Database and SQL Fundamentals
Who am I?
- Columbus State Alumni
- BSBA and MBA from THE Ohio State University
- Over 10 years of IT Experience in Columbus
- Currently working for Chase on their Knowledge Management application
What we will learn
- What is a database
- How to interact with a relational database
- What is on the horizon
Important Concepts
- Don't Repeat Yourself (Pragmatic Programmer)
- Convention over Configuration (Ruby)
- Be opinionated but not judgmental (Personal/ Opinionated Software)
- Standards Scale(IEEE)
- Be yourself (Life)
Required Technologies
- Git
- Postgres
- Node
Other important tools
- AWS(RDS, EC2)
- IDE (IJ, Eclipse, SublimeText, VSCode)
- Git viewer (GitKrakken, SourceViewer)
Review Blackboard
What Is a Database?
Day 1
Feedback
- Issues: Create Github Issue
- Suggestions: Create Github PR
- Help: https://cscc7730.slack.com
Lets get started!
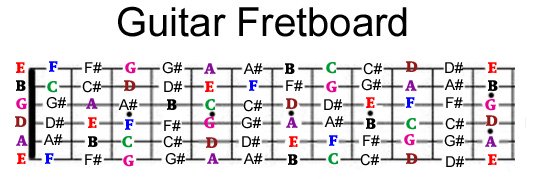

How is data stored?




File System


HFS(+)


Spreadsheets
Microsoft Access

Limitations
- Scalability
- Performance
- Locking
1960s Data Modeling

1970s Enter SQL

1990s Enter RDBMS



RDBMS
(Relational DataBase Management System)

Relation
Relation
RDBMS
SQL
User
Other applications
accept SQL!
RDBMS Structure
- Relations/Tables
- Rows/Tuples
- Attributes
Relations are orderless!
PSQL
Lab: Setup Local Database
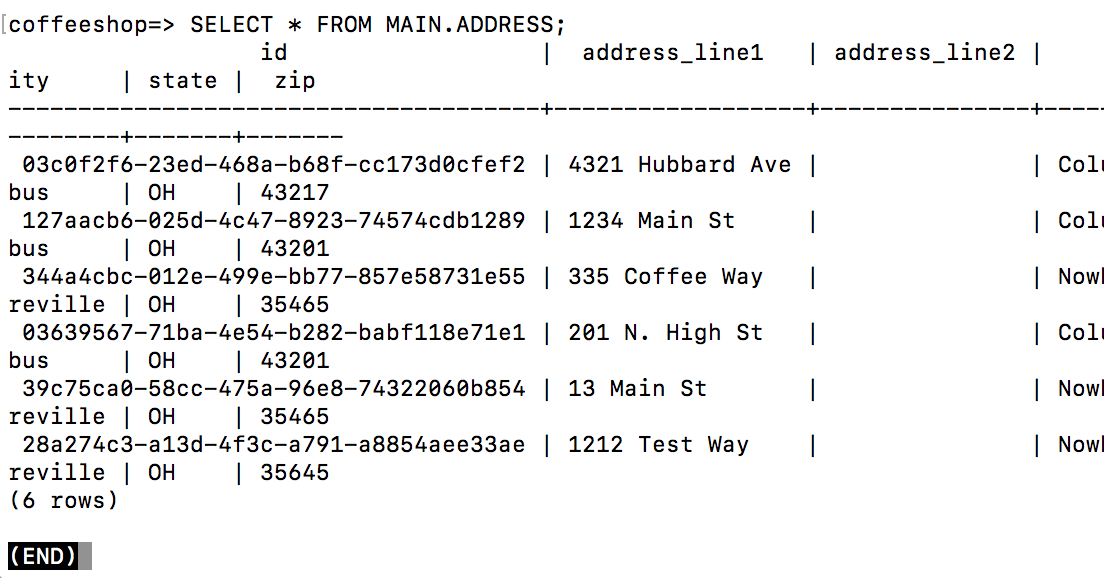
VS
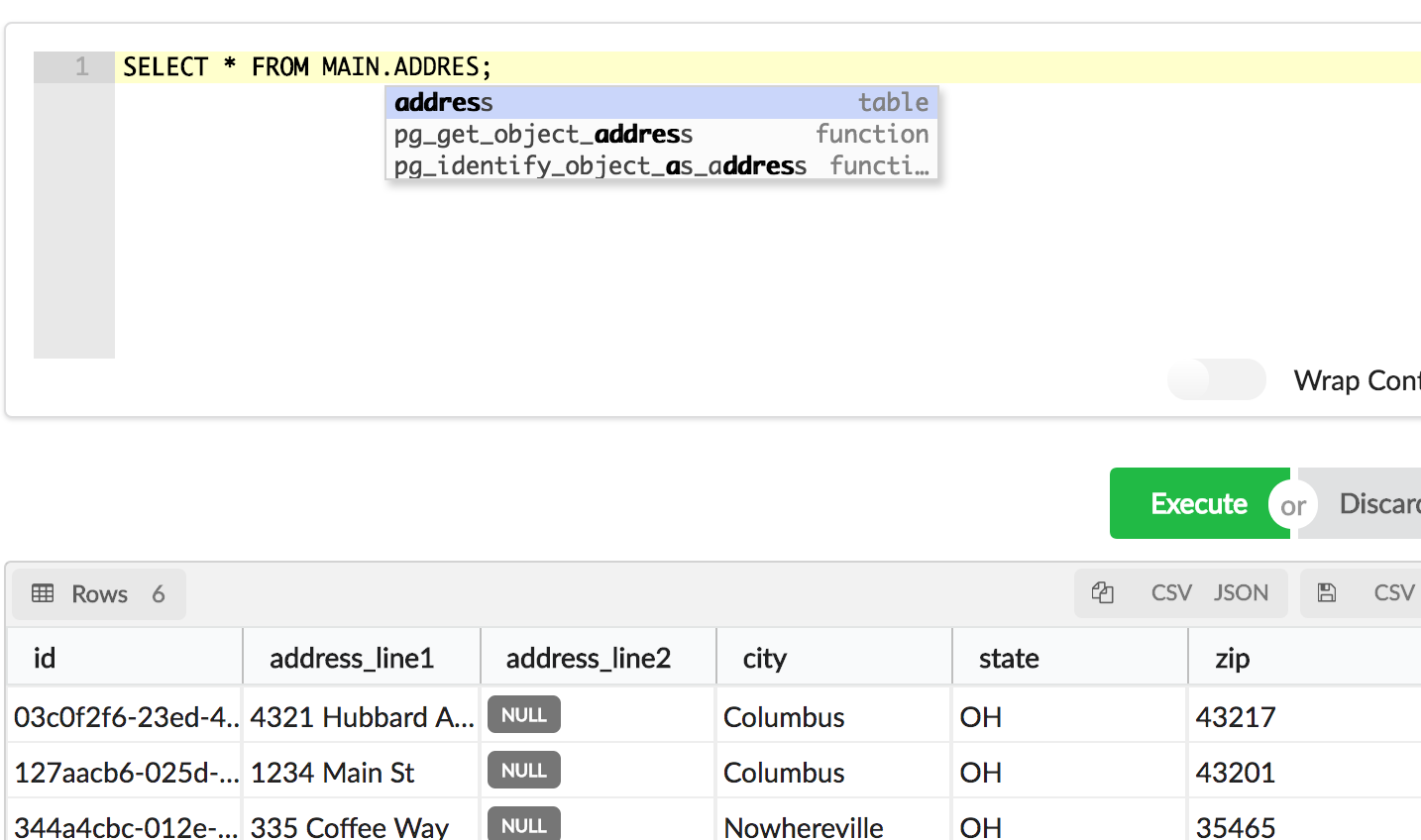
Lab: Connect Via Gui
SQL Fiddle
SQL Fiddle Lab
2010+ Cloud

