The Path to Mastery
Become a Great Software Engineer

$ whoami
Senior Software Engineer
The most important:
I like programming, JavaScript, movies, music and I'm a big fan of LOTR and Star Wars 🤓
May the Force be with you!
6 years at GlobalLogic
about 8 years in Web Development
Speaker, mentor, and Trusted Interviewer at GlobalLogic
Part of the program committee at Fwdays conference


Inna Ivashchuk




My path
From GIS Engineer to Senior Software Engineer
My programming journey began when I created my first program in Pascal while attending school and continued as I designed a website for my school.
But after school, I decided to become a GIS engineer and even have 4 years of experience in this field


Who is a GIS engineer?

After dedicating three years to working as a GIS engineer,
I decided to get back to programming

And since that's time I've been learning














and more

But something seems to be missing

- OOP principles
- Functional programming principles
- Algorithms and Data structures
- Desing Patterns

Let's get the basics down!
The basic skills and knowledge needed for software engineering
Programming languages











18

I'm curious, what happens if I become proficient in two programming languages?
1
Discover common programming concepts and paradigms
3
Broadens understanding and enables diverse problem-solving, fostering creativity in solution development
5
Understand OOP and Functional programming principles
2
Multi-language proficiency boosts employability, especially for roles requiring it
4
Easier to communicate and collaborate with your teammates, if they have backgrounds or expertise in different languages
Algorithms and Data structures

An algorithm is any well-defined computational procedure that takes some value, or set of values, as input and produces some value, or set of values, as output. An algorithm is thus a sequence of computational steps that transform the input into the output.

What is an algorithm?
„Software gets slower faster than hardware gets faster.“
Niklaus Virt

