Node Core #5
HTTP
Plan
- HTTP methods, headers and content-types
- REST API
- http module
HTTP methods, headers and content-types
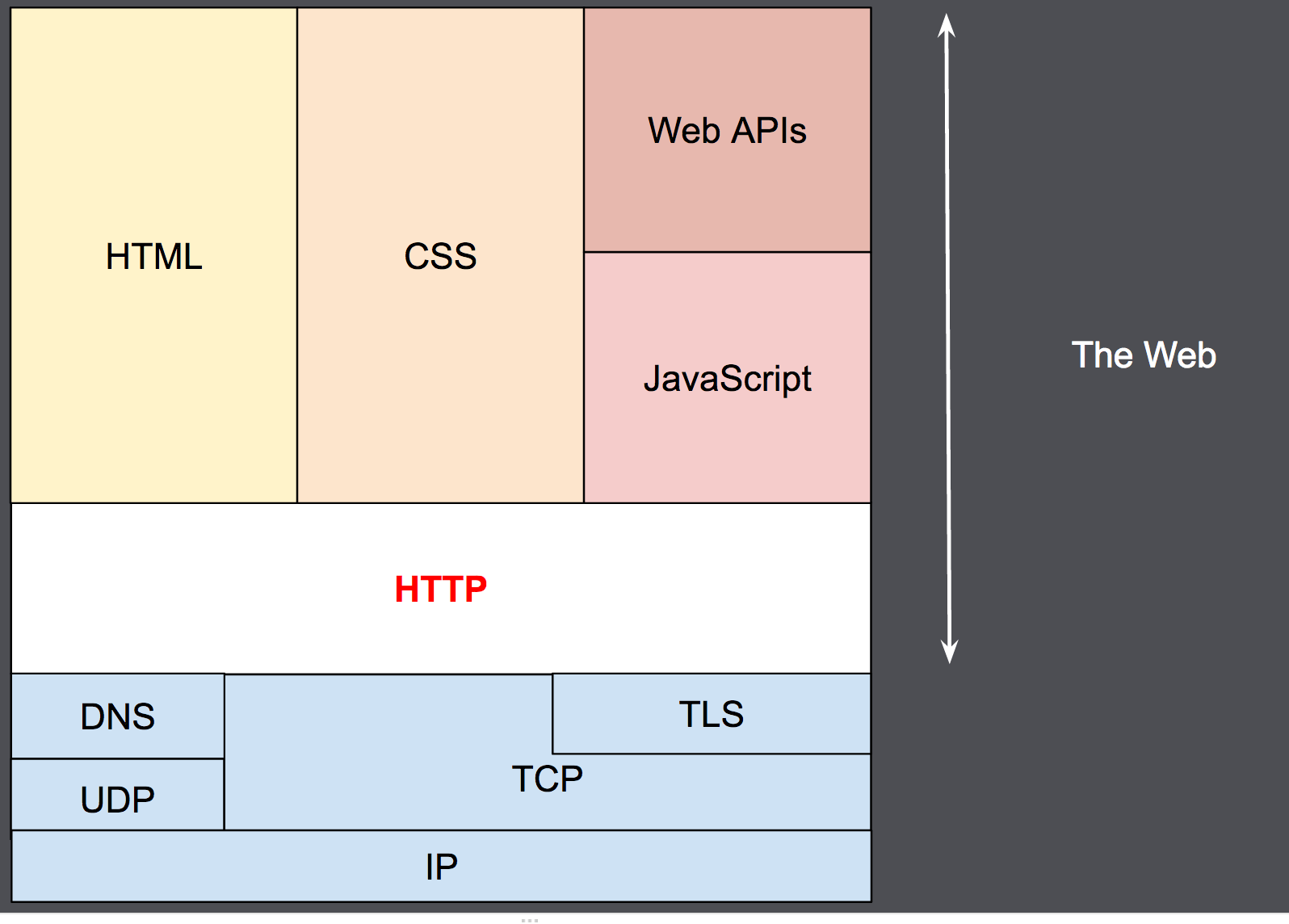
HTTP

Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is an application-layer protocol for transmitting hypermedia documents, such as HTML. It was designed for communication between web browsers and web servers, but it can also be used for other purposes. HTTP follows a classical client-server model, with a client opening a connection to make a request, then waiting until it receives a response. HTTP is a stateless protocol, meaning that the server does not keep any data (state) between two requests.
How HTTP works
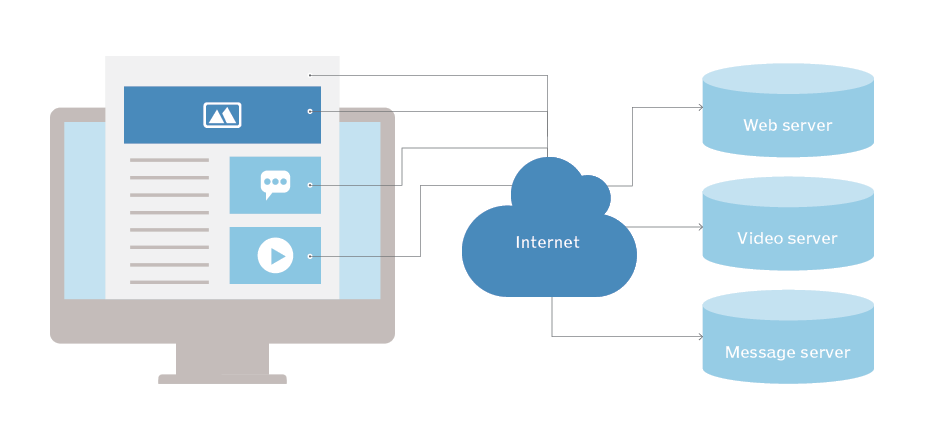
How HTTP works
HTTP methods
GET
POST
OPTIONS
PATCH
DELETE

PUT
TRACE
HEAD
CONNECT
HTTP methods
| GET | Get a representation of the target resource’s state. |
|---|---|
| GET | Requests a representation of the specified resource. Requests using GET should only retrieve data. |
| HEAD | Asks for a response identical to that of a GET request, but without the response body. |
| POST | Used to submit an entity to the specified resource, often causing a change in state or side effects on the server. |
| PUT | Replaces all current representations of the target resource with the request payload. |
| DELETE | Deletes the specified resource. |
| CONNECT | Establishes a tunnel to the server identified by the target resource. |
| OPTIONS | Used to describe the communication options for the target resource. |
| TRACE | Performs a message loop-back test along the path to the target resource (for proxy-debugging purposes) |
| PATCH | Used to apply partial modifications to a resource. |
Description
HTTP methods
HTTP header
HTTP headers let the client and the server pass additional information with an HTTP request or response. An HTTP header consists of its case-insensitive name followed by a colon (:), then by its value. Whitespace before the value is ignored.
HTTP headers
Authentication
Cookies
CORS
Caching
Proxies
Security
Redirects
HTTP header types
Headers can be grouped according to their contexts:
- Request headers contain more information about the resource to be fetched, or about the client requesting the resource.
- Response headers hold additional information about the response, like its location or about the server providing it.
- Representation headers contain information about the body of the resource, like its MIME type, or encoding/compression applied.
- Payload headers contain representation-independent information about payload data, including content length and the encoding used for transport.

HTTP header types
Headers can also be grouped according to how proxies handle them:
The most common response codes
408
Request Timeout
200
OK
301
Moved Permanently
401
Unauthorized
403
Forbidden
404
Not Found
429
Too Many Requests
409
Conflict
500
Internal Server Error
Headers: Content-Type
The Content-Type representation header is used to indicate the original media type of the resource (prior to any content encoding applied for sending).
In responses, a Content-Type header tells the client what the content type of the returned content actually is. Browsers will do MIME sniffing in some cases and will not necessarily follow the value of this header; to prevent this behavior, the header X-Content-Type-Options can be set to nosniff.
In requests, (such as POST or PUT), the client tells the server what type of data is actually sent.

