The Hack Programming Language
Um "novo" PHP
Por ítalo Lelis de Vietro / @italolelis
Quem sou eu





Github
Linguagem
Fortemente tipadas
Fracamente tipadas (dinâmicas)






Hack is a language for HHVM that interoperates seamlessly with PHP. The goal of Hack is to offer developers a way to write cleaner, safer and refactorable code while trying to maintain a level of compatibility with current PHP codebases.
O Type Checker
O real valor do Hack
Identifique esses tipos de erros antes
Mesmo quando estiver codando
Type checker robusto
O type checker é o sua melhor linha de defesa. Contudo, em tempo de execução é permitido coisas que o type checker não aprova.
... perdoando o runtime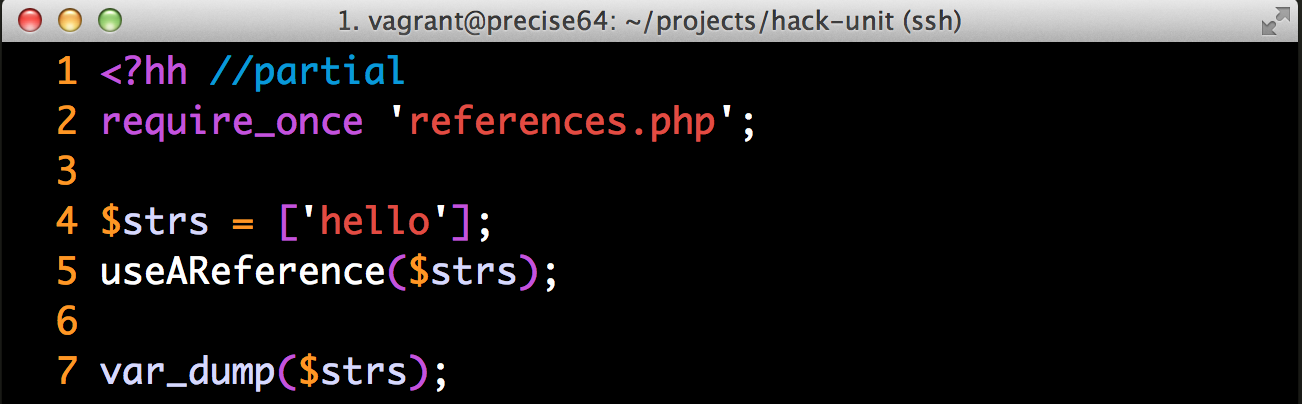
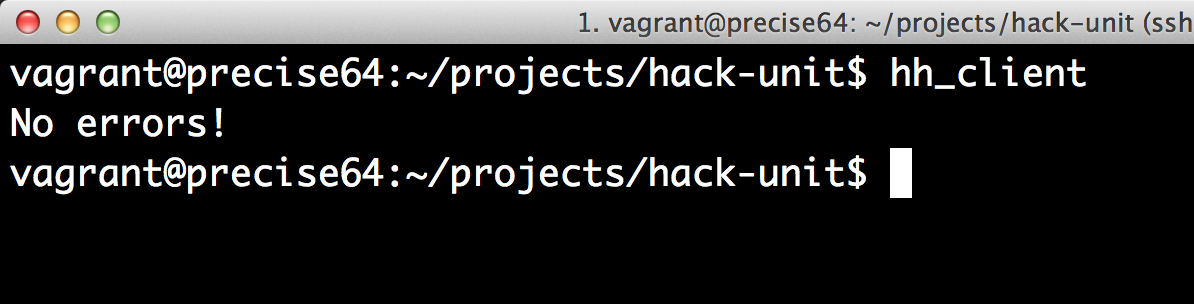
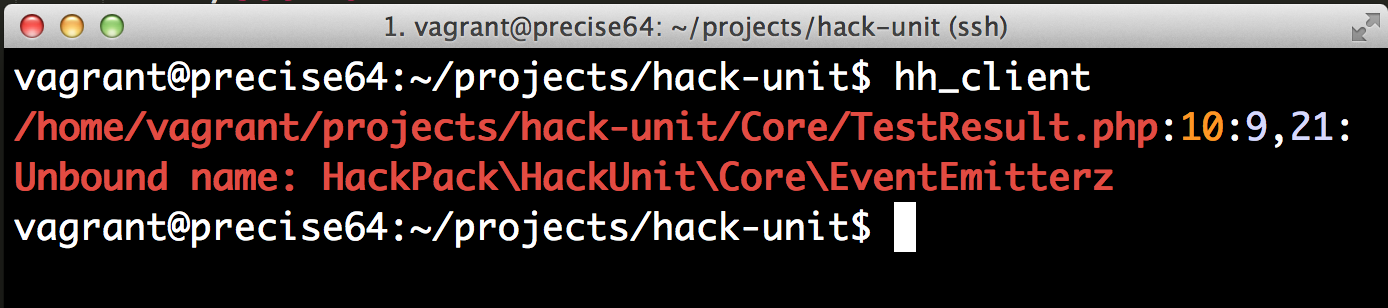
Usando o hh_client
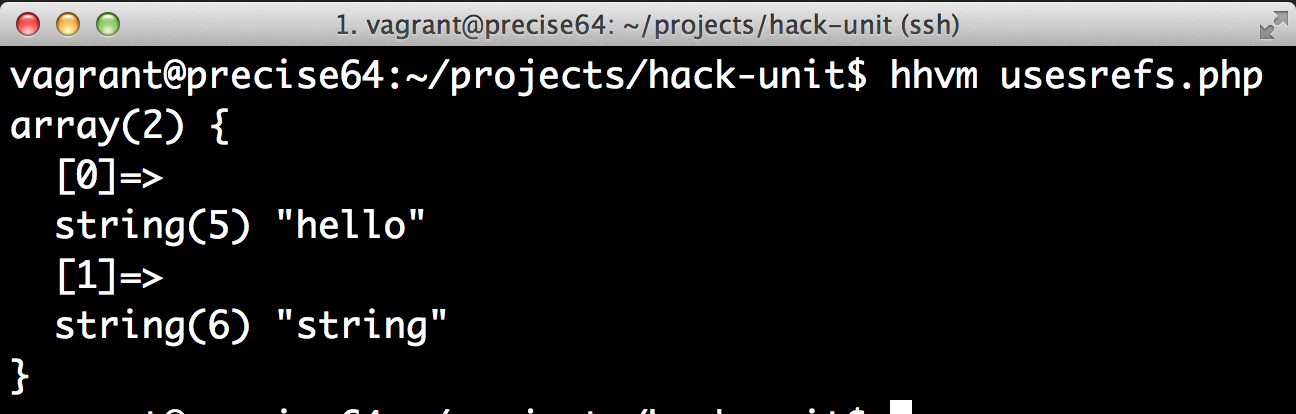
O type checker é invocado utilizando o hh_client que vem instalado com o Hack. Esse executável atualmente está disponível apenas para plataformas *nix.
... tenha certeza de procurar o caminho certo
Tipagem
Type annotations allow for PHP code to be explicitly typed on parameters, class member variables and return values (types are inferred for locals). These annotated types are checked via a type checker.
