System's Architecture
Memory

- Understand the different types of memory within a computer: RAM, ROM, Cache, Register.
- Know what the different types of memory are used for and why they are required.
- Understand the differences between main memory and secondary storage.
- Understand the differences between RAM and ROM.
Main Memory (RAM, ROM)
- Main memory is built inside the computer.
- As a result, data can be read from and written to main memory extremely quickly.
- This gives the processor fast access to the data and instructions that the main memory holds.
- There are two types of main memory:
- read-only memory (ROM)
- random access memory (RAM)


Read-Only Memory (ROM)
-
Non-volatile main memory - this means that its contents are not lost when the computer is turned off.
-
ROM can be read from, but not written to.
-
This makes ROM ideal for storing instructions and data that are needed for the computer to run.
-
These instructions and data are usually programmed by the computer's manufacturer and cannot be overwritten.


- The Basic Input Output System (BIOS) is an example of a program that is stored in ROM.
- The BIOS runs as soon as the computer is switched on.
- It checks that the hardware is functioning correctly, then runs a second program known as the bootup or bootstrap program that loads the computer's operating system from the hard drive into the RAM.
Read-Only Memory (ROM)
Random Access Memory (RAM)

-
Random access memory (RAM) is volatile main memory. This means that once the computer is switched off, the data and instructions held in RAM are lost.
-
RAM is given the term “random access” because data can be stored and accessed from any location within the memory.
-
RAM is used to hold data and programs that are currently in use.
-
In a modern PC, RAM is used to hold the operating system and any open documents and programs that are running.
Random Access Memory (RAM)

-
The contents of RAM can be changed at any time, simply by overwriting them with other data and instructions.
-
For example, a user might close one document and open a second, or run a different program.
-
The more RAM a computer has, the more data and programs it can hold simultaneously. RAM can also be upgraded fairly easily, unlike other types of main memory.
-
Cache is a small amount of high-speed random access memory (RAM) built directly within the processor.
-
It is used to temporarily hold data and instructions that the processor is likely to reuse.
-
The bigger its cache, the less time a processor has to wait for instructions to be fetched.
Cache

-
Small amounts of very fast memory
-
Built on the CPU
-
Holds data/instructions that are being used by the CPU
Registers
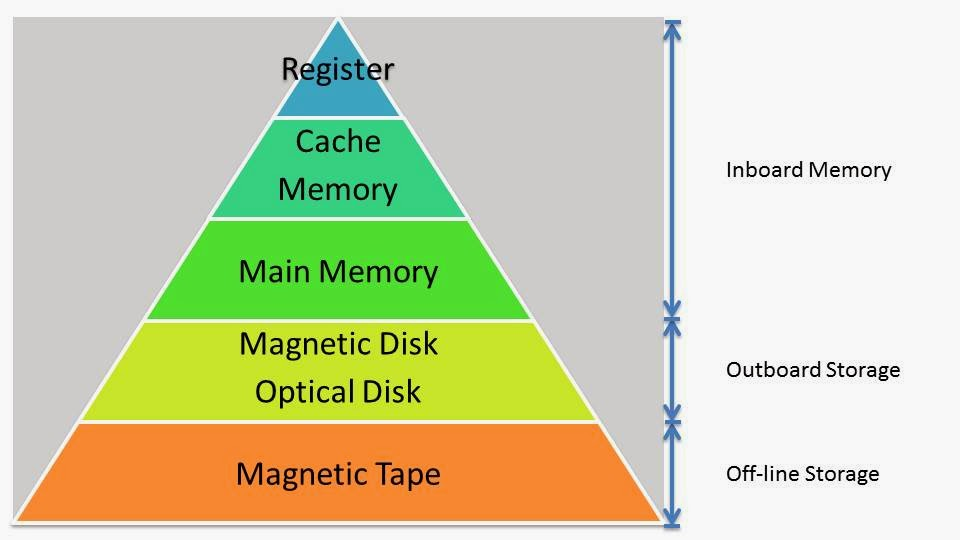
Questions
- State two differences between RAM and ROM.
- What is held in RAM while the computer is working?
- What is held in ROM on the computer?
RAM is volatile (needs power to operate), ROM is non-volatile (does not need power to operate), so ROM will store data when the computer is powered off.
RAM is read-write memory, ROM is read-only memory.
The operating system, applications that are running and associated data.
The instructions and data needed to get the system up and running and ready to load the operating system.