AN APPROACH TO CERVICAL DYSTONIA
Con Yiannikas

Evaluation of Cervical Dystonia in terms of:
- Postural deviation in the axial plane (torticollis)
- Coronal plane (laterocollis)


CLASSIFICATION OF CERVICAL DYSTONIA
- Saggital plane (anterocollis and retrocollis)
- Most patients with cervical dystonia have postural deviation in at least two of these planes.
- In addition, the presence of shoulder elevation and of saggital and lateral shift are important elements to note.

CLASSIFICATION OF CERVICAL DYSTONIA
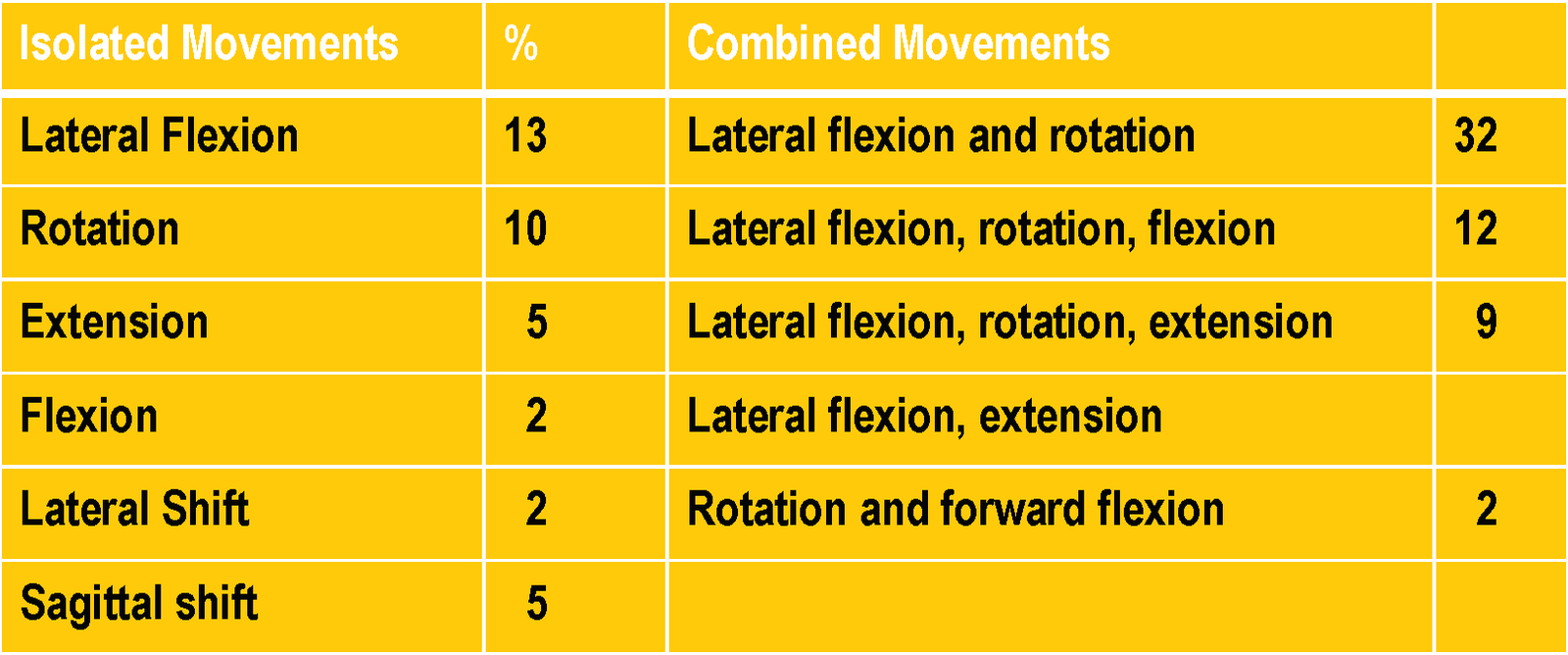
FREQUENCY OF ABORMAL HEAD POSTURES
CAPUT-COLLIS CONCEPT
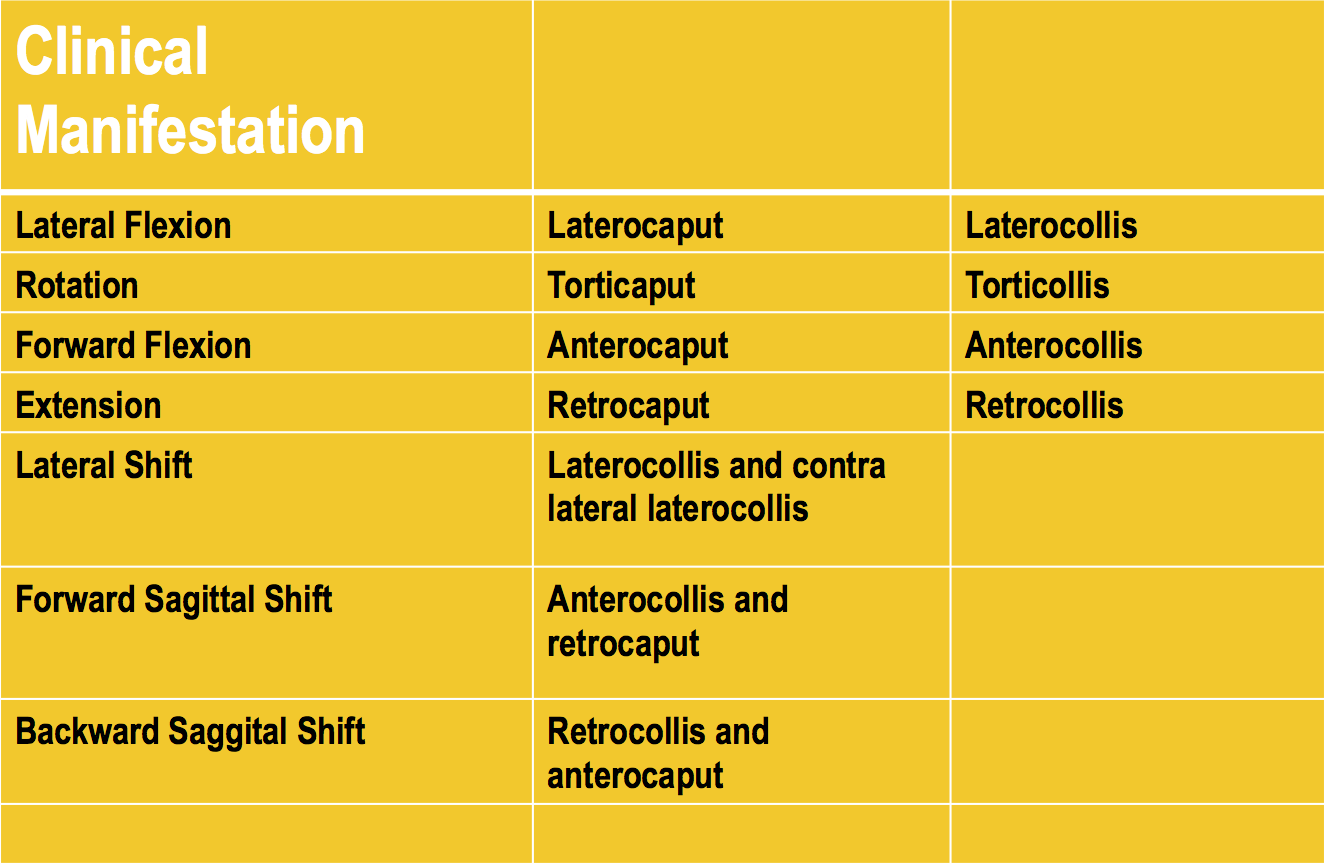
TORTICAPUT
C3
C7
Head rotated via C1-2 {Atlanto-axial joint}
C3-7 vertebral column column no movement
TORTICOLLIS
C3-6 rotate with C1-2 and head
C7
C3

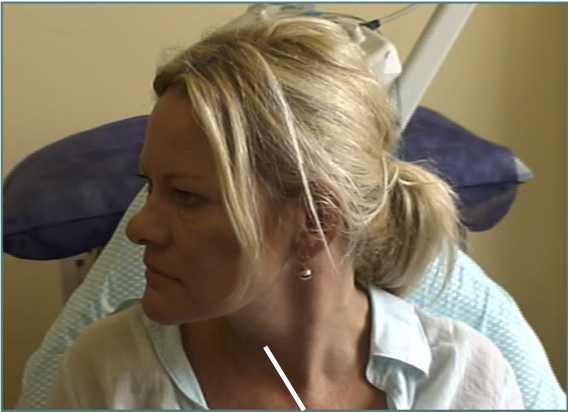
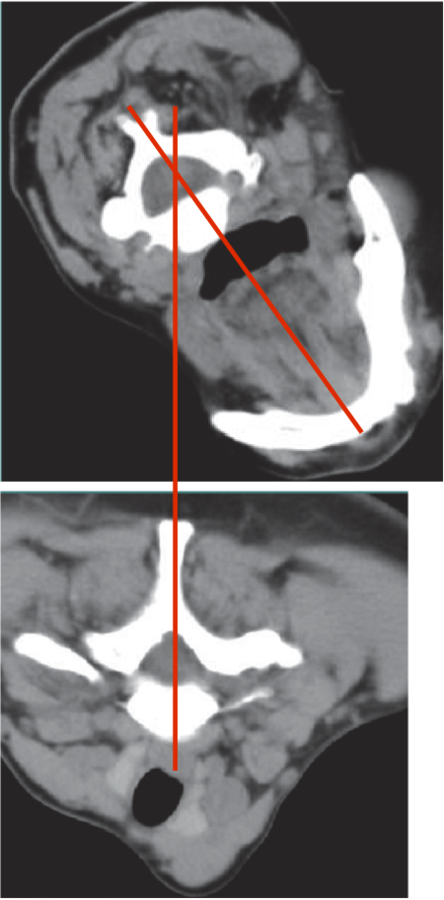
The larynx is not above the sternum
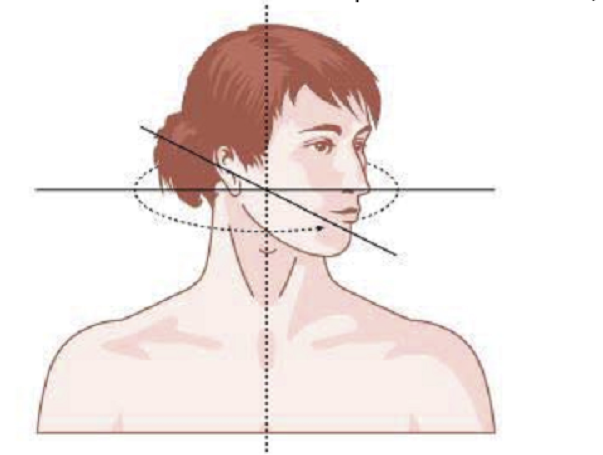
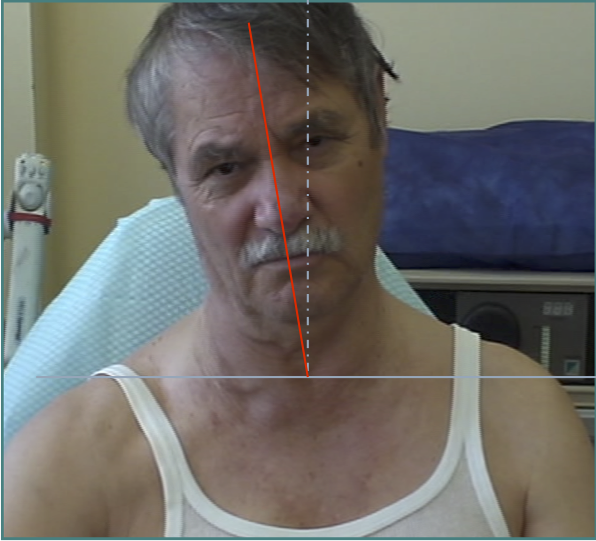
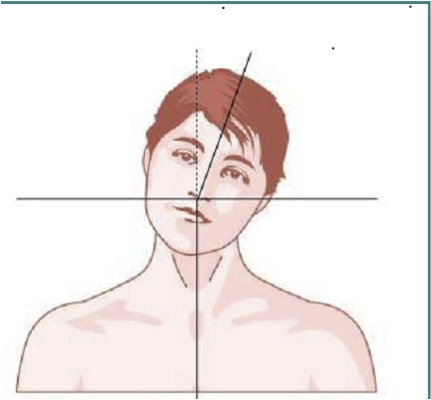
AXIAL ROTATION-TORTI
ROTATION OF HEAD
-
Attaching to skull
- Unilateral contraction

Anterolateral muscles contralateral rotation
Posteromedial contralateral rotation