2020+ Blockchain


Basic Database Interaction Pt 1
Day 2
Stand Up
Questions
Self-Hosted Servers
Tried and True
Hosted Dedicated Servers
-
Cheaper but still expensive
-
No infra cost
-
More reliable
Hosted Shared Servers
-
Cheaper still
-
Only get a portion of resources
-
Might have performance issues
PAAS Servers
-
Only pay for what you use
-
Slightly pricier if run all the time
-
Allow for either dedicated or shared servers




RDS
(AWS) Relational Database Service
Connecting Using PSQL
Local:
psql
Remote (RDS)
psql -h <address> -p <port> -U <user> <db>
Install Git And Download Repo
Why Caps?
Creating A Schema
-
To allow many users to use one database without interfering with each other.
-
To organize database objects into logical groups to make them more manageable.
-
Third-party applications can be put into separate schemas so they do not collide with the names of other objects.
Nouns == Relation
Creating A Relation
(Table)
Break It Down
Create <THING> <NAME>
Create TABLE THING(
NAME VARCHAR(50)
)
Create TABLE THING(
<ATTRIBUTE> <ATTR_TYPE> (,)
)
Attribute Constraints
- Not Null
- Reference
CREATE TABLE FOOBAR(
FOO INT NOT NULL,
BAR INT
)
INSERT INTO FOOBAR VALUES (1,0)
INSERT INTO FOOBAR (BAR) VALUES (1)

Attribute Data Types
Attribute Data Types
TLDR
- Numeric
- Varchar
- Boolean
- Other
Numeric
Scale Matters
INT
4 Bytes
-2147483648 to +2147483647
DECIMAL
Variable
Casting Numerics
CAST(5.00 as MONEY)
Varchar
Variable Character Array

Boolean

Other

Examples
- Byte String
- Points
- Custom
- Composite
- more
Other RDBMS Data Types
Altering A Table
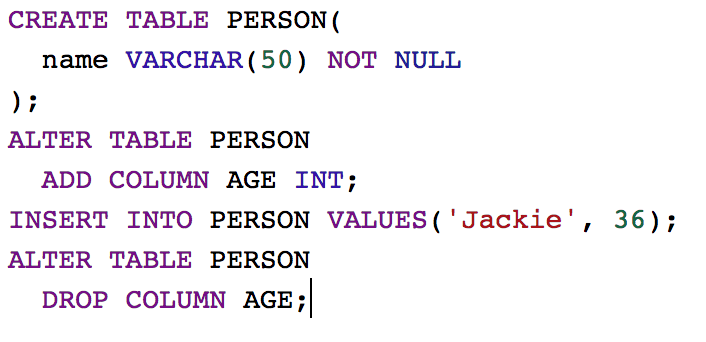
Be Careful!

-
Create Table With Constraint
-
Alter Table to add new attribute
-
Drop new attribute
Basic Create And Delete Lab
Inserting Into a Table
Try Inserting A Tuple
Updating Table Values
UPDATE <TABLE> SET <COLUMN>=<VALUE>

Selecting Data
SELECT retrieves rows from zero or more tables

Simple Select
SELECT 1+1;
From Clause
SELECT * FROM <TABLE>;
Where Clause
SELECT * FROM <TABLE> WHERE <COLUMN> = <VALUE>;
Logical Operators
- AND
- OR
- NOT
Comparison Operators
- =
- < <=
- > >=
- <> !=
Comparison Operators
Removing Table Values
Select Lab

Basic Database Interaction Pt 2
Day 3
Stand Up
Questions
Review

Creating Relations
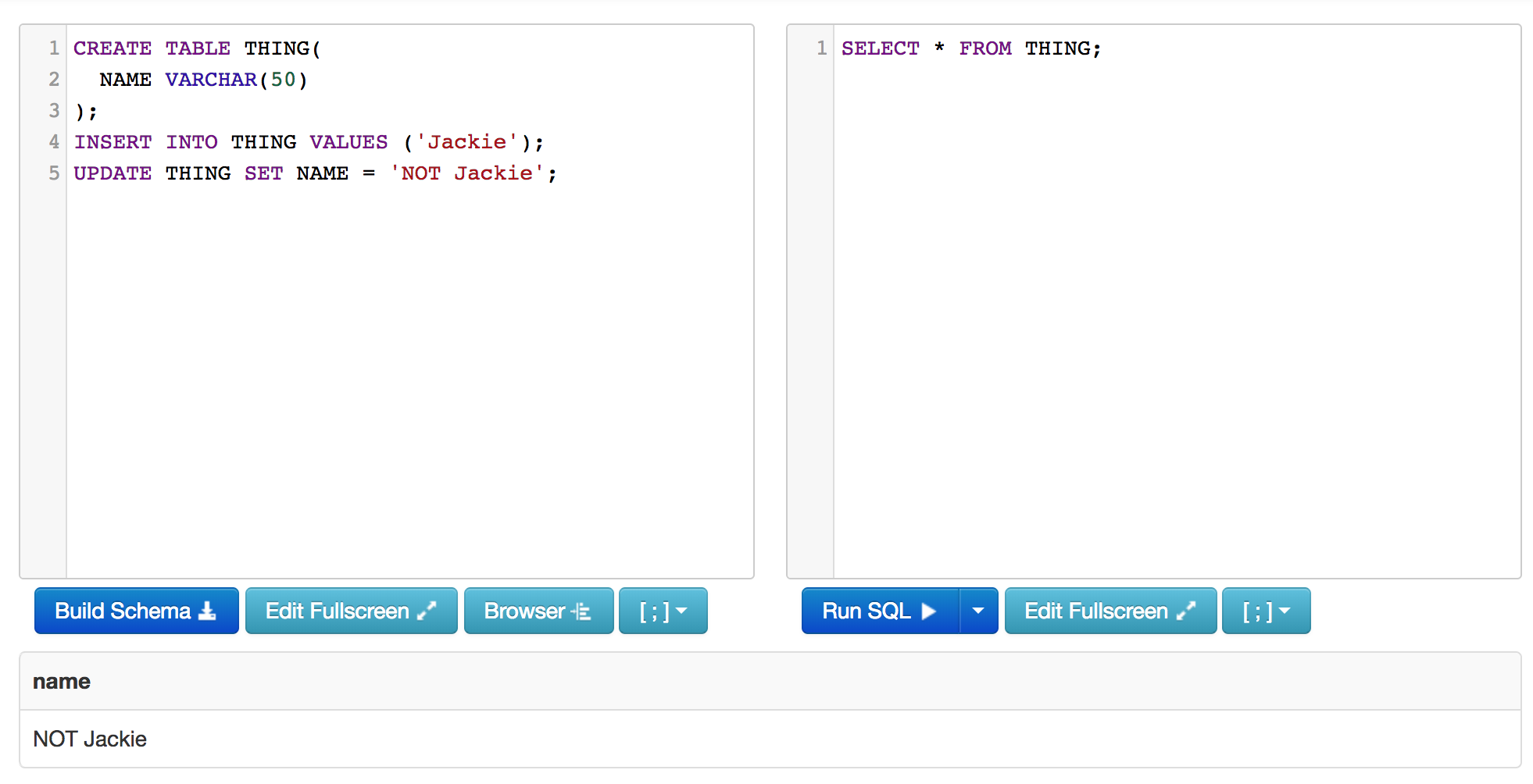
Adding Data
Selecting And Filtering Data

