Interlocking directorates affect structural transformation through increased collaboration and innovation.
Javier Garcia-Bernardo
Methodology class
31-May-'16
@javiergb_com / @uvaCORPNET
8 months paper: https://github.com/jgarciab/8_months_paper/
What is the effect of interlocks on structural transformation?
1. Interlocking directorates
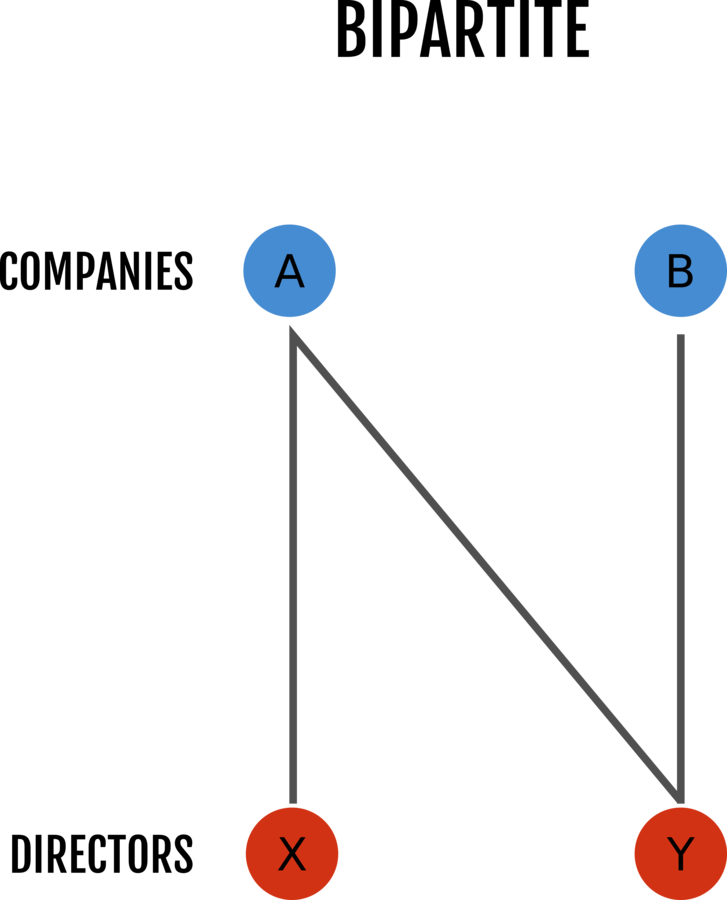
Corporate networks

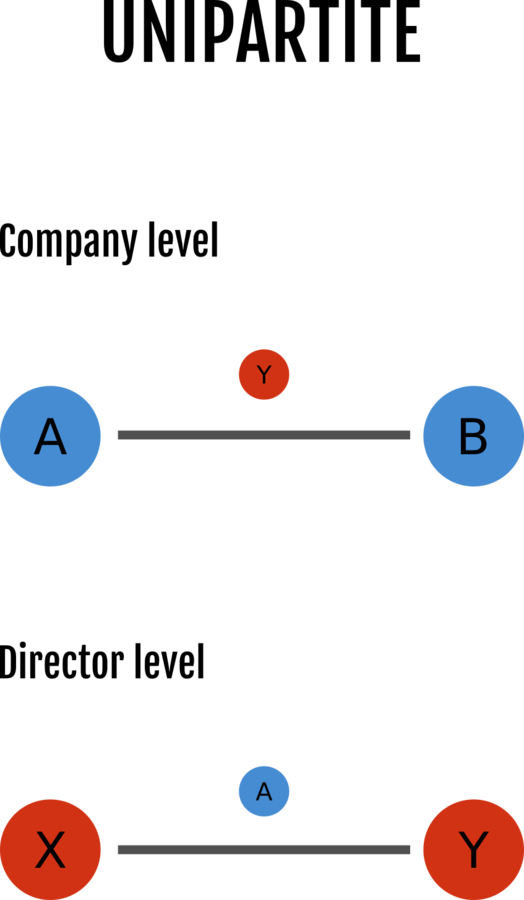
Corporate networks

2. Product-service space
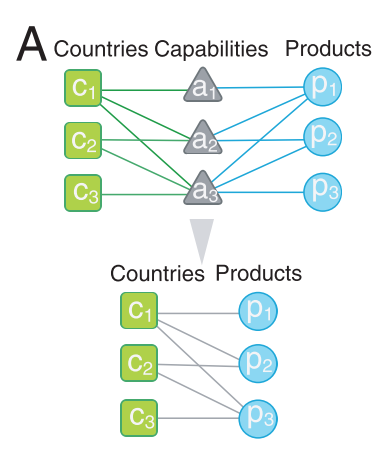
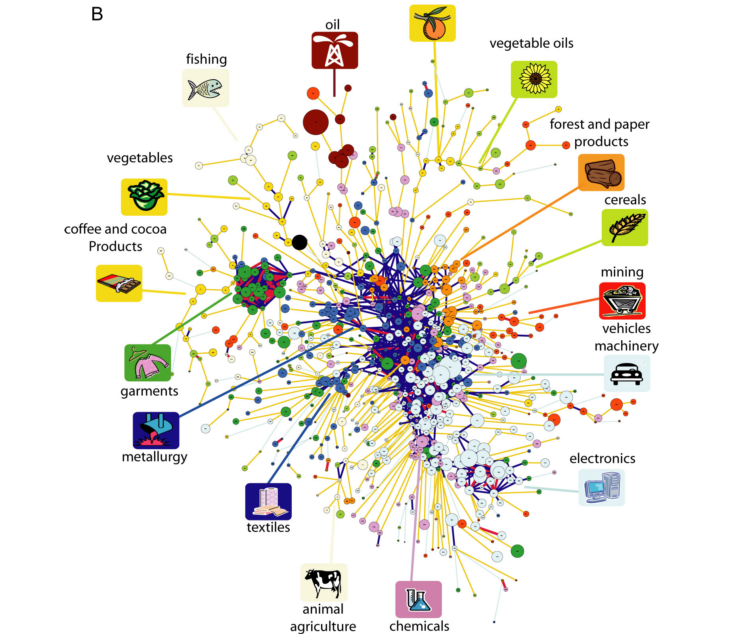
Countries require some underlying capabilities (infrastructure, education, institutions, human capital) to maintain specific companies, and those capabilities are similar for economic activities close together in the product space.