Posterolateral muscles ipsilateral rotation
Splenius capitus
Longissimus capitus
Splenius cervicus
Trapezius
SCM
- Semispinalis capitis
- Spinalis capitis
TORTICAPUT
Muscles attaching to skull –
- Trapezius
- Sternomastoid
Contralateral rotation
- Obliquis capitis inferior
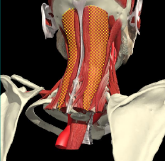
- Semispinalis capitis
- Spinalis capitis
Ipsilateral rotation
- Splenius capitis
- Splenius cervicis
- Longissimus capitis
Lateral
Midline
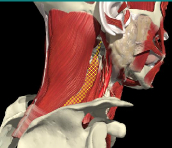
TORTICOLLIS
Muscles attached to spine
Contralateral rotation
-
Semispinalis cervicis
-
Scalenus anterior
Ipsilateral rotation
- Longissimus cervicis
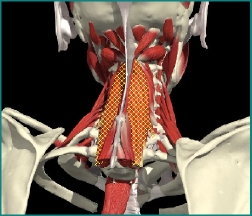
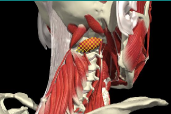
RETROCAPUT



RETROCOLLIS
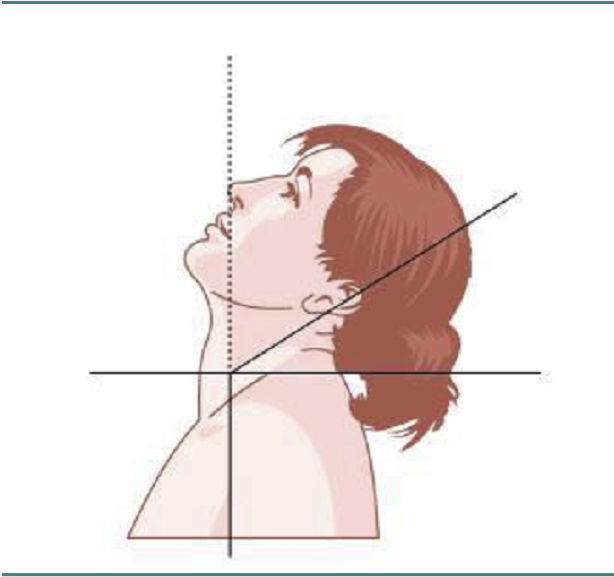
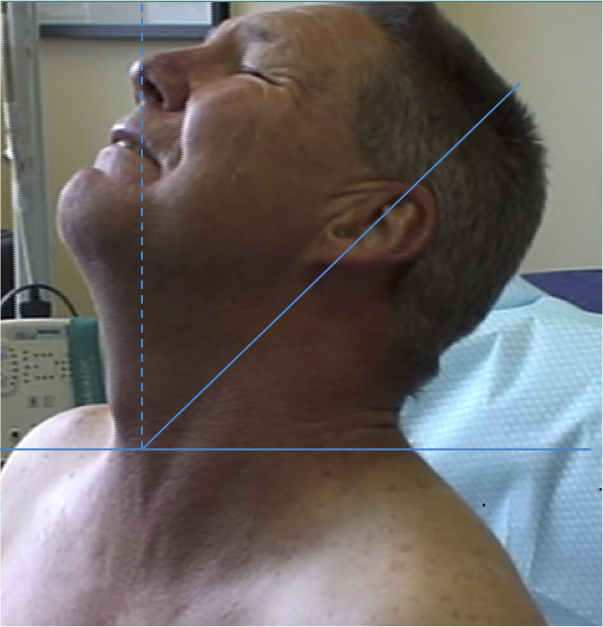
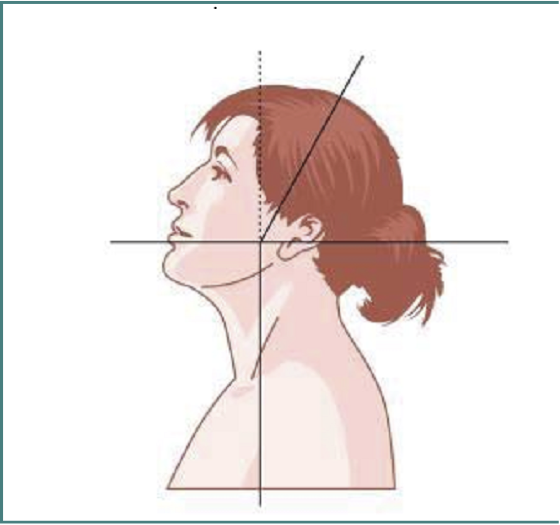
MOTION IN THE SAGITTAL PLANE-RETRO
EXTENSION
Posterior and posterolateral muscles acting together
RETROCAPUT- ATTACH TO SKULL
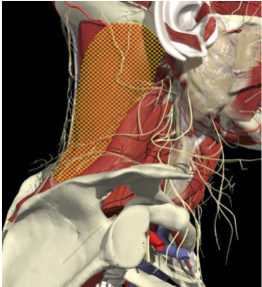
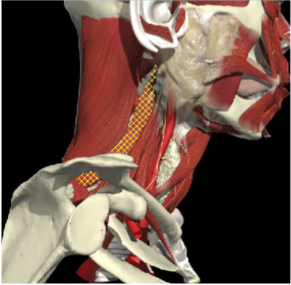
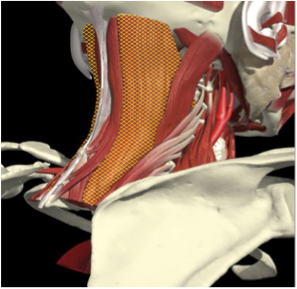
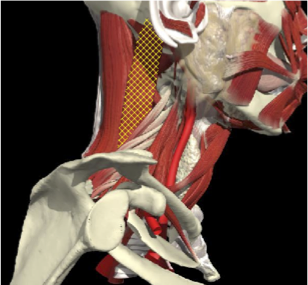
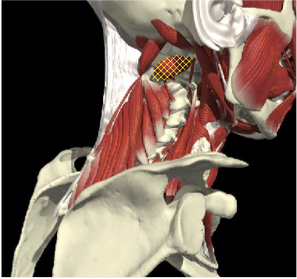
