Angular Getting Started
specific for react / vue developers
angular v11 / 2021-03
Will not teach you
typescript
rxjs
react
vue
what is dependency injection
how decorator work
...
Just like a summary
please still see the official documentation for more details
Angular in my opinion
reactive programing(rxjs) + component + dependency injection
// html
<input id="text" value="hello world" />
<span id="foo"></span>
<span id="bar"></span>
// ts
import { fromEvent } from 'rxjs';
import { map, distinctUntilChanged, startWith } from 'rxjs/operators';
const input = document.getElementById('text');
const foo = document.getElementById('foo');
const bar = document.getElementById('foo');
fromEvent(input, 'input')
.pipe(
map(event => event.target.value),
distinctUntilChanged(),
startWith(input.value)
)
.subscribe(text => {
foo.innerText = text;
bar.innerText = text;
});
Props in my opinion
easily manage complicated data flow
easily build form and separate logics and layouts
power of rxjs
Cons in my opinion
learning curve extremely high
extremely depends on rxjs and there are some pitfalls if u are not familiar w/ rxjs
difficultly to manipulate complicated UI
So
Be careful to choose the appropriate scene to use angular
Basic UI
Template / Directive / Component
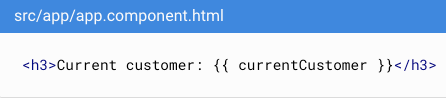
Text Interpolation
To react developers: similar to jsx but it is html

To react developer:
1. {{ not {
2. do not write logic on template

Directive / Component


Selector
same as document.querySelector()
@Directive({
selector: 'button[foo],a[foo]'
})
export class FooDirective {}
// template
// w/ foo directive instance
<button foo>
// no foo directive instance
<div foo>@Directive({
selector: 'foo'
})
export class FooComponent {}
// template
<foo>bar</foo>Template & Styles


Styles
Support non-css files: .sass/.scss/.less/.styl
ChangeDetectionStrategy


To react developers:
OnPush -> PureComponent
Default -> Component
ViewEncapsulation
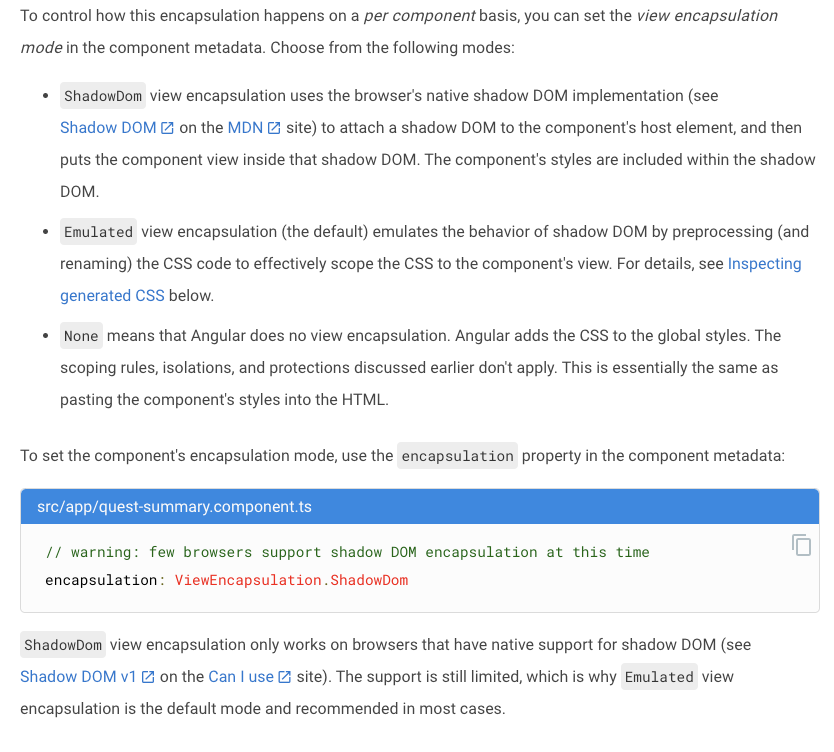


Emulated similar to
1. css modules
2. scoped in vue
Property Binding
How to pass data from parent to child
To vue developers: v-bind
To react/vue developers: props



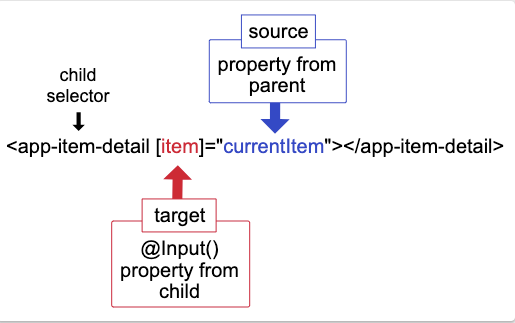
If the type is string
<foo name="bar"></foo>
===
<foo [name]="'bar'"></foo>Rename
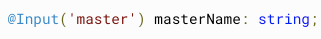
<child [master]=""></child>Getter / Setter


Event Binding
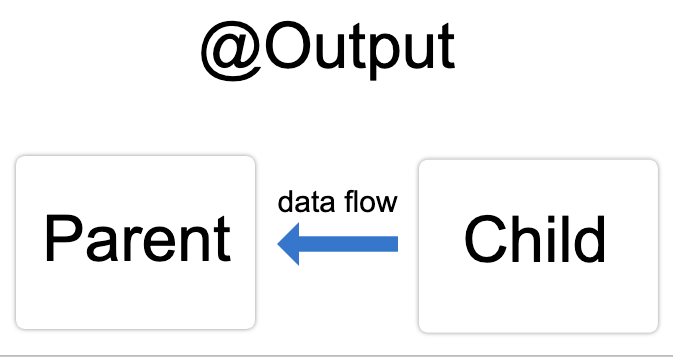
How to emit data from child to parent

To react developers: callback props
To vue developers: v-on/emit
Output



Two Way Binding



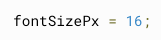
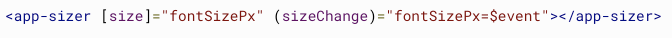
<ng-content>
Content Projection

To react developers: just children
In Angular
const Foo = ({ children, footer }) => (
<div>
{children}
<div>
{footer}
</div>
</div>
);
//
<Foo
footer={
<div>bar</div>
}
>
foo!!!
</Foo>In React
<ng-content></ng-content>
<div>
<ng-content select="[slot='footer']"></ng-content>
</div>
//
<foo>
foo!!!
<div slot="footer"></div>
</foo>
same as document.querySelector
View vs Content
// foo
@Component({
selector: 'foo',
template: `
<div>foo title</div>
<ng-content></ng-content>
<div>foo footer</div>
`
})
export class FooComponent {}
// bar template
<foo>
<div>bar</div>
</foo>View of Foo
Content of Foo
Host Element
angular always wrap your template into a html element called host
To react developer: yes, no fragment :)


// foo
@Component({
selector: 'foo',
template: `
<div>foo</div>
<ng-content></ng-content>
`
})
export class FooComponent {}
// bar template
<foo> ---> will create a real html element
<div>bar</div>
</foo>
// bar html result
<foo>
<div>foo</div>
<div>bar</div>
</foo>
Get HTMLElement of Host
Dynamic Component
see doc yourself
const componentMap = {
foo: Foo,
bar: Bar,
baz: Baz
};
const Parent = ({ type, ...rest }) => {
const Component = componentMap[type];
return (
<Component {...rest} />
);
};
In React
Attribute/Class/Style
Attribute


