Can Structural Joint Damage Measured with MR Imaging Be Used to Predict Knee Replacement in the Following Year?
Jason Hostetter
F Roemer, C Kwoh, et. al.
Background:
Preoperative decision making for knee replacement complex process
Radiography: only osseous structures, only advanced disease
MRI: bone marrow, synovitis, effusion, periarticular cystic lesions, meniscal tears
Does presence/severity of MR abnormalities differ between operative/non-operative joints?
Materials and Methods
Osteoarthritis Initiative
4796 participants studied with Xray and MRI for 5 years
Case Knees
- Knee replacement reported
- MRI available before replacement
Control Knees
- No knee replacement
- Matched 1:1 for sex, age, disease stage at enrollment (Kellgren-Lawrence)
Interpretation
- 2 MSK radiologists, 10 and 13 years experience
Assessed
- cartilage morphology and subchondral bone marrow lesions (BMLs) in 14 subregions
- meniscal status
- meniscal extrusion
- synovitis (Hoffa fat pad or effusion)
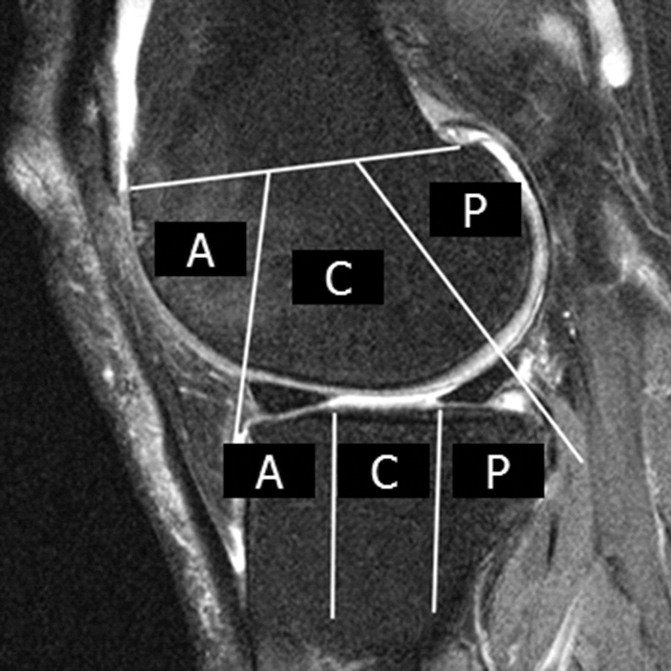
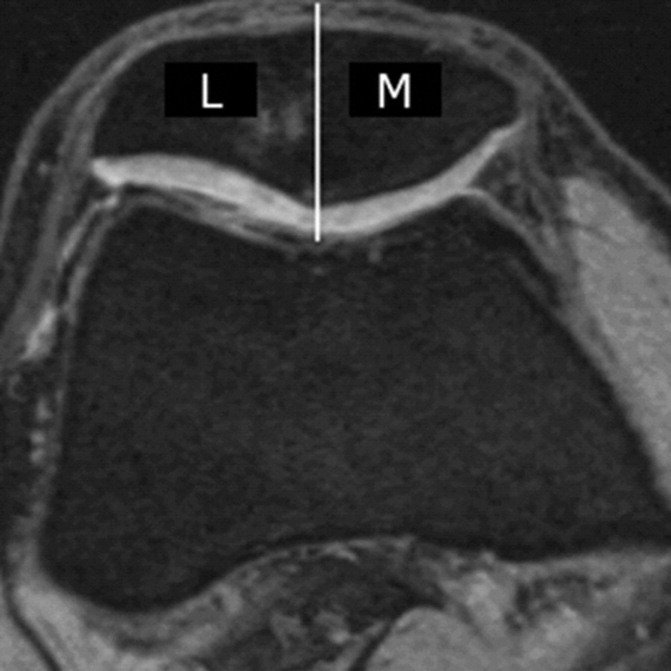
Subregional joint division using MRI Osteoarthritis Knee Score (MOAKS)
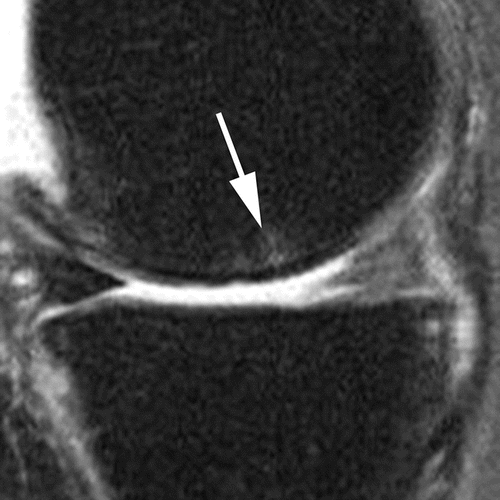
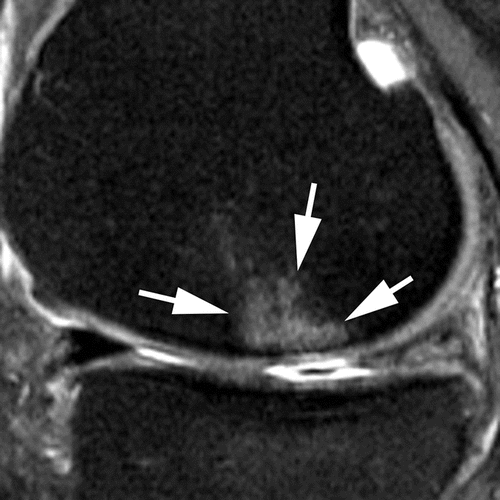
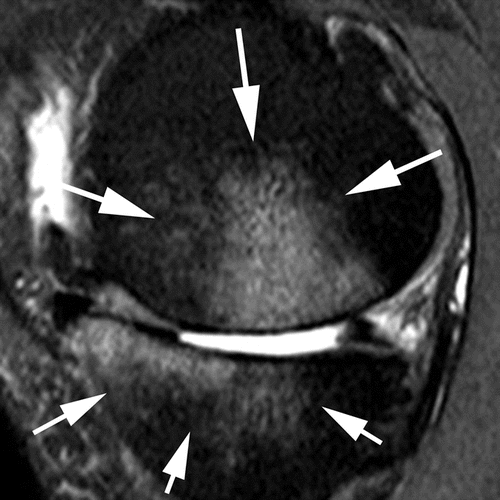
BML assessment according to size
Grade 1
Grade 2
Grade 3
Intra/inter-reader reliability
- 20 randomly chosen MRs rescored after 4 weeks by same reader
- Same 20 studies compared between two readers
Statistical Analysis