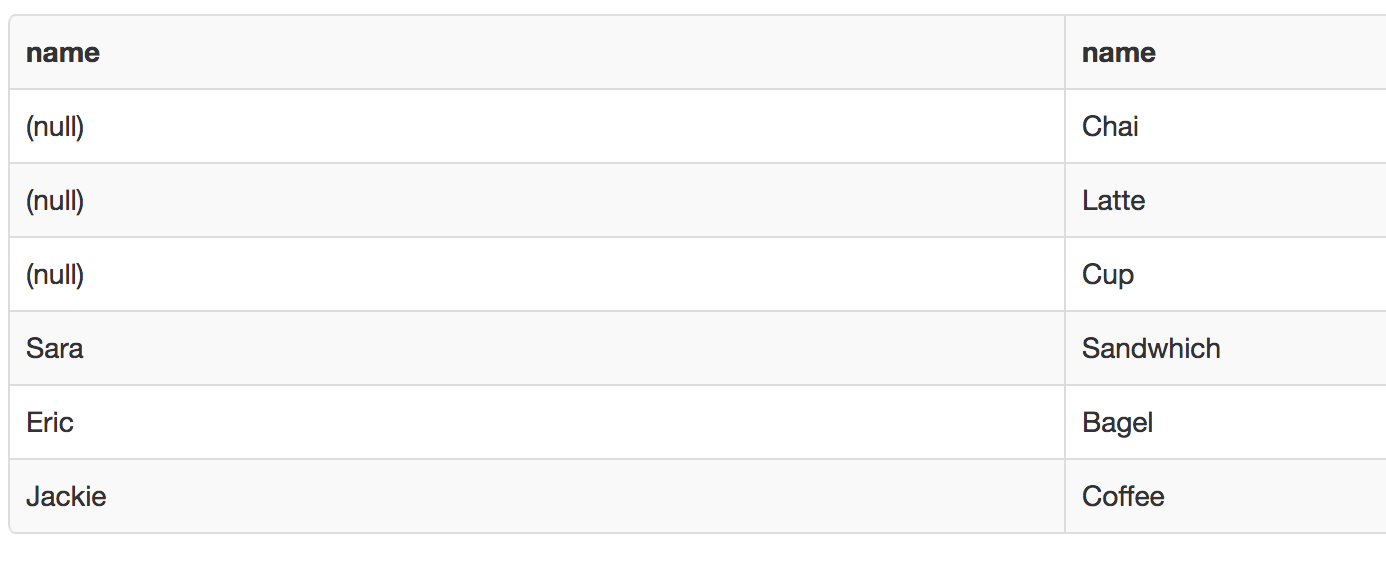
Person
Address
Customer
Profile
Employee
Info
Joins
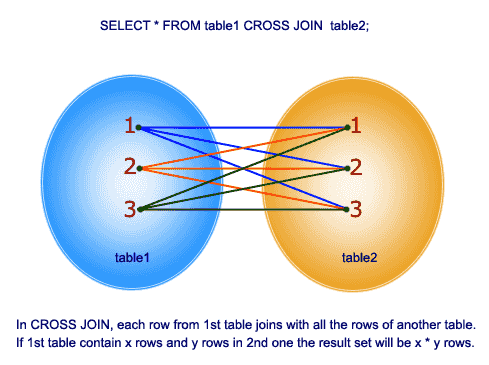
Joins Are Links Declared In The Query
Join Types
- Cross
- Repeated once per record (on both sides)
- With no Where same as Cartesian Product
- Qualified joins
- Has restrictions
- Inner is default
Cross Join
"Kind of" From Both Tables
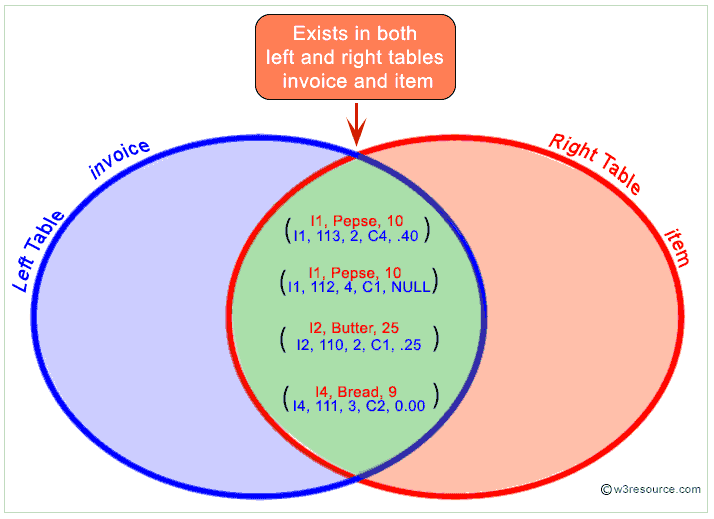
Qualified Join
T1 { [INNER] | { LEFT | RIGHT | FULL } [OUTER] } JOIN T2 ON boolean_expression
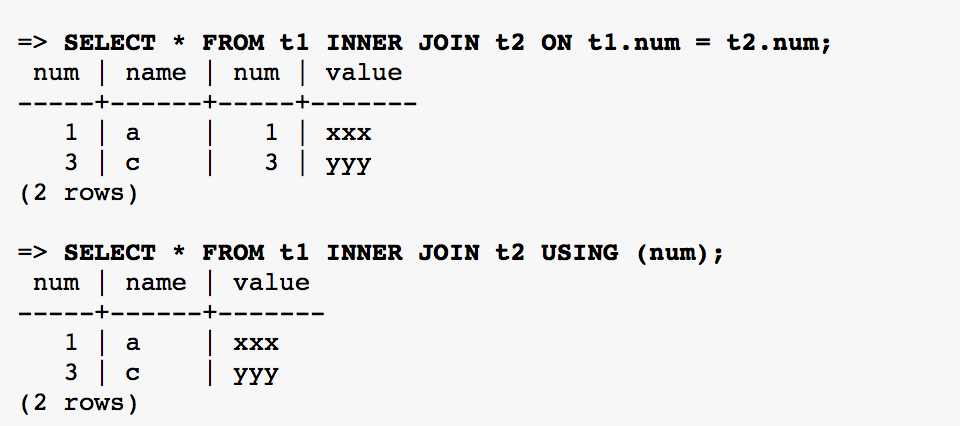
Inner Join
What we have in common
Directional
- Which side are you interested in?
- Sides
- Left
- Right
Left Join
Look to the left
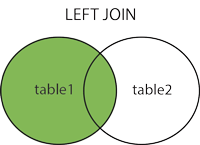

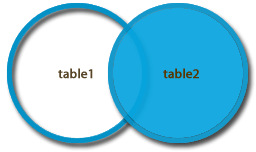
Right Join
Look to the right
Full Outer
Join
From Both Tables
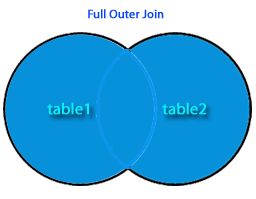
Constraint
- Check
- Not Null
- Unique
- Keys
Allows for more fine grained control over types.
Check
Limits Values Allowed

Not Null
Must Have Value
Unique


Basic Constraints Lab
Primary Key



Serial
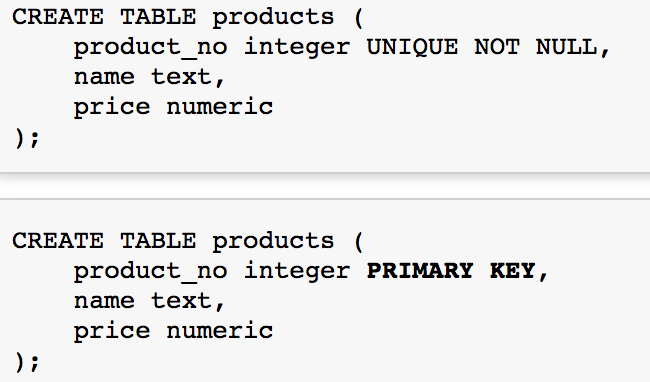
Foreign Key
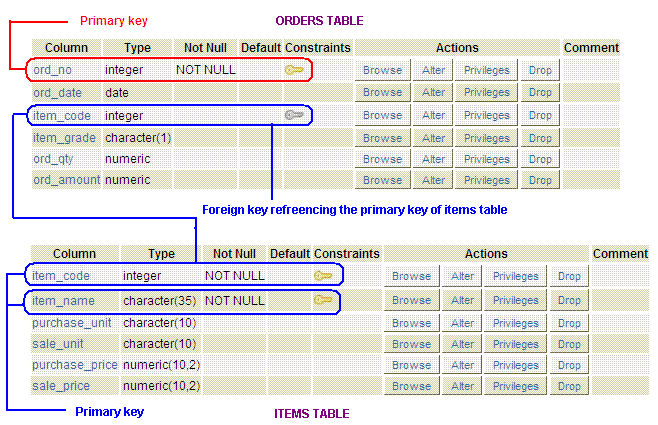
References
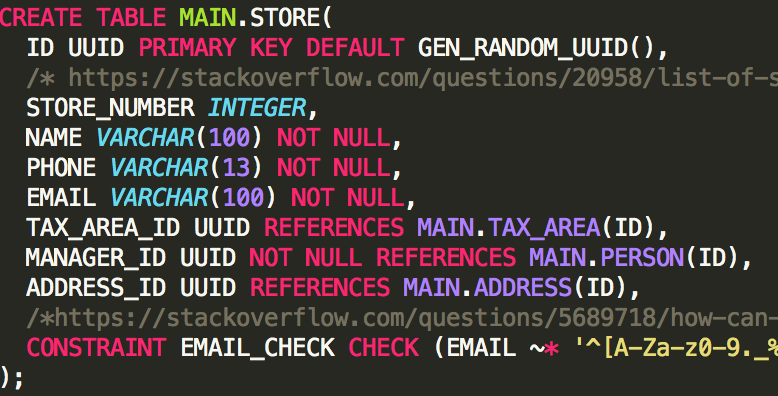
Cascade
- No Action (Default): Check end of transaction
- Restrict: Check now
- Cascade: Delete referencing row as well
- Set Null: Set the reference to null
- Set Default: Set all to a value
Cascade