Class
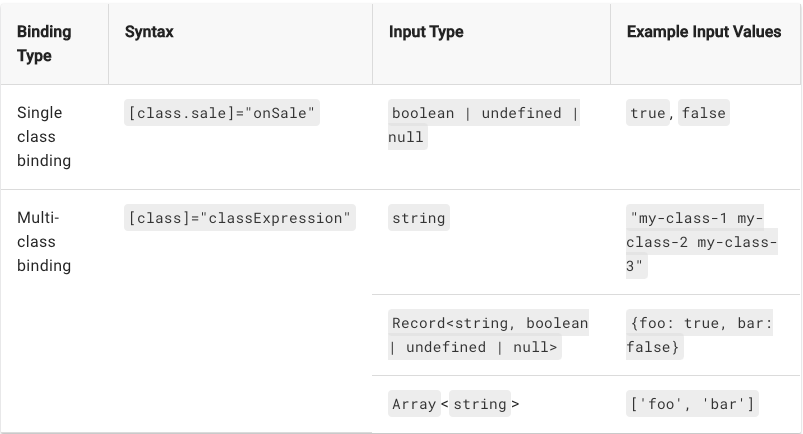
[ngClass]
Style


[ngStyle]
Style Precedence

@HostBinding

bind attribute/class/style to host
@HostListener


bind listener to host
Lifecycle
ngOnInit
Initialize the directive or component after
1. first displays the data-bound properties
2. sets the directive or component's input properties
Called once after first ngOnChanges

ngOnDestroy

Clean up just before Angular destroys the directive or component
ngOnChanges
Respond when Angular sets or resets data-bound input properties.
The method receives a SimpleChanges object of current and previous property values.
Called before ngOnInit and whenever one or more data-bound input properties change.
ngDoCheck
custom change detection hook
Do not use this if possible
ngAfterContent(Init|Checked)
Init:
Respond after Angular projects external content into the component's view, or into the view that a directive is in.
Checked:
Respond after Angular checks the content projected into the directive or component.
ngAfterView(Init|Checked)
Init:
Respond after Angular initializes the component's views and child views, or the view that contains the directive.
Checked:
Respond after Angular checks the component's views and child views, or the view that contains the directive.
constructor
OnChanges
OnInit
DoCheck
AfterContentInit
AfterContentChecked
AfterViewChecked
AfterViewInit
OnDestroy
mount
changes detection
No default value properties will be undefined before first ngOnChanges called
Directive
Component is a directive w/ template and styles
Attribute Directive
Built-ins: ngClass/ngStyle/...


Component Directive
@Directive({
selector: 'button[myButton]'
})
export class MyButtonDirective {
@HostBinding('class.my-button')
readonly bindHostClass = true;
}
//
<button myButton>click me</button>Structural Directive

*ngIf

return (
<div>
{items && items.map(...)}
{items ? items.map(...) : null}
</div>
)In React
<ng-container>


*ngSwitch

*ngFor

items.map(item => (
<div>
{item.name}
</div>
))In React

items.map(item => (
<ItemDetail item={item} />
))In React
items.map((item, i) => (
<div>
{i + 1} - {item.name}
</div>
))In React
items.map(item => (
<div key={item.id}>
{item.id} - {item.name}
</div>
))In React



Structure Shorthand
*xxx



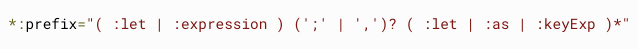



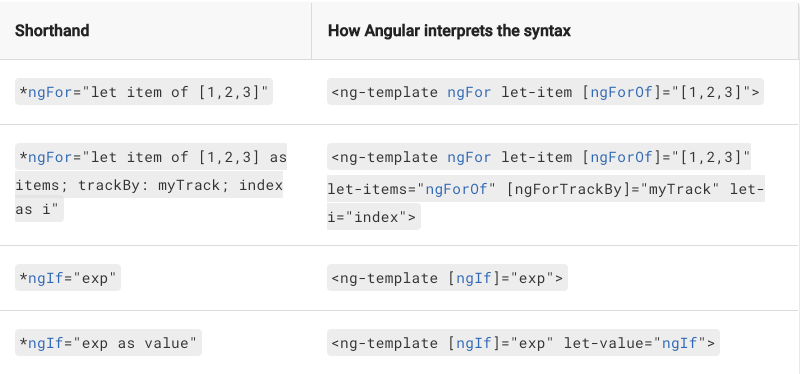
Template Variables

To react developers: similar to ref


exportAs
Get instance of specific directive
@Directive({
selector: 'myButton',
})
class MyButtonDirective {
}
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
template: `
// #button will get html element of button
<button myButton #button>click me</button>
`
})
class AppComponent {
}@Directive({
selector: 'myButton',
exportAs: 'myButton',
})
class MyButtonDirective {
}
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
template: `
// #button will get the instance of MyButtonDirective
<button myButton #button="myButton">click me</button>
`
})
class AppComponent {
}Scope


NgTemplate
<ng-template>


Template block for *ngIf


TemplateOutlet
In Angular
const Foo = () => {
const bar = (
<div>bar</div>
);
return (
<div>
foo
{bar}
</div>
);
};
In React
<ng-template #bar>
<div>bar</div>
</ng-template>
foo
<ng-template [ngTemplateOutlet]="bar"></ng-template>In Angular
const Foo = () => {
const renderBar = (bar, { baz: qux }) => (
<div>
{bar}
<div>
{qux}
</div>
</div>
);
return (
<div>
foo
{renderBar('hello', {
baz: 'world'
})}
</div>
);
};
In React
<ng-template #bar let-bar let-qux="baz">
<div>
{{ bar }}
<div>
{{ qux }}
</div>
</div>
</ng-template>
foo
<ng-template
[ngTemplateOutlet]="bar"
[ngTemplateOutletContext]="{
$implicit: 'hellow',
baz: 'world'
}"
></ng-template>TemplateRef From Input
@Component({ ... })
export class MyButton {
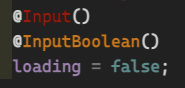
@Input()
loadingIcon?: TemplateRef<any>;
@Input()
loading: boolean = false;
}
// template
<ng-template #defaultLoadingIcon>
...
</ng-template>
<ng-template [ngTemplateOutlet]="loadingIcon || defaultLoadingIcon"></ng-template>
<ng-content></ng-content>
Interaction
w/ content and view
Interact child via variable


@(Content|View)Child/@(Content|View)Children
Query the content/view
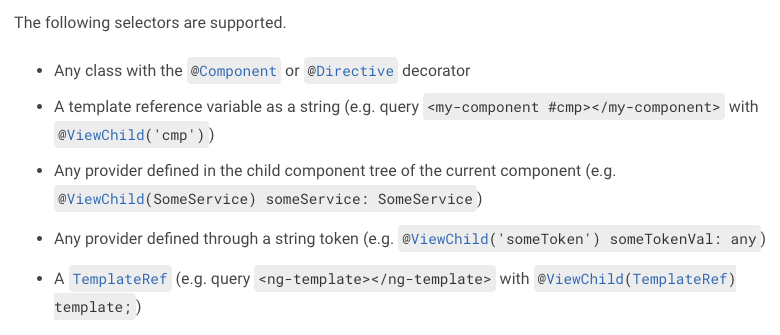

Get HTMLElement of component in view/content
To react developers: no need to add forwardRef everywhere
@ViewChild(FooComponent, { read: ElementRef })
fooElement: ElementRef;Get directive in view/content
@Directive({
selector: '[foo]'
})
export class FooDirective {}
// bar template
<div foo #foo></div>
// bar
@Component({ ... })
export class BarComponent {
@ViewChild('foo')
fooElement: ElementRef;
@ViewChild('foo', { read: FooDirective })
foo: FooDirective;
}const MyList = ({ children, items }) => (
<ul>
{items.map(item => (
<div key={item.id}>
{children(item)}
</div>
))}
</ul>
);
In React
Template From Content
To react developers: render props
In Angular
export interface MyListItem {
// ...
}
@Directive({
selector: '[myList]',
})
export class MyListDirective {
@Input()
items: MyListItem[];
@Content(TemplateRef)
itemTemplate: TemplateRef<{ $implicit: MyListItem }>;
trackByItem(_, item: MyListItem) {
return item.id;
}
}
// MyList template
<ng-container *ngFor="let item of items; trackBy: trackByItem">
<div>
<ng-template *ngTemplateOutlet="itemTemplate; context: { $implicit: item }"></ng-template>
</div>
<ng-container>
// Other template
<ul myList [items]="...">
<ng-template let-item>
...
</ng-template>
</ul>Pipe
Transform data





