檔案讀寫
何謂檔案讀寫
當我們想執行一個程式

太多數字要輸入了!
寫一份程式,生成另一個程式的輸入檔
將輸出檔寫至檔案中
使用時機
- 想要本機跑大測資
- 丟題目到OJ上要升測資
- 不同程式間做資料交換
- DEBUG (對拍)
- etc...
做法
#include<fstream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
ifstream fin( //輸入的文件名 );
ofstream fout( //輸出的文件名 );
}定義讀入檔案與輸出檔案的物件
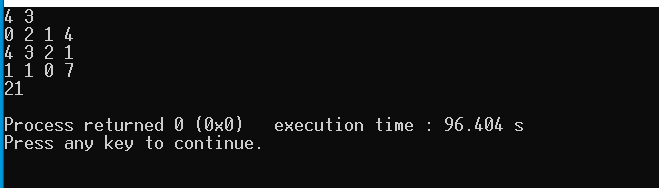
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
ifstream fin("data.txt");
ofstream fout("ans.txt");
int a, b;
fin>>a>>b;
fout<<a+b<<"\n";
fin.close();
fout.close();//記得關閉檔案
cout<<"ok\n";
return 0;
}然後他就可以做跟cin/cout一樣的事情
當然,是對檔案做處理
使用完記得關閉檔案
執行結果
生測資
簡單啦
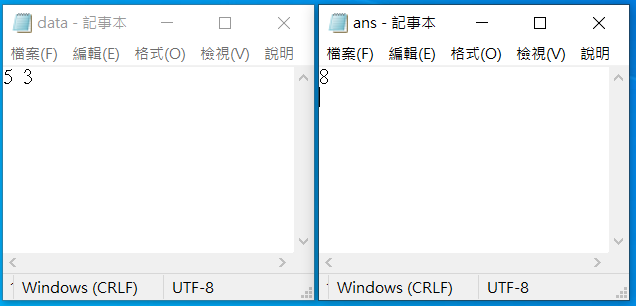
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
ofstream fout("test_data.txt");
srand(time(NULL));
int a=rand(), b=rand();
fout<<a<<" "<<b<<"\n";
fout.close();
cout<<"ok\n";
return 0;
}
注意事項
- rand()的值域只有0~65535,如果想要更大的數字可以rand()*rand()之類的,或是用其他的隨機數字產生器。
- 有些OJ吃的輸入輸出檔是.in和.out格式,其實做法是一樣的
對拍
使用時機
當你吃了一堆WA
使用時機
材料:
- 需要DEBUG的程式碼
- 一份保證正確的程式碼(e.g.暴力做)
- 測資生成器
做法:
將測資給兩份程式碼跑,比較結果是否相同
扣
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
for(int i=1;i<=1000;i++){
system("tioj2039_data.exe > data.txt");
system("tioj2039.exe < data.txt > try.out");
system("tioj2039_old.exe < data.txt > ans.out");
if(system("fc try.out ans.out > nul")){
cout<<"WA:\n";
system("fc try.out ans.out");
return 0;
} else{
cout<<"AC on testdata #"<<i<<"\n";
}
}
return 0;
}
在幹嘛
格式: system("執行的檔案名 < 輸入的檔案 > 輸出的檔案")