Analyzed on whole knee and compartmental level
Assessed risk of knee replacement related to:
- cartilage damage grade and number of subregions
- BML grade and number of subregions
- Meniscal damage grade, subregions, and extrusion
- Hoffa synovitis and effusion synovitis
Statistics performed...
Results
Cartilage Damage
Increased risk of replacement:
- grade 3 damage (OR 4.0)
- 2 or more subregions affected (OR 16.5)
Bone Marrow Lesions
Increased risk of replacement:
- 2 or more subregions affected (OR 4.0)
- grade 3 BML in any subregion (OR 5.5)
Meniscus
Increased risk of replacement:
- Maceration in the medial compartment (OR 1.8)
- At least one subregion in medial compartment with any meniscal damage (OR 1.6)
- Extrusion and lateral compartment damage not correlated
Synovium
Increased risk of replacement:
Any Hoffa or effusion synovitis (OR 2.2, 4.8)
Discussion
Summary
MR findings of degenerative change correlate with risk for replacement
Utility
Presence of MR risk factors in symptomatic patients may help decide whether to replace knee
Identify structure-modifying drugs to prevent or heal underlying abnormalities causing pain
Attempt to find earlier markers of disease to make structure modifying drugs effective
Limitations
Selection bias
- Pool of patients (Osteoarthritis Initiative) have known OA
Knees vs Patients
- 398 knees included, were any from the same patient?
Unclear question
- Not really predicting knee replacement
- Correlating structural damage with pain and knee replacement