Unwrapping Observable

Coercion
type will lie you
In Angular
<Icon loading />
--->
<Icon loading={true} />In React
<my-icon loading></my-icon>
--->
<my-icon [loading]="''"></my-icon>
since html
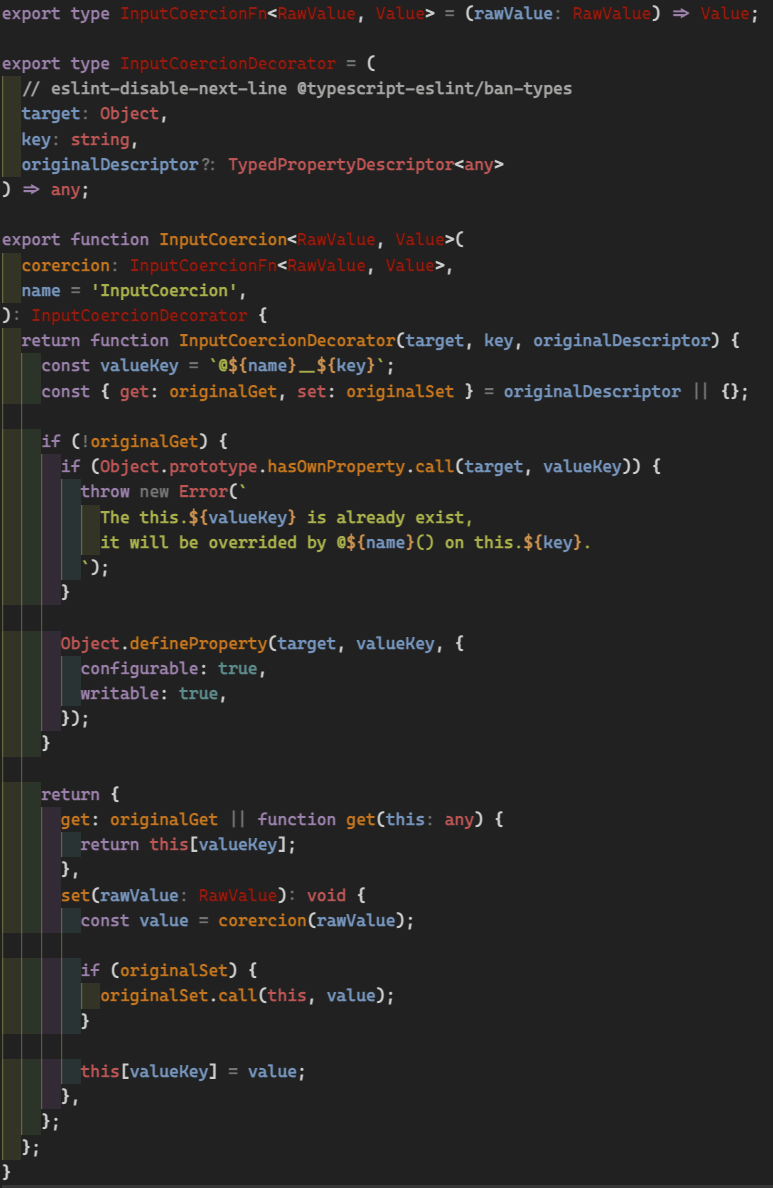
class Icon {
// for template type checking
static ngAcceptInputType_loading: boolean | '';
private _loading: boolean;
get loading(): boolean {
return this._loading;
}
// for correct type
set loading(value: boolean) {
this._loading = (value === '') || value;
}
}class Icon {
// really boolean ?
loading: boolean = false;
}CDK
official component development kit

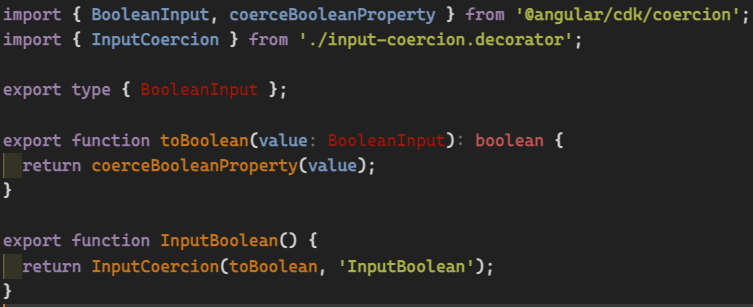
React developers:

Or just always write
<my-icon [loading]="true"></my-icon>
upon to you

Dependency Injection
Injection Token/Provider
To react developer: just like context
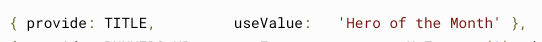

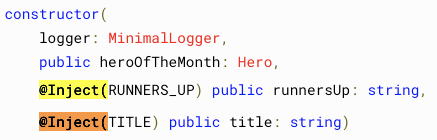
import { createContext } from 'react';
export const TitleContext = createContext<string>('title');<TitleContext.Provider value="Hero of the Month">
{children}
</TItleContext.Provider>const title = useContext(TitleContext);
description not default value
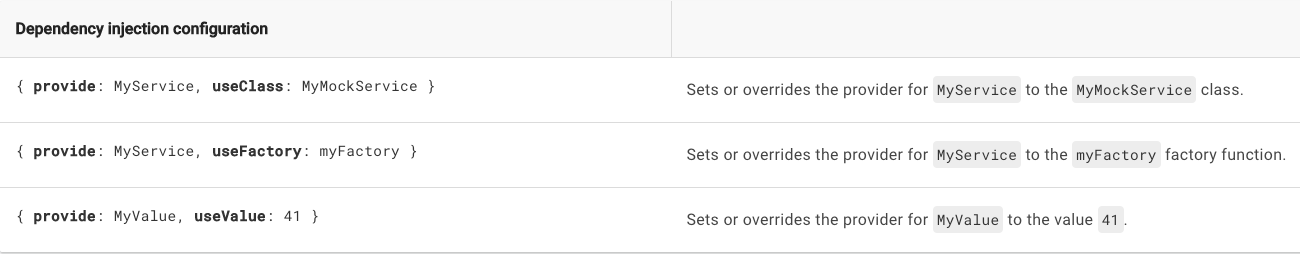
anything

The class placed on useClass should be injectable

no need to use @Inject

Token === Class

Alias


Service
To react developers: for modularity and usability, just like hooks


Service Lifecycle

only support constructor/ngOnDestroy
Injector
To react developer: a thing to provide multiple contexts
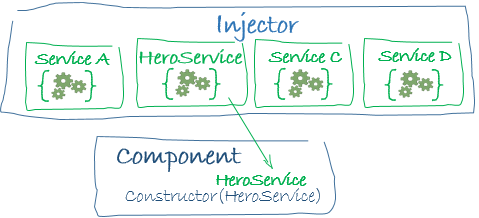
resolves and creates dependencies
maintains a container of dependency instances
NgModule


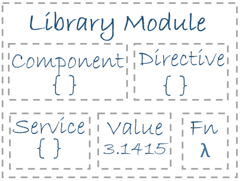


Injectable Scope

root
no other configuration, just inject
Injectable Scope
to specific module


Injectable Scope
to directive/component

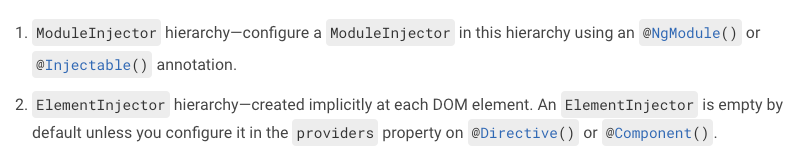
ModuleInjector


Special ModuleInjectors
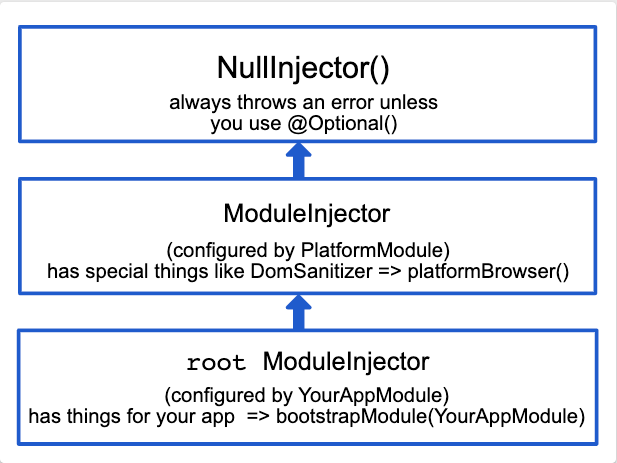
ElementInjector
providers on directive/component


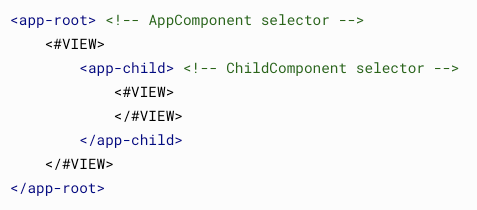
Hierarchy
@Injectable({
providedIn: 'root'
})
class Foo {}ReactDOM.render(
<PlatformModule>
<RootInjector>
<App />
</RootInjector>
</PlatformModule>
);
// foo module
@NgModule({
// ...
providers: [
// ...
],
declarations: [
FooComponent
],
// ...
})
class FooModule {}
// routes
{
loadChildren: () => import('./foo.module').then(m => m.FooModule)
}
const withModule = (providers) => (Component) => (props) => {
// ...
return (
<ModuleInjector>
<Component {...props} />
</ModuleInjector>
);
}
// foo module
export default withModule([])(Foo);
// routes
const Foo = lazy(() => import('./FooModule'));
@Component({
// ...
providers: [
// ...
]
// ...
})
class FooComponent {}const withProviders = (providers) => (Component) => (props) => {
// ...
return (
<ElementInjector>
<Component {...props} />
</ElementInjector>
);
}
// foo
export default withProviders([])(Foo);
To react developers: like hierarchy of context
Resolution Rules
how to inject things for directive/component
where to inject things from

Examples from Official
assume

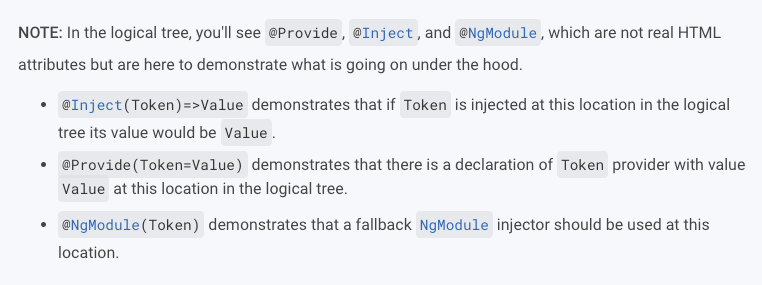


Provider


View Provider



only for view of component





child
inspector
root
from content
in view
Modifiers

modify resolution rules
@Optional
In Angular
export const FooContext = createContext('foo');
// some component
// assume there is no any ancestor provide the context
const foo = useContext(FooContext);
In React
export const FooToken = new InjectionToken<string>('foo');
// some component
// assume no one provide the token
// ...
constructor(
@Inject(FooToken)
foo: string
) {}
// ...Throw error
default value
// ...
constructor(
@Inject(FooToken)
@Optional()
foo?: string
) {}
// ...@Self


@SkipSelf
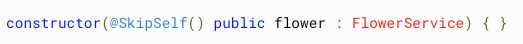

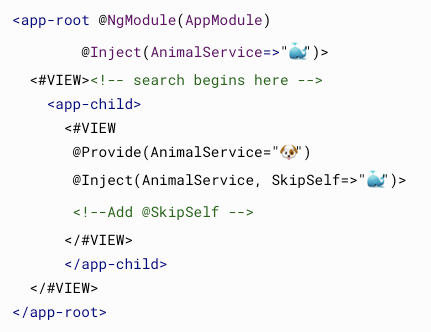
@Host

resolve until host of this directive/component
@Component({
providers: [
FooService
],
template: `
<bar></bar>
`
})
class Foo {
}
@Component({
})
class Bar {
constructor(
@Host()
fooService: FooService
){}
}
@Component({
providers: [
FooService
],
})
class Foo {
}
@Directive({
})
class Bar {
constructor(
@Host()
fooService: FooService
){}
}
// some template
<foo bar></foo>forwardRef
Allow to refer to references which are not yet defined
@Injectable()
export class FooService {
constructor(
@Inject(forwardRef(() => BarService)) barService: BarService
){}
}
@Injectable()
export class BarService {
constructor(
@Inject(forwardRef(() => FooService)) fooService: FooService
){}
}To react developer: not the forwardRef u often use
Scenarios
parent provide data to children
export interface FooGroupContextValue {
// ...
}
export const FooGroupContextToken = new InjectionToken<FooGroupContextValue>('foo context');
// foo group component
@Component({
// ...
providers: [
{
provide: FooGroupContextToken,
useExisting: forwardRef(() => FooGroupComponent),
},
],
// ...
})
export class FooGroupComponent implements FooGroupContextValue {
// ...
}
// foo component
@Component({
// ...
})
export class FooComponent {
// ...
constructor(
@SkipSelf()
@Optional()
@Inject(FooGroupContextToken)
fooGroup?: FooGroupContextValue,
) {}
}
Scenarios
reusable logics need following lifecycle of component
import { Injectable, OnDestroy } from '@angular/core';
import { Subject } from 'rxjs';
@Injectable()
export class DestroyService extends Subject<void> implements OnDestroy {
ngOnDestroy() {
this.next();
this.complete();
}
}
import { takeUntil } from 'rxjs/operators';
@Component({
// ...
providers: [
DestroyService
],
// ...
})
class ArticlesComponent implement OnInit {
// ...
constructor(
private articleService: ArticleService,
private destroy$: DestroyService
) {}
ngOnInit() {
this.articles = this.articleService.getAll()
.pipe(takeUntil(this.destroy$))
.subscribe(() => {
// ...
});
}
// ...
}Router
To react developers: outlet / layout, not component
ActivatedRoute
To react developers: useLocation / useRouteMatch / useParams



Router
To react developers: similar to history


Router Events

Route Configuration



To react developers: no '/' prefix for configuration
Parameters
To react developers: same
const routes: Routes = [
{ path: 'article/:articleId', component: ArticleComponent }
];

Wildcard
To react developers: ** not *
Redirect

To react developers: seem to have in react-router v6 but


Nesting
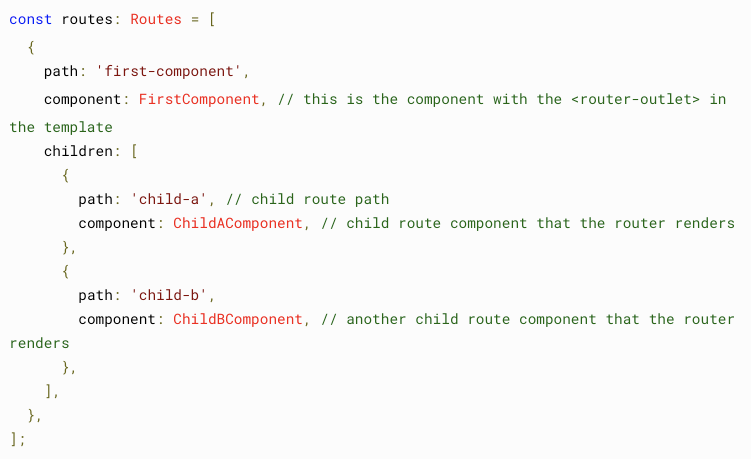
To react developers: do not need to add prefix to path of each children
Lazy Loading
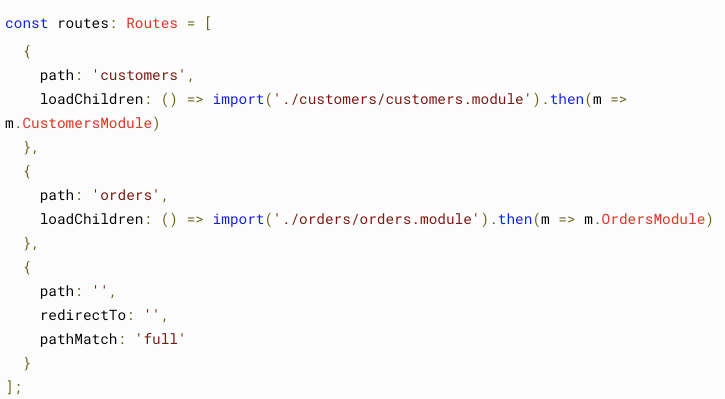
In react router
const Customers = lazy(() => import('./Customers'));

RouteLink

<a [routerLink]="['/team', teamId, 'user', userId]">link</a>
// /team/11/user/33Relative
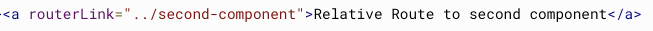
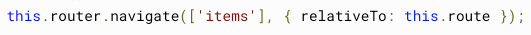
same as unix
State

Active Class
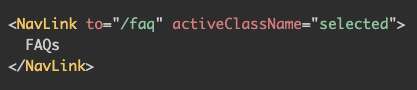

In react router
class will be added to element if the path active
Route Middleware

Guard
CanActivate





Resolve
pre-fetching data



RouterOutlet

Auxiliary Routes



/article/10/edit(left:some/left/path//right:/some/right/path)
separate outlets by //
Forms
To react developers: redux form / final form / react hook form ?
no, just one in angular provided by official
NgModel


<label>
<input type="radio" name="colors" value="yellow" [(ngModel)]="color">
Yellow
</label>
<label>
<input type="radio" name="colors" value="green" [(ngModel)]="color">
Green
</label>
<label>
<input type="radio" name="colors" value="red" [(ngModel)]="color">
Red
</label>Do not need to set attribute checked
Can use on nested