Start
Do you know algorithms?
Time to learn 🤓
Congratulations 🥳
You are a superhero
Resolved!
No
Yes
A data structure is a specialized format for organizing, processing, retrieving and storing data. There are several basic and advanced types of data structures, all designed to arrange data to suit a specific purpose.
What is data structure?
Tree
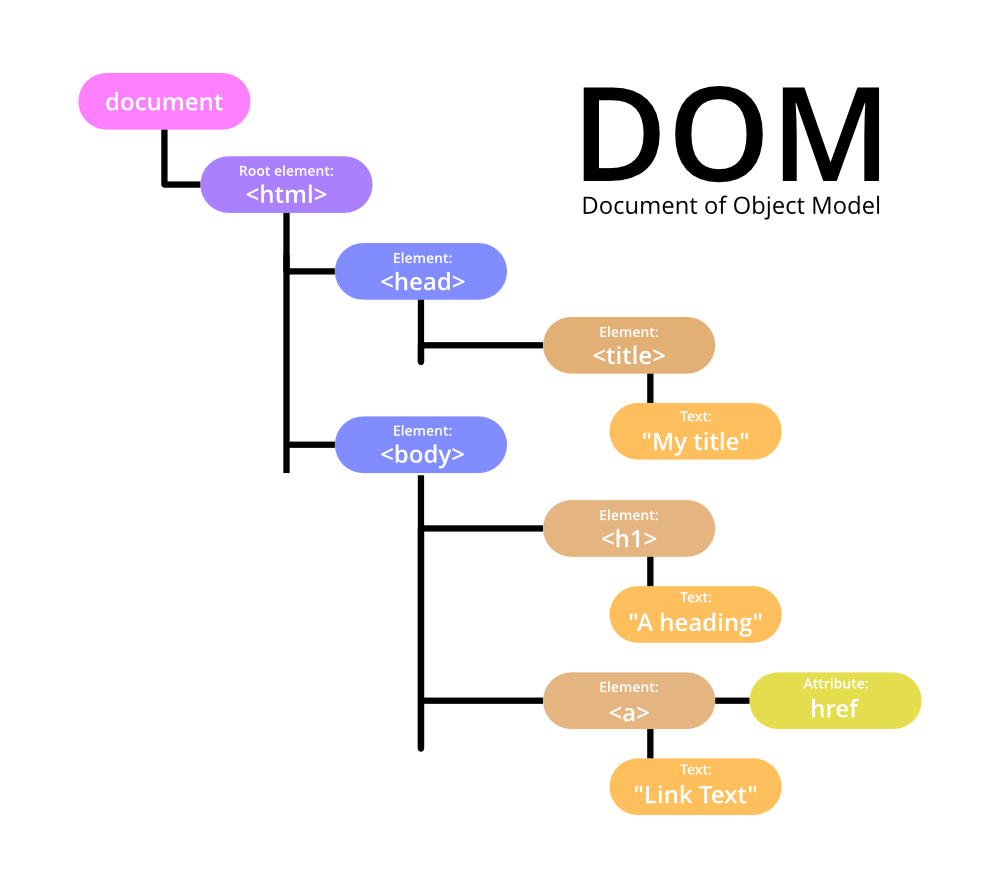
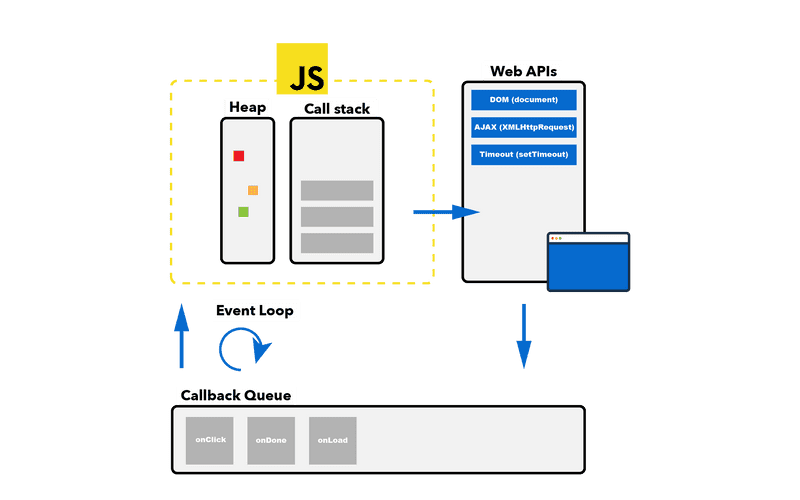
JS Event Loop: Heap, Queue, Stack
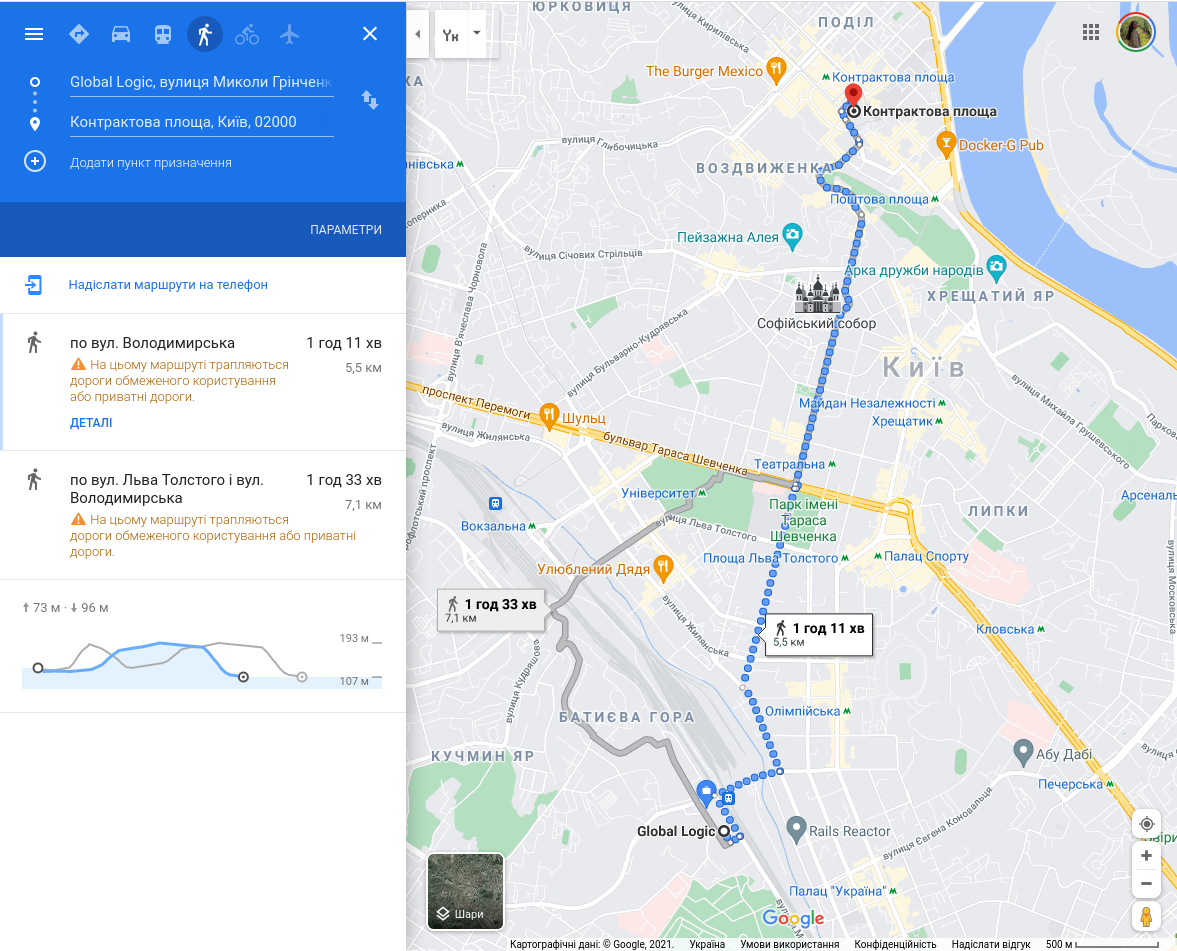
Google Maps: Dijkstra algorithm and Weighted Graph
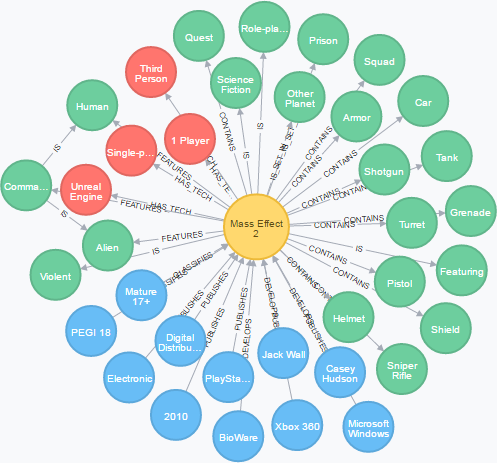
Recommendation system/engine: Graph










