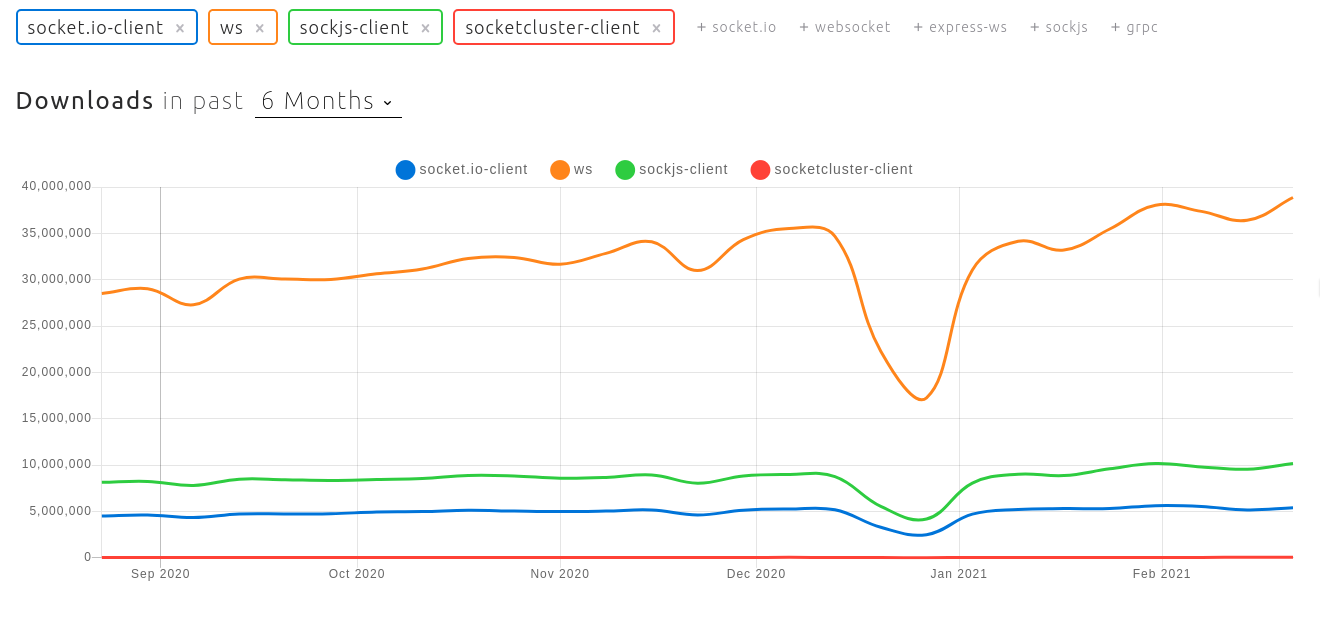
Socket.IO is a JavaScript library for realtime web applications. It enables realtime, bi-directional communication between web clients and servers.

What is socket.io?
-
WebSocket should reconnect automatically in case of disconnection due to server failure or some other reason.
-
WebSocket doesn't work ideally in presence of Firewall, Proxy and Load Balancer either and Antivirus. (the only HTTP may be allowed)
-
Old browsers
-
Disconnection detection
-
Multiplexing support
-
Room support
These problems solved by the Socket.IO
Why socket.io?

Whats next?

I guess its time to build a chat



But first
few words about NestJS gateways

@UsePipes(new ValidationPipe())
@UseInterceptors(new ClearCacheInterceptor())
@SubscribeMessage('events')
handleEvent(client: Socket, data: string) {
const event = 'events';
return { event, data };
}You can change the protocol with one annotation
Example of the "Gateway Controller"
Controllers vs Gateways

Most of the concepts such as dependency injection, decorators, exception filters, pipes, guards and interceptors, apply equally to gateways.
Let's build a chat
step by step!