Change Listener

Template Driven Form
see doc yourself, just use [(ngModel)]
Reactive Form

FormControl
control the value and validation status of a form field

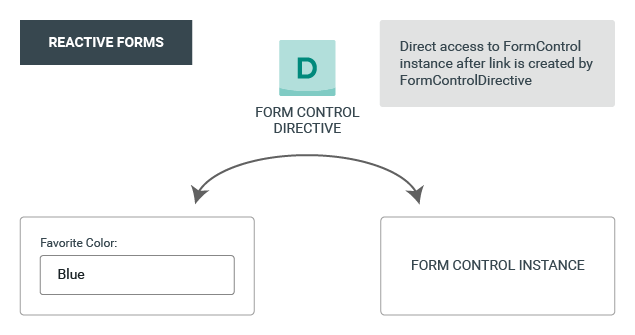
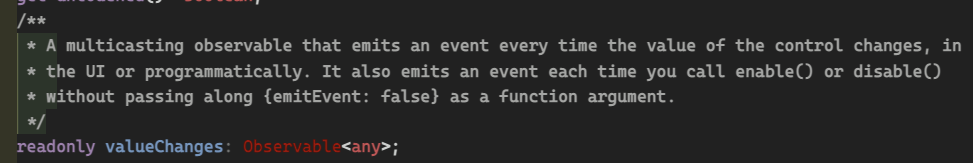

control.setValue('foo');setValue vs patchValue

replace all
partial update
FormGroup
control group of FormControls




Nested FormGroup


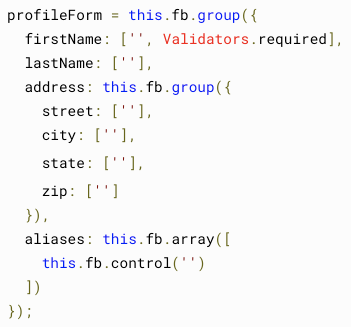
FormBuilder



each field is a tuple, [value,[validators | options]?]
FormArray

control array of FormControls




Validation

for reactive form
Built Ins



Custom Validator

Cross Field Validator


Async Validator
similar to custom validator but
wrap the return result w/ Promise / Observable
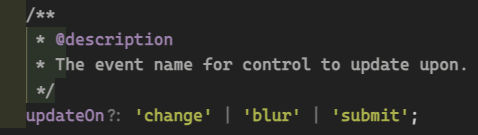
Configure updateOn
usually for optimizing performance for async validators

ControlValueAccesor
An interface as a bridge between
angular forms api and native element in the DOM.
For custom ngModel or FormControl
Please see doc to know how to implement
After implement ControlValueAccessor

<address-form formControlName="address"></address-form>Custom FormControl

Roadmap
strict typing for forms
Animation
FSM
Web Animation Api
animation of angular is similar to



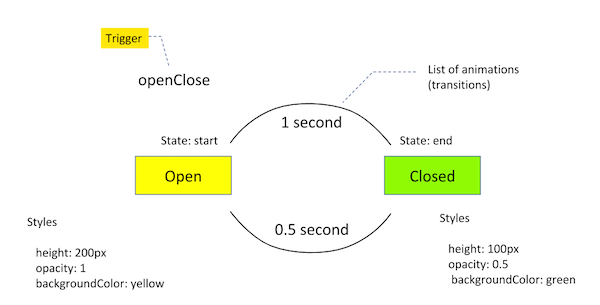

similar to css transition


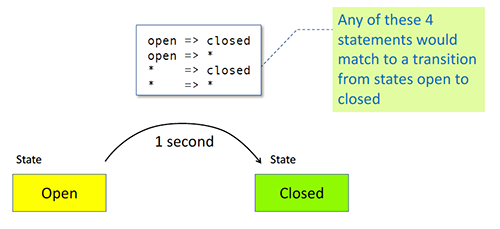
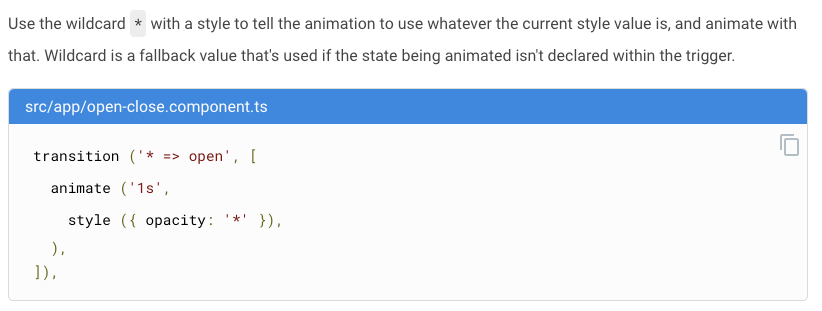
Wildcard
glob / regex ?
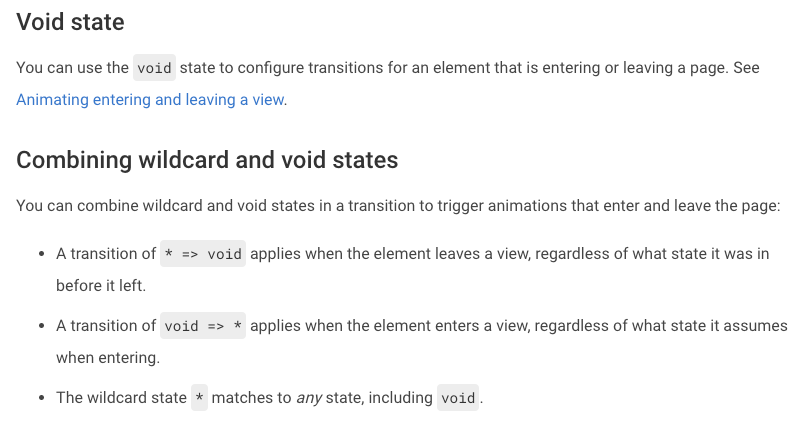
Void State
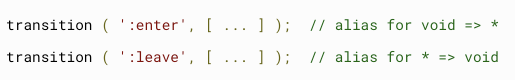
Disabled
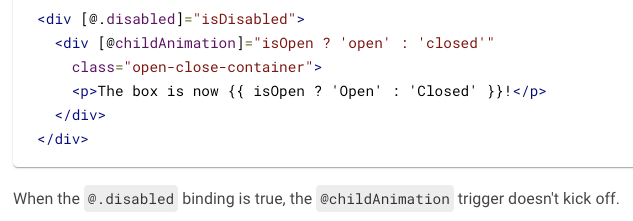
Callback

Keyframes
offset
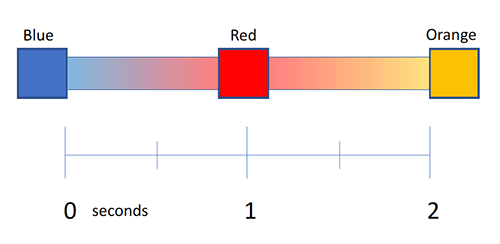

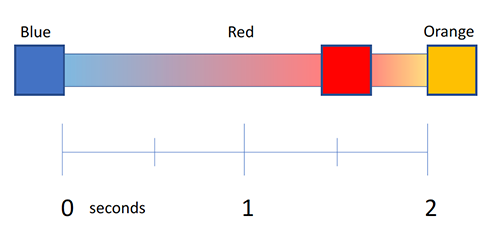

Parameters


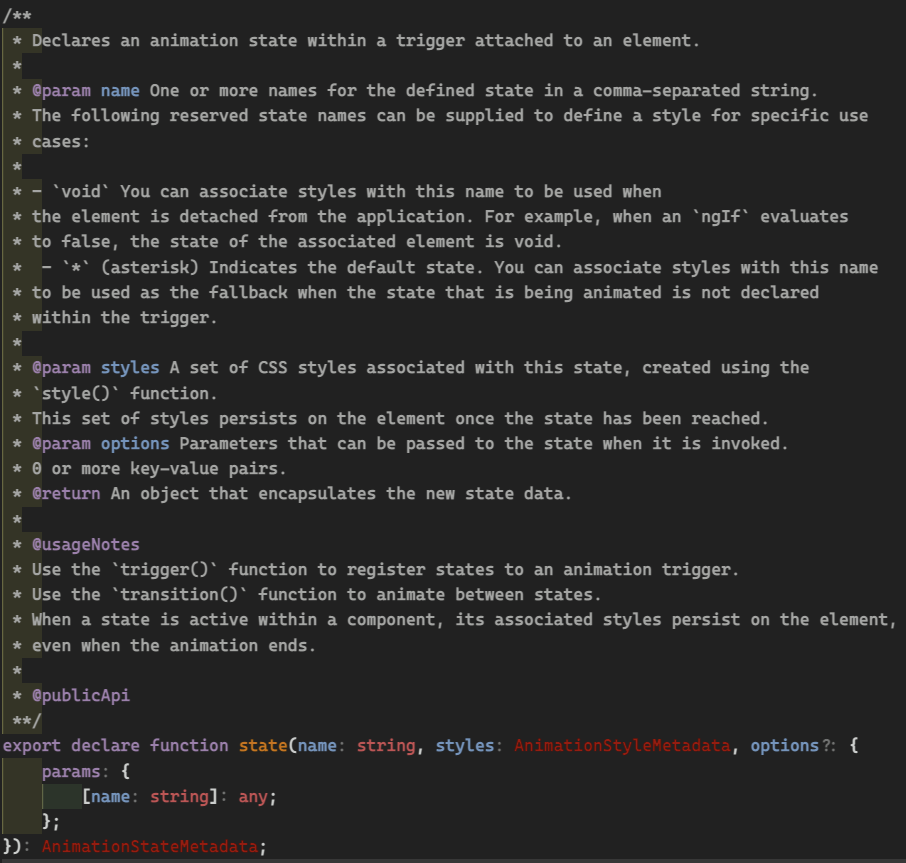
Not documented in
official
But in comments
state('foo', style({
maxHeight: '{{ maxHeight }}px',
overflow: 'hidden'
}), { params: { maxHeight: 1 } }),
<div [@bar]="{
value: isBar,
params: { maxHeight: foo * 10 }
}">
bar
</div>