Keys, Joins and Cascade Lab
Composite Keys

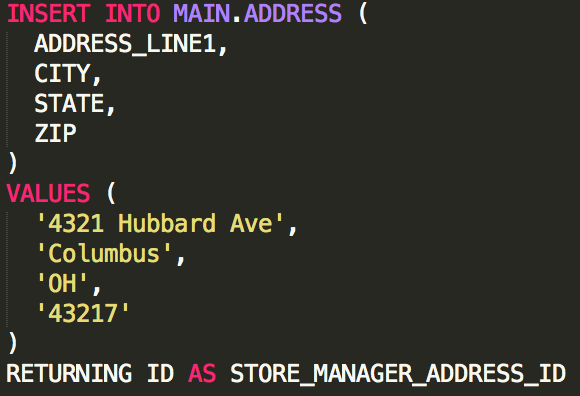
Returning
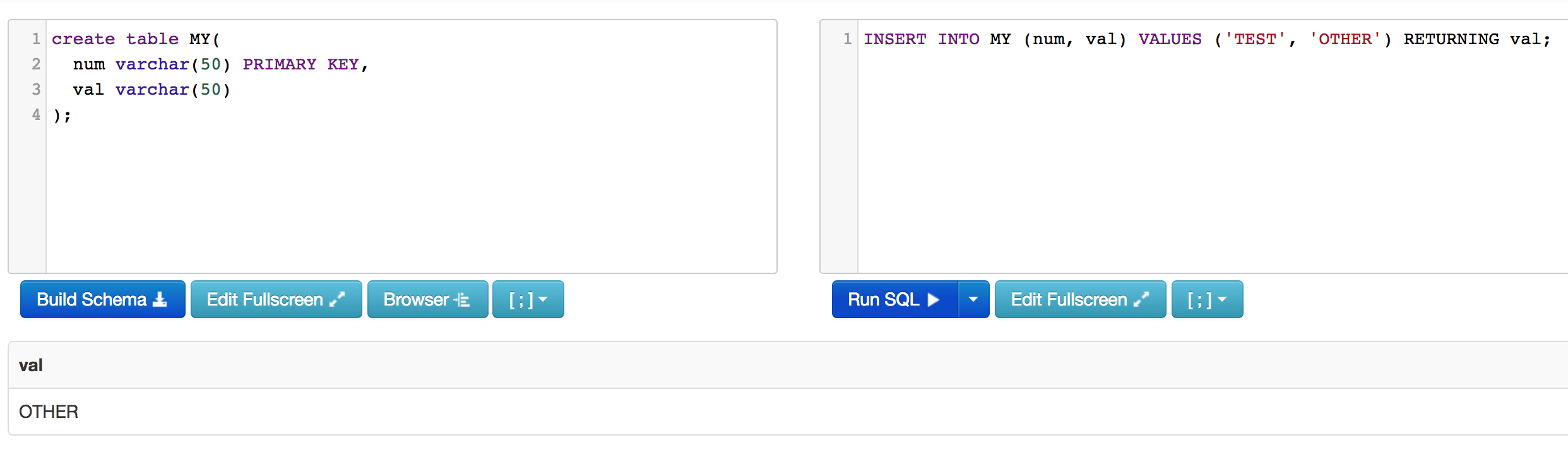
Running SQL Script Files

Functions
- Built-in
- Declared
Mathematical Operators
+ - / * %
abs() pi() sqrt()
cos() sin() tan()

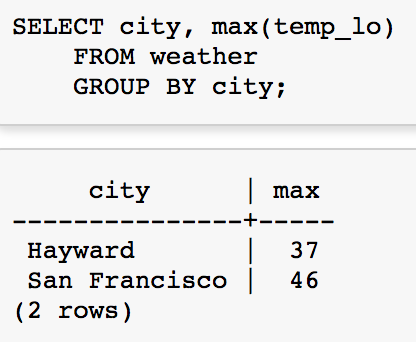
GROUP BY
Create Receipts Lab
Advanced Database Interactions Pt 1
Day 4
Standup
Questions
Like Clause

Posix Regex

REGEXP_MATCHES(NAME, '(.+)(e)$')
Comparison Predicates
HAVING

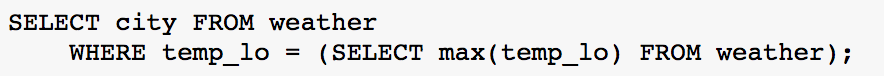

As
SELECT NAME AS PRODUCT_NAME
FROM PRODUCT
Other Important
Complex Search Lab
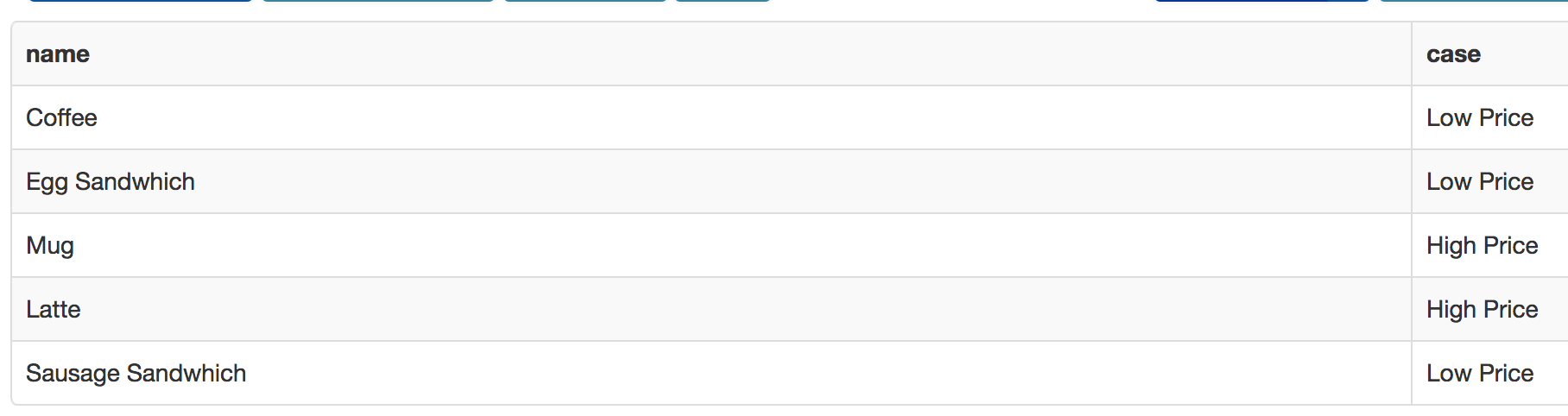
Case