- 13 degrees
Attach to skull
- Trapezius
- Sternomastoid
- Splenius capitus, cervicus
- Semispinalis/Spinalis capitus
- Longissimus capitus
- Obliques capitus inferior
Range of motion
capitus
cervicus
RETROCOLLIS- ATTACH TO NECK
Midline -attach to spine
- Semispinalis cervicis
- Longissimus cervicis
Range of Motion
- 66 degrees
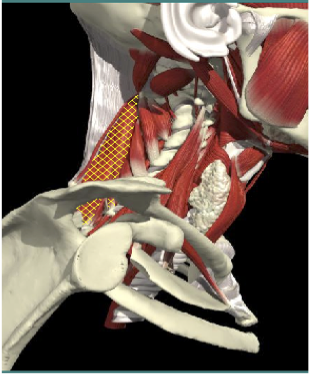
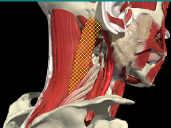
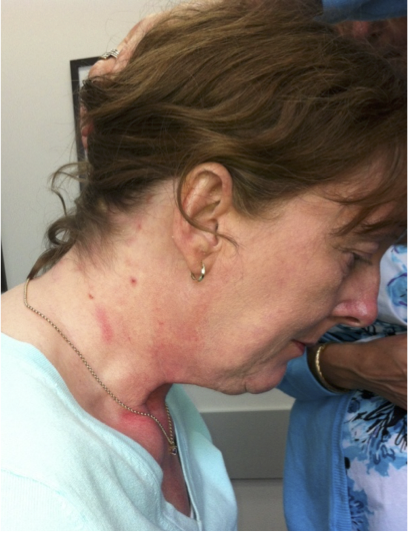
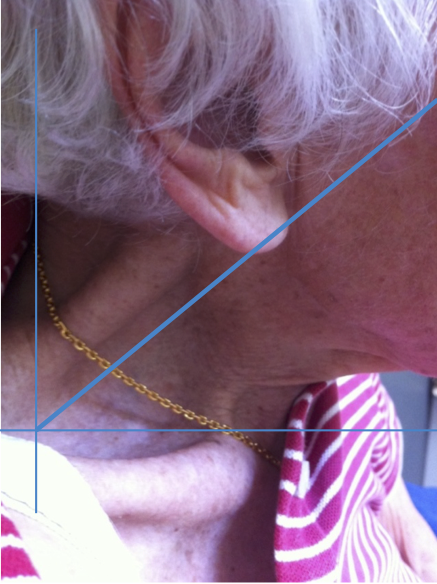
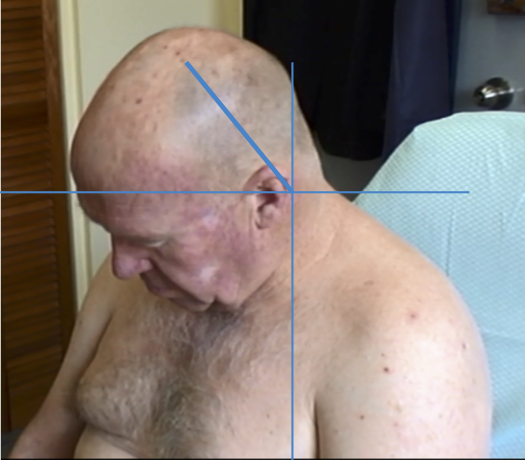
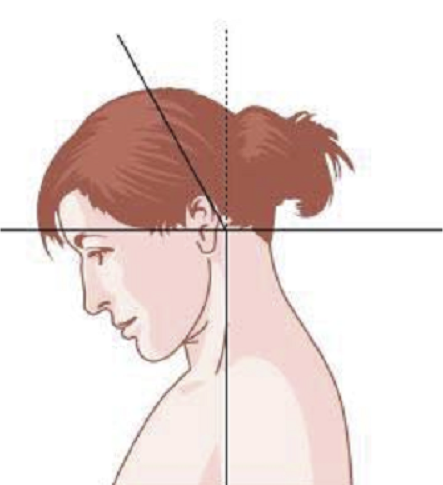
ANTEROCOLLIS

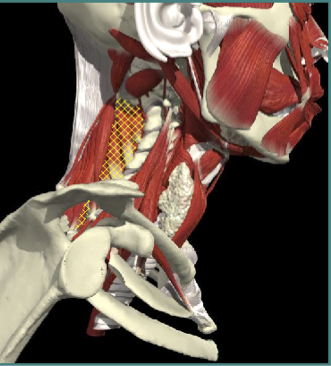
ANTEROCAPUT
MOTION IN SAGITTAL PLANE- ANTERO
FLEXION
Anterior muscles acting together

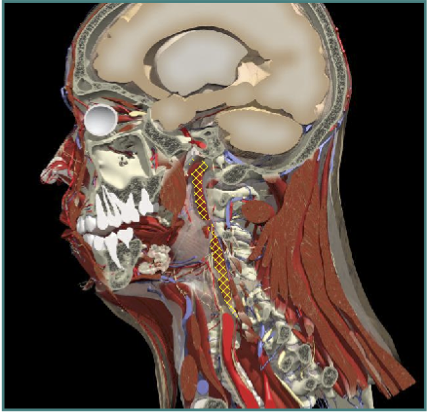
ANTERO- CAPUT
- Longus Capitis
- Platysma
- Digastric/submental
Insert base of skull or jaw
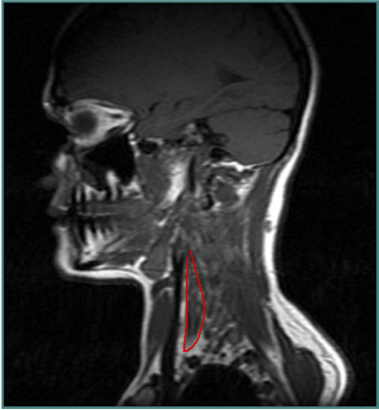
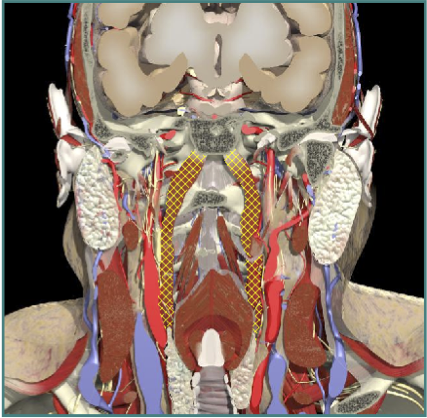
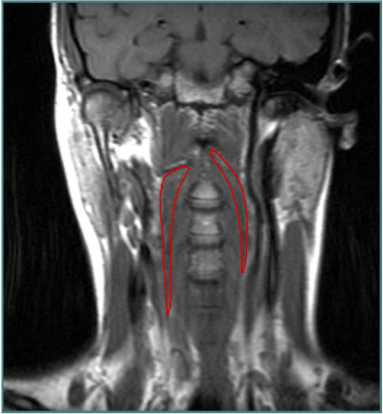
ANTEROCOLLIS
- Scalenus medius and anterior
- Longus Colli
Insert Spine
- Extends head and flexes spine
SCM
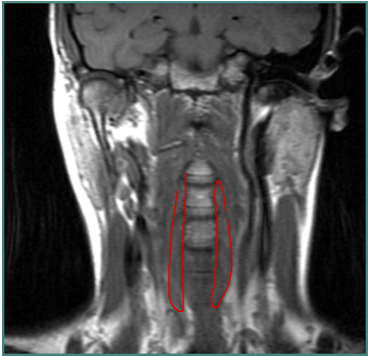
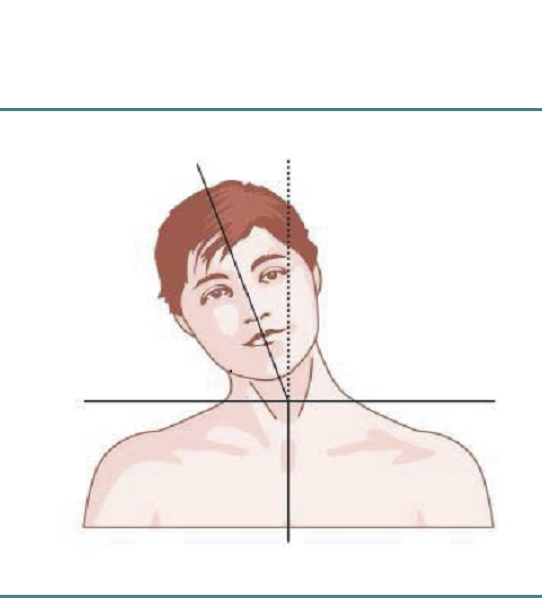
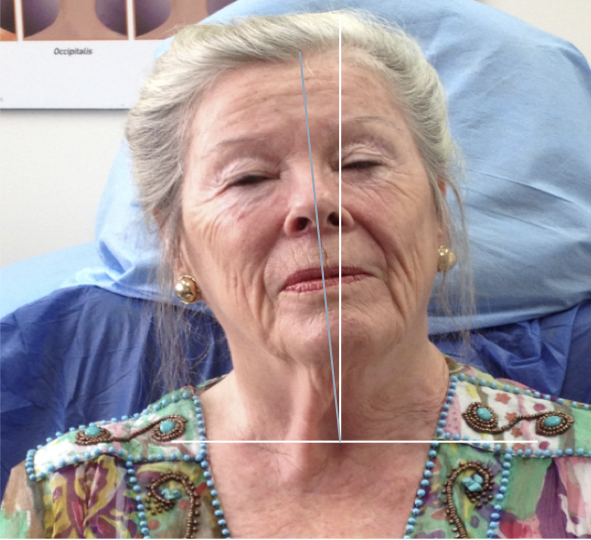
