JavaScript Functions
Jisoo Yoon
jyoon006@gmail.com
JavaScript Functions
JavaScript function is a block of code designed to perform a particular task and is only executed when something invokes the particular function

Above example is how you create a function to do "something", in above case, it returns Hello!
Basic Structure of Function
- JavaScript function is always constructed with keyword 'function'
- Needs something invoking the function in order to process
- Function name can be anything after the keyword 'function' except for certain cases. function name has to comply same rule as variable names, which it must start with $, _, or any character in the unicode categories
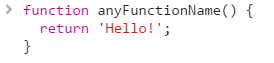
note: Return statement only works inside functions and will end processing of the function. Returning nothing out of function will result in 'undefined'
Return Statement in Function
Return statement will hop out of the function so anything after the return statement will not be executed

Not returning any value out of function will result in returning undefined

Invoking a Function
You need to somehow tell JavaScript to run, execute, or "invoke" the function. If you do not invoke the function, function will not do anything
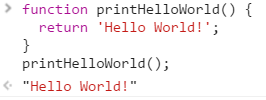
To invoke a function, write the name of the function you're trying to invoke in your code followed by opening and closing parenthesis ()
Function Declaration vs Function Expression
Function Declaration
- Defines a named function variable without requiring variable assignment
- Constructs and cannot be nested within non-function blocks
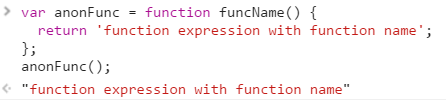
Function Expression
- Defines a function as a part of larger expression syntax (variable assignment)
- Can be named or anonymous
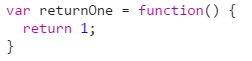
note: Anonymous function is when there is no name for the function

This is also called a self invoking function express or commonly known as IIFE (Immediately-invoked function expression)
Function Expression
You can also declare a function name when using function expression but not necessary. Most developers just use anonymous function
Function Parameters vs Arguments
Parameters - Variable in a function definition
Arguments - Data you pass into function's parameters

parameter
argument
Parameter names can be anything following the general variable declaration rule
Functions can have many arguments and parameters passed in

- You want to use parameter names that will be relevant to the data that is passed as argument(s)
- Order of parameters and arguments does matter
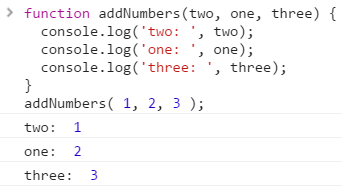
Because the order of parameter is different from arguments passed, JavaScript function will reference whichever order they are passed. JavaScript will not automatically correct this for you so be sure to pass in arguments and parameters in order
console logs
What happens when argument(s) are passed during invocation but function doesn't have parameter(s)?
JavaScript will not throw an error if an argument is passed to function but there is no parameter. It will actually keep the arguments passed in into array like object called arguments
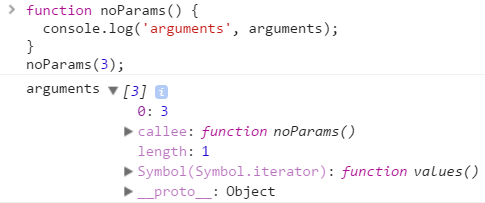
Remember that this is not an array but array like object.
Doesn't matter how many arguments are passed in, the arguments object will have reference to all the data values passed in
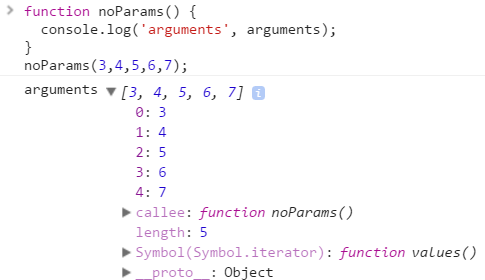
In case you're wondering, the arguments object will look something like this in REPL
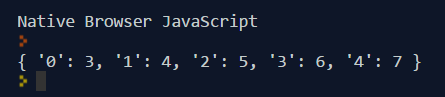
What if there is parameter but an argument is not passed in?
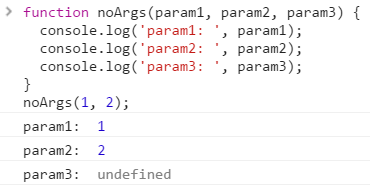
Again, JavaScript will not throw an error when a specific argument was not passed in for specific parameter. It will just treat the parameter value as undefined
You can also skip an argument passing into parameter by giving the argument value null if you need to
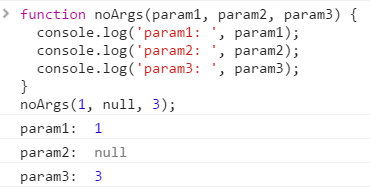
We passed in null for param2 to pass argument for param3
Order of parameters and arguments still matter. You cannot just pass in less argument for JavaScript to automatically interpret which parameter data values should arguments bind to
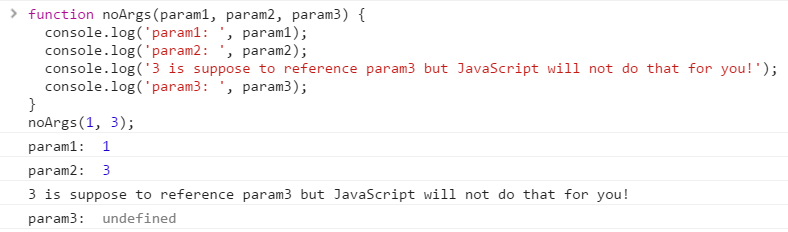
Function Scope
- Scope is set of variables you have access to
- Unlike other languages, JavaScript has only function scope. Meaning scopes are only set inside a function and changes inside functions

Trying to access variable outside of function that was declared inside function will throw an error because the variable has function scope
Global Scope

- Any variable declared outside of function is in global scope. Global scope variable is accessible anywhere in JavaScript. Any functions will have access to the global scope
Function Scope Variable Delegation
If there is same variable name from global scope and function scope, depending on where you're trying to access the variable, it will either reference global scope or function scope

Accessing variable foo after declared inside function will grab "local scope" variable in function. JavaScript will search and see the closest variable name matched and if it can't find it, it will look in global scope to check and access the variable

Because there is no variable name "foo" in function scope, it looks in global scope to find and access the variable. In this case, both inside function and outside of function will access the same variable

JavaScript has only function scope so conditional statements or any other enclosing block code will not keep in it's scope. (pre ES6 - ES6 has let and const to have block-level scoping)
Quiz
- What is difference between function express and function declaration? Write simple code for each function.
- What does return statement do? What happens when nothing is returned in a function?
- What is output of below function and why?
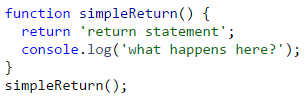
4. How do you invoke a function? Write code to show.
5. What is parameter and what is an argument?
6. What is the output of below function?

7. How do you access the parameters in below function?

8. Describe what function scope is and what global scope is.
9. What do you expect the output to console log for below function? Why?
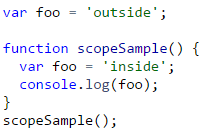
10. What is the output of console logs in below function? Why?

Questions
jyoon006@gmail.com