Parâmetros e retornos tipados
<?hh //strict
function sum(int x, int y): int {
return x + y;
}
Propriedades tipadas
<?hh //strict
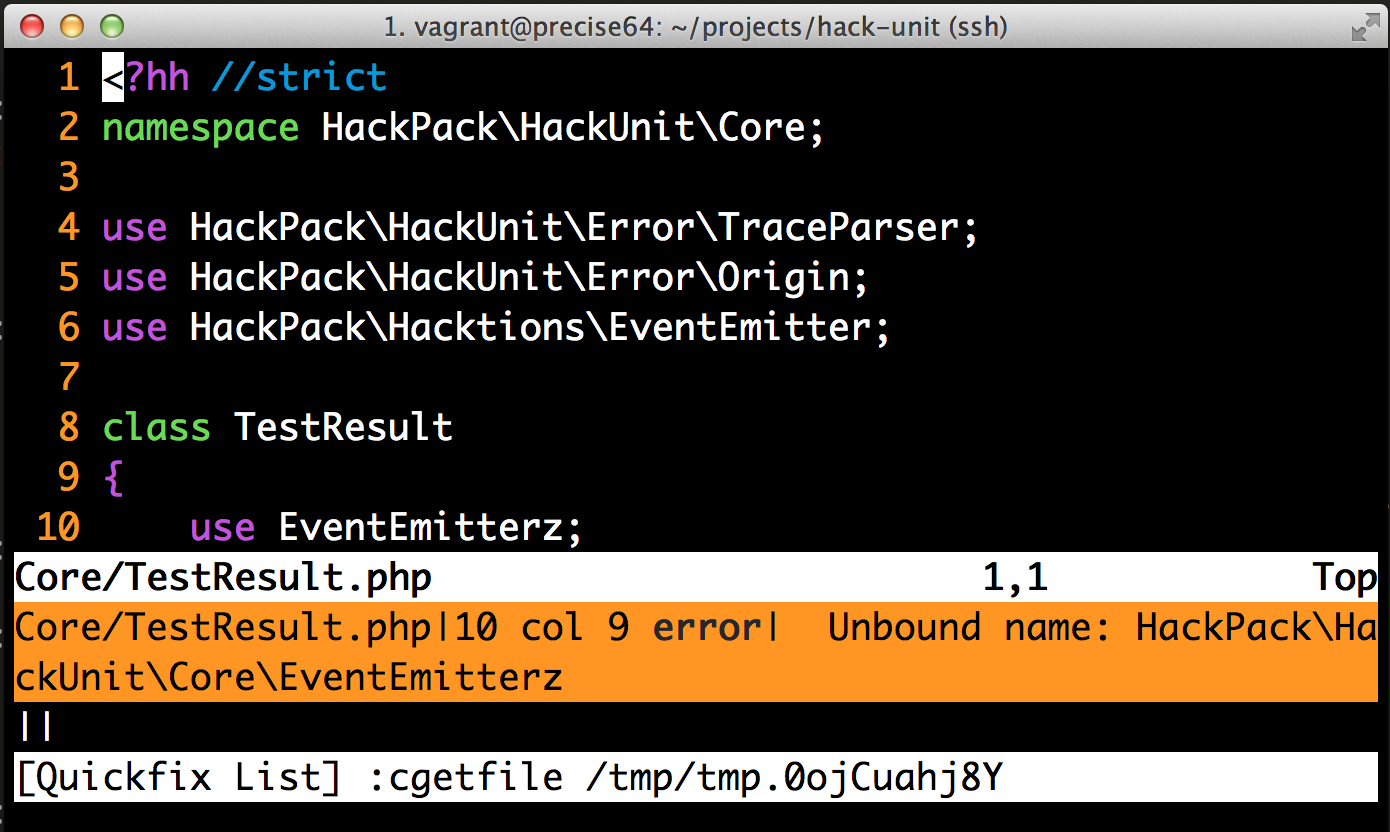
class TestResult
{
protected int $runCount;
protected array<Failure> $failures;
}
Closures anotadas
<?hh //strict
function invoke((function(int $x): int) $fn): int {
return $fn(1);
}
Anotação com o $this
<?hh //strict
class FluentObject
{
public function doThing(): this
{
//do something
return $this;
}
}
... ainda precisa de um pouco de trabalho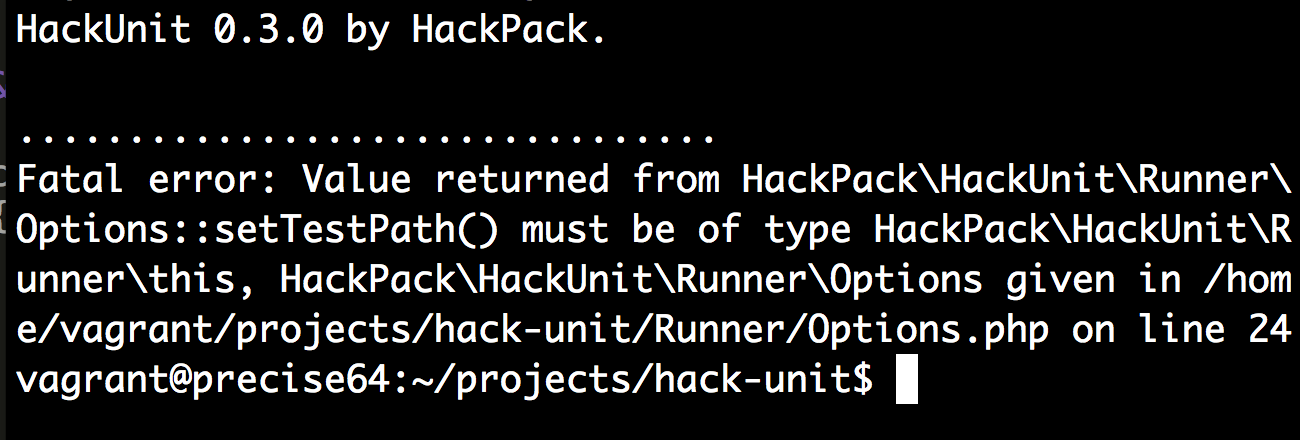
... podemos fazer um workaround por enquanto
<?hh //strict
namespace HackPack\HackUnit\Runner;
class Options
{
protected string $testPath;
/**
* Use Options type since "this" annotation is broken
* when namespaces are used
*/
public function setTestPath(string $testPath): Options
{
$this->testPath;
return $this;
}
}
O tipo mixed
O type checker do Hack tem algumas maneiras interessantes de lidar com o tipo "mixed", que para muitos programadores PHP é familiar. O compilador irá identificar quando você tentar validar o tipo.
... precisa ser verificado
<?hh
function sum(mixed $x): void {
if (is_array($x) || $x instanceof Vector) {
$s = 0;
foreach ($x as $v) {
$s += $v;
}
return $s;
}
//... do something else or throw an exception...
}
Generators e co-rotinas
Generators tipados