Subqueries
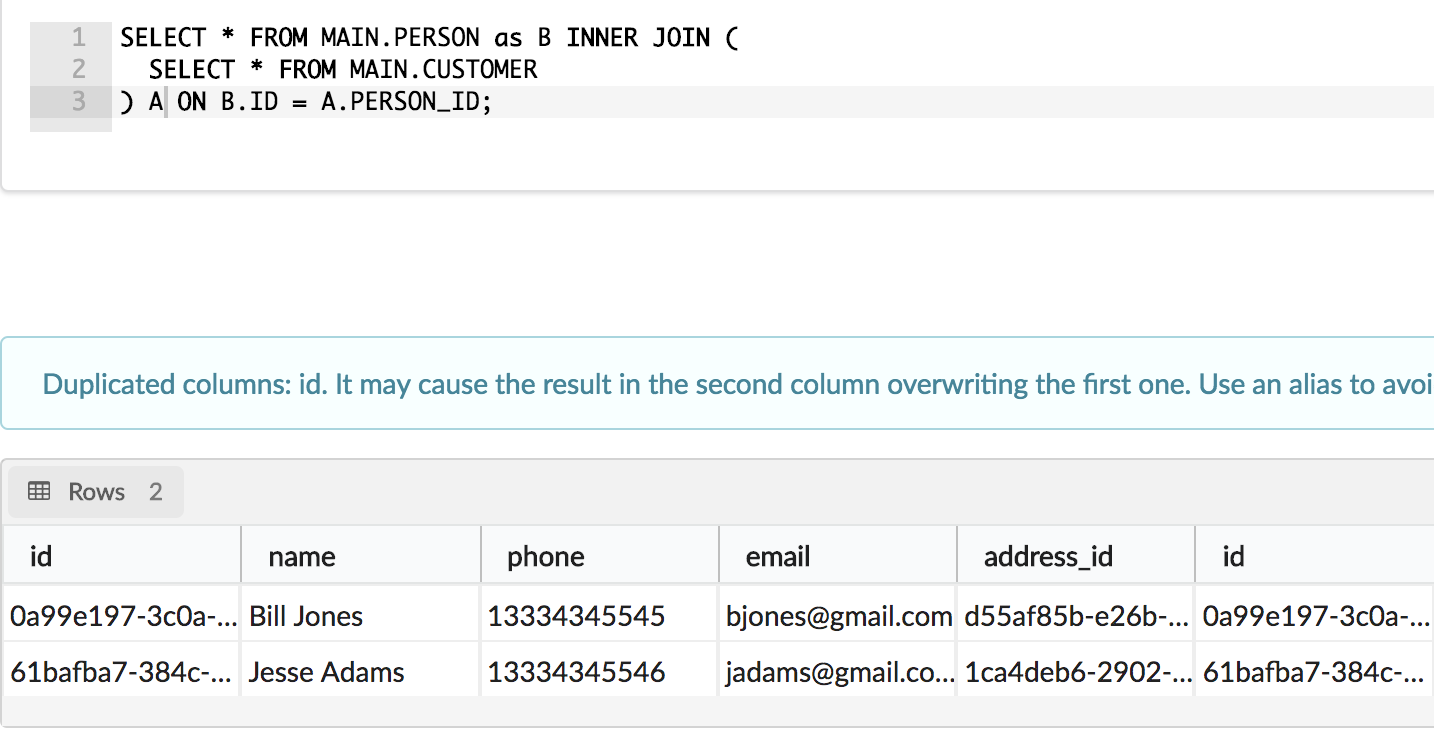
Challenge!
Using nested selects, query all of the items purchased which were over $3 per Person. The result should be Person Name, Product Purchased and Price. There should be only 1 record for Person/Product Combo
Custom SQL Functions
Create Function
CREATE FUNCTION <Function Name>(<Param Type>...) RETURNS <Return Type> AS <Function Query>
LANGUAGE <Lang>
`OR REPLACE`
"It is not possible to change the name or argument types of a function this way (if you tried, you would actually be creating a new, distinct function)"
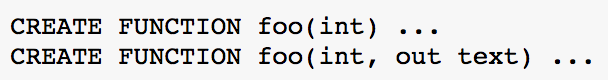
Function Overloading
Now Lets Create A Function!
Use Case
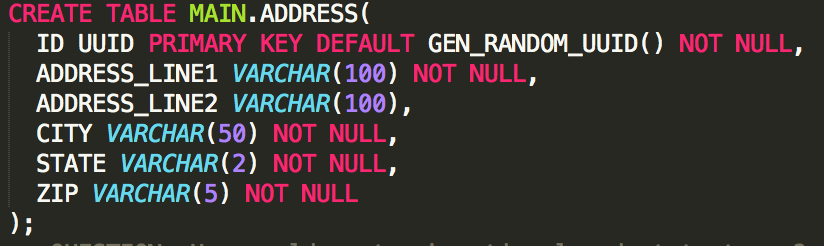
We to take the following schema...
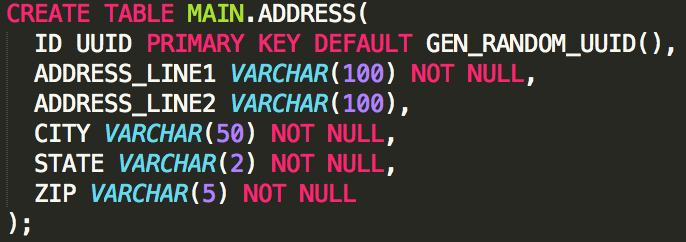
CREATE TABLE ADDRESS(
ID SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
ADDRESS_LINE_1 VARCHAR(50),
ADDRESS_LINE_2 VARCHAR(50),
CITY VARCHAR(50),
STATE VARCHAR(2),
ZIPCODE VARCHAR(5)
);
INSERT INTO ADDRESS (ADDRESS_LINE_1, CITY, STATE, ZIPCODE) VALUES ('301 W. 2nd Ave', 'Columbus', 'OH', '43201');
And create a function to concat the values
|| concats a string so `SELECT 'A' || 'B';` returns `AB`
Variable Naming
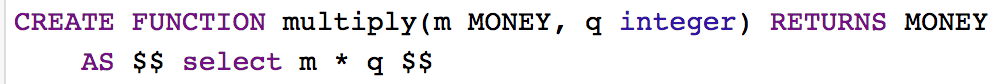
$$ vs '
Create Function Lab

