Getting Started with Node.js
Code Club Suggestions
https://vh7.uk/supper
What is Node.js?
Node.js is a JavaScript runtime built on Chrome's V8 JavaScript engine. Node.js uses an event-driven, non-blocking I/O model that makes it lightweight and efficient. Node.js' package ecosystem, npm, is the largest ecosystem of open source libraries in the world.
Node.js vs Python
Print to Console "Fetching Info from Database"
Get Info from Database and Print to Console
Print to Console "Fetching Info from Website"
Get Info from Website and Print to ConsoleNode.js
Python
Fetching Info from Database
Fetching Info from Website
Website: Jeff
Database: HelloFetching Info from Database
Database: Hello
Fetching Info from Website
Website: JeffNode.js vs Python
Node.js
Python
. . .
db.query("SELECT * FROM people", def(names):
for name in names:
print(name)
). . .
db.query("SELECT * FROM people")
names = db.output;
for name in names:
print(name)The code on the left is not JavaScript! It is to show how callbacks work in JavaScript with Python code (which won't work in real life!).
NPM
NPM stands for Node Package Manager. It's the number one place to go to download Node packages (or libraries or modules).
Like pip for Python but better.

Trying it out!
Go to https://runkit.com/ and you should get a 'notebook':
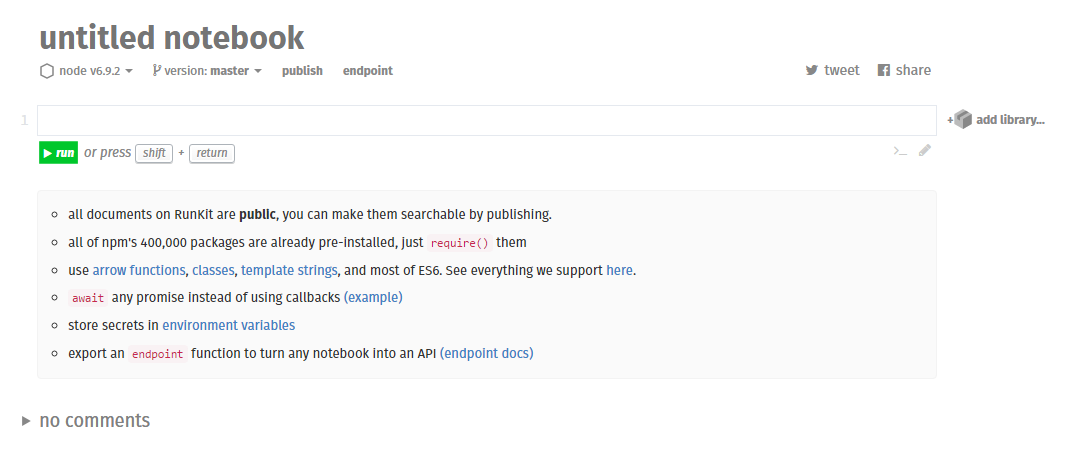
run your code
write your code here
add a new code block (like a new file)
import library from npm
Syntax
Statements are separated by semicolons:
Comments:
var a = 5;
var b = 10;
var c;
c = a + b;// Hello There! I'm a comment!Printing to the Console
// Print Normal Text to the Console
console.log("Hello World");Functions
function myFunction() {
console.log("Hello!");
}
myFunction();
thisFunctionIsAfter();
function thisFunctionIsAfter() {
console.log(`In Python, functions that are called before
they are defined won't work. Will it in Node.js?`);
}Functions with Arguments
parrot("hello");
function parrot(text) {
console.log(text);
}Importing Libraries
var name = require("library");Input
var readline = require("readline");
var rl = readline.createInterface({
input: process.stdin,
output: process.stdout
});
rl.question("What do you think of Node.js? ", function(answer) {
console.log("Thank you for your valuable feedback: ${answer}");
//make sure to close when you've finished
rl.close();
});Input
// . . .
rl.question("Q1: What is your favourite colour? ", function(answer) {
console.log("Awesome!");
rl.question("Q2: What is your favourite ice cream flavour? ", function(answer) {
console.log("Awesome!");
});
});// . . .
rl.question("Q1: What is your favourite colour? ", function(answer) {
console.log("Awesome!");
});
rl.question("Q2: What is your favourite ice cream flavour? ", function(answer) {
console.log("Awesome!");
});Variables
var name = "Jeff";
console.log("Hello " + name);
console.log("Hello ${name}");var age = 18;console.log("Hello " + name + ". You are " + age + ".");
console.log("Hello ${name}. You are ${age}.");MySQL
Hey! MySQL sounds a bit like SQLite
You'd be right there! Both use SQL queries and they are both databases. MySQL databases are hosted on servers as opposed to inside a file. And the commands for MySQL are a little different to SQLite.
Getting Started
Import with:
var mysql = require("mysql");Make a new connection:
var connection = mysql.createConnection({
host: "carbon.vh7.uk",
user: "codeclub",
password: "icanhascheezburger",
database: "codeclub"
});Connect:
Disconnect:
connection.connect();connection.end();Executing Queries
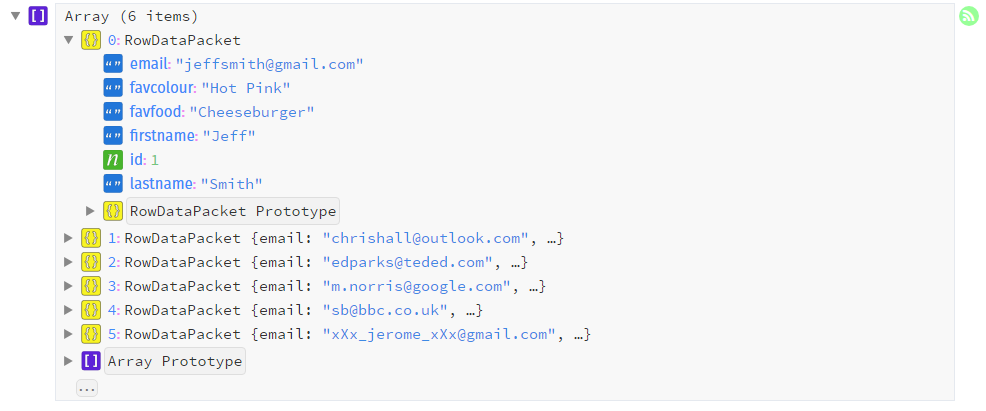
Execute Queries
connection.query("SELECT * FROM people", function (error, results, fields) {
if (error) throw error;
results.forEach(function(result) {
console.log(result.firstname);
});
});
Databases
Challenges
- Add someone into the database.
- Add a new column to the database (e.g favanimal)
- Make a new table (e.g animals)
- Make a program which asks the user questions then inserts them into the database
Ask for help or Google what you want to do followed my MySQL (e.g "insert data mysql").