When a country acquire new capabilities, new products can be developed along the product space.
Countries require some underlying capabilities (infrastructure, education, institutions, human capital) to maintain specific companies, and those capabilities are similar for economic activities close together in the product space.
When a country acquire new capabilities, new products can be developed along the product space.
The causal argument is symmetrical from Hidalgo, Hausman and Klinger’s argument but at the city level:
- Allows to explain why some cities thrive while others don't.
- Cites have became innovation hubs.
- Allows to study interlocks.
- Don't impose a country level organization in the capabilities.
3. Interlocks and the product-service space
What is the effect of interlocks on structural transformation?
Development influences the presence of interlocks. The establishment of companies within a city allows for greater possibilities of interlocks. However it is not clear if interlocks also affect development.
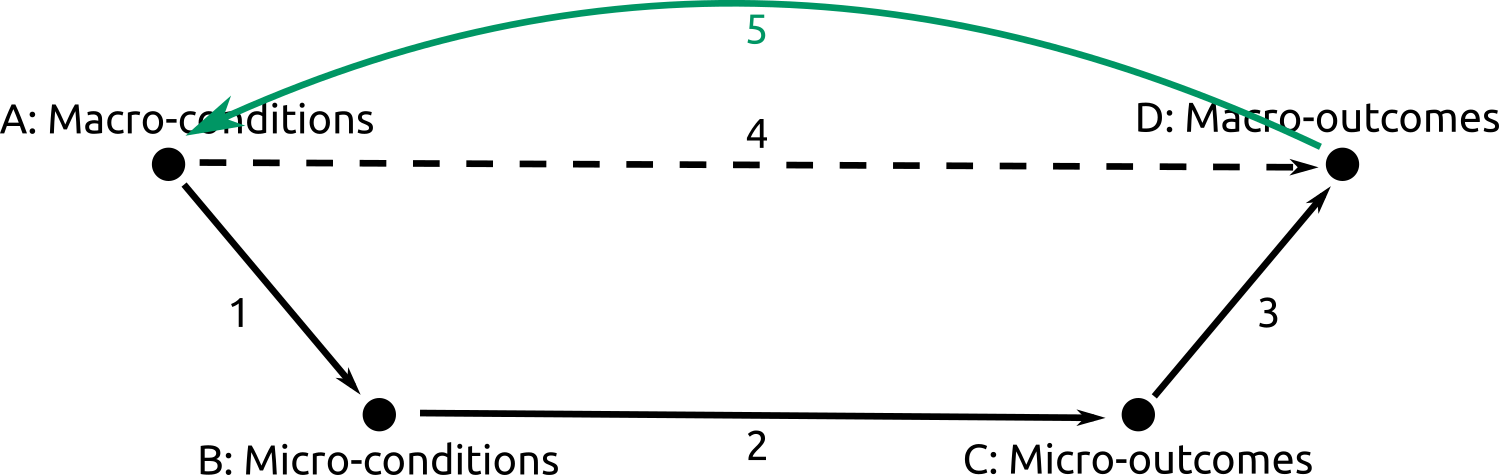
Development influences the presence of interlocks. The establishment of companies within a city allows for greater possibilities of interlocks. However it is not clear if interlocks also affect development.
Interlocks provide a communication channel between companies, and serve as a link for the spread of strategies and structures.
Development influences the presence of interlocks. The establishment of companies within a city allows for greater possibilities of interlocks. However it is not clear if interlocks also affect development.
Interlocks provide a communication channel between companies, and serve as a link for the spread of strategies and structures.
We hypothesize that interlocks allows for the spread of business opportunities and collaboration, thus increasing investment and R&D funding in promising sectors. Increased investment allows the city to acquire new capability, and expand in the product-service space.
Development influences the presence of interlocks. The establishment of companies within a city allows for greater possibilities of interlocks. However it is not clear if interlocks also affect development.
Interlocks provide a communication channel between companies, and serve as a link for the spread of strategies and structures.
We hypothesize that interlocks allows for the spread of business opportunities and collaboration, thus increasing investment and R&D funding in promising sectors. Increased investment allows the city to acquire new capability, and expand in the product-service space.
We can investigating the relative effect of interlocks, city characteristics and institutions on structural transformation.
Data:
- Companies: Orbis
- Directors: Orbis
- Cities:
* OECD Metropolitan area level: Population, GDP, pollution, unemployment rates, number of patents, and geographic and administrative forms.
* OECD Regional level: R&D spending, type of employment (business) and education.
* Innovation Cities index: Innovation
* Data on patents: Collaboration and Innovation
What's the plan:
1. We will study structural transformation at the city level.
2. We will analyze if interlocks foster structural transformation.
3. We will test if interlocks affect the development of capabilities through increased innovation.