Auto calculation
transition on height between 0 and 'auto' not work
export const collapseMotion: AnimationTriggerMetadata = trigger('collapseMotion', [
state('expanded', style({ height: '*' })),
state('collapsed', style({ height: 0, overflow: 'hidden' })),
// ...
]);
Transition
Transition
import { Transition } from 'react-transition-group';
const duration = 300;
const defaultStyle = {
transition: `opacity ${duration}ms ease-in-out`,
opacity: 0,
}
const transitionStyles = {
entering: { opacity: 1 },
entered: { opacity: 1 },
exiting: { opacity: 0 },
exited: { opacity: 0 },
};
const Fade = ({ in: inProp }) => (
<Transition in={inProp} timeout={duration}>
{state => (
<div style={{
...defaultStyle,
...transitionStyles[state]
}}>
content
</div>
)}
</Transition>
);
<CSSTransition in={inProp} timeout={300} classNames="fade">
<div>
content
</div>
</CSSTransition>
// css
.fade-enter {
opacity: 0;
}
.fade-enter-active {
opacity: 1;
transition: opacity 200ms;
}
.fade-exit {
opacity: 1;
}
.fade-exit-active {
opacity: 0;
transition: opacity 200ms;
}react transition group
will add additional <div />
or use cloneElement / render props to control but still need to handle ref of children since Transition also need to pass ref to children
Transition
angular
export const fadeMotion: AnimationTriggerMetadata = trigger('fade', [
transition(':enter', [
style({ opacity: 0 }),
animate('200ms', style({ opacity: 1 }))
]),
transition(':leave', [
animate('200ms', style({ opacity: 0 }))
]),
]);<div @fade *ngIf="open">
content
</div>Api
Restful
HttpClient
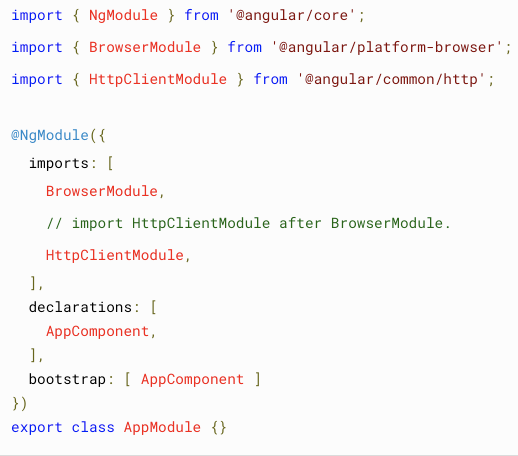



Options

Observe Result

Headers


Params

query string
Handle error



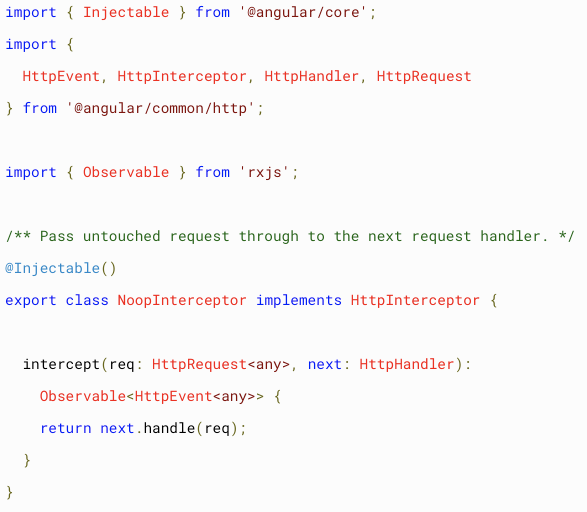
Interceptor


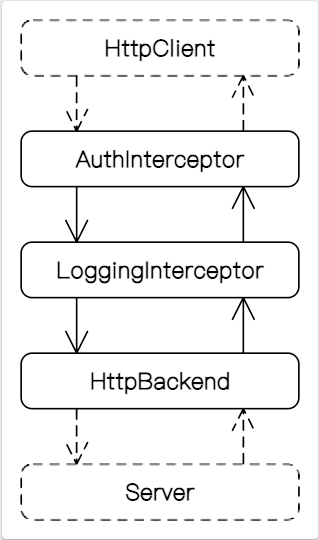


Use Cases
authorization


Use Cases
logging

Tracking Progress
File Upload
this.http.post('/api/upload', file, { observe: 'events', reportProgress: true })
.pipe(
map(event => {
switch (event.type) {
case HttpEventType.Sent:
return `Uploading file "${file.name}" of size ${file.size}.`;
case HttpEventType.UploadProgress:
const percentDone = Math.round(100 * event.loaded / event.total);
return `File "${file.name}" is ${percentDone}% uploaded.`;
case HttpEventType.Response:
return `File "${file.name}" was completely uploaded!`;
default:
return `File "${file.name}" surprising upload event: ${event.type}.`;
}
})
)
.subscribe(() => {
// ...
});
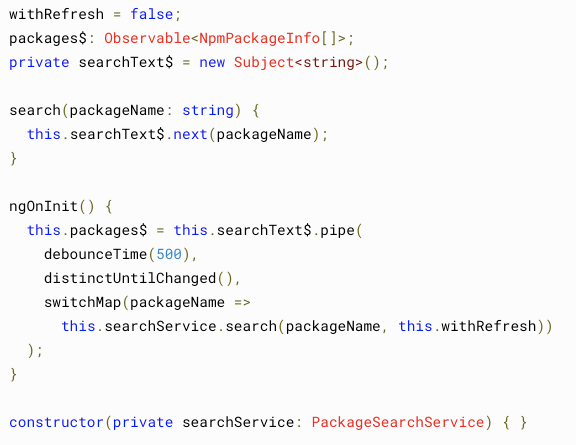
Optimizing
GraphQL
apollo

Query
by client

Query
inject query

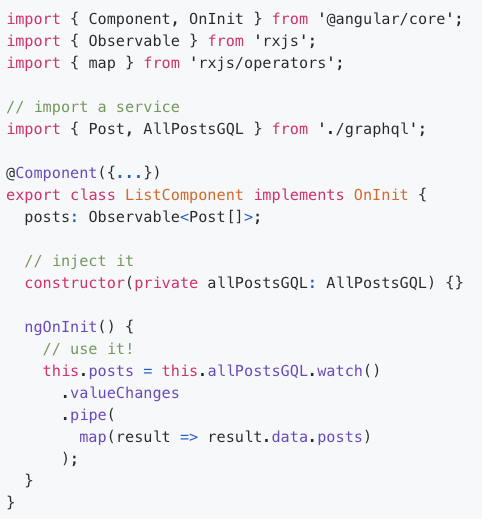
Query
variables
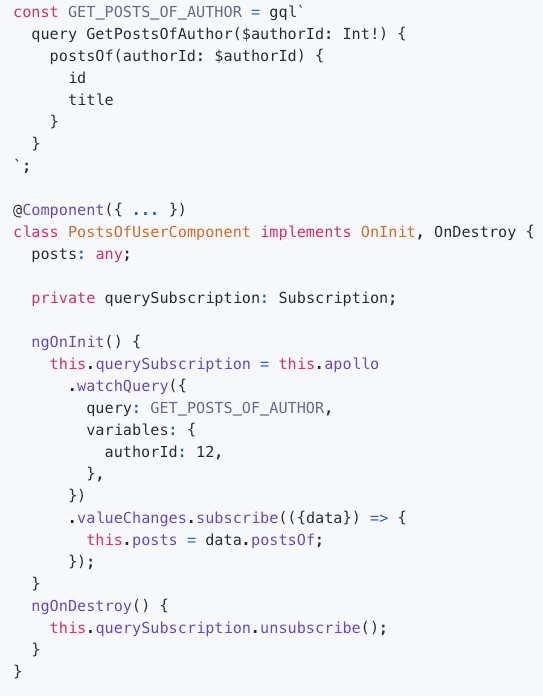
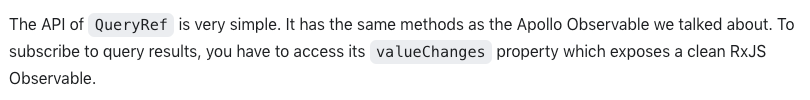
QueryRef
Query
refetch