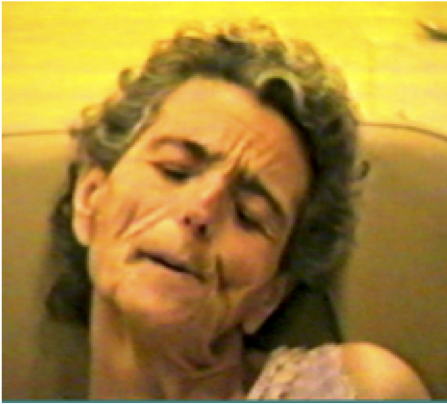
LATEROCOLLIS
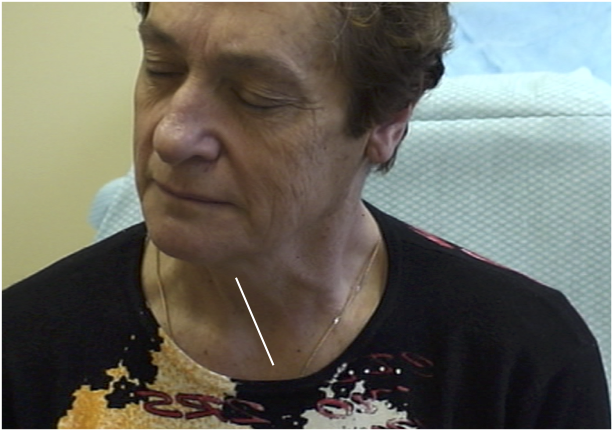
Larynx shifted relative to sternum
LATEROCAPUT

MOVEMENT IN THE CORONAL PLANE
-
Majority of patients (60%) have lateral flexion of head and neck in varying proportions.
- 20% head only, 20% neck only
LATERAL FLEXION
Lateral muscles acting in isolation

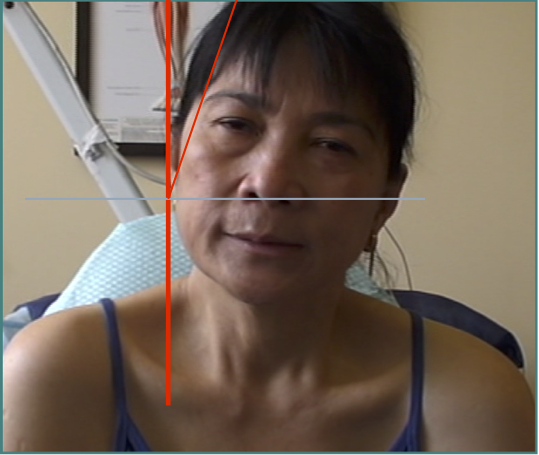
LATEROCAPUT




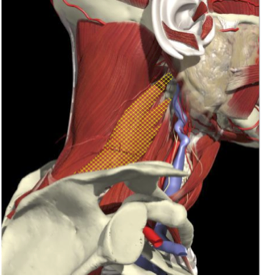
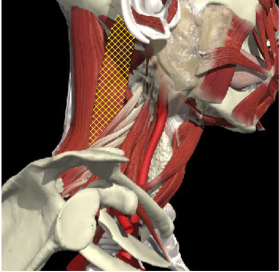
Muscles that insert into skull (mastoid/ occiput)
- Trapezius
- Sternomastoid
- Splenius capitus/cervicus
- Levator scapulae
- Longissimus capitus
Range of movement
- 8 degrees
LATEROCOLLIS
Long muscles transversing spine
- Levator scapulae
- Scalenus Anterior/medius
- Semispinalis cervicis
- Longissimus cervicis
Biomechanical advantage
- Range - 37 degrees
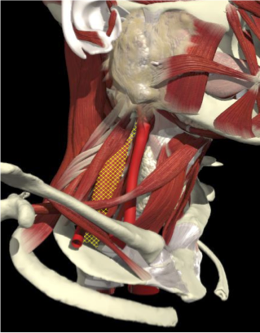
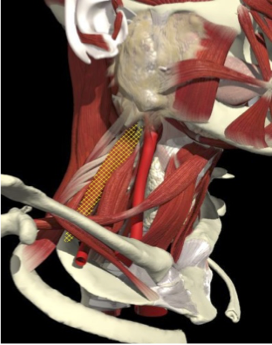
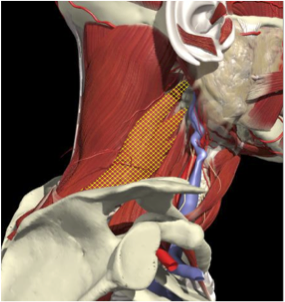
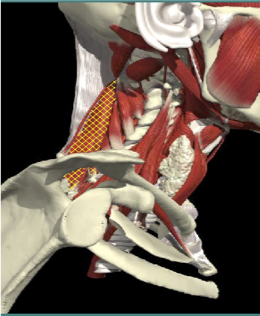
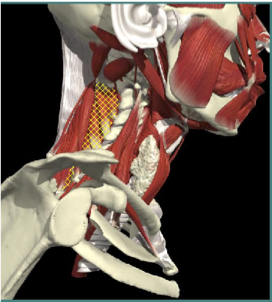
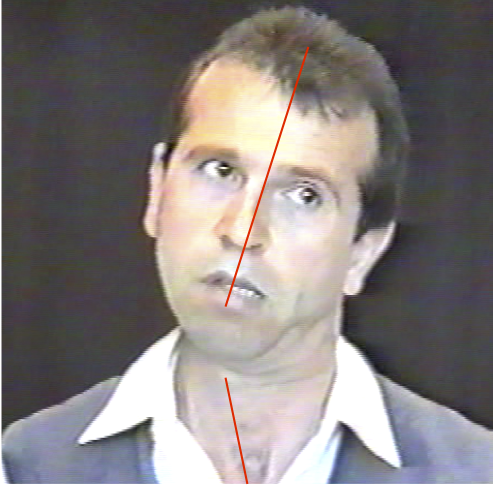
LATERAL SHIFT
Secondary to lateral flexion of the spine and flexion of the head in the opposite direction.