....and many others


Big O notation is a convenient way to describe how fast a function is growing. It is often used in computer science when estimating time complexity.
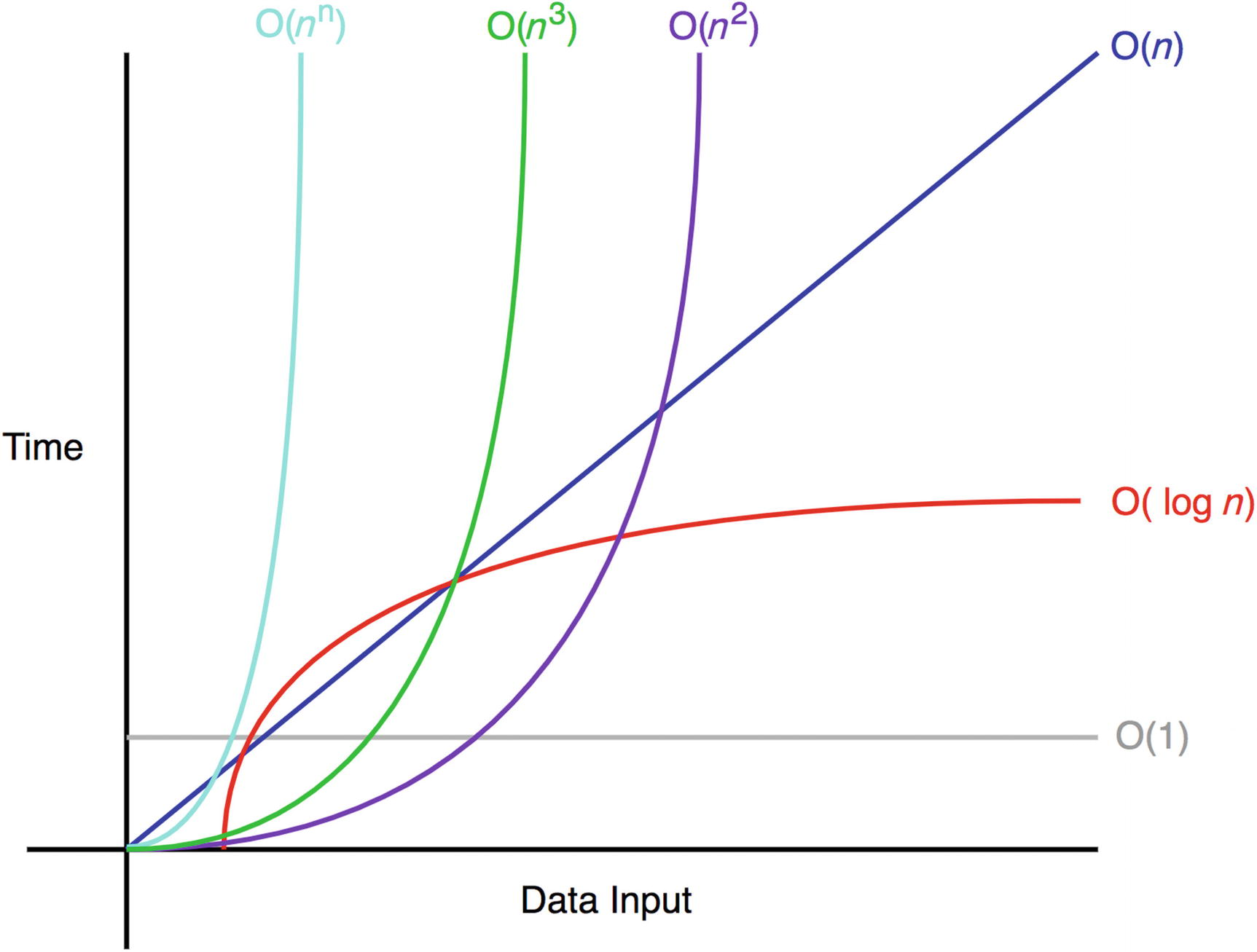
Let's try to analyze the an example 1:
// Find sum of all numbers in array
function sumNumbersInArray(arr) {
let result = 0;
for (let i=0; i < arr.length; i++) {
result += arr[i];
}
return result;
}

