圖論基本算法(一)
最短路演算法
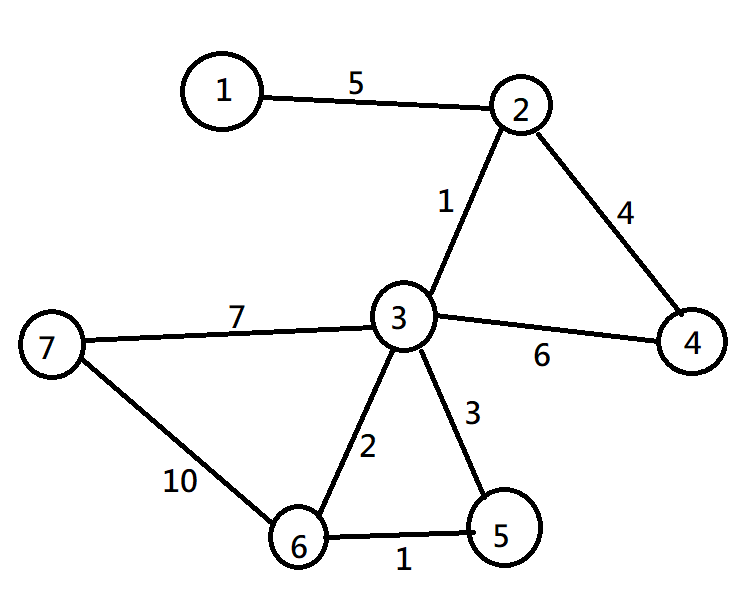
連通a與b的路徑中,最短者稱為最短路。
4
a=1
b=5
dijkstra
還記得BFS嗎?
BFS:可用來處理"不帶權圖"的最短路徑問題
那如果圖帶權怎麼辦?


4
還是一樣的概念:由近到遠搜索

4
0
5
9
9
8
13
6
code
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
int n,m,s,t,ans;
struct path{
int a;
int b;
int w;
};
bool operator<(path a,path b){
return a.w>b.w;
}
vector<path> mapa[1000010];
int dist[1000010];
priority_queue<path> Q;
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
int a,b,w;
memset(dist,-1,sizeof(dist));
cin>>n>>m;
for (int i=0;i<m;i++){
cin>>a>>b>>w;
mapa[a].push_back(path{a,b,w});
mapa[b].push_back(path{b,a,w});
}
cin>>s>>t;
Q.push(path{0,s,0});
path from;
while (Q.size()){
from=Q.top();Q.pop();
if (dist[from.b]==-1){
dist[from.b]=from.w;
for (path x:mapa[from.b]){
if (dist[x.b]==-1){
Q.push(path{x.a,x.b,x.w+from.w});
}
}
}
}
cout<<dist[t]<<'\n';
return 0;
}
最小生成樹演算法
生成樹:在有向圖中,讓所有節點連通的樹。
最小生成樹:所有生成樹中,邊權和最小者。

概念:所有邊照邊權排序,然後看此邊之兩端點是否連過,若否則新增此邊至最小生成樹

kruskal:
怎麼判斷兩點有無連過?
並查集


| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |


| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 7 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 7 |

| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 7 |


| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 7 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
code
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
int n,m,MST;
struct edge{
int a;
int b;
int w;
int id;
};
bool operator<(edge a,edge b){
return a.w<b.w;
}
edge edges[200010];
int DSU_parent[200010];
int DSU_sizset[200010];
int get_parent(int x){
if (DSU_parent[x]!=x){
DSU_parent[x]=get_parent(DSU_parent[x]);
}
return DSU_parent[x];
}
signed main(){
cin>>n>>m;
for (int i=0;i<m;i++){
cin>>edges[i].a>>edges[i].b>>edges[i].w;
edges[i].id=i;
}
sort(edges,edges+m);
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++){
DSU_parent[i]=i;
DSU_sizset[i]=1;
}
int pa,pb;
for (int i=0;i<m;i++){
pa=get_parent(edges[i].a);
pb=get_parent(edges[i].b);
if (pa!=pb){
if (DSU_sizset[pa]<DSU_sizset[pb]){
DSU_parent[pa]=pb;
DSU_sizset[pb]+=DSU_sizset[pa];
}else {
DSU_parent[pb]=pa;
DSU_sizset[pa]+=DSU_sizset[pb];
}
MST+=edges[i].w;
}
}
cout<<MST;
return 0;
}
概念:所有邊照邊權排序,然後看此邊之兩端點是否連過,若否則新增此邊至最小生成樹

prim:
code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n;
double ans=0;
struct node{
int x;
int y;
}test[5010];
double dist(node a,node b){
int dx=a.x-b.x;
int dy=a.y-b.y;
return sqrt(dx*dx+dy*dy);
}
double distfromtree[5010];
int main()
{
cin>>n;
for (int i=0;i<n;i++){
cin>>test[i].x>>test[i].y;
}
for (int i=0;i<n;i++){
distfromtree[i]=dist(test[0],test[i]);
}
for (int i=1;i<n;i++){
int nowit;
double nowdist=1e9;
for (int i=0;i<n;i++){
if (distfromtree[i]!=0&&distfromtree[i]<nowdist){
nowit=i;
nowdist=distfromtree[i];
}
}
ans+=nowdist;
for (int i=0;i<n;i++){
distfromtree[i]=min(distfromtree[i],dist(test[nowit],test[i]));
}
}
cout<<ans;
return 0;
}
kruskal vs prim
設N為點數,M為邊數。
O(MlogM)
O(N^2)
例題:
dijkstra:
kruskal:
prim: