Abbreviated Breast MRI for Screening
Kuhl CK, Schrading S, et. al.
Introduction
- MRI associated with high direct and indirect costs
- conventional protocols time consuming to acquire and read
- limited access to screening MRI
Introduction
- Propose abbreviated MRI protocol
- early postcontrast period only
- MIP for fast overview of imaging volume
- Reduce time and cost associated with screening breast MRI
- Increase access
Methods - design
- Prospective, 2009 - 2010
- Hypothesized abbreviated protocol (AP) associated with reduced diagnostic accuracy
- May be worth it for increased speed/decreased cost
Methods - protocol
- T1 pre
- T1 post (1st acquisition)
- T1 subtracted
- MIP
- T1 post (2nd acquisition)
- T1 post (3rd acquisition)
- T1 post (4th acquisition)
- T1 post (5th acquisition)
- Coronal T1
- Axial T2
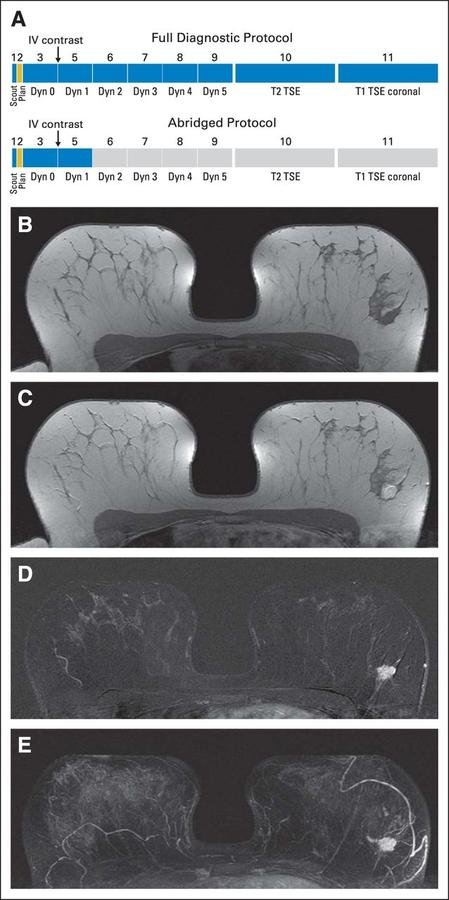
Methods - inclusion
- Women referred for screening MRI on clinical grounds
- 24% Dense breast tissue
- 26% Family history
- 50% Personal history (screening contralateral breast)
Methods - interpretation
- Two readers, 18 and 6 years experience
- Images read immediately
- 1st with AP
- MIPs read first, recorded presence of abnormal enhancement
- then rest of AP, given BI-RADS category
- then with FDP (full diagnostic protocol)
- 1st with AP
- Time to establish diagnosis recorded
Results - participants
- 443 women (163 underwent 2 annual screening rounds)
- 606 MRIs
- 82% of exams in women with mildly or moderately increased risk
- All were asymptomatic and had negative or benign mammogram at time of MRI
- 427 of 606 had negative or benign US
Results - cancer yield