<?hh //strict
function infiniteIterator(): Continuation<int> {
$i = 0;
while (true) {
yield ++$i;
}
}
Coroutines tipadas
<?hh
async function f(): Awaitable<int> {
return 42;
}
async function g(): Awaitable<string> {
$f = await f();
$f++;
return 'hi test ' . $f;
}
Hack Modes
O compilador do Hack tem vários níveis de tolerância. Eles são conhecidos como modes, e são disparados por comentários.
Strict mode
O nível mais purista. Tudo deve estar tipado e tudo é verificado pelo type checker. Código no modo strict não pode chamar um código que não é escrito em Hack.
... um exemplo do modo strict
<?hh //strict
class TestCase
{
public function __construct(protected string $name)
{
}
public function setUp(): void
{
}
public function expect<T>(T $context): Expectation<T>
{
return new Expectation($context);
}
}
... strict mode
O modo strict é tão rigoroso que você não poderá ter um ponto de partida no sistema, ou seja, você não pode ter um "main", uma vez que ele estará fora dos padrões strict. Para isso usamos o Partial ou UNSAFE.
Sobre as interfaces hhi
... interfaces hhi
Os arquivos hhi contém interfaces para quase todas as funções do core do PHP. Esses arquivos basicamente disponibilizam informações sobre os tipos de cada função para o compilador do Hack. Você só precisa garantir que eles estejam na raiz do seu projeto.
