Introduction to PyAudio
A convenient audio package in Python
Presentation by Jean Cruypenynck/@nonatomiclabs
Why?
- Audio is fun…
- but always a problem!
Audio + Computers = 💔 ?
- huge variety of devices, standards, formats, etc.
- huge variety of native APIs, often complex
Audio + Python = 💔 ?
- no “correct” audio module in standard library
- some attempts: winaudio, Carbon.snd, sunaudiodev, ossaudiodev, …
- platform-dependent
- limited features
- often deprecated
PortAudio
A famous C library to deal with audio
Famous because:
- cross-platform
- open-source
- tried and tested
- simple interface to deal with audio
PortAudio
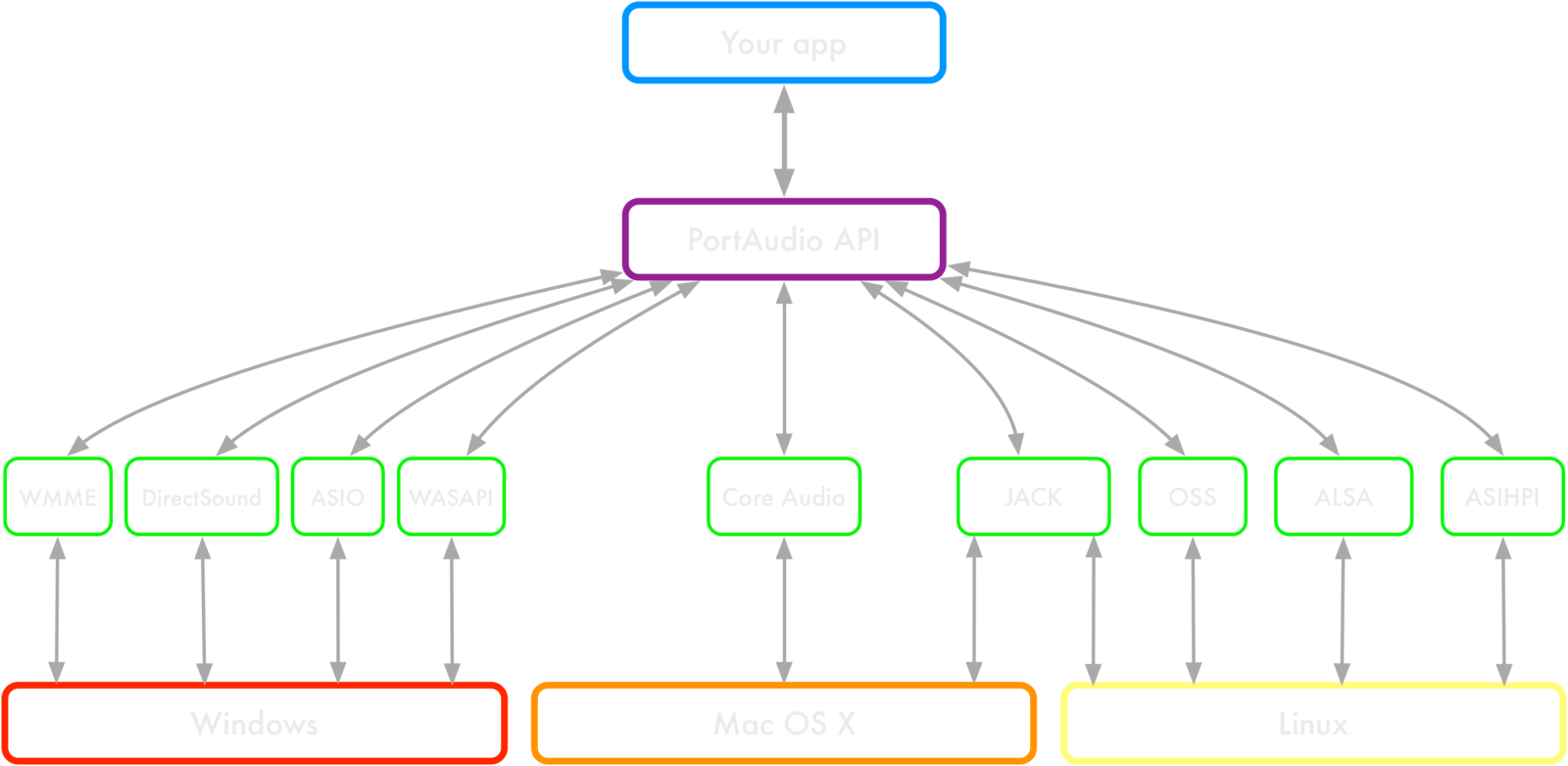
PyAudio
- provides Python bindings for PortAudio
- allows to play audio
- allows to record audio
- open-source
- cross-platform
import pyaudiopip install pyaudioClasses
-
pyaudio.PyAudio
- start/terminate PortAudio
- open/close streams
- access audio devices
-
pyaudio.Stream
- real audio processing is here!
