Policy Training
Introduction to Policy and Policy Enforcement Points
Policy Training
Introduction to Policy and Policy Enforcement Points

Jason Coposky
@jason_coposky
Executive Director, iRODS Consortium
August 3-6, 2020
KU Leuven Training
Webinar Presentation
Data Management

"The development, execution and supervision of plans, policies, programs and practices that control, protect, deliver and enhance the value of data and information assets."
Policy

A set of ideas or a plan of what to do in particular situations that has been agreed to officially by a group of people...
A Plan : The real world decisions about the actions to be taken
Particular Situations : The circumstances around which the plan is invoked
Real world decisions

"Every data object shall have at least 3 replicas, two on premises and one off premises."
"Every replica of every data object shall have a SHA256 checksum which will be verified monthly."
"Every data object older than one month will be moved to an object store, every object older than a year will be moved to tape storage."
"Every data object older than 10 years containing personally identifiable information will be deleted."
Categories of Policy

- Data Movement
- Data Verification
- Data Retention
- Data Replication
- Data Placement
- Checksum Validation
- Metadata Extraction
- Metadata Application
- Metadata Conformance
- Replica Verification
- Vault to Catalog Verification
- Catalog to Vault Verification
- ...
Automation

ONLY with the automation of policy can your system provide the types of guarantees that you are actually interested in
- integrity
- provenance
- quality metadata enforcement
- reproducibility
Leaving the humans in charge of policy enforcement is a mistake.
- People should craft the policy together.
- Machines should enforce the defined policy.
Automation

Reflect real world data management decisions in computer actionable code
What : computer actionable code in any programming language
When : Policy Enforcement Points
Why : Drive Data Management through Metadata
The Why : Metadata

Creation and curation can be either:
-
manual - by humans
- richness in meaning
- slow
- inconsistent
- error prone
-
automatic - by machines
- derived - from the system
- extracted - from within
- harvested - from elsewhere
Metadata

Can be of one of three types:
- descriptive - about the content, author, etc.
- structural - about the format, layout, implementation details
- administrative - about the management, processing of the data
We're primarily interested today in administrative metadata.
Metadata

- Structural helps to capture Descriptive
- Administrative drives the policy
- Leads to understanding and confidence
- Leads to meaning and science
Metadata Everywhere
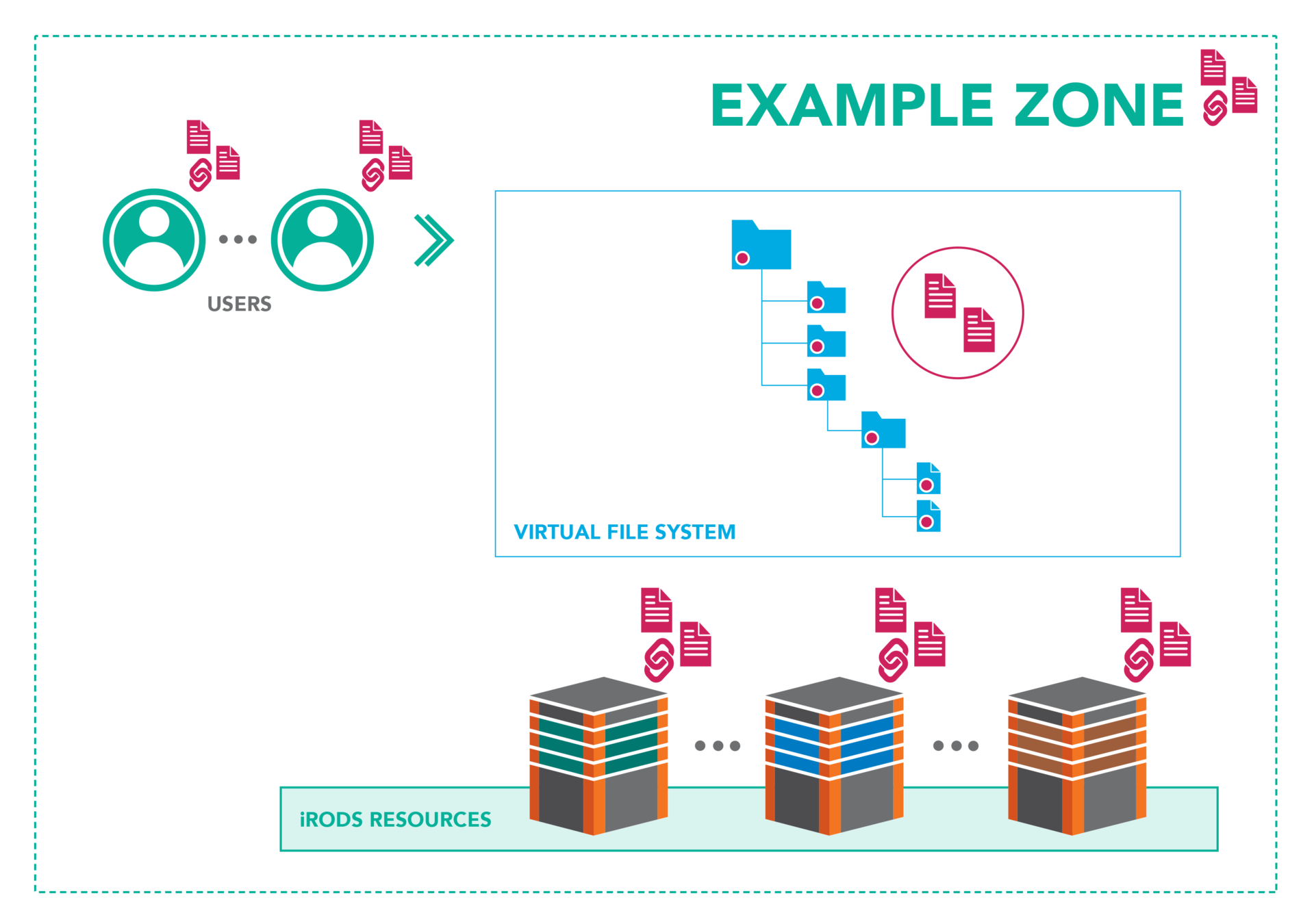