result - O(n)
Example 2
// Calculation
function calculate(arr) {
const a = 3 + 1;
const b = 3 + 3;
let c = arr.length;
console.log('Calculating...');
return a + b + c;
}
calculate([1,2,3,4,5]);
result - O(1)

Example 3
// Calculation
function calculationInArray(arr) {
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < arr.length; j++) {
arr[i] = arr[i] + arr[j];
}
}
return arr;
}
calculationInArray([1,2,3,4,5]);

result - O(n*n)
Functional programming principles

Functional programming is a programming paradigm that emphasizes the use of functions to solve problems


Immutability: In functional programming, once a value is assigned to a variable, it cannot be changed. This helps to avoid unwanted side effects and makes the code more predictable.
const game = {
name: 'Cyberpunk 2077',
year: 2020,
buggy: false,
}
// mutable code
game.buggy = true;
// immutable code
const cyberpunk = {
...game,
buggy: true,
}Higher-order functions: Functions in functional programming can take other functions as arguments and return functions as values. This allows for powerful abstractions and code reuse.
// Using a Higher-Order Function (filter)
const games = [{
name: 'Cyberpunk 2077',
year: 2020,
buggy: true,
}, {
name: 'The Witcher 3',
year: 2007,
buggy: false,
}];
const nonBuggyGames = games.filter(game => !game.buggy);
// Using a Higher-Order Function (map)
const num = [10, 20, 30];
const num10 = num.map(i => i * 2);
Pure functions: Pure functions are functions that always produce the same output for a given input and have no side effects. They are easier to reason about and can be used in parallel programming.
function add(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
function square(x) {
return x * x;
}
// not a pure function
const PI = 3.14;
function getCircleSquare(r) {
return PI * r * r;
}
Recursion: Functional programming encourages the use of recursion instead of loops for repetitive tasks. This can lead to more concise and readable code.
function factorial(num) {
if (num < 0) {
throw new Error("num must not be negative");
}
if (num <= 1) {
// Both 1! and 0! are defined as 1
return 1;
}
return num * factorial(num - 1);
}
Function composition is the act of combining two or more functions to create a new function that performs both operations in sequence.
// Function composition example
function add(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
function double(x) {
return x * 2;
}
const result = double(add(2, 3));
console.log(result); // Output: 10OOP principles

Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a computer programming model that organizes software design around data, or objects, rather than functions and logic.
In object-oriented programming, Inheritance is the mechanism of basing an object or class upon another object or class, retaining a similar implementation. Also defined as deriving new classes from existing ones such as super class or base class and then forming them into a hierarchy of classes.
Polymorphism (from Greek πολὺ - multiple, і μορφή - forms) is the method in an object-oriented programming language that performs different things as per the object's class, which calls it.