LATERAL SHIFT


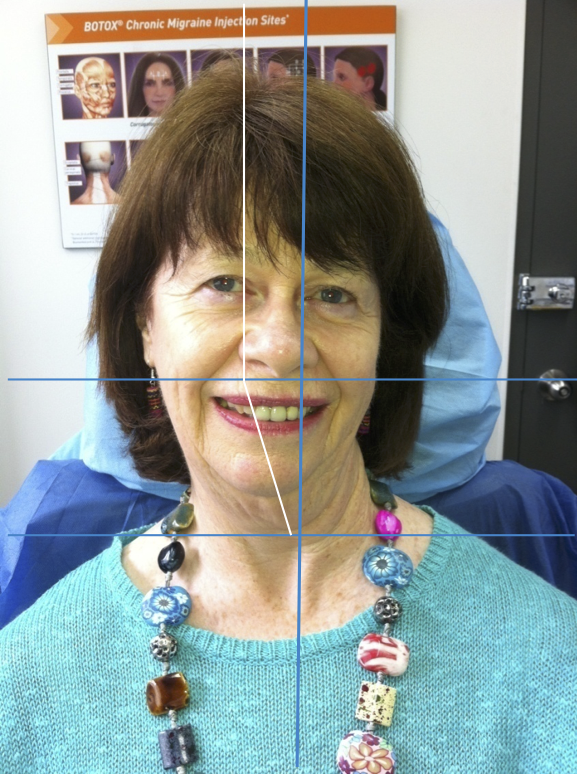
LATERAL SHIFT
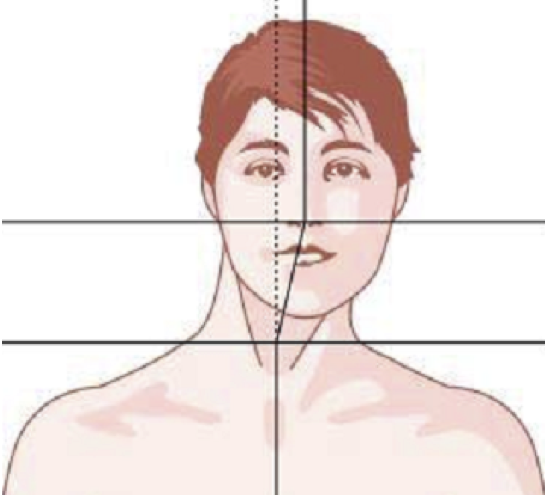
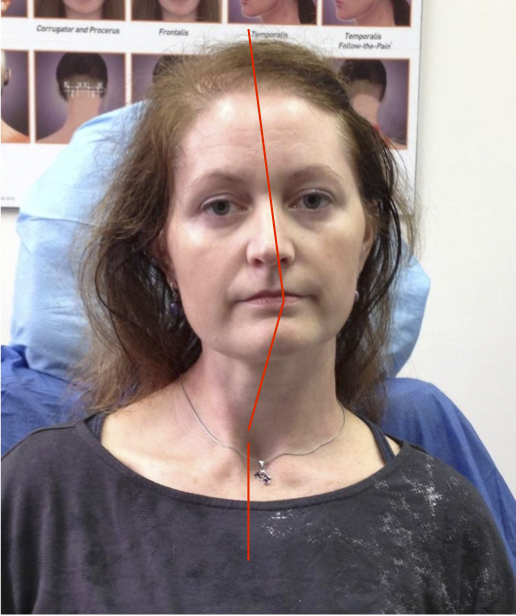
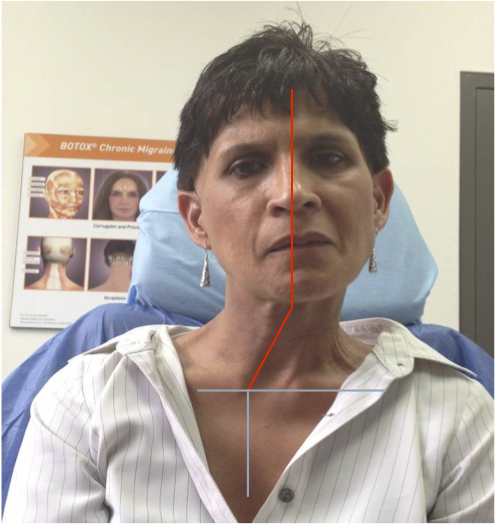
LATERAL SHIFT
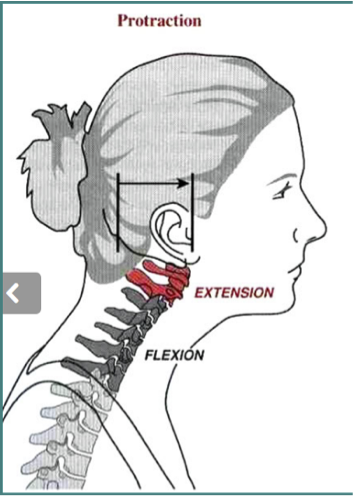
SAGITTAL SHIFT- PROTRACTION
Due to a combination of extension of head and flexion of neck.
Often due to bilateral tonic contraction of Sternomastoid
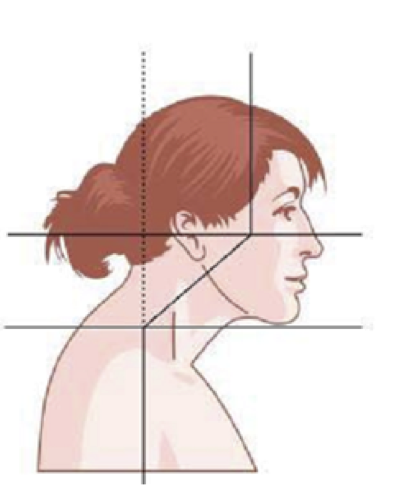
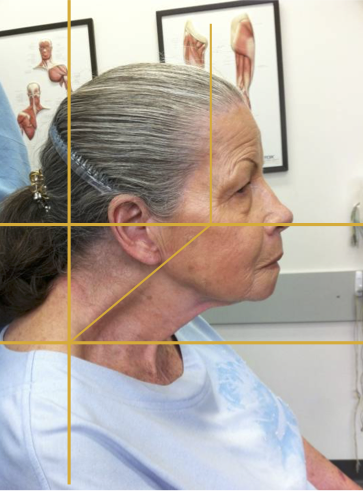
SAGITTAL SHIFT- RETRACTION
Due to a combination of neck extension and head flexion.
Produces “double chin” look.
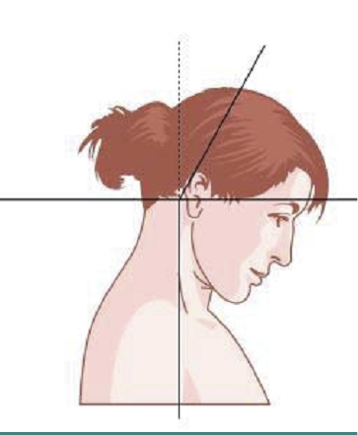
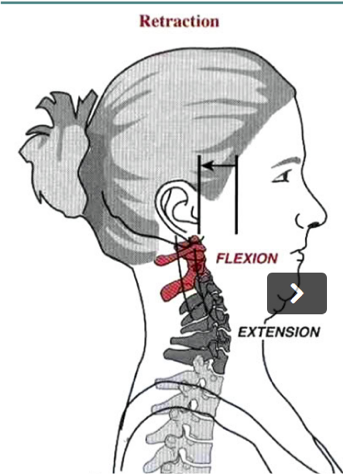
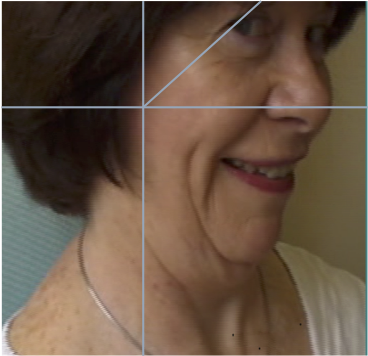
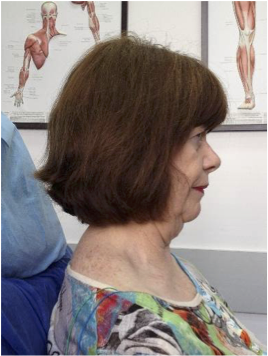
LATERAL AND SAGITTAL SHIFT
CLINICAL ASSESSMENT OF CERVICAL DYSTONIA
- Voluntary movement is affected by co-contracting muscle pairs- it is important to assess range of individual neck movements but also the effort required and the localisation of pain associated with the movement.