Backup
What is Important?
Schema

Data
Data
- SQL Dump
- File Level Archive
- Continuous Archiving
SQL Dump

Standard Out


Cons
- Large databases may require info to partitioned across multiple files.
- Issues query so can lock DB tables
Pros
- Super easy for small DBs
- Can be specific by using params like --table public.tablename dbname
File System Backup
Database MUST be STOPPED
To back up an individual table copy "pg_clog/*" as well!
Other issues if clustered
Cons
Pros
- Doesn't require any Postgres specific interfaces
- Easily scripted and automated
- No SQL to Restore
- No DB Locks
- Very space intensive
- High I/O on storage
- Cannot be specific
Write Ahead Log
Postgres
Logs Query
Log
Storage and Playback
Stores Query For Backup
Cons
Pros
- Allows for sets of commands to be "rolled" back or forward in time.
- Can provide the ability to "fix" a broken transaction.
- Very complex to implement this robustly
- Does not provide a "snapshot" of existing data
- Most space intensive option
Custom Types
- Composite
- Enumerated
- Range
- Base
- Array
Custom Type Lab
Views
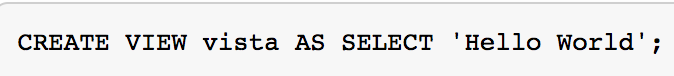
View Creation Lab
Advanced Database Interactions Pt 2
Day 5
Standup
Relationships
- One to One
- One to Many
- Many to Many
One To One
- Used for organizing data
- Not easy to insert at the same time
- Sometimes used for metadata
- Red flag
Person
Customer
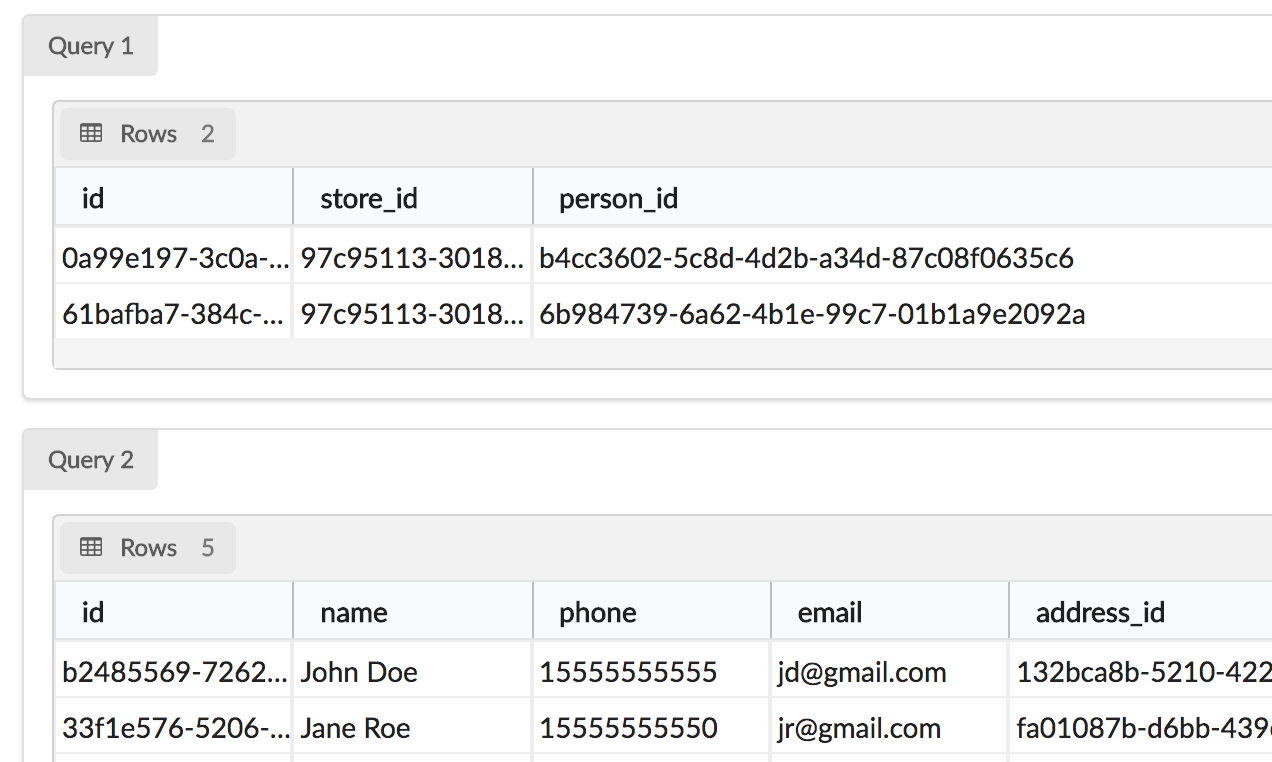
Customer
Customer
Transaction
Transaction
Transaction
TransactionProduct
Product
Product
Product
AKA Mapping Table
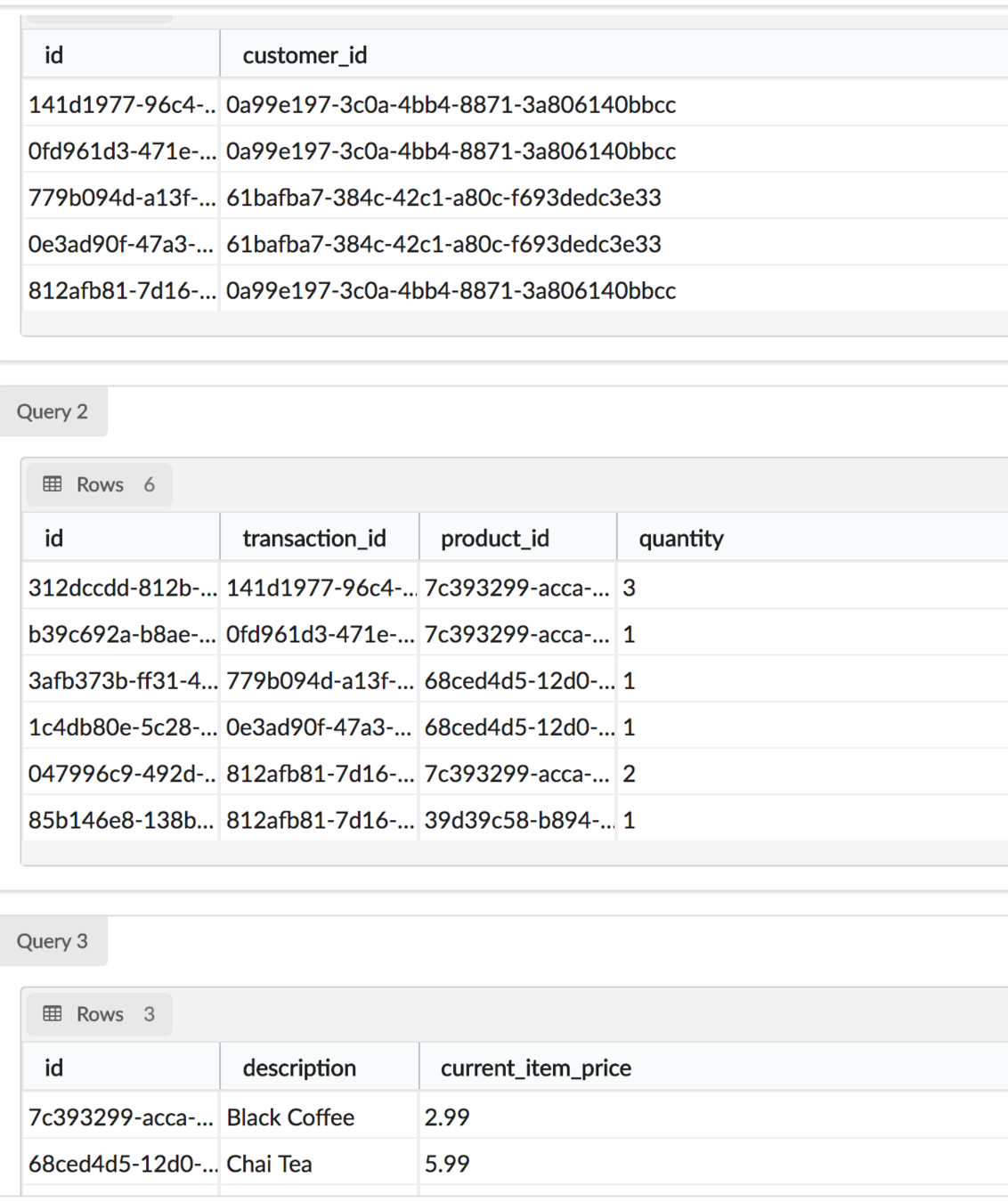
RDBMSs
Struggle With Multi-Level Relationships
Speaking of Performance!
Indexing
Review
Relations are Orderless Unless You Specify In Query
OR....
You Declare An Index

