Echocardiography in TAVR Implantation
Irina Staicu, MD, FACC, RPVI
Director Noninvasive Cardiology
Echo Lab
Good Shepherd Hospital


Objectives
- Understand novel alternatives for treatment of AS
- Identify candidates for TAVR

- Review the pre, intra and post procedure role of Echo
- Role of Echo in intraprocedural evaluation of position, size, complications of TAVR
WHY TAVR AND WHY ECHO IN TAVR

" Treat 4 to save 1" or 1000 for 250
The strongest treatment effect on mortality trials in Cardiology


Dr Henning Rud Andersen, 1988
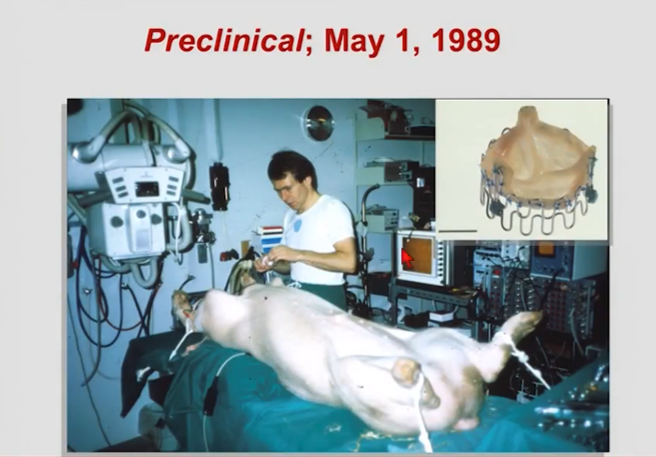
"VIP" PIG

France, Dr Alain Cribier, April 2002
Pre TAVR Planning Echo check list
American Society of Echocardiography - 2017
Confirm trileaflet/bileaflet AV morphology
Presence/Degree of AR, MR, TR
Presence of basal septal hypertrophy/LVOT obstruction
Presence of Pericardial effusion
Exclude LA or LV thrombus
TAVR: Echo Measurements Pre, Post And Intra Procedure
2017 ASE Florida, Orlando, FLhttp://asecho.org/wordpress/wp-content/uploads/2017/.../2017_10_10_Saric_TAVR-1.pdf
Intra /post TAVR implantation Echo check list American Society of Echocardiography - 2017
Ensure proper prosthesis placement
Assess prosthesis position/function after deployment
Assess ventricular function
Identify immediate post deployment complications
TAVR: Echo Measurements Pre, Post And Intra Procedure
2017 ASE Florida, Orlando, FLhttp://asecho.org/wordpress/wp-content/uploads/2017/.../2017_10_10_Saric_TAVR-1.pdf
FDA approved valves for TAVR

Medtronic Melody

Edwards Sapien 3
Medtronic Corevalve
Echo for TAVR
-
Select the device size (Annular size/perimeter)
-
Extent and location of calcification
-
TAVR function
-
Optimal implantation
-
Severity of Aortic Regurgitation
-
Intraprocedural complications
Select the device size (Annular size/perimeter)
Undersized prosthesis
-
Periprosthetic AR
-
Device migration
-
Prosthesis -patient mismatch
Oversized prosthesis
-
Underexpansion with central AR
-
Annular rupture
-
Coronary ostial obstruction
Select the device size (Annular size/perimeter)
How do we do sizing?
-
2D echo
-
3D TEE
-
CT
-
3D TEE and CT
Aortic annulus and LVOT

Ovoid shape
2D echo underestimates the valve area
CT overestimates the valve area
-
Undersizing predicts AR
-
CT better than TTE/TEE diameter
-
3D TEE equivalent to CT in sizing and predicting AR

-
Select the device size (Annular size/perimeter) -
Extent and location of calcification
-
TAVR function
-
Optimal implantation
-
Severity of Aortic Regurgitation
-
Intraprocedural complications

Asymmetric, nodular calcification- primary risk factor for PAR

-
Annular size/perimeter -
Extent and location of calcification -
TAVR function
-
Optimal implantation
-
Severity of Aortic Regurgitation
-
Intraprocedural complications


TAVR Function : Shape, Gradient, PAR
Valve Shape and location
-
short axis: circular rather than ovoid
-
long axis: 2-3 mm in the LVOT


TAVR Function
If Suboptimal
-
Reposition
-
Post dilatation
-
Valve in Valve implantation
Valve Regurgitation
-
No significant PAR, or Central Regurgitation
Valve Gradient
-
< 2.0 m/sec
-
Annular size/perimeter -
Extent and location of calcification -
TAVR function -
Optimal implantation
-
Severity of Aortic Regurgitation
-
Intraprocedural complications

Everything is about landing
Optimal valve position at deployment

-
2-3 mm bellow the annulus
-
2 mm coverage of native cusps.
During deployment there is an upward movement of the valve and shortening

Optimal valve position at deployment

-
Superior motion
-
Shortening
5-6 mm below annulus during pacing, just before deployment
Malposition : too low in the ventricle

-
Uncovered native leaflets
-
Entrapment of THV in native leaflets
-
Severe central A R
Malposition : too low in the ventricle
Malposition : too high in the aorta

-
Aortic regurgitation
-
Valve embolization
-
Coronary obstruction,
-
Aortic dissection
Malposition : too high in the aorta

Malposition : too low in the ventricle
Malposition : too low in the ventricle

Optimal
Too high
Aorta
Too low
LVOT
-
Annular size/perimeter -
Extent and location of calcification -
TAVR function -
Optimal implantation -
Severity of Aortic Regurgitation
-
Intraprocedural complications
Paravalvular Aortic Regurgitation PAR
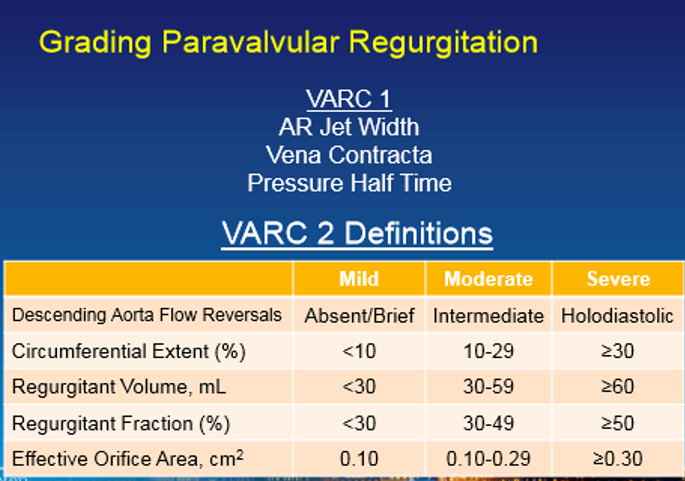
Grading PAR by VARC- valve academic research consortium
Grading of PAR by Circumferential Extent

Mild PAR :jet arc lengths are discontinuous, but total <10% of the AV annulus
Moderate PAR :jet arc lengths are discontinuous, but total 10% to 30% of the AV annulus
Severe PAR :jet arc lengths are discontinuous, but total >30% of the AV annulus
Mild PAR
Moderate PAR
Text
Severe PAR

-
Annular size/perimeter -
Extent and location of calcification -
TAVR function -
Optimal implantation -
Severity of Aortic Regurgitation -
Intraprocedural complications

Intraprocedural Complications

Stiff wire entanglement in the mitral apparatus.
Stiff wire entanglement
Ballon aortic valvuloplasty complications
-
Coronary occlusion
-
Severe aortic regurgitation
-
Aortic trauma
LM Coronary Artery Occlusion
with BAV
With BAV the bulky calcium occludes the ostium of LM . LM stent performed after TAVR


Aortic Trauma Predicted by BAV
Periaortic hematoma within minutes of transcatheter valve deployment
BAV Complication
Avulsed leaflet , resulting in severe aortic regurgitation
-
1. Exclude acute valvular regurgitation
-
2. Exclude aortic root trauma
-
3. Exclude acute ventricular dysfunction
-
4. Exclude coronary obstruction
-
5. Exclude pericardial effusion/tamponade
Acute Hemodynamic compromise
Secondary to superior motion of balloon during BAV in setting of large sigmoid septum/dynamic LVOT obstruction
Failure to implant / Malposition

LVH/dynamic LVOT obstruction

Invaluable, real time for intraprocedural imaging
-
TAVR position and function
-
PAR
-
Complications
Thank you Irina Staicu



See you in 2019
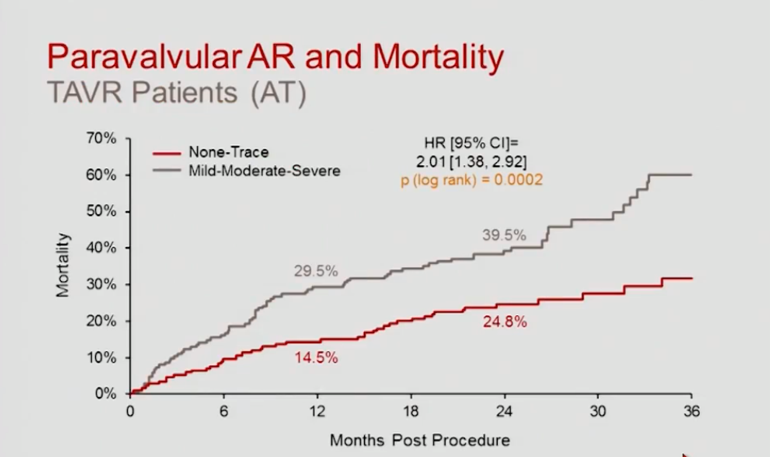
PARTNER 1 B - Inoperable Cohort
TAVR vs Standard Tx


TAVR vs SAVR
Trials
Mortality
NYHA class
Six minutes walking test

-
Annular size/perimeter -
Extent and location of calcification -
TAVR function -
Optimal implantation
-
Severity of Aortic Regurgitation
-
Intraprocedural complications
Malposition : too low in the ventricle

Paravalvular Aortic Regurgitation PAR


THV malposition and Central Aortic Regurgitation

Salvage
Valve in Valve

Ms Coolkissovsky, 89 YOF , with heavy European accent, presents with Syncope
Admitted with Chest Pain
On the floor, a nursing student hears a faint, "tiny" murmur
Cardiology eval: loud 4/4 systolic murmur, radiating everywehere
Severe AS
HTN, CKI, on HD, COPD on 2L O2