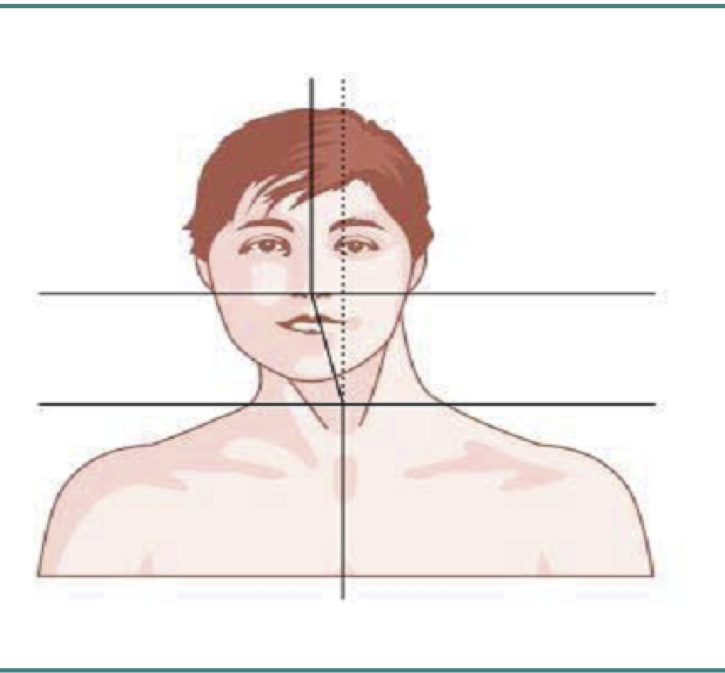
Line from Sternum to larynx
- Sensory Tricks/ Triggers
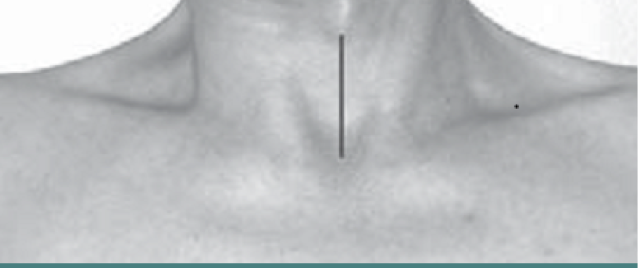
- Determination if neck or head or both are involved, description of abnormal posture and determination of muscles to be targeted.
- Determination of axis
GENERAL PRINCIPLES- CO-CONTRACTION
Voluntary movement is affected by co-contracting muscle pairs. It is important to assess range of individual neck movements but also the effort required and the localisation of pain associated with the movement.
In this patient there is co-contraction of ipsilateral Trapezius and Levator scapulae on the left, restricting rotation to the left and causing local pain
ASSESS DYSTONIA IN VARIOUS POSTURES
Assessment of head position sitting, walking and laying down as this may change .
SENSORY TRICKS OR TRIGGERS
ROLE OF EMG
-
Accuracy of Muscle Localization
-
Planning of muscles to inject - determination of active muscles
-
Localization of endplates
- Less problems with diffusion
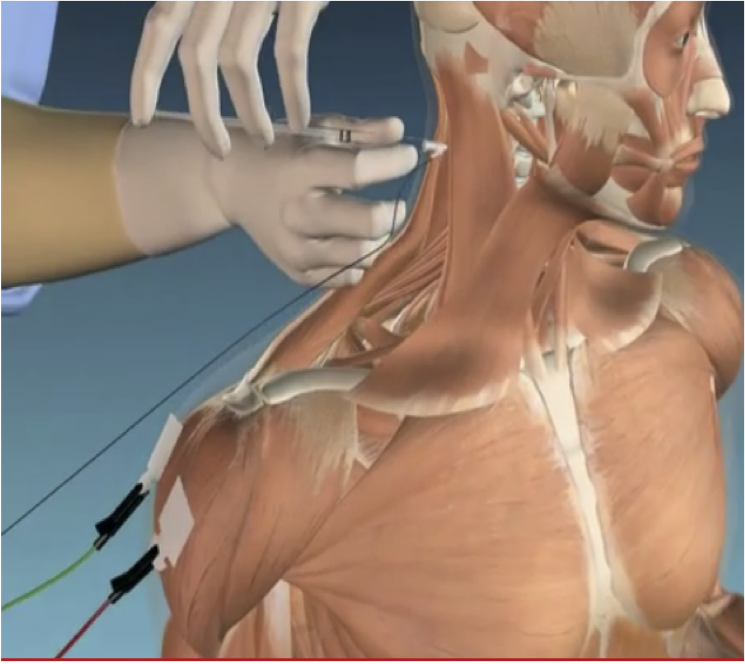
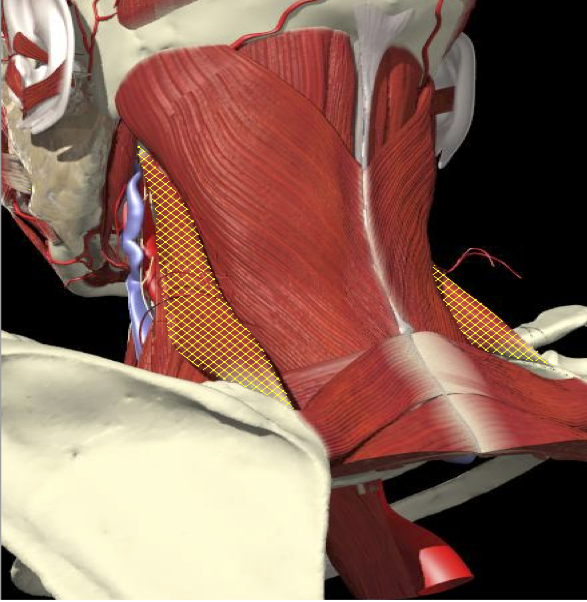
ACCURACY OF MUSCLE LOCALIZATION
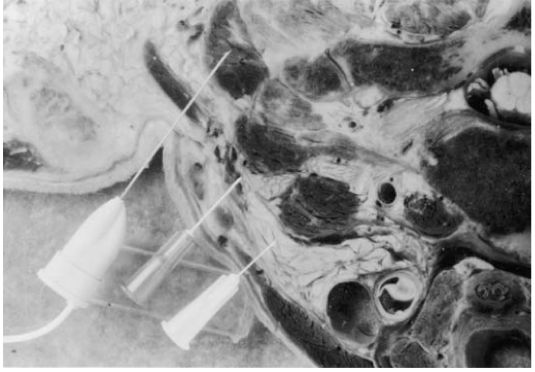
- Muscles deep
- Not easily identified by surface landmarks
- Not palpable on examination


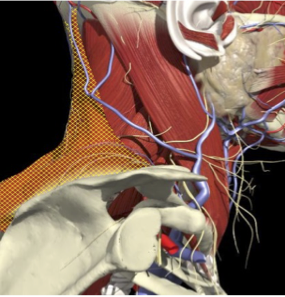
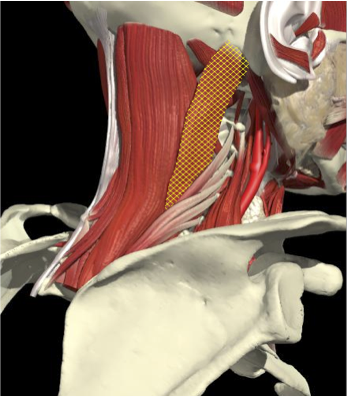
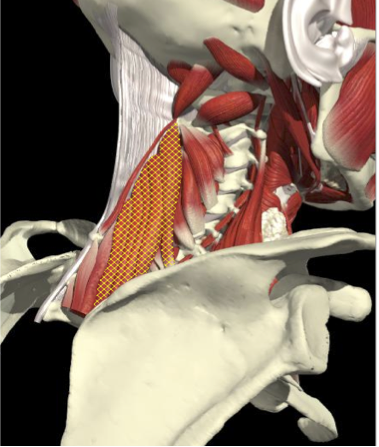
