TECHNOLOGY STRATEGIES
Chapter 10
Competing on Knowledge: How the Power of
Information Can Enable Great Things
slides by :
[Group One]
Major Brock
Nicole Stroble
John Hunt
Business Use of Information
- We live in digital age
- Information is the the heart of all commerce
- Knowledge is the basis of all competition
- Information Asymmetry
- Differences in information
- Explains why companies adapt differently
- Pros of Advances in Technology
- Better information
- Timelier Information
- Cons of Advances in Technology
- Overabundance of Information
- Insufficient time to decrypt all of the information
-
Competitive advantage relies on the ability to decipher and act on undiscovered opportunities.
How to Analyze your business
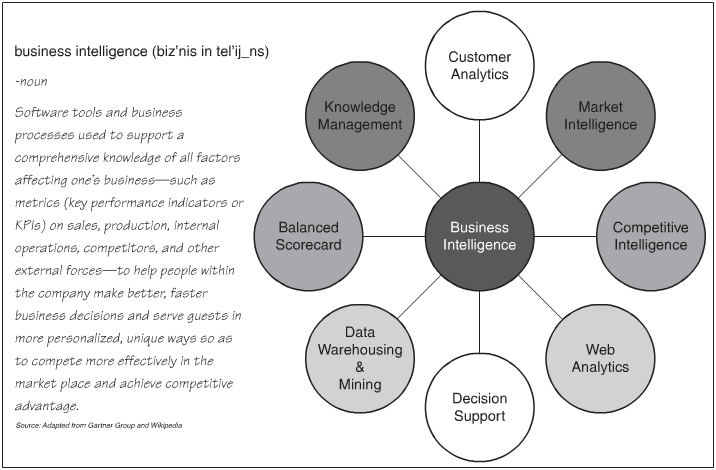
Dr. Kellie Keeling defines business intelligence as
“Technologies and Processes that use data to understand and analyze business performance”
she takes that from Davenports, “Competing on Analytics”
*Davenport, Thomas H. "Competing on Analytics." Harvard Business Review (2006): 1-11. Web. 22 July 2014.
- Considered the organizations Brain
- Informationalize: “Keep and analyze information about everything related to one’s business and use it to inform business decisions.”
- Compatibility is a big factor
- Same Operating systems
- Network infrastructure
The Importance of INFRASTRUCTURE
- Technology infrastructure is everything necessary to support the analyzing and implementing of data for a company.
- Usually behind the scenes, yet an integral part of the company that can quickly lead to downfall.
- It is important for the systems to all be connected so that something that impacts one part of the company will coordinate with other parts of the company.
INFORMATION: A VALUED ASSET
- Information is one of the most important and under-appreciated assets in the hospitality industry.
- When used properly, information can provide a business with a competitive advantage
- Hospitality companies can use information about their guests to provide them with great customer service
DATA VS. INFORMATION
- Data and information is often thought to be the same thing
- Data are "the raw ingredients that comprise information (Nyheim, 175). "
- Information is when "patterns begin to emerge (Nyheim 175)" in data
- Moe Russel says the following when talking about technology used in agriculture:
- "Data is one thing - information is another. Growers need information, not data."
- RUSSELL, M. (2011). DATA VS. INFORMATION. Corn & Soybean Digest , 71 (10), 64.
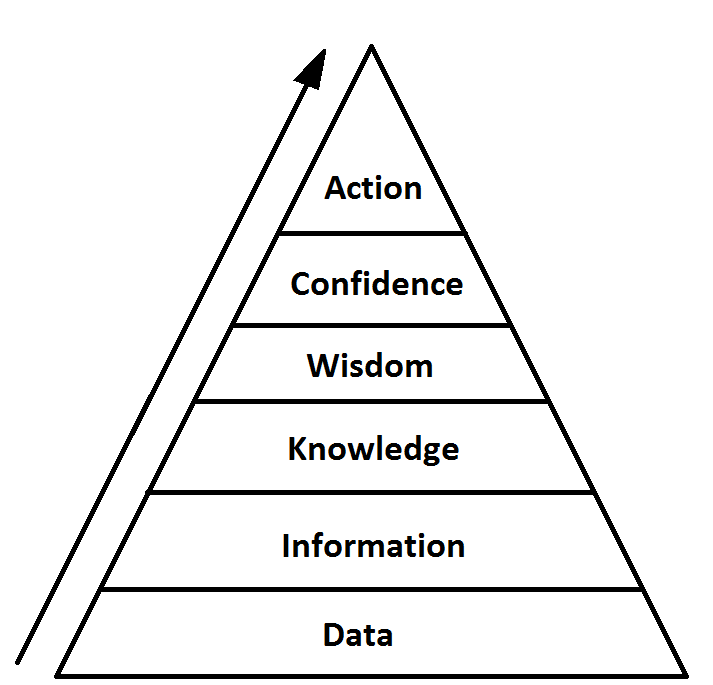
Data Hierarchy
- Data is like the foundation, everything is built on top off it
- This is why data integrity is important
- "Information is gained from analyzing and interpreting the data and conclusions represent the actions to be taken based on the information. "
-
Rogers, Y., Sharp, H., & Preece, J. (2011). Data Gathering.