Pros
- Speeds up most selects if applied properly
Cons
- Tends to slow down inserts and updates.
Types of Indices
- B-tree
- Hash
- GiST
- SP-GiST
- GIN
- BRIN
B-Tree
- Default
- Mathematically Complex balanced tree
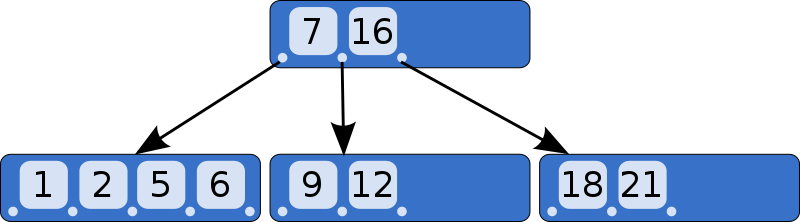
Large Objects
- Provides ability to store large objects
- Objects are split into chunks in a B-Tree
- End of the day there are better options
Transactions
- "The essential point of a transaction is that it bundles multiple steps into a single, all-or-nothing operation."
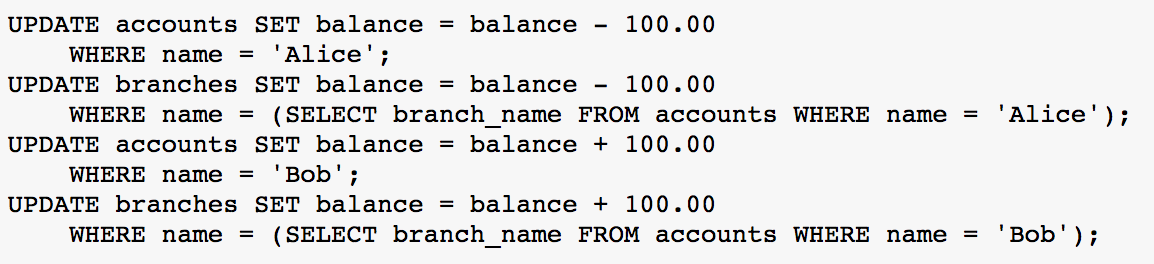
BEGIN;
<Do Something>
SAVEPOINT <Savepoint_Name>;
<Do More Stuff>
ROLLBACK TO <Savepoint_Name>;
<Do Even More Stuff>
COMMIT;
tomicity
A
C
I
D
urability
solation
onsistency
Atomicity
All or Nothing.
Transaction is a unit.
Consistency
Database goes from a valid state before the transaction to a valid state after the transaction.
Consistency
Database goes from a valid state before the transaction to a valid state after the transaction.
Isolation
Transactions happen in isolation of other transactions.
Durability
Once committed a transaction remains committed.
Postgres is ACID Compliant
Other DBs might not be fully complaint
Security
- Authentication
- Acess
Trust Authentication
Everyone gets in
Password Authentication
Stores passwords in PostGres
LDAP, ETC Authentication
Stores Password in LDAP
Roles


Grant
Roles Lab
Statistics
Clustering

Normalization and Data Modeling
Day 6
Using Data
Day 7
Triggers
`When Validation Isn't Enough`
Triggers
- Can be used with tables or views
- Calls a function
Also Interesting
- If multiple triggers of the same kind are defined for the same event, they will be fired in alphabetical order by name.
- SELECT does not modify any rows so you cannot create SELECT triggers.
Trigger Lab
LibPQ
C Library For Postgres Communication
...
#include <libpq-fe.h>
...
PGconn *conn = PQconnectdb("user=postgres dbname=postgres");
if (PQstatus(conn) == CONNECTION_BAD) {
...
}
PGresult *res = PQexec(
conn,
"DROP TABLE IF EXISTS Cars"
);
if (PQresultStatus(res) != PGRES_COMMAND_OK) {
...
}
ODBC
JDBC
Native server driver, must be installed per OS
Same drive all OSes but must have Java
ORM and JPA
Object
Relational
Mapping
Complex SQL
Complex SQL
JSON Object
ORM
Spring
Java Persistence API
JPA == ORM for Java
REST Controller
Mapping Service
JPA Repo
JPA Lab
JPA
- @Entity
- @Id
- @OneToMany
- @ManyToOne
SQL
- Table
- Primary Key
- Foreign Key
- Mapping Table
- spring.jpa.show-sql
- spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto
- spring.jpa.database-platform
@Qualifier
@Entity("Schema1")
...
@Qualifier("Schema1")
@Entity("Schema2")
...
@Qualifier("Schema2")
Schema1.User
Schema2.User
Also Works With Spring
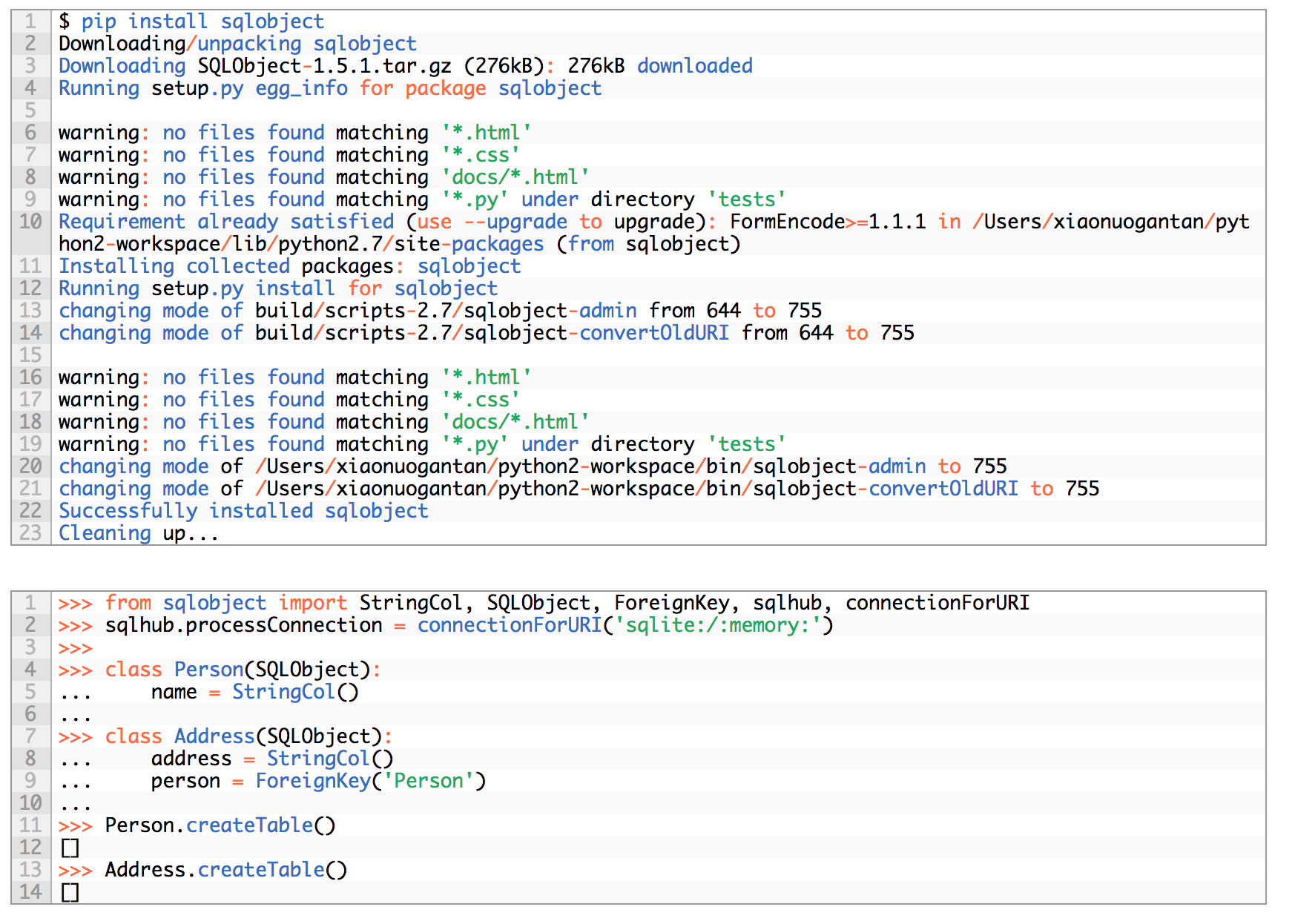
SQLObject