- 11 cancers diagnosed (incidence = 2.5%)
- 4 DCIS
- 7 invasive
- All had (false) negative or benign mammograms
- 10 of 11 had (false) negative or benign US, 11th had negative targeted US at site of MRI detected cancer
- 8 high-risk lesions
- 3 papillomas
- 2 LCIS
- 2 ADH
- 1 radial scar
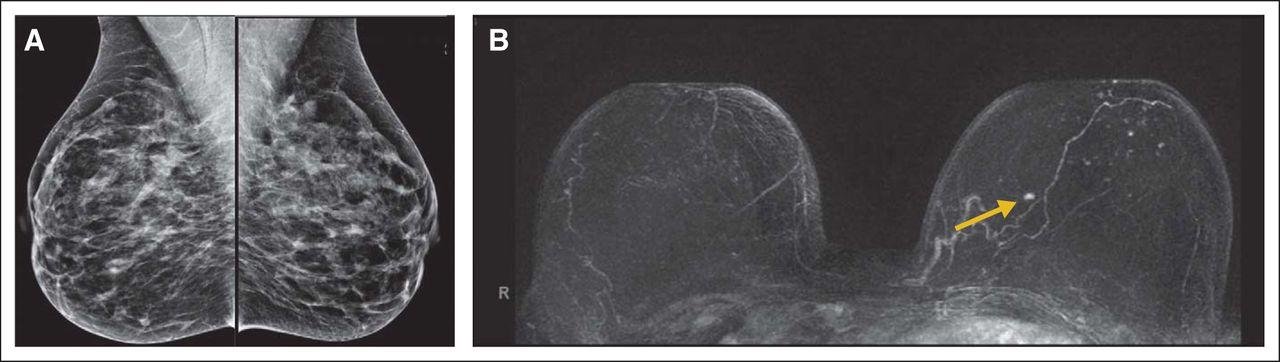
Results - timing
- Acquisition time
- AP: 3 m, 4 s
- FDP: 17 m, 4 s
- Reading time
- MIP: 2.8 s
- AP: 28 s
Results - diagnostic accuracy
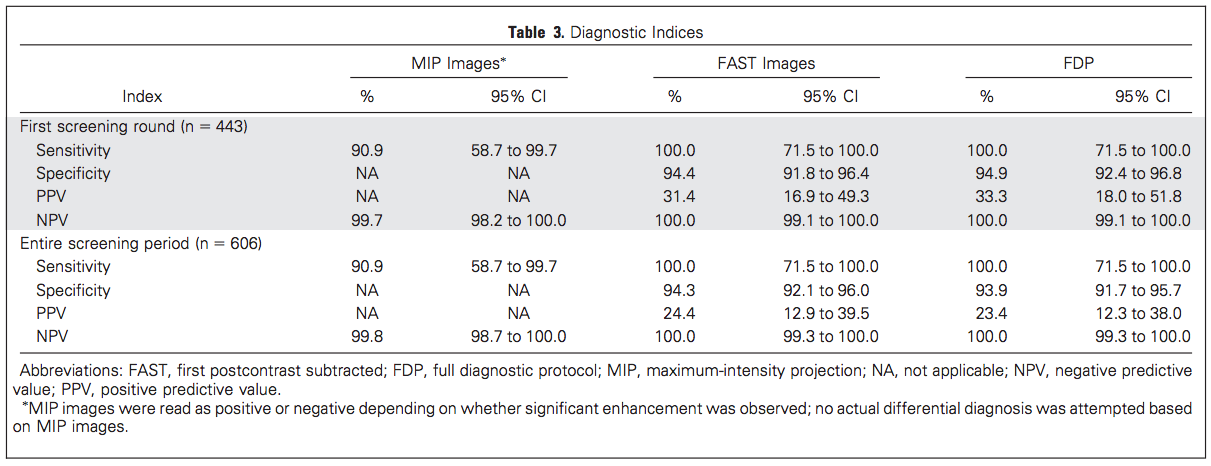
p=0.317
Discussion
- Cancer yield and diagnostic accuracy equivalent between abbreviated and full protocols
- Substantially reduced time of acquisition and reading
- NPV of MIPs alone 99.8%
- Sens/spec of AP identical to FDP
Discussion
- FDP mainly needed for lesion characterization
- 38% of BI-RADS 3 lesions diagnosed on FAST images downgraded to BI-RADS 2 after reading full protocol
- Will decreased costs of AP justify increase in BI-RADS 3 diagnoses?
Discussion - limitations
- High volume MRI readers, perhaps not transferrable to community practice
Editorial - Elizabeth Morris
- MRI superior to mammography and US
- Likelihood of finding cancer at biopsy < 10% if performed on basis of US findings, 30% if on basis of MRI findings
- MRI geared to detect more biologically relevant cancers (neovascularity, inflammation)
Editorial
- Currently, MRI limited to high risk populations
- Limited access
- expensive
- time-consuming
Editorial
- FAST MRI could reduce barriers to MRI screening
- MRI screening should be offered to all eligible patients
- MRI should be next additional screening modality, not US