Meeting II | 6/30/21
Regional Broadband American Rescue Plan Convening
POST IN THE CHAT!
Your Name and Affiliation
Favorite Summer Food Item

Agenda
Welcome and Communications Update
Community Exchange Waterfall
ARPA Funding Breakdown
Principles for ARPA Spending
Digital Access Issues Explained

Potential ARPA Funded Uses
Please post questions and comments in the chat!
Meeting Goals

Clarify ARPA guidance regarding use for digital access / broadband
Outline principles and potential vehicles for ARPA spending

Organize stakeholder priorities as related to digital access and broadband
MAPC'sGoals

Support municipalities in acheiving their goals related to Digital Access
Advocating for State resources that will support municipal and community efforts to close the digital divide.

Develop purchasing or other procurement vehicles for collective uses.
Communications Update:
Regional Digital Access Slack Channel
MAPC can provide a guest Slack account for use.
- Post updates, articles, data sources, insights.
- Allow for cross organizational sharing and coordination.
- Save inboxes and allow for ongoing conversations
Guidelines for the Slack Channel
- Be respectful
- Acknowledge different backgrounds and levels of familiarity with topic
- No pressure to participate!

Community Exchange Waterfall
POST IN THE CHAT!
Update on Digital Access work
Questions for related to Digital Access or ARPA
American Rescue Plan Funding Breakdown
| ARPA Provision | Administering Agency | Mass Allocation (Approximates) |
Physical Network Build Out | Device Support | Broadband Subscription | Digital Literacy Training |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elementary and Secondary School Emergency Relief Fund | DESE - School Districts | $1,83B | X | X | ||
| Emergency Connectivity Fund | FCC (Federal) | $148M | X | X | X | |
| Institute of Museum and Library Services | Board of Lib Commissioners - Local Libraries | $3,5M | X | X | X | X |
| Economic Adjustment Assistance | EDA (Federal) | $64,5M | X | |||
| Homeowner Assistance Fund | DHCD | $178M | X | |||
| Coronavirus State Fiscal Recovery | ANF | $5,28B | X | X | X | X |
| Coronavirus State Local Recovery | DoR - Local Municipalities | $3,38B | X | X | X | X |
| Coronavirus Capital Projects Fund | ANF | $174M | X | X |
ARP Guidance:
State and Local Allocations
- Support public health expenditures, by, funding COVID-19 mitigation efforts, medical expenses, and certain public health and safety staff
- Address negative economic impacts caused by the public health emergency, including economic harms to workers, households, small businesses, impacted industries, and the public sector
- Replace lost public sector revenue, using this funding to provide government services to the extent of the reduction in revenue experienced due to the pandemic
- Provide premium pay for essential workers, offering additional support to those who have and will bear the greatest health risks because of their service in critical infrastructure sector
- Invest in water, sewer, and broadband infrastructure, making necessary investments to improve access to clean drinking water, support vital wastewater and stormwater infrastructure, and to expand access to broadband internet
ARP Guidance:
State and Local Allocations
Broadband Infrastructure Guidance
"Infrastructure investments in areas that lack wireline connection that reliably delivers 25/3 service"
"Prioritize middle mile and last mile connections"
"Prioritize projects that use modern technology delivering 100/100 service"
"Recipients are encouraged to pursue fiber optic investments"
Demonstate COVID Impact
Source: US Treasury Fact Sheet, 5/10/21
https://home.treasury.gov/system/files/136/SLFRP-Fact-Sheet-FINAL1-508A.pdf
ARP Guidance:
State and Local Allocations
Broadband Infrastructure Guidance - "Reliably"
"Treasury’s Interim Final Rule provides that investments in broadband be made in areas that are currently unserved or underserved... lacking a wireline connection that reliably delivers minimum speeds of 25 Mbps download and 3 Mbps upload"
"The use of “reliably” ... provides recipients with significant discretion to assess whether the households and businesses have access to wireline broadband service that can actually and consistently meet the thresholds of at least 25Mbps/3Mbps—i.e., to consider the actual experience of current wireline broadband customers. Whether there is a provider serving the area that claims to offer speeds that meet the 25 Mbps download and 3 Mbps upload speed thresholds is not dispositive"
ARP Guidance:
State and Local Allocations
Digital Divide
"In view of the wide disparities in broadband access, assistance to households to support internet access or digital literacy is an eligible use to respond to the public health and negative economic impacts of the pandemic, as detailed above."
"Recipients may use funds to provide assistance to households facing negative economic impacts due to Covid-19, including digital literacy training and other programs that promote access to the Internet."
ARP Guidance:
State and Local Allocations
Cybersecurity
"Recipients may also use funds for modernization of cybersecurity, including hardware, software, and protection of critical infrastructure, as part of provision of government services up to the amount of revenue lost due to the public health emergency."
ARP Summary

Infrastructure investments in areas that are underserved by reliable high speed internet.
Cybersecurity
Offset Tax Reduction
Pensions
Debt Service
Digital literacy and connectivity programs



Stabilization Funds


Other demonstrate disproportionate COVID impact

Guiding Principles for State and Local Government
DRAFT Principles for Local Government
Remove affordability and adoption barriers that prevent universal access to reliable and high speed internet.


Ensure all residents who desire to improve their digital / technology literacy have a pathway to educational opportunities at a range of skill levels, offered in community appropriate languages and settings.
Augment the capacity of key stakeholders such as IT Departments, School Districts, Libraries, Community based organizations, and municipal staff to address the digital divide
Promote competition among internet service providers offering broadband service.
Recognize the importance of proactively investing in cybersecurity measures.


DRAFT Principles for State Government
Augment ARPA funds made available to municipalities for those municipalities who have been hit hardest by COVID (health and unemployment) and likely have competing needs for funds in other areas that may outweigh digital divide issues.

Build the nascent capacity of local government and community groups in the area of the digital divide and digital infrastructure.
Catalyze additional investment by municipalities and private sector actors to improve affordability, reliability, and speed of the internet; as well as market competition for broadband service.
Diagnosing the Problem
Draft Research Findings from Chelsea, Everett, and Revere Digital Access Planning Process
Digital Justice Principles: Access
- Digital justice ensures that all members of our community have equal access to media and technology, as producers as well as consumers.
- Digital justice provides multiple layers of communications infrastructure in order to ensure that every member of the community has access to lifesaving emergency information.
- Digital justice values all different languages, dialects and forms of communication.
Source: Allied Media, Teaching Community Technology Handbook

Three Determining Factors of Digital Access



Connection
Adequate Device
Literacy
Fast
Affordable
Router
Personal Computer /Laptop
Use of Technology
Ensuring functioning equipment
Evaluating quality of information and privacy risks

Connection
Is it Fast?
40 – 50%
of households in Chelsea Everett, and Revere with internet access do not have "broadband" speeds

Speed Sources: MLab, Microsoft US Broadband Usage, Demographic Source: US Census ACS 5 Year, 2019
"I live in a 40 unit mid-rise and am told by the internet provider that most of the issues are because the wiring in the building is old. The provider says it's not their problem. We have interruptions all the time, no notice, residents just start calling each other to see if they have wi-fi. Could be down for hours. I work from home and it's a real issue for me."
Is it Reliable?

Connection
~19% of
Chelsea, Everett, and Revere households lack internet service.
~40%
of survey respondents do not believe their internet service is affordable.
72%
of survey respondents have had to cancel or change their internet subscription because it is too expensive

Is it Affordable?
Sources: US Census ACS 5 Year, 2019.
MAPC Community Digital Needs Assessment 2021
"Necesitamos que el costo del internet sea mas justo
-
We need the cost of the internet to be fairer"
Device Access
How accessible are devices?
12%
of Chelsea & Revere households have no computing device at all
23%
of survey respondents disagree with "People in my household always have access to a computer if needed."
About 60%
of Chelsea, Everett and Revere households with internet lease a router from their service provider

Are routers adequate?

