Professor Con Yiannikas

HEAD TREMOR
Head Tremor and ET

Cervical Dystonia
Head Tremor
-
Isolated tremor syndrome of bilateral action/postural tremor
Characteristics of ET
-
At least 3 years duration
-
May have associated Head or Voice tremor
-
Absence of other neurological signs
Head Tremor and ET

Cervical Dystonia
-
Isolated head tremor is excluded from ET - need at least a 5 year history of hand tremor
Head Tremor
-
The phenotype of hereditary ET was studied in 20 index patients and their kindred: tremor of the head never occurred in isolation
-
The relationship between isolated head tremor and focal tremulous cervical dystonia is a topic of ongoing controversy
-
Head tremor was present in 30-40% of ET cases. Female gender was associated with a fourfold increased risk of head tremor
Head Tremor
Head Tremor and ET

Cervical Dystonia
-
75 year old woman history of tremor since her early 20’s. The tremor is there predominantly when she is using her hands and she has not known a resting tremor. It initially did not affect her head or her voice. There is no family history of tremor.
-
Over the last 10 years her speech and head have become affected.
Head Tremor
Head Tremor and ET

Cervical Dystonia
-
54 yr old male has had tremor of his arms since he was a young boy probably aged between three and four years.
-
He has not noticed a tremor in his voice.
-
Over the last twenty years he has had a tremor affecting his head which is troubling him greatly.
Head Tremor
Tremor Analysis

Cervical Dystonia
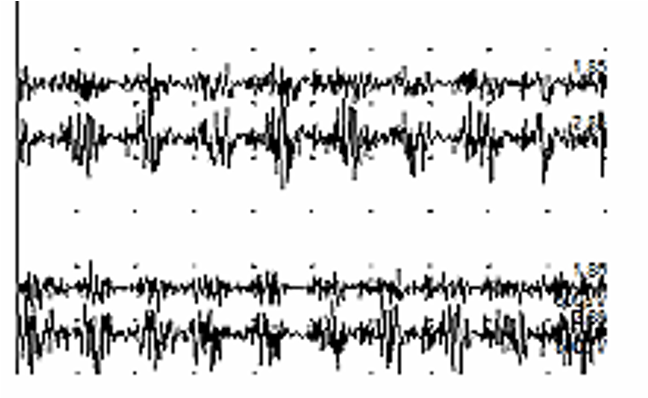
FDP
EIP
SCM
L&R
8-9 Hz tremor
Synchronous bursting pattern
Head Tremor
Head Tremor and ET

Cervical Dystonia
Head Tremor
Null Point

Cervical Dystonia
Head Tremor
Dystonic Head Tremor

Cervical Dystonia
-
Head tremor can be the presenting feature of cervical dystonia and may remain isolated for long periods
Characteristics
-
The frequency and amplitude of dystonic tremor is often variable, typically irregular
-
May disappear when the affected body part assumes a dystonic position (the “null point”) and be exacerbated when turning away from dystonic position.
Head Tremor
Head Tremor and ET

Cervical Dystonia
-
CD head tremor can be multidirectional at the start compared to ET which is usually unidirectional (most commonly “no no”).
Head Tremor
Abnormal Posturing

Cervical Dystonia
Clinical Assessment
-
Dystonic posturing of neck, other dystonias affecting face or limbs point towards a dystonic head tremor.
-
CD head tremor can be multidirectional at the start compared to ET which is usually unidirectional (most commonly “no no”).
Head Tremor and ET

Cervical Dystonia
Clinical Assessment
-
Dystonic tremor often has task or position specificity, persistence at rest, and overflow to neighbouring body segments.
-
ET head tremor more likely to resolve in the supine position compared to dystonic tremor.
Focal Tremors

Cervical Dystonia
Clinical Assessment
-
Rare focal tremors that may occur in the absence of other neurological signs, such as hereditary geniospasm, isolated jaw tremor, isolated tongue tremor, rabbit syndrome, and tremor during smiling.
Dystonic Tremor

Cervical Dystonia
Clinical Assessment
-
Dystonic tremor is often suppressed by sensory tricks (geste antagoniste)
Null Point

Cervical Dystonia
Clinical Assessment
-
Tremor may disappear when the affected body part assumes a dystonic position (the “null point”) and be exacerbated when turning away from dystonic position.
Head Tremor and ET

Cervical Dystonia
Clinical Assessment
Whats driving tremor extension or flexion?
Parkinsonian Head Tremor

Cervical Dystonia
Clinical Assessment
-
Jaw tremor is a type of cranial tremor that is classically associated with PD but can affect lips and tongue.
-
May reset like arm tremor
-
Head tremor is rare
Resting Tremor

Cervical Dystonia
Clinical Assessment
PD vs Dystonia
Titubation

Cervical Dystonia
Clinical Assessment
Missing Video -
Big Upload

-
Titubation occurs as a component of midline cerebellar ataxia and is accompanied by cerebellar findings
Muscles Involved in Tremor

Cervical Dystonia
Clinical Assessment
-
Tremor occurring to the side of dystonia as it tries to bring back to midline (anti-null).
-
Splenius capitis (SPL), semispinalis capitis and obliquus capitis inferior muscles (OCI)
-
Burst-like tremor activity was present in both OCI in 25 and in one in 10 patients. In 18 patients, tremor activity was present in one SPL and in 2 in both SPL.
-
Null point in action that releases dystonic muscles?
Where to Inject

Cervical Dystonia
Clinical Assessment
-
Null -? Looking left
-
Yes–Yes in all directions except extension where it converts to No-No

Cervical Dystonia
Clinical Assessment