Animal
Dog
Cat
.speak() // woof!
.speak() // meow!
Encapsulation – in software systems, refers to the bundling of data with the mechanisms or methods that operate on the data. It may also refer to the limiting of direct access to some of that data, such as an object's components.
E
n
c
a
p
s
u
l
a
t
i
o
n
Variables
Methods
Class
Don't forget about object Oriented Design principles
DRY
S.O.L.I.D.
KISS
GRASP
YAGNI
"You aren't gonna need it"
General responsibility assignment software pattern
"Don't repeat yourself"
"Keep it simple, stupid!"
Design patterns

Singleton
Factory Method
Abstract Factory
Prototype
Builder
Creational Patterns: These patterns are focused on creating objects and are used to encapsulate complex object-creation processes.

Composite
Adapter
Bridge
Facade
Decorator
Structural Patterns: These patterns are focused on the relationship between objects and provide ways to manage object structures.
Flyweight
Proxy
Mediator
Command
Chain of Responsibility
Iterator
Memento
Behavioral Patterns: These patterns are focused on communication between objects and are used to manage algorithms, responsibilities, and patterns of communication between objects.
Observer
Interpreter
State
Strategy
Template Method
Best practices
The best practices in software engineering
1
Debugging:
- debug JS code
- use Profiler for React
- other dubug tools
3
Version control:
- one code base
- contribution guidelines
- ...
5
Code review:
- knowledge sharing
- improved code quality
- enhancing maintainability of the code
2
Testing:
- unit-tests
- e2e tests
- integration tests
4
CI/CD:
- automated checks
- improved release process
- ...

Collaboration and communication
The soft skills are matter
1
Teamwork
2
Empathy
3
Effective feedback
Possible manager suggestions
Code review

Benefits
Improved code quality
Knowledge sharing and skill development
Improved code consistency and maintainability
More efficient development process
Reduced technical debt
Example
function addIdToMovies(movies) {
return movies.map(movie => {
const index = movies.fin(m => m.name === movie.name);
return ({ ...movie, id: `movie-${index}`});
})
}
addIdToMovies([{
name: 'The Lord of the Rings',
genre: 'fantasy',
}, {
name: 'Dark Knight',
genre: 'comics',
}, {
name: 'Joker',
genre: 'comics',
}, {
name: 'Iron Man',
genre: 'comics',
}]);

Example improvement
function addIdToMovies(movies) {
return movies.map(
(movie, index) => ({ ...movie, id: `movie-${index}`})
);
}
addIdToMovies([{
name: 'The Lord of the Rings',
genre: 'fantasy',
}, {
name: 'Dark Knight',
genre: 'comics',
}, {
name: 'Joker',
genre: 'comics',
}, {
name: 'Iron Man',
genre: 'comics',
}]);
Pair programming

Pair programming is a technique in software development where two developers work collaboratively on the same task, sharing a computer and working together to write code.

Programmer 1


Programmer 2
Benefits
Higher code quality
Collective code ownership
Stronger communication between developers
Shared best practices
More efficient work
Faster training of new team members
Mob programming

Dev: navigator
Dev: driver




Mob programming is a collaborative approach to software development in which a group of developers work together in real-time on one task. Mob programming has its roots in pair programming, an Extreme Programming (XP) technique in which two developers work as a team on the same task, using just one computer.
Dev: navigator
Dev: navigator

Mob programming rules:
Benefits
Higher code quality
Collective code ownership
Enhanced communication
Improved Decision-Making
Knowledge sharing
Team Building
(because it’s fun!)
Let's Keep Growing!
Anyone who stops learning is old, whether at twenty or eighty.
– Henry Ford
- OOP principles
- Functional programming principles
- Algorithms and Data structures
- Design Patterns

+
- System Design

Quiz: question 1
"4" + 8 - 6
result - 42

Quiz: question 2
const names = ["Luke", "Neo", "Aragorn"];
const helloMsgs = names.map((name) => `Hello, ${name}!`);
Big O(n)

Let's estimate Big O()
Quiz: question 3
function fibonacci(n) {
if (n < 2){
return 1;
}
return fibonacci(n-2) + fibonacci(n-1);
}
fibonacci(7);
//Returns 21It is recursion

What principle of Function programming is used in this example?
Thanks to AFU(ЗСУ)
Keep working, learning, developing and definitely donate and help our Ukrainian Army and volunteers