Interaction Design
. West Sussex: John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
- Knowledge is built on experience using information
- Wisdom comes with the use of knowledge over time
- Confidence comes as you ascend the data hierarchy
- With intelligence comes confidence and power
- Action comes after building the confidence to act on
Data Hierarchy
- Knowledge is built on experience using information
- Wisdom comes with the use of knowledge over time
- Confidence comes as you ascend the data hierarchy
- With intelligence comes confidence and power
- Action comes after building the confidence to act
Information as a Valued Asset
- Information is one of the most important and under-appreciated assets in the hospitality industry.
- When used properly, information can provide a business with a competitive advantage
- Hospitality companies can use information about their guests to provide them with great customer service
Information Overload
- Technology gives access to so much it causes information overload
- Businesses experience this when they cannot manage the information they are collecting
- "Many organizations are frustrated by the sheer volume of information they receive, but most know that there is value in this information, if only they knew how to extract it (Morrish 46)."
-
Morrish, I. (2013, February 1). How to Manage Information Overload. NZBusiness, 46-47.
- Technology can cause information overload but can also help prevent it through the use of data management systems.
- Data management systems include:
- executive information systems (EIS)
- decision support systems (DSS)
- database management system (DBMS)
- intranets and the corporate data network.
Working Smarter With Information
The problem
-
Managing and making decisions should be done by informed business individuals.
-
Unfortunately many do not use up to date technology and still rely on (out of date) analyzing.
- Out of date corporate based analyzing often leads to lagging indicators.
- Better Tools
- DSS - Decision Support System
-
EIS - Executive Information System
At the heart of a DSS is its statistical tools used for modeling, simulation, and predictive analysis (trying to forecast future trends, behavior, and outcomes). Whereas an EIS focuses more on communicating performance results, a DSS’ primary emphasis is on understanding these results over time and what they mean in terms of future -Nyheim p182
These tools can be used to get real time data, in a way that is catered towards the needs of the user.
They integrate into other systems, such as the DBMS, the website, and other programs that are already using, analyzing, or creating data and information.
They integrate into other systems, such as the DBMS, the website, and other programs that are already using, analyzing, or creating data and information.
Balanced Scorecard
With all of these tools available it is vital to have a 'balanced scorecard'. In other words give proper and balanced attention to the information different tools that you have access to.
Instead of a single measure or single category of measures, what is proposed is a composite of integrated and telling measures or key indicators, [or]critical success factors, across a variety of categories
Kaplan and Norton who invented the balanced scorecard idea suggest Four Perspectives:
The financial perspective.
The customer's perspective.
The customer's perspective.
The internal business perspective.
The innovation and learning perspective.
Wrapping it Up
We need data and information that explains that data.
In gaining knowledge we can gain wisdom of how to act.
Technology can give us vast amounts of this data & information.
We must selectively sort through it, technology can help.
Technology can also expedite the process of assimilating and applying information through systems (such as EIS and DSS)
Sources/Links
- Nyheim,,P and Connolly, D. (2012). Technology Strategies for the Hospitality Industry. Prentice Hall ,
- Davenport, Thomas H. "Competing on Analytics." Harvard Business Review (2006): 1-11. Web. 22 July 2014.
- "Data Mining: What Is Data Mining?" Data Mining: What Is Data Mining?N.p., n.d. Web. 22 July 2014.
- Russell, M. (2011). Data VS. Information. Corn & Soybean Digest , 71 (10), 64.
- Rogers, Y., Sharp, H., & Preece, J. (2011). Data Gathering. Interaction Design . West Sussex: John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
- Morrish, I. (2013, February 1). How to Manage Information Overload. NZBusiness, 46-47.
¿ Questions ?
-
What are certain tactics companies could use to improve the way they informationalize their business? Primarily, what are technology factors that could go into this?
In terms of Customer Analytics, what would be the differences of using a program such as Google Analytics, compared to other types of online market research, such as data mining?