Device Source, Computers: US Census ACS 5 Year, 2019. Device Source, Routers: MAPC Survey - 6/29/21
"Our internet speed greatly improved after we bought our own router; the routers provided by our provider don't seem to be very good"
Literacy in Chelsea & Revere
Using Technology
~75%
of survey respondents agree with "I feel confident in my ability to use a computer/laptop/Chromebook
~50%
of survey respondents agree with "I feel confident that I am able to resolve issues related to my internet connection"

Ensuring Functioning Equipment

Evaluating Information and Privacy Risks
Anecdotal information gleaned from stakeholder conversations indicates that there are serious concerns related to privacy, particularly among the immigrant population
Source: MAPC Survey - 5/26/21
Internet Subsidies
~500,000
families in Massachusetts are eligible for Internet Essentials and the Emergency Broadband benefit fund
Comcast Internet Essentials Plan offers basic internet service for $10 / Month to income eligible households (SNAP, Free or Reduced Lunch, etc)
The Emergency Broadband Benefit program will subsidize $50 for all service plans - as of June 29th only 30,000 households in the program
Only 30,000
households have taken advantage of EBB since May 16 2021
Source: Universal Services Administrative Co, National Center for Education Statistics, MAPC Digital Access Survey 6/29/2021
"سمعت بأن شركة كومكاست توفر انترنت مجاني لأصحاب الدخل المحدود .هل هذا صحيح؟
-
I heard that internet service companies provide free internet to people with limited income. Is this true?"
Legacy of Cable
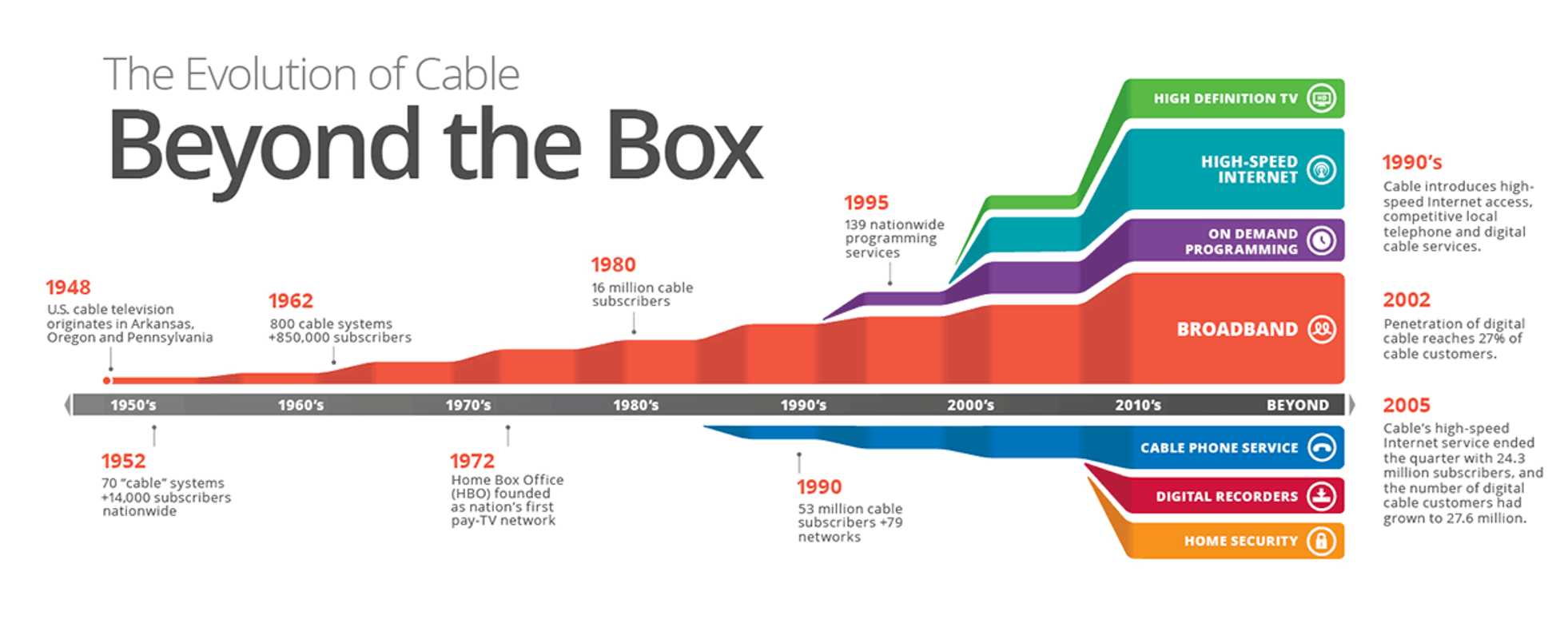
Image Source: https://calcable.org/learn/history-of-cable/
Why is it this way?
The cable infrastructure at the household level is likely impacting service and reliability.
A lack of competition, shrinking cable service revenues, and a lower income service area are likely disincentives for investment from the private sector.
At the household level, individuals are likely using outdated or ineffective routers and devices.
Internet subscribers may not have the confidence or technical skills to trouble shoot internet speed or function issues.
Larger households who may need faster speed packages may be cost burdened and unable to afford those plans.
Individuals who are eligible for subsidized services may not be taking advantage of them due to a lack of information, trust, stable housing, documentation, or other structural and social factors.
Potential ARPA Funded Uses
Starting Practices
- Quantify the issue and understand the needs
- Coordinate stakeholders
- Guide decision making
- Better understanding current public assets that could be leveraged (fiber, rooftops infrastructure, etc.)
Develop a Digital Equity and Access Plan
Digital Equity Trust Fund to Purchase PC's, Routers, and Bulk Internet Subscriptions
Examples
Examples
Plans w/ MAPC underway in Everett, Revere & Chelsea