Headers: Content-Type
MIME types:
- application (application/zip , application/javascript an etc)
- audio (audio/mpeg, audio/vorbis)
- font (font/woff, font/ttf, and font/otf)
- image (image/jpeg, image/png, and image/svg+xml)
- text (text/plain, text/csv, and text/html)
- video (video/mp4)

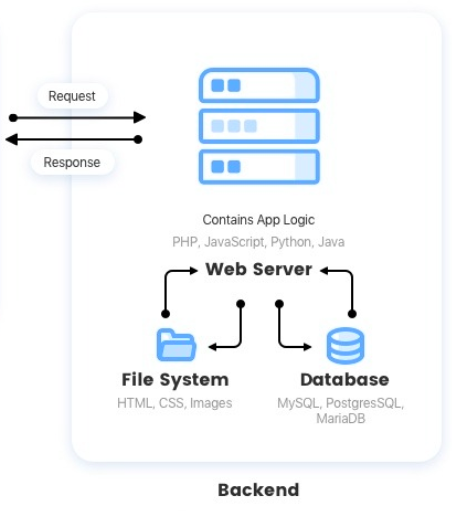
REST API
App 2
API
App 3
App 1
App 4




Standard situation
What is REST API?
A REST API (Representational state transfer) is an application programming interface (API or web API) that conforms to the constraints of REST architectural style and allows for interaction with RESTful web services. REST stands for representational state transfer and was created by computer scientist Roy Fielding.


Client
Database
GET, POST, PUT, PATCH, DELETE
REST API Model
JSON data
REST API
Architectural constraints
In order for an API to be considered RESTful, it has to conform to six criteria:
- A client-server architecture
- Stateless client-server communication,
- Cacheable data that streamlines client-server interactions.
- A uniform interface between components so that information is transferred in a standard form.
- A layered system that organizes each type of server (those responsible for security, load-balancing, etc.) involved the retrieval of requested information into hierarchies, invisible to the client.
- Code-on-demand (optional): the ability to send executable code from the server to the client when requested, extending client functionality.

Applied to web services
Web service APIs that adhere to the REST architectural constraints are called RESTful APIs. HTTP-based RESTful APIs are defined with the following aspects:
- a base URI, such as http://api.example.com/;
- standard HTTP methods (e.g., GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE);
- a media type that defines state transition data elements (e.g., Atom, microformats, application/vnd.collection+json,:91–99 etc.).
The semantics of HTTP methods
The following table shows how HTTP methods are intended to be used in HTTP APIs, including RESTful ones.
| GET | Get a representation of the target resource’s state. |
|---|---|
| GET | Used to get a resource from a server. The server looks for the data you requested and sends it back to you. A GET request performs a READ operation |
| POST | Used to create a new resource on a server. On a POST request, the server creates a new entry in the database and tells you whether the creation is successful. POST request performs a CREATE operation. |
| PUT / PATCH | These two requests are used to update a resource on a server. Using such requests the server updates an entry in the database and tells you whether the update is successful. PUT or PATCH request performs an UPDATE operation. |
| DELETE | Used to delete a resource from a server. On a DELETE request, the server deletes an entry in the database and tells you whether the deletion is successful. |
Description
HTTP methods
The anatomy of a Request
It’s important to know that a request is made up of four things:
The endpoint (or route)
The methods
The headers
The data (or body)
Endpoints or routes
- https://api.github.com/users (fetch all users)
- https://api.github.com/users/1 (fetch one user by ID)
- https://api.github.com/users?per_page=5 (fecth first 5 users)
GET
- https://api.github.com/users (create a user with provided data)
POST
{
login: "mojombo",
// id should be created
node_id: "MDQ6VXNlcjE=",
avatar_url: "https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/1?v=4",
gravatar_id: "",
url: "https://api.github.com/users/mojombo",
....
type: "User",
site_admin: false
}Endpoints or routes
PATCH / PUT
- https://api.github.com/users/1 (delete a user by ID)
DELETE
{
login: "mojombo",
id: 1,
node_id: "MDQ6VXNlcjE=",
avatar_url: "https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/1?v=4",
gravatar_id: "",
url: "https://api.github.com/users/mojombo",
....
type: "User",
site_admin: false
}- https://api.github.com/users/1 (update a user by ID with provided data)
cURL
GET
curl -X GET \
-H "Accept: application/json" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/1
- https://api.github.com/users/1
cURL is a computer software project providing a library and command-line tool for transferring data using various network protocols. The name stands for "Client URL", which was first released in 1997.
cURL
POST
curl -X POST \
-H "Content-Type: application/json; charset=UTF-8" \
-d '{"title": "The best actor", "body": "Keanu Reeves", "userId": 1}' \
https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts- https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts
http module
http module
To use the HTTP server and client one must require('http').
The HTTP interfaces in Node.js are designed to support many features of the protocol which have been traditionally difficult to use. In particular, large, possibly chunk-encoded, messages. The interface is careful to never buffer entire requests or responses, so the user is able to stream data.
const http = require('http');
// request from the server to an API
http.get('http://localhost:3000/api/users', { agent }, (res) => {
res.on('data', (data) => {
// Do nothing or do something =)
});
});Create a server
const http = require('http');
const server = http.createServer((request, response) => {
// magic happens here!
});
server.on('request', (request, response) => {
// the same kind of magic happens here!
})Any node web server application will at some point have to create a web server object. This is done by using createServer.
The function that's passed into createServer is called once for every HTTP request that's made against that server, so it's called the request handler.
The Server object returned by createServer is an EventEmitter.
Method, URL and Headers
const { method, url, headers } = request;
const userAgent = headers['user-agent'];
if (url === '/login') {
// redirect to login
}The request object is an instance of IncomingMessage.
Request Body
let body = [];
request.on('data', (chunk) => {
body.push(chunk);
}).on('end', () => {
body = Buffer.concat(body).toString();
// at this point, `body` has the entire
// request body stored in it as a string
});
When receiving a POST or PUT request, the request body is important to your application. The request object that's passed into a handler implements the ReadableStream interface.
The chunk emitted in each 'data' event is a Buffer.
HTTP Status Code
const http = require('http');
const server = http.createServer((request, response) => {
// set correct status code
response.statusCode = 404;
// magic happens here!
});
If you don't bother setting it, the HTTP status code on a response will always be 200.

Setting Response Headers
response.setHeader('Content-Type', 'application/json');
response.setHeader('X-Powered-By', 'bacon');
Headers are set through a convenient method called setHeader.
We can explicitly write the headers to the response stream. To do this, there's a method called writeHead, which writes the status code and the headers to the stream.
response.writeHead(200, {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
'X-Powered-By': 'bacon'
});Sending Response Body
response.write('<html>');
response.write('<body>');
response.write('<h1>Hello, World!</h1>');
response.write('</body>');
response.write('</html>');
response.end();Since the response object is a WritableStream, writing a response body out to the client is just a matter of using the usual stream methods.
Or to send as the last bit of data on the stream:
response.end('<html><body><h1>Hello, World!</h1></body></html>');A Quick Thing About Errors
request.on('error', (err) => {
// This prints the error message and stack trace to `stderr`.
console.error(err.stack);
});Since the request object is a ReadableStream, it's also an EventEmitter and behaves like one when an error happens.
Note: If we don't have a listener for that event, the error will be thrown, which could crash your Node.js program.

Quiz time