- Jaimin Gohel
Pwning JS
About Speaker
- InfoSec Enthusiast
-
Speaker
- Null Ahmedabad
- Mozilla Gujarat

What?
- Javascript is a dynamic computer programming language. It is lightweight and most commonly used as a part of web pages, whose implementations allow client-side script to interact with the user and make dynamic pages.
- Javascript was developed by NetScape in 1995
- JavaScript is used by 95.1% of all the websites in 2018.
- It is an interpreted programming language with object-oriented capabilities.
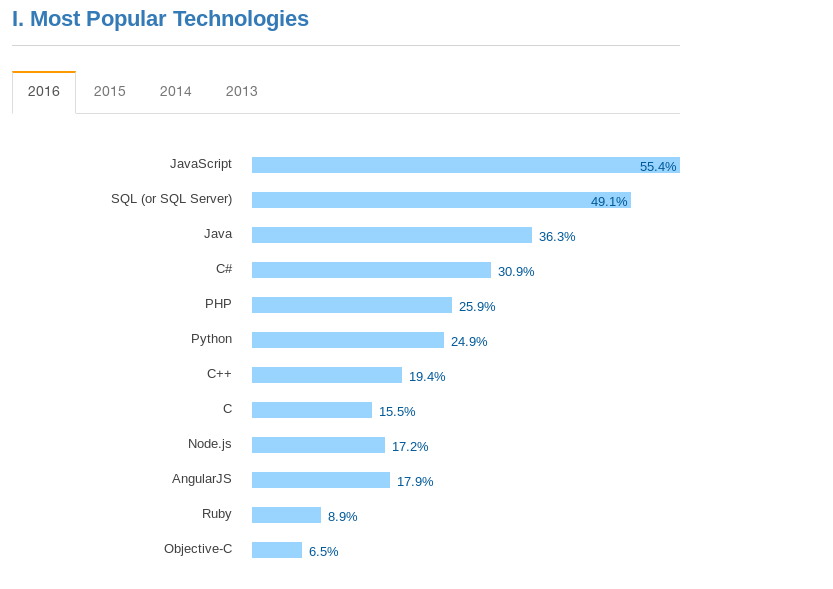
Survey by stackoverflow.com
Why is it so popular?
-
JavaScript is a lightweight, interpreted programming language.
-
Increased interactivity for users.
-
Complementary to and integrated with HTML.
-
Open and cross-platform.
-
It’s a syntantically simple language.
-
Extensible - Javascript can be coupled with many powerful tools that give it a ton of utility: JSON, AJAX, Nodejs, MongoDB, jQuery.
Role in security
-
Its Everywhere!
-
Code re-usability(Third-party modules)
-
jQuery, React, Vue.js, Moment.js
-
-
Bad security practices
-
somediv.innerHTML= '<p>Hello, '+name+'</p>';
-
Role in security cont.
-
77% of 433,000 Sites Use Vulnerable JavaScript Libraries
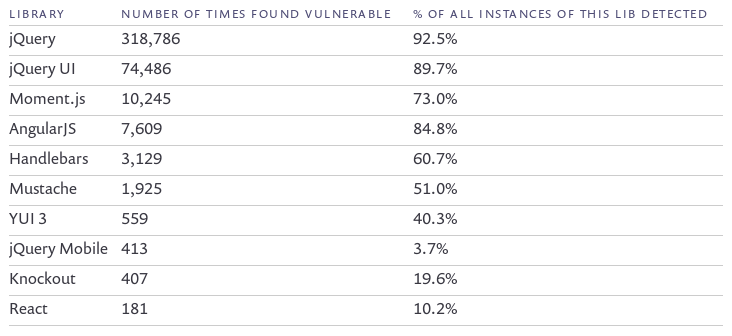
Source: https://snyk.io
Role in security cont.
-
Libraries with no known vulnerabilities

Source: https://snyk.io
Common threats
-
Client-side
-
DOM-based cross-site scripting (XSS)
-
Client-side logic and data storage
-
- Server-side JS injections
- NodeJS
How ?
- Using JSprime- https://github.com/dpnishant/jsprime
- Its a static analysis tool
- Written in JavaScript

Sources & Sinks
- Source
- document.URL
- location.hash
- Sinks
- eval
- anyElement.innerHTML
JsPRIME color codes
- Orange: Active Source
- Brown: Unused Source
- Gray: Unused Source Assignments
- Yellow: Active Source Assignments
- Red: Active Sink
- Pink: Functions that leads to sinks
DEMO
Recommendation
- Keep all your JAVASCRIPT libraries up to date
-
Avoid setInnerHtml() and .innerHtml =. Instead, use setInnerText() or DOM-based operations (to make sure you don't introduce script tags, i.e., to avoid DOM-based XSS). Avoid document.write().
-
Avoid eval(). Its use tends to be correlated to security flaws. Similarly, avoid other APIs that turn a string into code and execute it, like setTimeout() with a string argument, setInterval() with a string argument, or new Function().
Resources and credits
- Thanks to: @dpnishant
- https://github.com/dpnishant/jsprime
- https://www.computerweekly.com/tip/Vulnerabilities-in-JavaScript-Secure-coding-insights-and-tips
- https://www.slideshare.net/nishantdp/jsprime-bhusa13new
- https://www.tutorialspoint.com/javascript/javascript_overview.htm
- https://w3techs.com/technologies/details/cp-javascript/all/all
- https://snyk.io/blog/77-percent-of-sites-still-vulnerable/