Um exemplo de interface hhi
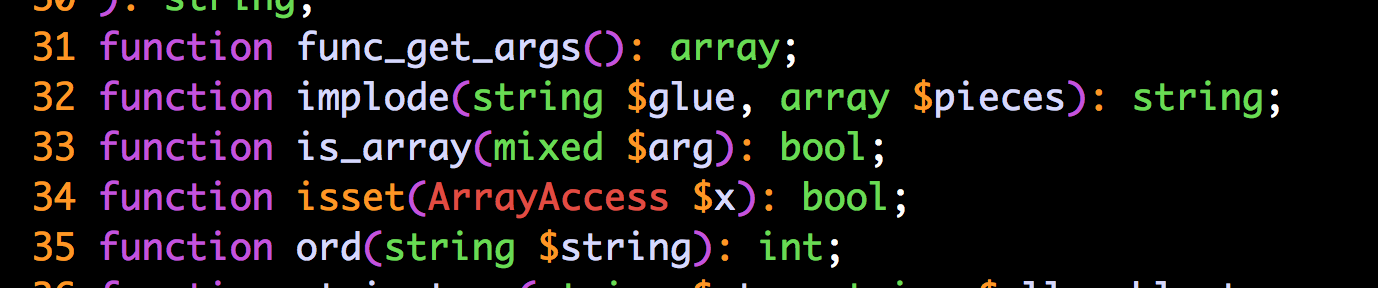
Partial mode
Partial mode is the default of Hack. In partial mode, the type checker checks all types other than that encompassed by an // UNSAFE comment. Partial mode also allows for the partially typing of a class, method or function (e.g., only type a subset of its arguments). And, also unlike strict mode, partial mode allows engineers to call code that has not yet been "Hack-ified" (in other words, they can call into untyped code).http://docs.hhvm.com/manual/en/hack.modes.partial.php
... a melhor aposta para o incio do programa
Ja que o modo strict não permite código de nível superior, o modo parcial é o método para entrada do programa, ou seja o nosso metodo "main".
https://github.com/HackPack/HackUnit/blob/master/bin/Hackunit
Decl mode
Decl mode is used to allow Hack code written in strict mode to call into legacy code, without having to fix the issues that would be pointed out by partial mode. The type checker will "absorb" the signatures of the code, but will not type check the code. Decl is mainly used when annotating old, existing APIs (i.e., when the code does note meet Hack's stricter subset of PHP).
UNSAFE
// UNSAFE disables the type checker from the point of unsafe declaration until the end of the current block of code (where the end of the current block generally refers to the associated ending brace (}) of which the // UNSAFE is declared).https://github.com/HackPack/HackUnit/blob/master/Runner/Loading/StandardLoader.php#L98
Generics
Hack introduces generics to PHP (in the same vein as statically type languages such as C# and Java). Generics allow classes and methods to be parameterized (i.e., a type associated when a class is instantiated or a method is called).
Interfaces genéricas são boas para design
<?hh //strict
namespace HackPack\Hacktions;
trait EventEmitter
{
protected Map<string, Vector<(function(...): void)>> $listeners = Map {};
}
... o sonho é melhor que a realidade
Inferência
A preferência por inferência parece ser um golpe para a legibilidade. Os seguintes resultados são obtidos por um erro de tipo:
$fun = () ==> { $fn = $this->callable; $fn(); }
$this->expectCallable($fun)->toThrow<ExpectationException>();
//Tests/Core/CallableExpectationTest.php|54 col 70 error| This operator is not associative, add parentheses
... mas isso funciona
$fun = () ==> { $fn = $this->callable; $fn();};
$this->expectCallable($fun)->toThrow('\HackPack\HackUnit\Core\ExpectationException');
Generic não se acumulam
A generic method must not collide with any existing, non-generic method name (i.e, public function swap and public function swap).
... mesmo se eles tivessem que ser
<?hh //strict
class Cook
{
use Subject<Waiter>;
use Subject<Busboy>;
}
//throws type errors
Em resumo
Tipos Nullable
Hack introduces a safer way to deal with nulls through a concept known as the "Nullable" type. Nullable allows any type to have null assigned and checked on it.
Seja explícito sobre a possibilidade de um tipo nulo
<?hh //strict
class Options
{
protected ?string $HackUnitFile;
public function getHackUnitFile(): ?string
{
$path = (string) getcwd() . '/Hackunit.php';
if (! is_null($this->HackUnitFile)) {
$path = $this->HackUnitFile;
}
$path = realpath($path);
return $path ?: null;
}
}
... não deixe de conferir os tipos nulos
<?hh //strict
class TestResult
{
protected ?float $startTime;
public function getTime(): ?float
{
$time = null;
$startTime = $this->startTime;
$time = microtime(true) - $startTime;
return $time;
}
//TestResult.php|39 col 35 error| Typing error
//TestResult.php|39 col 35 error| This is a num (int/float) because this is used in an arithmetic operation
//TestResult.php|13 col 15 error| It is incompatible with a nullable type
}
... isso funciona
<?hh //strict
class TestResult
{
public function getTime(): ?float
{
$time = null;
$startTime = $this->startTime;
if (!is_null($startTime)) {
$time = microtime(true) - $startTime;
}
return $time;
}
}
Em resumo
Collections
-
Fornecer um framework que e simples e intuitivo.
-
Fornecer uma performance igual ou melhor que os arrays do PHP.
-
Fornecer uma implementação de coleções que permitam tipagem estática, integrando-se com o Hack.
-
Fornecer uma migração fácil já que foi construído em cima das funcionalidades padrão do PHP5.
Vectors
A Vector is an integer-indexed (zero-based) collection with similar semantics to a C++ vector or a C#/Java ArrayList. Random access to elements happen in O(1) time. Inserts occur at O(1) when added to the end, but could hit O(n) with inserts elsewhere. Removal has similar time semantics.
... um exemplo
Maps
A Map is an ordered dictionary-style collection. Elements are stored as key/value pairs. Maps retain element insertion order, meaning that iterating over a Map will visit the elements in the same order that they were inserted. Insert, remove and search operations are performed in O(lg n) time or better
... um exemplo
Sets
A Set is an ordered collection that stores unique values. Unlike vectors and maps, sets do not have keys, and thus cannot be iterated on keys.
... um exemplo
Nota: Sets suportam apenas chavez inteiras ou string por enquanto.
Pairs
A Pair is an indexed container restricted to containing exactly two elements. Pair has integer keys; key 0 refers to the first element and key 1 refers to the second element (all other integer keys are out of bounds).
... um exemplo
Uma nota sobre as coleções imutáveis
Uma nota sobre array
Lambdas
To address the shortcomings of PHP closures, HHVM introduced a "lambda expression" feature. Lambda expressions offer similar functionality to PHP closures, but they capture variables from the enclosing function body implicitly and are less verbose in general.
Tão recente, mas tão limpo
$ui = new Text();
$this->runner->on('testFailed', (...) ==> $ui->printFeedback("\033[41;37mF\033[0m"));
$this->runner->on('testPassed', (...) ==> $ui->printFeedback('.'));
Funções de alto nível ficam mais agradáveis de se ver
$squared = array_map($x ==> $x*$x, array(1,2,3));
Uma grande vitória
$ui = new Text();
$this->runner->on('testFailed', (...) ==> $ui->printFeedback("\033[41;37mF\033[0m"));
//vs
$this->runner->>on('testFailed', function(...) use ($ui) {
$ui->printFeedback("\033[41;37mF\033[0m";)
});
Perguntas

Obrigado!