DIAGNOSIS AND CLASSIFICATION OF CERVICAL DYSTONIA

Professor Con Yiannikas
Prevalence

-
Primary CD is the most common form of adult-onset focal dystonia.
-
Prevalence of six to nine per 100,000 population.
-
The peak age at onset is between 40 and 45 years.
-
Females are more commonly affected than males (male-to-female ratio 1.4:2.2)
Cervical Dystonia
Diagnosis & Classification
Time to Diagnosis

Cervical Dystonia
Anatomy
-
Journal Neurological Sciences - 2015
108 patients-
Less than 10 years - mean time 2.2 yrs
-
Greater than 10 years - mean time 4 yrs
-
-
Journal of Neurology 2015
1017 patients-
The mean time since diagnosis was 9.6 years
-
Over half (54%) of patients surveyed were not diagnosed in the first year
-

Symptoms & Time to Diagnosis

Cervical Dystonia
Anatomy
-
66% of patients reported being misdiagnosed.
-
The most frequent misdiagnoses were:
-
Psychological illness or stress disorder (37%)
-
Cervical muscle strain (23%)
-
Tremor (15%)
-

Cervical Dystonia
Anatomy
Symptoms & Time to Diagnosis


Cervical Dystonia
Anatomy
Symptoms & Time to Diagnosis
-
Pain, which is often described as ‘aching’ or ‘pulling’ and occurs in 70–75% of patients.
-
The maximum pain is usually felt in the muscles ipsilateral to the side of the chin deviation.
Classification

Cervical Dystonia
Anatomy
Evaluation of Cervical Dystonia in terms of:
-
Postural deviation in the axial plane (torticollis)
-
Coronal plane (laterocollis)


Classification

Cervical Dystonia
Anatomy
- Saggital plane (anterocollis and retrocollis)
-
Most patients with cervical dystonia have postural deviation in at least two of these planes.
-
In addition, the presence of shoulder elevation and of saggital and lateral shift are important elements to note.

Abnormal Head Postures

Cervical Dystonia
Anatomy
Frequency

Caput-Collis Concept

Cervical Dystonia
Anatomy

Torticollis/caput

Cervical Dystonia
Anatomy
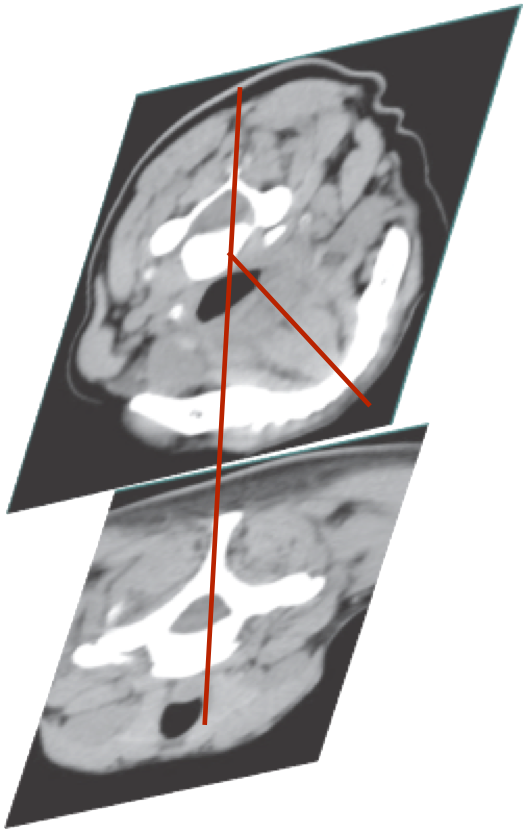
Head rotated via C1-2 (Atlanto-axial joint)
C3-7 vertebral column no movement
Torticaput
C3-6 rotate with C1-2 and head
Torticollis
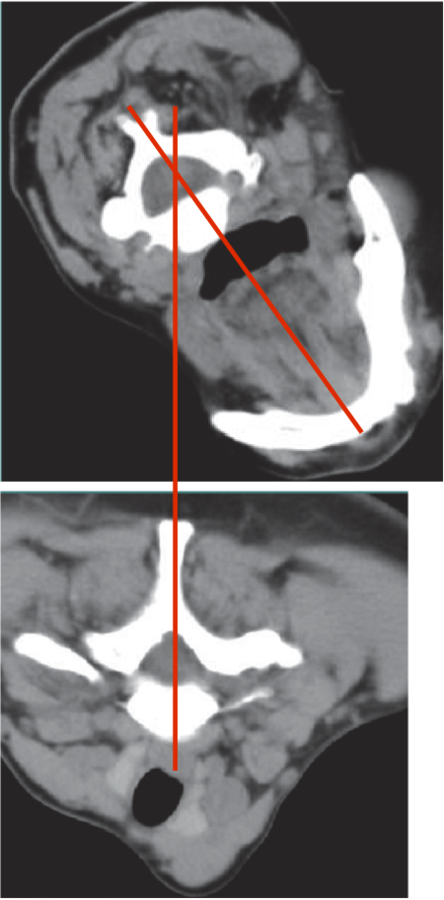


Retrocollis/caput

Cervical Dystonia
Anatomy
Head extended past 15 degrees
Head extended less than 15 degrees


Laterocollis/caput

Cervical Dystonia
Anatomy

Missing Video - Big Upload



Laterocaput
Laterocollis
Larynx shifted relative to sternum
Anterocaput/collis

Cervical Dystonia
Anatomy



Anterocaput
Anterocollis
Missing Video - Big Upload
Combination of Postures

Cervical Dystonia
Anatomy
Most common rotation and tilt -30%.
Rotation tilt flexion or extension 20%
Lateral Shift

Cervical Dystonia
Anatomy
Secondary to lateral flexion of the spine and flexion of the head in the opposite direction

Saggital Shift

Cervical Dystonia
Anatomy
Due to a combination of extension of head and flexion of neck.





Missing Video - Big Upload
Due to a combination of neck extension and head flexion.
Produces “double chin” look.