Chat
config
Chat
overview
protocol
#create new project
nest new chat-service
#navigate to new folder
cd chat-service
#install deps
yarn add @nestjs/platform-socket.io @nestjs/websockets
yarn add -D @types/socket.io
#generate new module
nest g module chat
#take a look what we have
cd src/chat/
ll
#generate new gateway
nest g ga chatGenerate new project
const capitalize = require('lodash/capitalize');
/**
* this file is just for fun, to generate random nckname while we don't have Auth system
*/
const intesifiers = [
'absolutely',
'quite',
'totally',
'utterly',
'particilarly',
'complettely',
'totally',
'really',
];
const adjectives = [
'great',
'cool',
'ambitious',
'generous',
'cute',
'dear',
'nice',
'reliable',
'solid',
'trusty',
'simple',
'pure',
'brave',
'manly',
'fearless',
'artful',
'vivid',
'utopic',
'lucid',
'radiant',
'stinky',
'supreme',
'successful',
'holly',
'happy',
'giant',
'lucky',
'weird',
'extreme',
];
const names = [
'phoenix',
'centaur',
'mermaid',
'leviathan',
'dragon',
'pegasus',
'siren',
'hydra',
'sphinx',
'unicorn',
'wyvern',
'behemoth',
'griffon',
'dodo',
'mammoth',
'pirate',
'eminem',
'hacker',
'parrot',
'derp',
];
function random(limit) {
return Math.floor(Math.random() * limit);
}
function getRandomElement(arr) {
return capitalize(arr[random(arr.length)]);
}
function randomLogin() {
return []
.concat(Math.random() > 0.5 ? getRandomElement(intesifiers) : '')
.concat(getRandomElement(adjectives))
.concat(getRandomElement(names))
.join('');
}
export default randomLogin;Random nicknames
import {
ConnectedSocket,
MessageBody,
OnGatewayConnection,
OnGatewayDisconnect,
SubscribeMessage,
WebSocketGateway,
WebSocketServer,
} from '@nestjs/websockets';
import randomLogin from '../utils/genNickname';
import { Logger } from '@nestjs/common';
import { Socket } from 'socket.io';
@WebSocketGateway({ namespace: 'chat' })
export class ChatGateway implements OnGatewayConnection, OnGatewayDisconnect {
private readonly logger = new Logger(ChatGateway.name);
private connected: Map<string, string> = new Map();
@WebSocketServer() server;
handleDisconnect(client: Socket) {
const nick = this.connected.get(client.id);
this.logger.log(nick + ' Client disconnected ' + client.id);
this.connected.delete(client.client.id);
this.server.emit('userDisconnected', nick);
this.server.emit('message', { msg: `~ ${nick} disconnected` });
}
handleConnection(client: Socket) {
const nick = randomLogin();
this.logger.log(client.id + ' Client connected ' + nick);
this.connected.set(client.id, nick);
client.emit('message', { msg: `Welcome #${nick}`, currUserId: nick });
client.emit('activeUsers', Array.from(this.connected.values()));
client.broadcast.emit('message', { msg: `${nick} connected to the chat` });
this.server.emit('userConnected', nick);
}
@SubscribeMessage('message')
async handleMessage(
@MessageBody() msg: string,
@ConnectedSocket() client: Socket,
) {
const time = new Date();
const nick = this.connected.get(client.id);
this.server.emit('message', {
msg,
user: nick,
time: `${time.getHours()}:${time.getMinutes()}`,
});
}
}Gateway
Bonus
WS vs SSE

Server Sent Events
Is this a WebSocket ?

WebSocket

- No reconnection by default
- Custom authentication logic
- Scaling problems
- More app complexity
SSE
- Reconnection out of the box
- HTTP authentication
- No scaling problems
- Easy to use
Except one thing...
SSE is unidirectional. When you open a SSE connection, only the server can send data to the client (browser, etc.). The client cannot send any data.

A few simple examples of applications that could make use of Server-Sent Events:
- A real-time chart of streaming stock prices
- Real-time news coverage of an important event (posting links, tweets, and images)
- A live Github / Twitter dashboard wall fed by Twitter’s streaming API
- A monitor for server statistics like uptime, health, and running processes.
@Sse('sse')
sse(): Observable<MessageEvent> {
return interval(1000).pipe(map((_) => ({ data: { hello: 'world' } })));
}
// client:
const eventSource = new EventSource('/sse');
eventSource.onmessage = ({ data }) => {
console.log('New message', JSON.parse(data));
};
NestJS integration
Q & A

