GraphDBs & Neo4J
@lifeistooshort
What We Will Learn
- What is Graph Theory
- Why should I use a GraphDB
- What is Neo4J and how is it used
Best Resource I Have Found

What is a Graph?
Definition
"A collection of vertices and edges that join pairs of vertices"
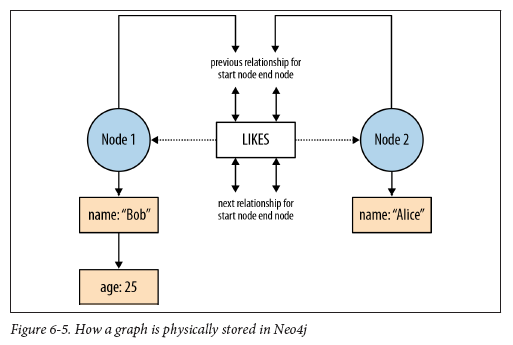
In Neo4J this means Nodes and Relationships
The definition is G(V,E)
2|E|=Σdeg(v)
Not Just For Computer Science
Cartography
Electrical Engineering
Physics
Biology
Leonhard Euler

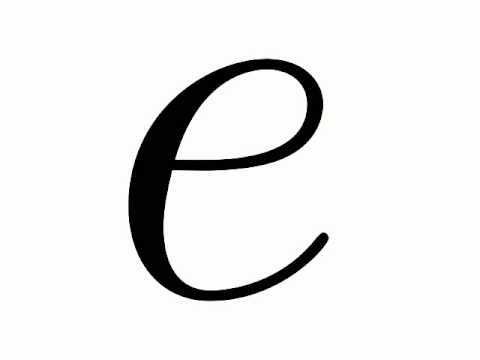
Seven Bridges of Königsberg

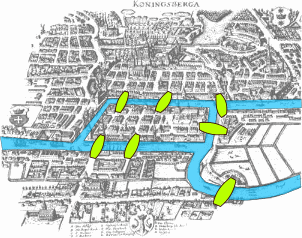
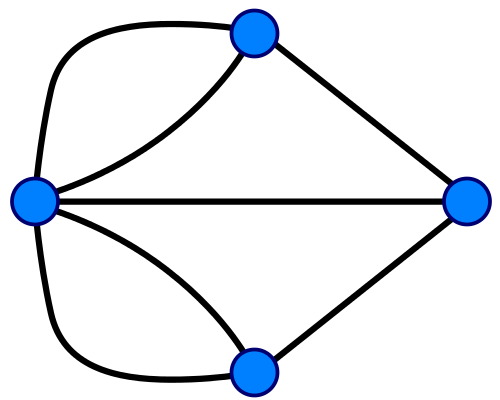
Eulerian Path
All bridges are crossed once and only once
Eulerian Circuits start and stop on same node
Depends on Degrees (0 or 2 odd)
Zombieland
Bill Murray
Bill Murray
ACTS_IN
ACTS_IN
Directed vs Non-Directed
Non-directed graphs do not have a start or end node.
We can also weight these relations
Directed graphs allow for a direction in a relationship.
Advantages
Graphs can morph into many views
Great for inferring relationships
Quickest way to find related nodes
Why Use a GraphDB?
Relational DBs
Tried and true technology for highly structured data.
Joins use keys
May require mapping tables
Finding friends of friends becomes memory intensive
Non-Native storage translates from relational to graph
Example Using Relational