Metadata Driven

With an open, policy-based platform, metadata can be elevated beyond assisting in just search and discoverability. Metadata can associate datasets, help build cohorts for analysis, coordinate data movement and scheduling, and drive the very policy that provides the data governance.
Data management should be data-centric and metadata driven.
The When : Policy Enforcement Points

Every operation within the system has the potential to invoke policy
- RPC API
- Authentication
- Storage Interaction
- Database Interaction
- Network Activity
Policy may be invoked from one or more PEPs depending on the desired outcome
Policy Enforcement Points

A tour of dynamic policy enforcement points
Anatomy of a Policy Enforcement Point

Every PEP begins with pep_
- _pre
- _post
- _except
- _finally
And ends with a 'policy clause':
pep_api_data_obj_put_post
For example:
Policy Enforcement Point Flow Control

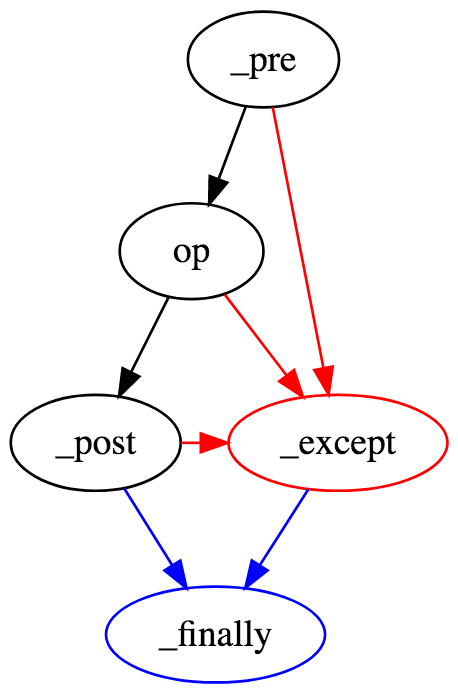
If the pre succeeds, the operation fires, if it fails the except clause is invoked
If the post succeeds, the finally clause is invoked, if it fails the except clause is invoked
If the operation succeeds, the post clause is invoked, if it fails the except clause is invoked
If the except is invoked the finally clause is invoked
Policy Enforcement Signatures

Signatures for the plugin policy enforcement points:
pep_resource_resolve_hierarchy_pre(irods::plugin_context & context,
const std::string * operation,
const std::string * current_host,
irods::hierarchy_parser * out_parser,
float * out_vote)pep_resource_resolve_hierarchy_pre(*INSTANCE_NAME, *CONTEXT, *OUT, *OPERATION, *HOST, *PARSER, *VOTE) {
# Your Policy Here
}Becomes :
All plugin PEPs begin with *INSTANCE_NAME, *CONTEXT and *OUT
Then add the rest of the signature after the plugin_context of the plugin operation
Policy Enforcement Signatures

- INSTANCE_NAME : The plugin's instance name
- CONTEXT : Connection handle, First Class Object, etc
- OUT : A string to pass information to the operation or other policy clauses
Policy Enforcement Signatures

Signatures for the API policy enforcement points:
pep_api_data_obj_put_pre(rsComm_t * rsComm,
dataObjInp_t * dataObjInp,
bytesBuf_t * dataObjInpBBuf,
portalOprOut_t ** portalOprOut)Becomes :
pep_api_data_obj_put_pre(*INSTANCE_NAME, *COMM, *DATAOBJINP, *BUFFER, *PORTAL_OPR_OUT) {
# Your Policy Here
}Prepend *INSTANCE_NAME and follow the API's signature
Useful API Policy Enforcement Points

pep_api_auth_request_[pre, post, except, finally] (*INST, *COMM, *REQ)
pep_api_coll_create_[pre, post, except, finally] (*INST, *COMM, *COLL_INP)
pep_api_data_obj_open_[pre, post, except, finally] (*INST, *COMM, *OBJ_INP)
pep_api_data_obj_close_[pre, post, except, finally] (*INST, *COMM, *CLOSE_INP)
pep_api_data_obj_put_[pre, post, except, finally] (*INST, *COMM, *OBJ_INP, *BYTES_BUFF, *OPR_OUT)
pep_api_data_obj_get_[pre, post, except, finally] (*INST, *COMM, *OBJ_INP, *OPR_OUT, *BYTES_BUFF)
pep_api_data_obj_unlink_[pre, post, except, finally] (*INST, *COMM, *UNLINK_INP)
pep_api_mod_avu_metadata_[pre, post, except, finally] (*INST, *COMM, *MOD_INP)
pep_api_mod_access_control_[pre, post, except, finally] (*INST, *COMM, *MOD_INP)
API Policy enforcement points are triggered on the server to which the client is connected
Useful Resource Policy Enforcement Points

pep_resource_resolve_hierarchy_* (*INSTANCE_NAME, *CONTEXT, *OUT, *OPERATION, *HOST, *PARSER, *VOTE)
pep_resource_create_* (*INSTANCE_NAME, *CONTEXT, *OUT)
pep_resource_open_* (*INSTANCE_NAME, *CONTEXT, *OUT)
pep_resource_close_* (*INSTANCE_NAME, *CONTEXT, *OUT)
Plugin Policy enforcement points are triggered on the server which invokes the operation which allows for policy around direct data access
Most policy will be driven by the API unless specific to a given object replica
Questions?