Basic PyAudio flow
import pyaudio1. Import the package
2. Create an instance of PyAudio
p = pyaudio.PyAudio()3. Open an audio stream
stream = p.open(…)4. Start the stream
stream.start_stream()5. Close the stream when you're done
stream.close()Opening the stream
open(rate,
format,
channels,
input=False,
output=False,
input_device_index=None,
output_device_index=None,
frames_per_buffer=1024,
start=True,
input_host_api_specific_stream_info=None,
output_host_api_specific_stream_info=None,
stream_callback=None)What is sound?
open()
parameters
- rate: sampling frequency (usually 44.1/48 kHz)
- format: bit depth (usually 16/24 bits)
- channels: number of audio channels
- input: to use the stream as input
- output: to use the stream as output
- input_device_index: input device to use
- output_device_index: output device to use
- frames_per_buffer: length of the audio buffer
- start: to start the stream directly after opening
- input_host_api_specific_stream_info: …
- output_host_api_specific_stream_info: …
- stream_callback: function used to process audio
stream_callback
The
def callback(in_data, frame_count,
time_info, status_flags):
# PROCESSING
out_data = in_data
return (out_data, pyaudio.PaContinue)Function called every time audio is needed
(full input buffer/empty output buffer)
Example 1
Audio level meter
Initialisation
import sys
import pyaudio
import math
import struct
import time
# Instantiate PyAudio
p = pyaudio.PyAudio()Stream creation & shutting
# Open stream using callback
stream = p.open(format=pyaudio.paInt16,
channels=1,
rate=48000,
frames_per_buffer=1024,
input=True,
output=True,
stream_callback=callback)
# Close the stream after 10 seconds
time.sleep(10)
stream.close()Callback definition
def callback(in_data, frame_count, time_info, status):
levels = []
for _i in range(1024):
levels.append(struct.unpack('<h', in_data[_i:_i + 2])[0])
avg_chunk = sum(levels)/len(levels)
print_audio_level(avg_chunk, time_info['current_time'])
return (in_data, pyaudio.paContinue)Example 2
Audio player
Initialisation
import pyaudio
import wave
import sys
BUFFER_SIZE = 1024
# Opening audio file as binary data
wf = wave.open(sys.argv[1], 'rb')
# Instantiate PyAudio
p = pyaudio.PyAudio()Stream creation & shutting
file_sw = wf.getsampwidth()
stream = p.open(format=p.get_format_from_width(file_sw),
channels=wf.getnchannels(),
rate=wf.getframerate(),
output=True)
data = wf.readframes(BUFFER_SIZE)
while data != '':
stream.write(data)
data = wf.readframes(BUFFER_SIZE)
stream.stop_stream()
stream.close()
p.terminate()Other applications
- audio recorder
- frequency recognition
- filtering
- audio effects
- …
all real-time!