
The XN Framework
Brought to you by the good folks at
Introduction to
What is the XN Framework?
- Rapid development.
- Extensible API.
- Powerful data modeling using your favorite graph DB.
- Maintainable code.
-
Security and reliability
- Granular permission control.
- View your data at any point in time.
Why should I use it?
- An enterprise framework.
- Used for building web applications.
- Utilizes the power of graph databases.
Why graph databases?
- A graph might be the best structure for your data.
- More flexible than tables and key-value stores.
- Naturally represent entities and relations using vertices and edges.
- Storing a graph in a relational DB = Reinventing the wheel.
- Graph queries are expensive in non-graph databases.
- Multiple joins for relational databases.
- Multiple queries for various key-value solutions.
Graph vs. Non-Graph databases
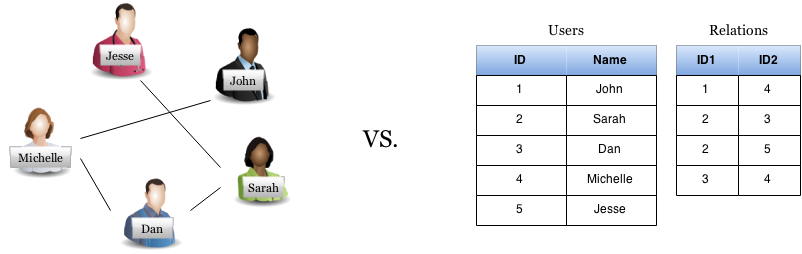
- Following edges (cheap) vs. Joining tables (expensive).
- How would you query for friends?
- Or, friends of friends?
- Or make recommendations based on common friends?
Highlights
- Extensible API
Query the graph using your domain-specific language. - Rich Data Modeling
An inheritance tree may not suit your data model. - Performance!
- JRuby = JVM speed + Ruby expressiveness.
- Supports Neo4j, OrientDB, TinkerGraph.
As well as any other Blueprints-enabled graph. - Production ready.
LightMesh uses the XN framework and is deployed in many data centers around the world. - Enterprise features - Security and integration.
- History Graph (aka Time Machine).
The Stack
- Graph database
- Flexible, general-purpose structure.
- Pacer
- JRuby library, written by our own Darrick Wiebe.
- Super fast graph traversal & extensible object model.
- XN Framework
- Enterprise data modeling.
- Extensible API.
- History graph (aka Time machine).
- Permission control and data integration.
- And more ...
Setting Up
- Development VM with a fully configured stack.

- Requirements:
- Vagrant (1.7.x and above)
- One (or more) of the following Vagrant providers:
Developing Your Application
- Basic setup:
- XN stack runs in the VM.
- Application code lives on the host machine, and mounted on the VM.
- Two ways to run your application:
- Server (production & QA).
- Interactive, using the xn-console (development).
- Common development pattern:
- Edit code on the host machine, using your favorite IDE.
- Test the changes on the VM, using the xn-console.
Your First XN Application
- Install the command-line tool, and create the application:
~$ gem install xnlogic
~$ xnlogic application my_app --key xn_user:xn_password --up- Log into the VM:
~$ cd my_app
~/my_app$ xnlogic ssh- Start the xn-console and create a database:
➜ ~ xn-console
...
jruby-1.7.18 :001 > PM.create_client('my_app', 'db01')What's next?
- Your application is ready.
- Next, we will dive deeper into the XN framework:
- Model your data entities and their relations.
- Extend XN with custom queries.
- Access your data using the API.