ACCURACY OF LOCALIZATION - SCALENES
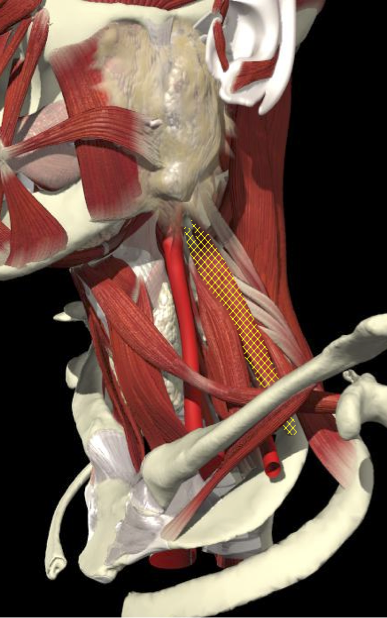
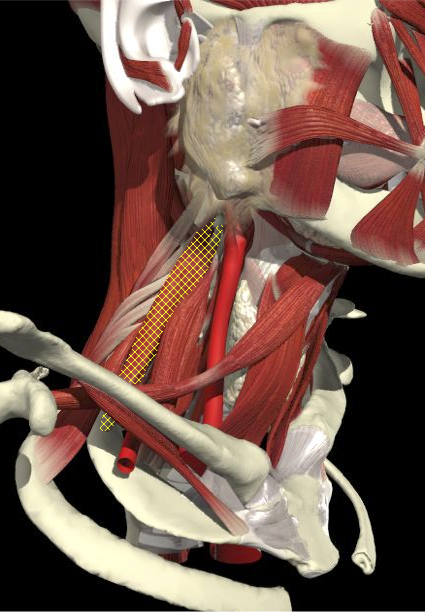
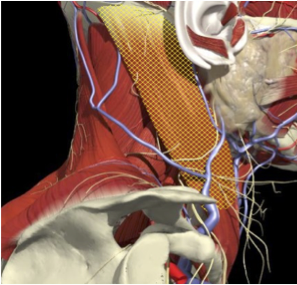
ACCURACY OF LOCALIZATION LEVATOR SCAPULAE
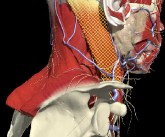
LOCALIZATION OF MUSCLES IN DEEPER LAYERS
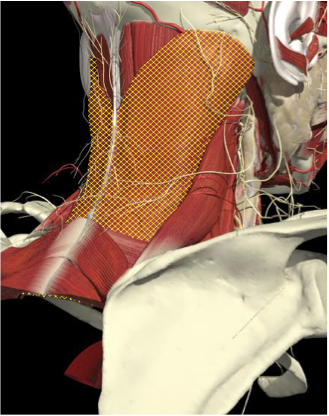
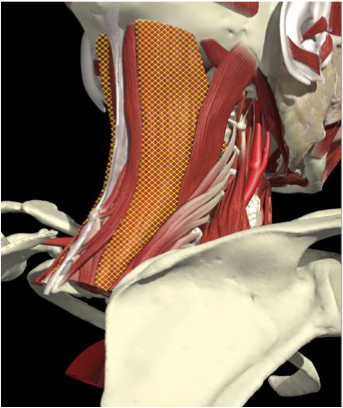
Layer 1
Layer 2
Layer 3
Splenius Capitis
Semispinalis Capitis
Longissimus Capitus
Semispinalis Cervicis
ACCURACY OF LOCALIZATION – DEEPER LAYERS

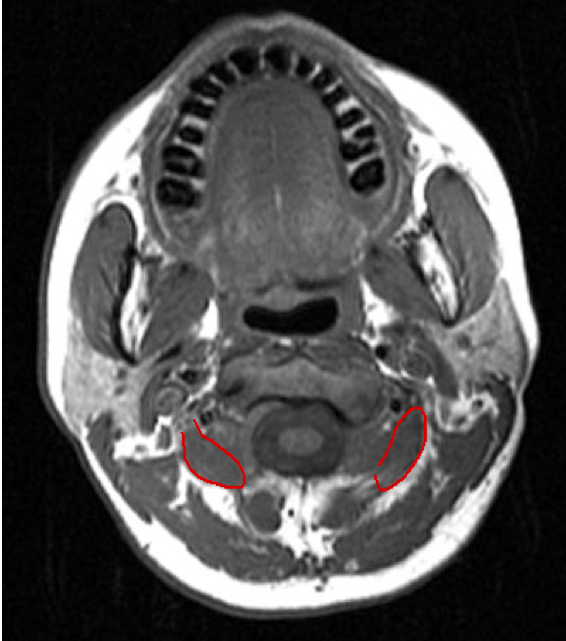
INJECTION SITES
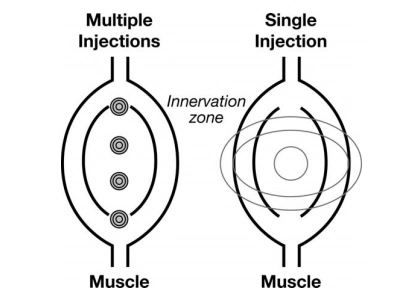
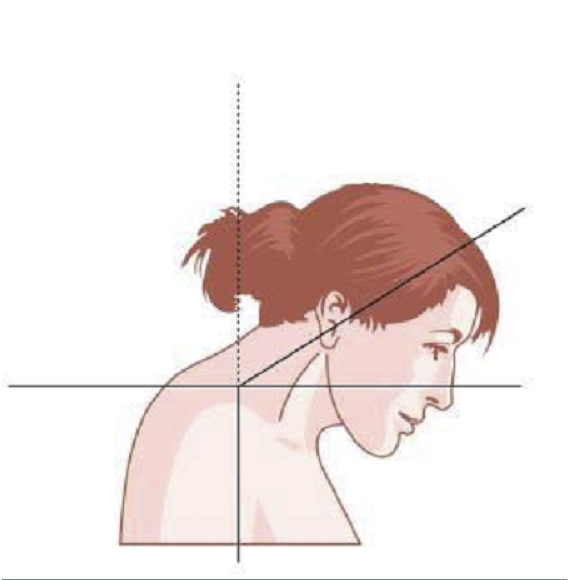
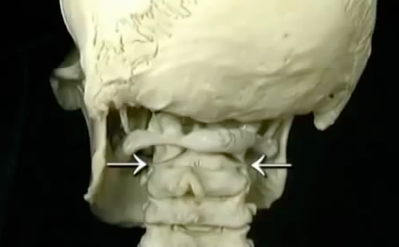
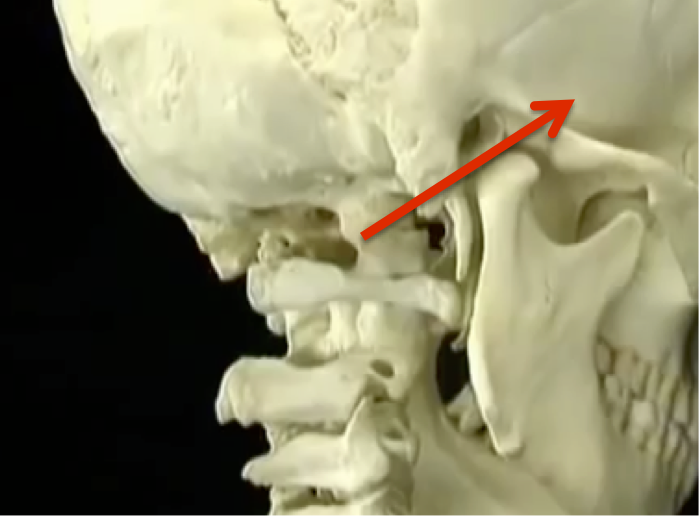
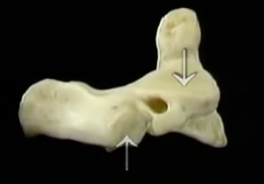
BIOMECHANICS OF HEAD MOTION
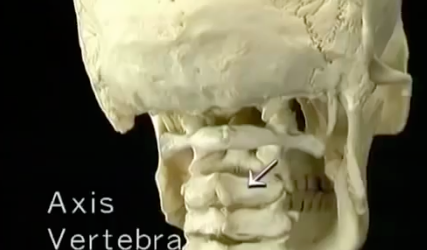
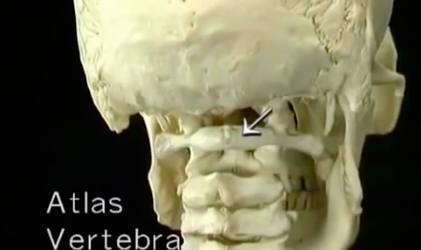
MOTION OF THE HEAD ON NECK
LATERAL TILT OCCURS BETWEEN C0-C1
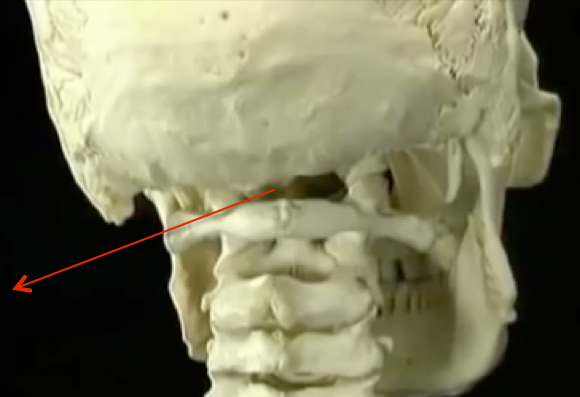
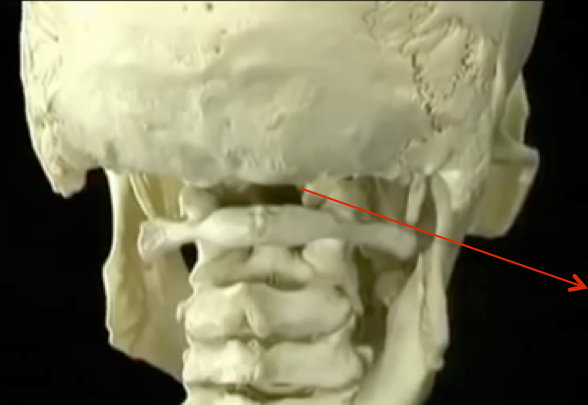
ROTATION AT C1-2, FLEXION EXTENSION MAINLY AT C0-1
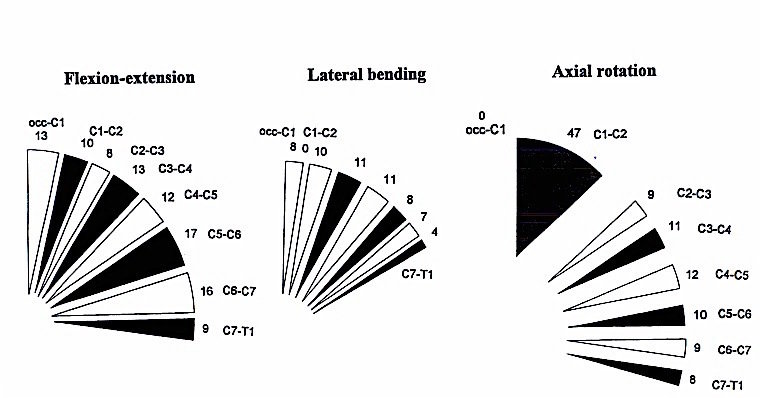
BIOMECHANICS OF NECK MOVEMENT
| Flexion/
extension |
Lateral flexion | Rotation |
|---|
| Occipital bone - C1 | 13 degrees | 8 degrees | None |
|---|
| C1 - C2 | 10 degrees | None |
|---|
| C2 - C7 |
|---|
| 47 degrees |
|---|
| 66 degrees | 37 degrees | 42 degrees |
|---|
RANGE OF MOTION