Query
fetchMore

Query
update variables imperative

Query
variables from observable
@Component({ ... })
class PostsComponent {
variables$ = new BehaviorSubject({ ... });
posts$: Observable<Post[]>;
ngOnInit() {
this.posts$ = this.variables$
.pipe(
startWith(this.variables$.value),
switchMap(variables =>
this.apollo
.watchQuery({
query: GET_POSTS,
variables
})
.valueChanges
),
map(({ data }) => data.posts)
);
}
}Mutation
by client
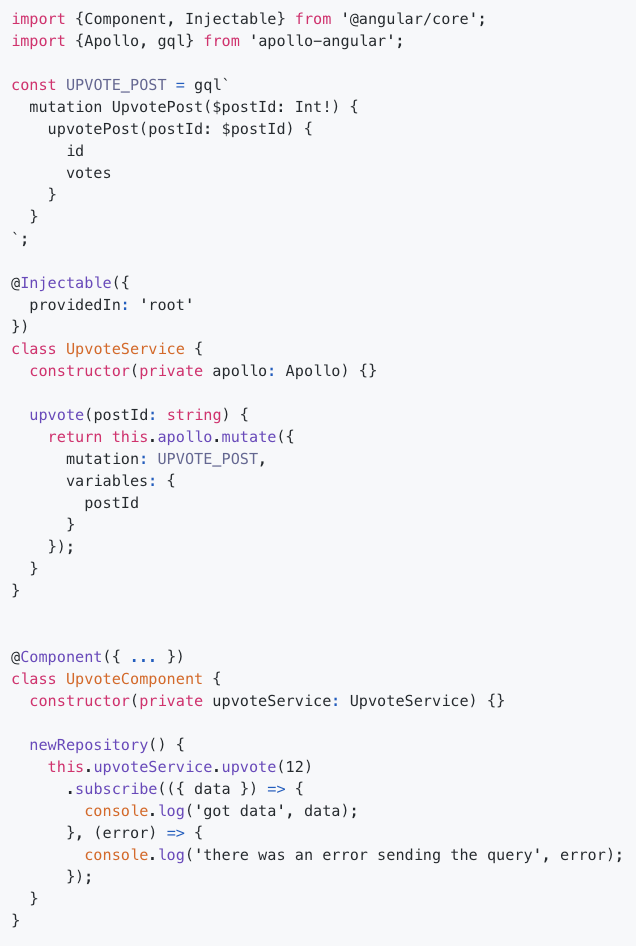
Mutation
inject mutation


Subscription
by client
this.apollo.subscribe({
query: // ...,
variables: {
// ...
}
})Subscription
inject subscription
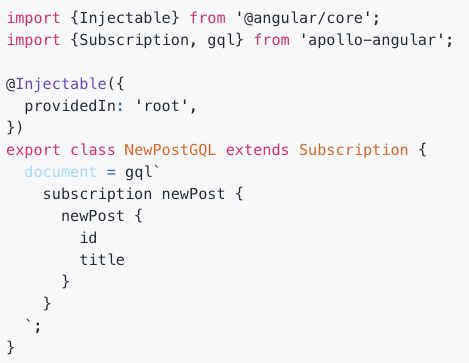

Subscription
QueryRef.subscribeToMore

Code Generation
dto (data transfer object) - object transferred from network
Rx in Angular
Turn everything to stream
If possible
this.currentHeroId$ = this.route.paramMap
.pipe(
map(params => Number(params.get('id')))
);
this.selectedHero$ = currentHeroId$
.pipe(
switchMap(id =>
this.heroService.getHeroById(id)
.pipe(shareReplay())
)
);this.currentHeroId$ = this.route.queryParams
.pipe(
map(params => Number(params.get('id')))
);
If currentHeroId changed from param to query, just
But sometimes need promise
for complicated flow control
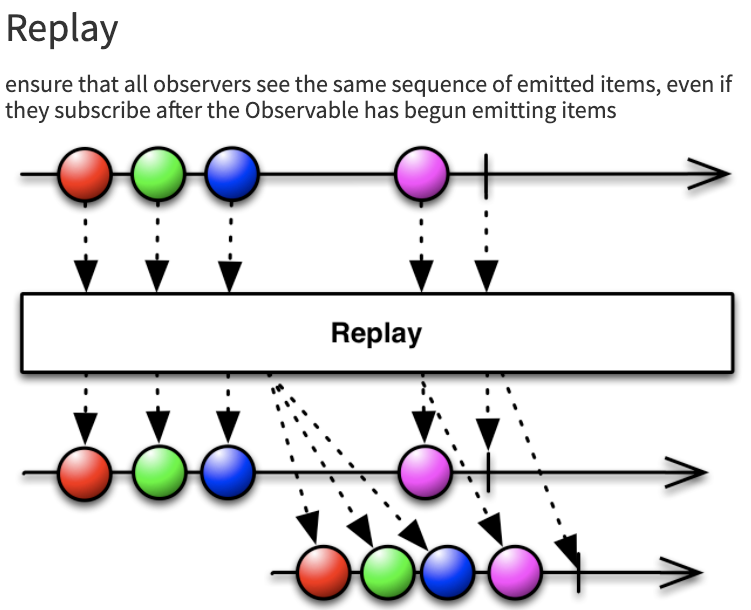
Cold Observable
each subscriber create a new stream after subscribing
one stream to one subscriber
Hot Observable
singleton stream shared by every subscribers
one stream to many subscribers
Warm Observable
cold -> hot
similar to hot observable but stream start after first subscription
Pitfalls
Forget to unsubscribe
To avoid from memory leak
Do not need to unsubscribe cold observables or observables only used on async pipe
Or use takeUntil() operator
To react developers: similar to forget to cleanup in effect
HttpClient is cold

nothing happens

remember to subscribe
HttpClient is cold

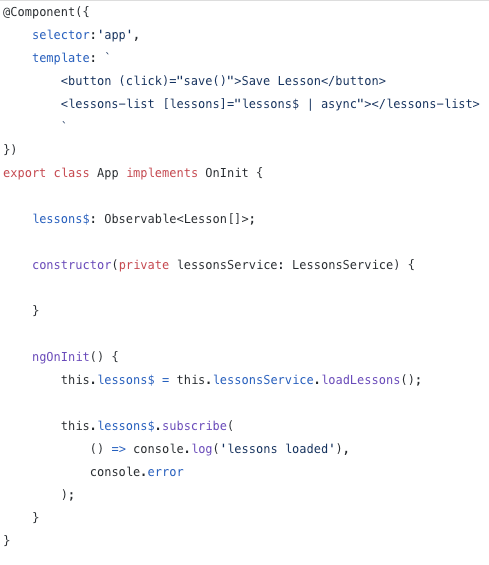


share: make a cold observable warm
Avoid using multiple async pipe on same observable in one template
<div *ngIf="(articles$ | async) as articles">
// ...
</div>
<div *ngIf="(articles$ | async) as articles">
// ...
</div><ng-container *ngIf="(articles$ | async) as articles>
<div>
// ...
</div>
<div>
// ...
</div>
</ng-container>Keep observable completion