SQLAlchemy

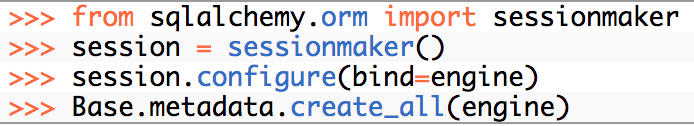

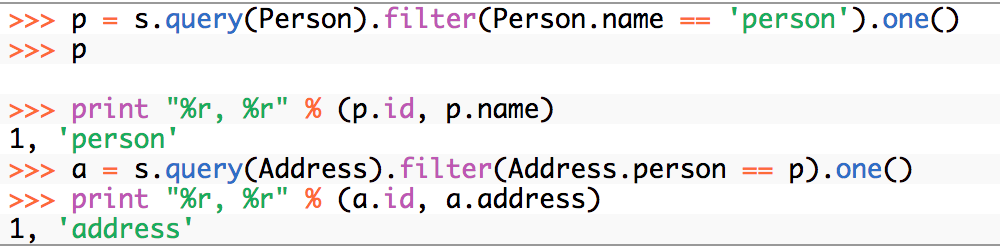
SQL Injection
"SQL statement that you will unknowingly run on your database"



Mitigation
Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP)
Prepared Statements

Escape Input
Visualization
Tableau
Tableau Lab
D3
SQL in IoT
- On Disk
- In Memory
SQLLite

Basic Advantage:
Deals with streams of real time data
Secret Sauce:
In Memory
What are the factors the affect your needs?
Capstone
Create a real-world use case
Use a Postgres DB to store the data for this use-case
Give a presentation on the Use Case
- Create a schema
- Create at least 4 tables
- Create at least 1 Function
- Create at least 1 view
- SQL Schema
- PG_DUMP
- JPA Code
- Tableau Graph (Optional)
- 10 minute Presentation
Deliverables
The Future of Databases
Final Class
Review
Relational Databases are the equivalent of structured Binary Trees

NoSQL
"No SQL" or Non-Relational


Real Time Data Streams
Extremely Large Datasets
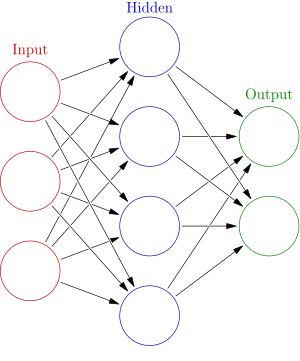
Neural Network
Tables
Why do We Care?
Document Oriented Database
Pros
- Really fast if you are looking for a particular item.
- 2nd most popular
- Allows for storing rather large documents
- Highly scalable
- Resilient
Cons
- Searches are slow
- Need to "manage" relationships.
- More verbose
- Doesn't line up exactly with certain paradigms
AWS Dynamo
Real Time Data Streams
Common Use Cases
- IoT
- Market Making
- Issue Mitigation

Topic
Subscriber
Subscriber
Subscriber
Pros
- Can go up and down
- Can be replayed (stream capture)
- Easily filtered
- Super fast processing
Cons
- Verbose
- Chatty (Network)
- Not reliable
- Doesn't natively maintain a record
"Big Data"
Extremely large datasets
Distributed or parallel
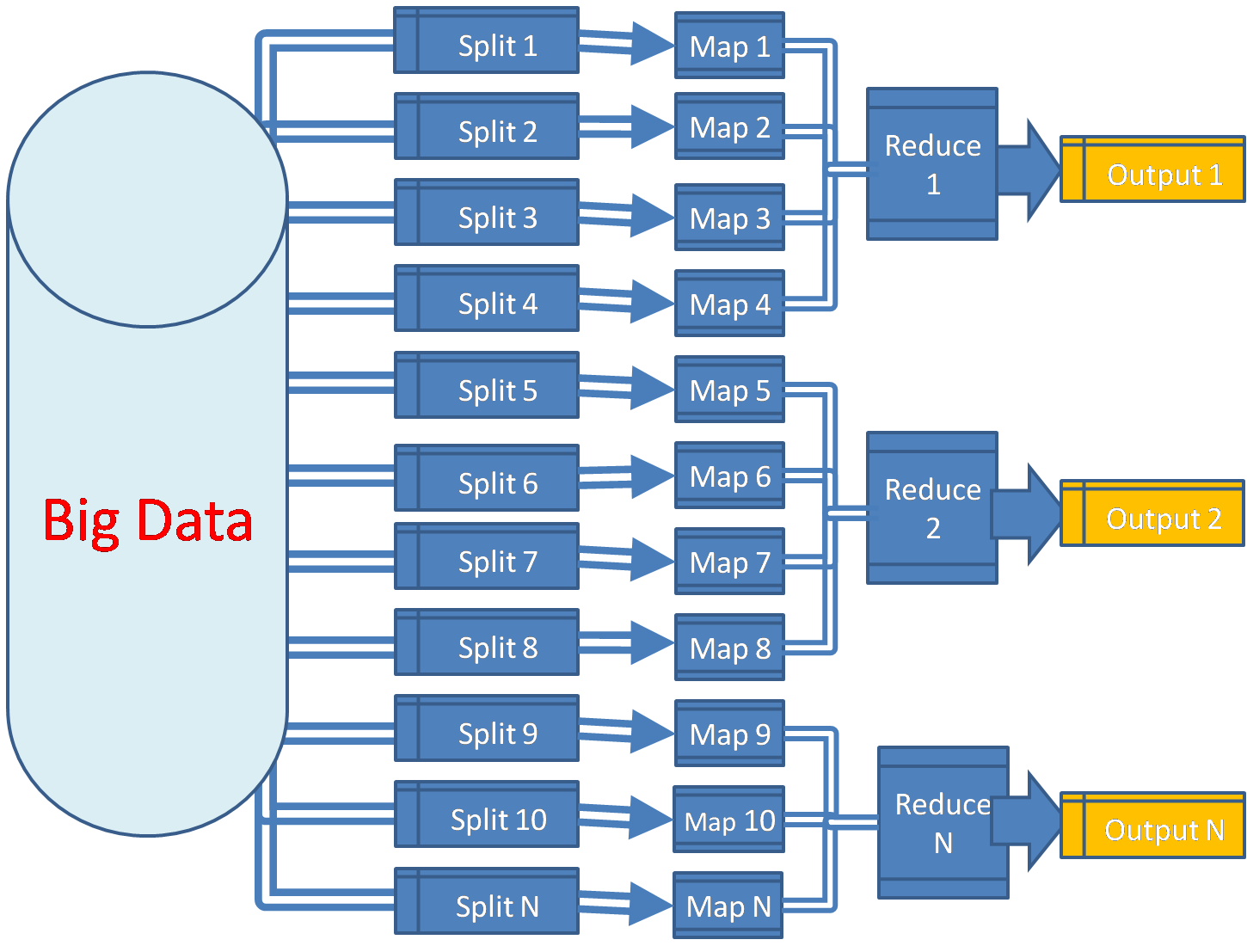

HDFS: Distributed File System
Mapreduce: Distributed Computational Engine
2 Parts
Mapreduce
Spark
Flatmap Vs Spack Map
Allows for parallel processing


Neural Networks
Graph Theory

G = (V, E)
G: Graph
V: Vertices
E: Edges
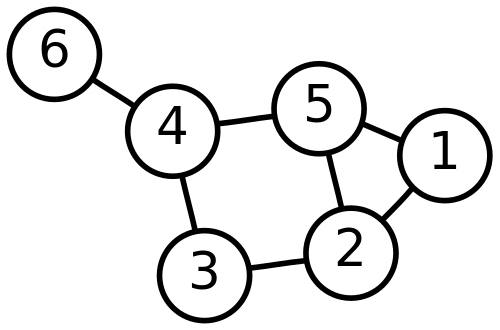
Blockchain
Qubits
Presentations
What we will learned
- What is a database
- How to interact with a relational database
- What is on the horizon
What is a Database
- A Repository for information
- A BTree Representation
- Not Magic
Interacting with RDBMS
- Connect and Create DBs and Schemas
- Add data to tables within the schema
- Use this data to answer questions using SQL
What is on the horizon
- Using visualization tools
- Working with non-relational dbs
- Integrating technologies together
Thanks
You guys did great!