Library / School Device Lending Programs
- Develop funding pool to invest in community initiatives
- Make devices available through programs at libraries & schools
- Support computer purchasing or refurbishment programs

Digital Navigators / Digital Stewards
Digital Navigators
Digital Stewards
- Different from Navigators, Digital Stewards are community members who receive advanced training in internet network technology.
- They are able to support community-focused WiFi programs that support free and open internet networks.
- Individuals who address the whole digital inclusion process — home connectivity, devices, and digital skills
- Navigators can be volunteers or cross-trained staff who already work in social service agencies, libraries, health, and more who offer remote and socially distant in-person guidance. Can help support the critical issue of adoption as well as access.
Examples
Examples
Open WiFi
Affordable Housing Open Networks
Community Mesh Networks
Examples
Education Super Highway ESH in Oakland
- Utilize commercial or municipal internet networks to access high-speed wireless signals via a rooftop receiver.
- Make wifi access default. Leverage common spaces and broadcast on an open access router system for in-unit access.
Examples

The People's Network Helium Routers
- A distributed system of routers and devices that work in concert to provide internet access to users within a given geography, owned and managed by the community.
- Explore revenue-generating equipment like Soofa Signs and Helium Routers
Increased Competition & Infrastructure Options
Open Access & Institutional Networks
Partnerships with ISPs

Examples
Examples
- Public ownership does not mean being Internet Service Provider
- Different models exist some connect to residences, other connect anchor institutions like municipal networks and high education.
- An opportunity that expands municipal fiber infrastructure, networks and connect
- Partnering with Public or Private Equity to bringing fiber closer to the end-user by pulling it into buildings
- Retrofitting buildings with outdated wiring
- Leverage cable franchise agreement
- RFP for use of assets like rooftops
- Qualifying residents based on need, removing the administrative burden from resident and companies.
Infrastructure Upgrades
Pull Fiber to Buildings and Retrofit Coaxial
Expand Municipal Fiber Infrastructure

ISP Fiber is typically limited to privately owned infrastructure. Bringing fiber closer to the end user by pulling it into buildings will improve speed and reliability of service (although may not impact price without other strategies).
Municipal fiber has traditionally been limited to a loop that connects public buildings like schools, town hall, and libraries. Expanding municipal fiber, or at least conduit can serve to open new options for public and commercial connectivity.
Fiber Retrofits
Examples
San Francisco Public Housing
Cambridge MA
Expanded Municipal Infrastructure
Santa Monica