nothing happens
stay at the original screen and the UI does not get updated

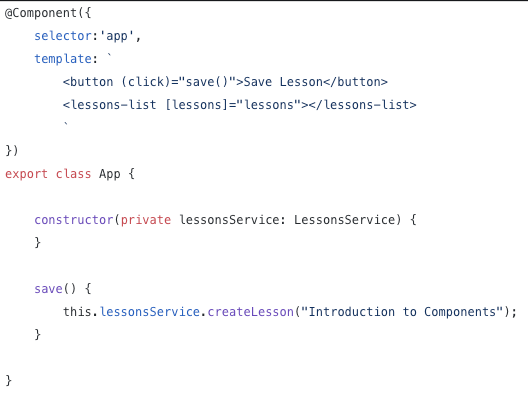
this.lessonsService
.findLessonByUrl(route.params['id'])
.pipe(
first()
// take(1)
);
Architecture
w/ simple example
Single Responsibility Principle
Only do one thing
Aspect Oriented Programming
api
state
component
author
comment
article
view layer
core layer
state management
facade
data layer
abstraction layer
service layer
presentation
container
Core Layer
Domain / Application Logic
Data Layer
communicate w/ http, just api
@Injectable()
export class ArticleApi {
readonly url = '/api/cashflowCategories';
constructor(private readonly http: HttpClient) {}
getArticles(options = {}): Observable<Article[]> {
const { authorId } = options;
return this.http.get<Article[]>(this.url, { authorId });
}
getArticleById(id: string): Observable<Article> {
return this.http.get<Article>(this.url, { id });
}
}State Management
maintains a lot of BehaviorSubjects/Observables and methods
import * as jwtDecode from 'jwt-decode';
@Injectable({
providedIn: 'root'
})
export class AuthState {
private readonly accessToken$$ = new BehaviorSubject<string | null>(localStorage.getItem('accessToken'));
accessToken$ = this.accessToken$$.asObservable();
isAuthenticated$ = this.accessToken$
.pipe(
map(token => !!token)
);
get accessToken() {
return this.accessToken$$.value;
}
get payload() {
return jwtDecode(this.accessToken);
}
setTokens(accessToken, refreshToken) {
this.accessToken$.next(accessToken);
// ...
}
removeTokens() {
this.accessToken$.next(null)
// ...
}
}Do not expose BehaviorSubjects to avoid from mutating data by outside methods
conditional, sometimes just in service
Service Layer
domain business logics, like auth/form
@Injectable()
export class EditArticleForm {
readonly form = this.fb.group({
// ...
});
constructor(private readonly fb: FormBuilder) {}
validate() {
// ...
}
validateSomeField() {
// ...
}
}@Injectable({
providedIn: 'root'
})
export class AuthService {
constructor(
private readonly authApi: AuthApi,
private readonly authState: AuthState
) {}
login(email, password) {
this.authApi.login(email, password)
.subscribe(({ accessToken, refreshToken }) => {
this.authState.setTokens(accessToken, refreshToken);
});
}
logout() {
this.removeTokens();
// ...
}
updateAccessToken() {
const { refreshToken } = this.authState;
if (refreshToken) {
this.authApi.updateAccessToken(refreshToken)
.subscribe(
({ accessToken, refreshToken: newRefreshToken }) => this.authState.setTokens(accessToken, newRefreshToken),
() => this.logout()
);
}
}
}@Injectable({
providedIn: 'root'
})
export class ArticleService {
// ...
getArticles$() {
return this.articleApi.getArticles()
.pipe(shareReplay());
}
getArticlesOfAuthor$(authorId: string) {
return this.articleApi.getArticle({ authorId })
.pipe(shareReplay());
}
// ...
}Facade
Facade pattern
Compose specific logics/flow control
Control router
Cache
...
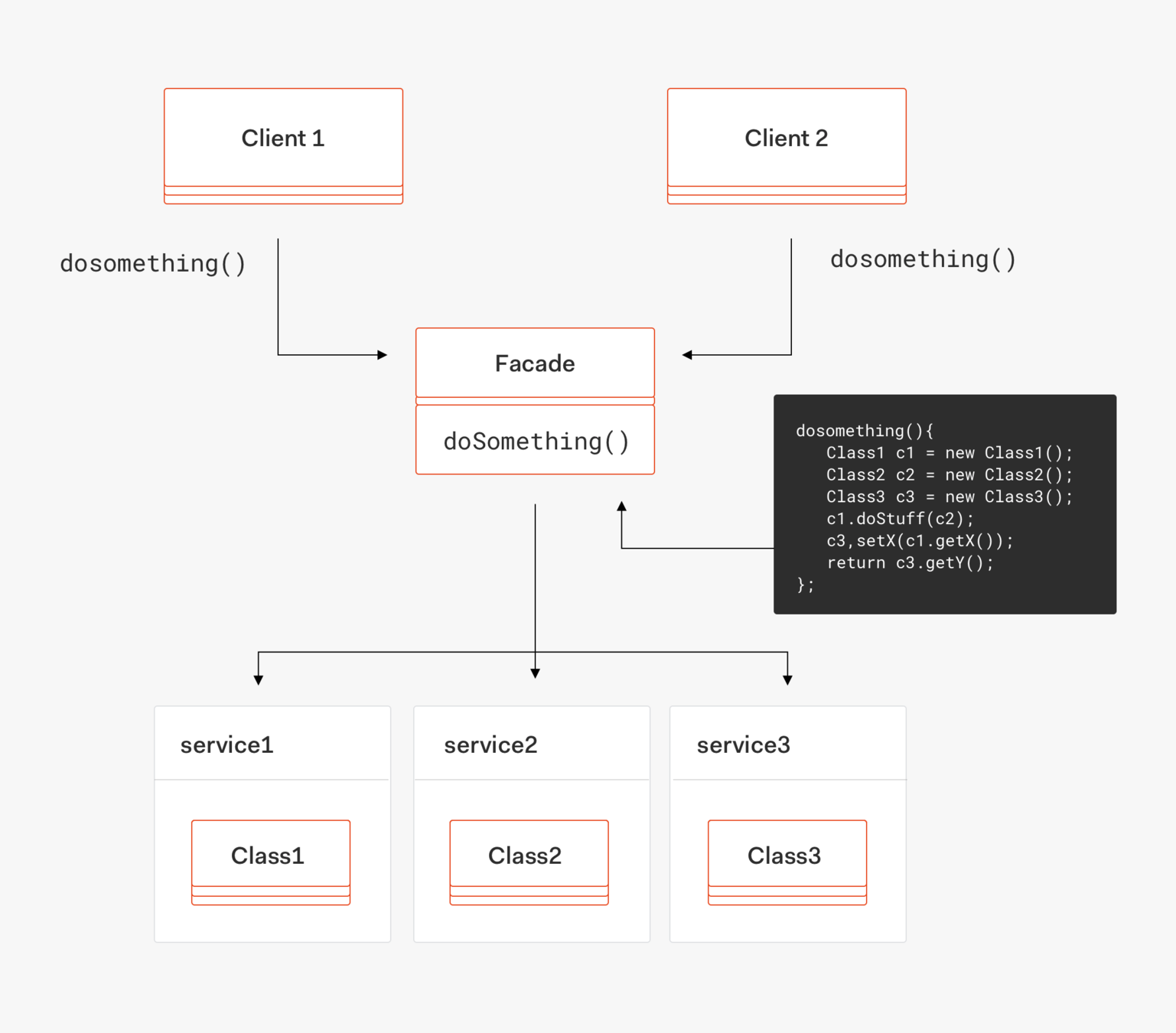
@Injectable()
export class AuthorPageFacade {
author$ = this.authorService.getAuthorProfile$();
articles$ = this.author$
.pipe(
switchMap(author =>
author
? this.articlesService.getAritclesOfAuthor$(author.id)
: of([])
)
);
constructor(
private readonly authorService: AuthorService,
private readonly articleService: ArticleService
) {}
navigateToAriclePage(artcile: Article) {
this.router.navigate(['/article', article.id]);
}
}
Example in wiki
View Layer
Presentation
export class AritcleListComponent {
@Input()
articles: Article[];
@Output()
articleSelect = new EventEmitter<Article>();
onArticleSelect(article: Article) {
this.articleSelect.next(article);
}
}
//
<article-list-item
*ngFor="let article of articles"
[article]="article"
(select)="onArticleSelect($event)"
></article-list-item>Do not know anything except @Input and @output
Container
export class AuthorPageComponent {
author$ = this.authorPageFacade.author$;
articles$ = this.authorPageFacade.articles$;
constructor(
private readonly authorPageFacade: AuthorPageFacade
) {}
onArticleSelect(article: Article) {
this.authorPageFacade.navigateToArticlePage(article);
}
}
//
<author-profile [author]="author$ | async"></author-profile>
<article-list
[articles]="articles$ | async"
(articleSelect)="onArticleSelect($event)"
></article-list>Communicate w/ facade and presentational views
author page facade
author service
article service
author profile component
author page component (container)
article-list
author$
articles$
getArticles(author.id)
getAuthor
@Input()
author$ | async
@Input()
articles$ | async
Whatever facade or service changes, it won't affect view layer if the facade provide same things to container.