BIOMECHANICS OF NECK MOTION
-
Most lateral flexion and flexion/extension occur serially from C2 through C7.
-
Long muscles spanning these segments have great advantage in lateral flexion and in flexion/extension.
-
The majority of head rotation occurs at the atlanto-axial joint, so that muscles that act across this joint (e.g. obliquus capitis inferior, splenius capitis, SCM) have advantage in producing turning movements
- Rotation at C1-2 requires some extension and lateral tilt
UNIQUE ACTION OF STERNOMASTOID
Extends the head and flexes neck when longus colli relaxed
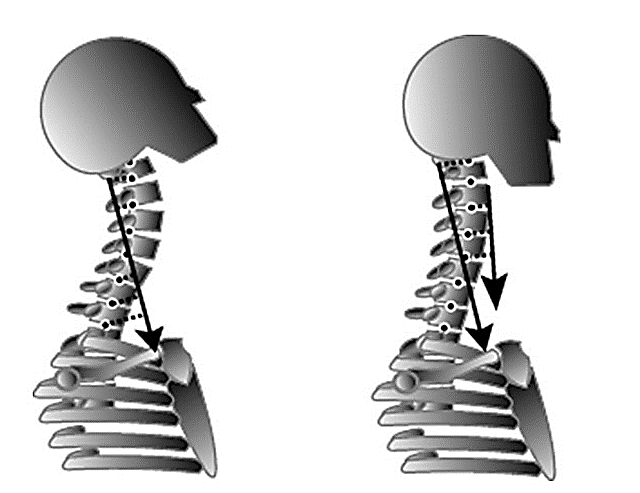
Flexes head and cervical spine if deep
flexors [longus colli] are contracted
F UNIQUE ACTION LEVATOR SCAPULAE
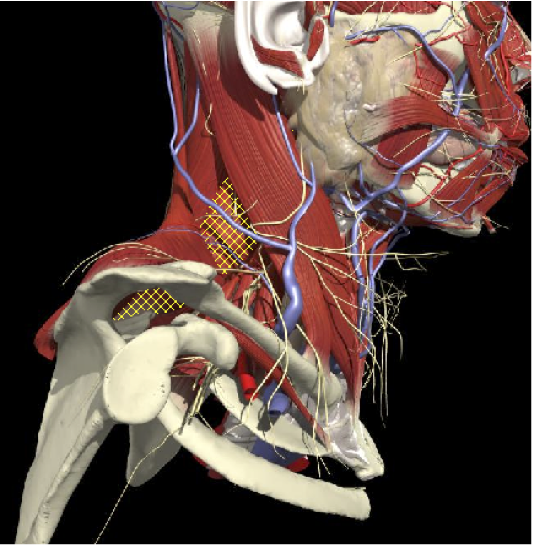
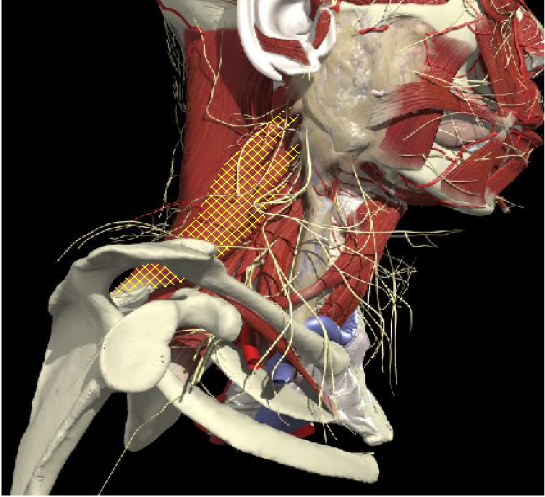
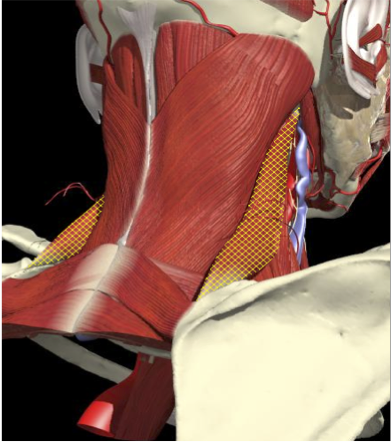
Insertion
Medial edge of the scapula, between the superior angle and the root of the spine.
Origin
First to the fourth cervical vertebrae
LEVATOR SCAPULAE
Action
Acts as a checkrein for the bent head
LEVATOR SCAPULAE AND NECK MOTION
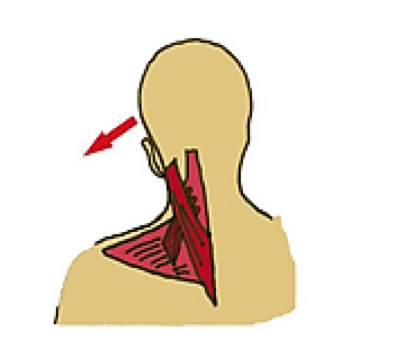
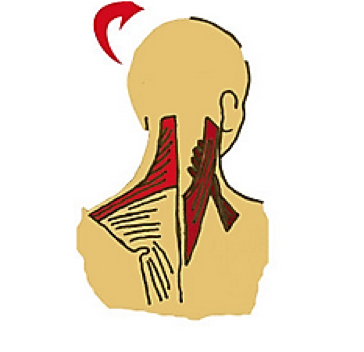
Left Lateral Flexion
Right Rotation
Extension
Left UTrapezius, SCapitus and Levator Scapulae
Left UTrapezius, Right SCapitus, Levator Scapulae
Bilateral U Trapezius Scapitus, Levator Scapulae
LEVATOR SCAPULAE IN DROPPED NECK