SELECT p1.Person AS PERSON, p2.Person AS FRIEND_OF_FRIEND FROM PersonFriend pf1 JOIN Person p1 ON pf1.PersonID = p1.ID JOIN PersonFriend pf2 ON pf2.PersonID = pf1.FriendID JOIN Person p2 ON pf2.FriendID = p2.ID WHERE p1.Person = 'Alice' AND pf2.FriendID <> p1.ID
NoSQL DBs
Describes storing data as documents, columns, key-value pairs and more
Less rigid
Can create a relationship by storing a document's ID field
Now the application is responsible for joins (map-reduce)
Graph DBs
Can create models that more closely resemble the domain
Relationships are first-class citizens
No need to match means less resource usage
Use Native Storage
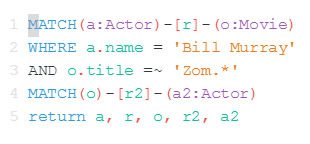
Cypher
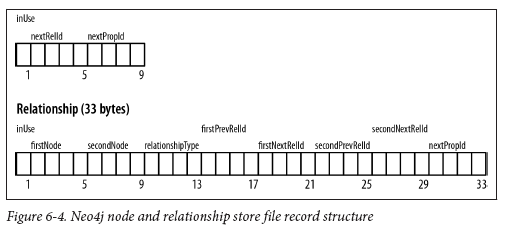
Store Files
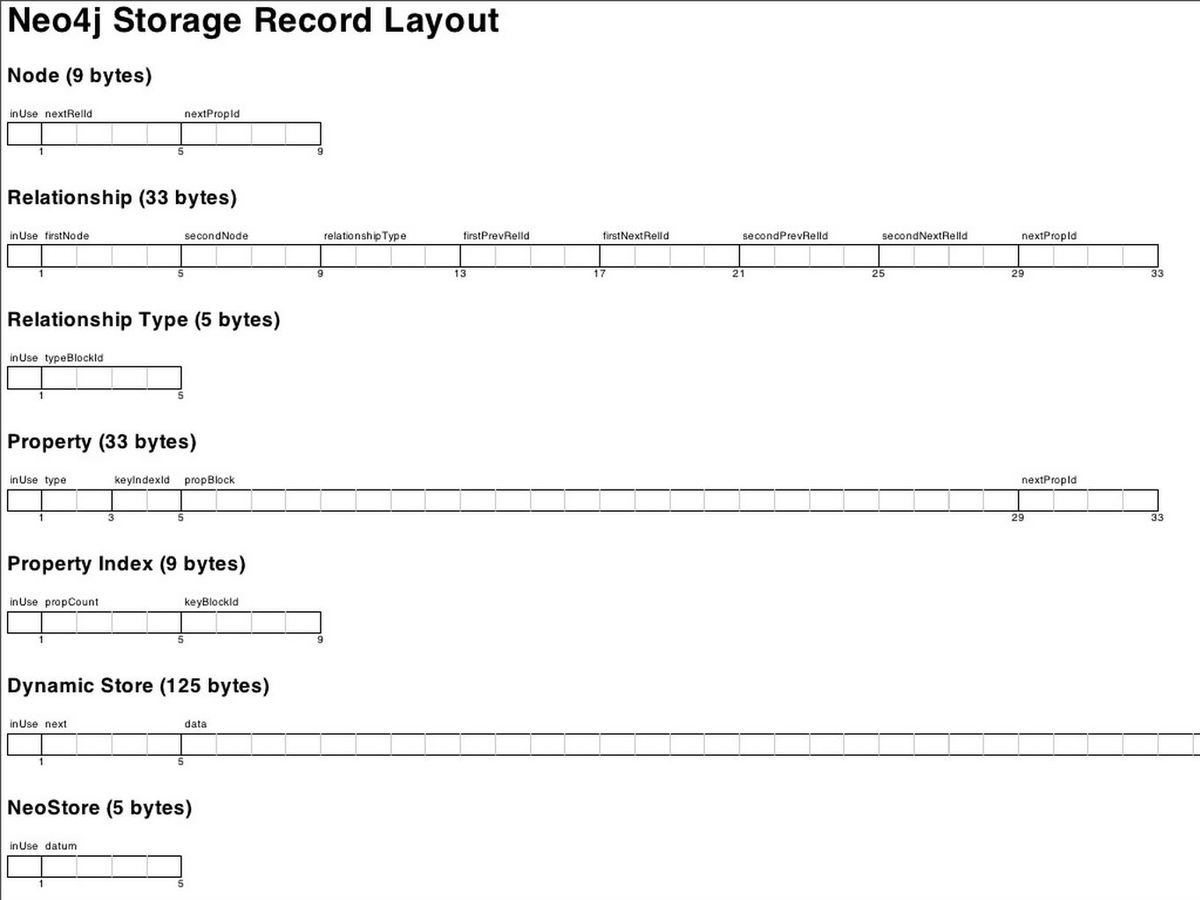
Nodes 9 bytes, Relationships are 33
IDs are based on position (exp 100*9)
InUse is like a delete field
Traversal
Graph Techniques
"They (graph techniques) are especially useful when we want to gain insight into a new domain--or even understand what kind of insight it's possible to extract from a domain" -- Graph Databases
Depth Search
Pop items on stack till there is no place to go. Then we pop off
Once the stack is empty we are done.
Breadth Search
All related nodes are added to a queue.
After all related nodes are visited the base node is popped off the queue.
Triadic Closures



Graphs In The Wild
- Social
- Geo-spatial
- Recommendations
- Access Control
Other Types of Graphs
- Property Graph
- Node contains properties
- Hypergraph
- Relationship can connect n nodes
- Triples
And of course...
What is Neo4J?
Java based GraphDB
Native & REST Interfaces
Server & Embedded Versions
Supports Scaling and Sharding
Advantage
Index-free adjacency allows for millisecond response.
Reduces object-relational impedance mismatch
Easy to change and adapt
ACID
Disadvantages
You still want a relational store
Memory is more expensive than space
Lack of developers
Almost Forgot
It Is Open Source!
Steps to set it up
Download Neo4J
Default port is 7474
Run Neo4J just like Tomcat
You can add JAX-RS endpoints
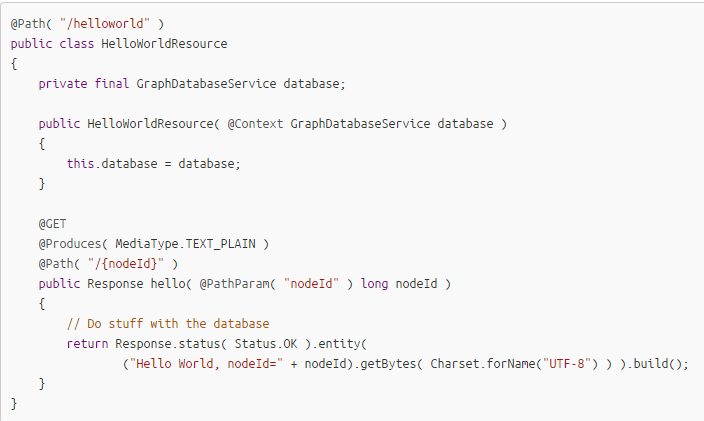
Ways to interact with Neo4J
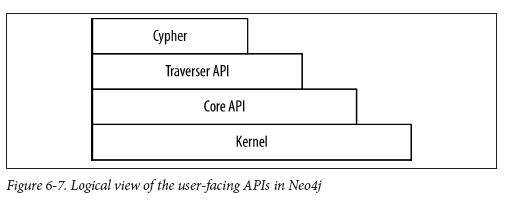
Kernel
Listen directly for transactions
Only called on write transactions that will be commited
Can be used to prevent physical deletions
Java-Based
Core
Allows for imperative declaration
Java-Based
Relationships are only traversed when accessed
You will need domain info in code
// Index lookup for the node representing the doctor is omitted for brevity
Iterable<Relationship> relationships = doctor.getRelationships(Direction.INCOMING, COMPANION_OF );
for ( Relationship rel : relationships )
{
Node companionNode = rel.getStartNode();
if ( companionNode.hasRelationship( Direction.OUTGOING, IS_A ) )
{
Relationship singleRelationship = companionNode.getSingleRelationship( IS_A, Direction.OUTGOING );
Node endNode = singleRelationship.getEndNode();
if ( endNode.equals( human ) )
{
// Found one!
}
}
}
Traverse
Java-Based
Used to gain specific control over traversals
Declarative Interface
You can fall back to the Core APIs
Cypher
Accessible Via Java or REST
Typically results in JSON
Query language
Most common way to interface
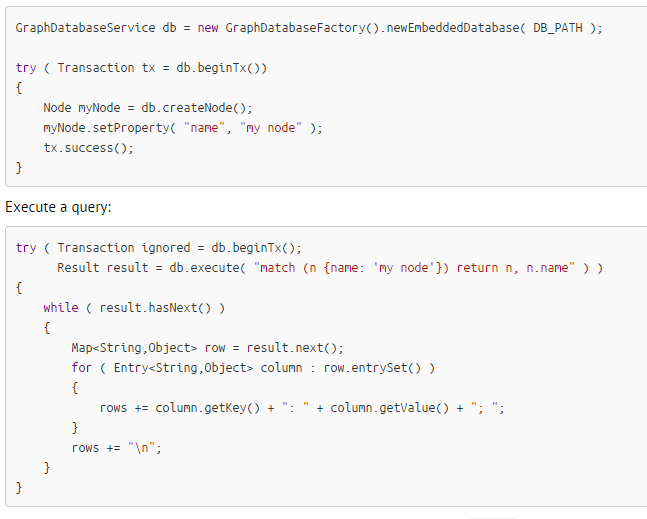


Demo Time!
MATCH
Match reads nodes/relationships
CREATE
Creates a nodes/relationships
MERGE
Creates nodes/relationships if none exist, otherwise it updates the existing one
Delete
Removes nodes/relationships
MATCH
CREATE
MERGE
DELETE
GET
POST
PUT
DELETE
Review
- Graphs are a way to express data in nodes and relationships.
- GraphDBs provide the ability to graph data natively.
- Neo4J is a GraphDB that provides a powerful query language Cipher
Questions?
Links and More Info
JackieRGleason.com
neo4j.com/graphacademy