Cluster-size decay in kernel-based spatial random graphs
Joost Jorritsma
joint with Júlia Komjáthy, Dieter Mitsche

Recent trends in Spatial Stochastic Processes
October 2022



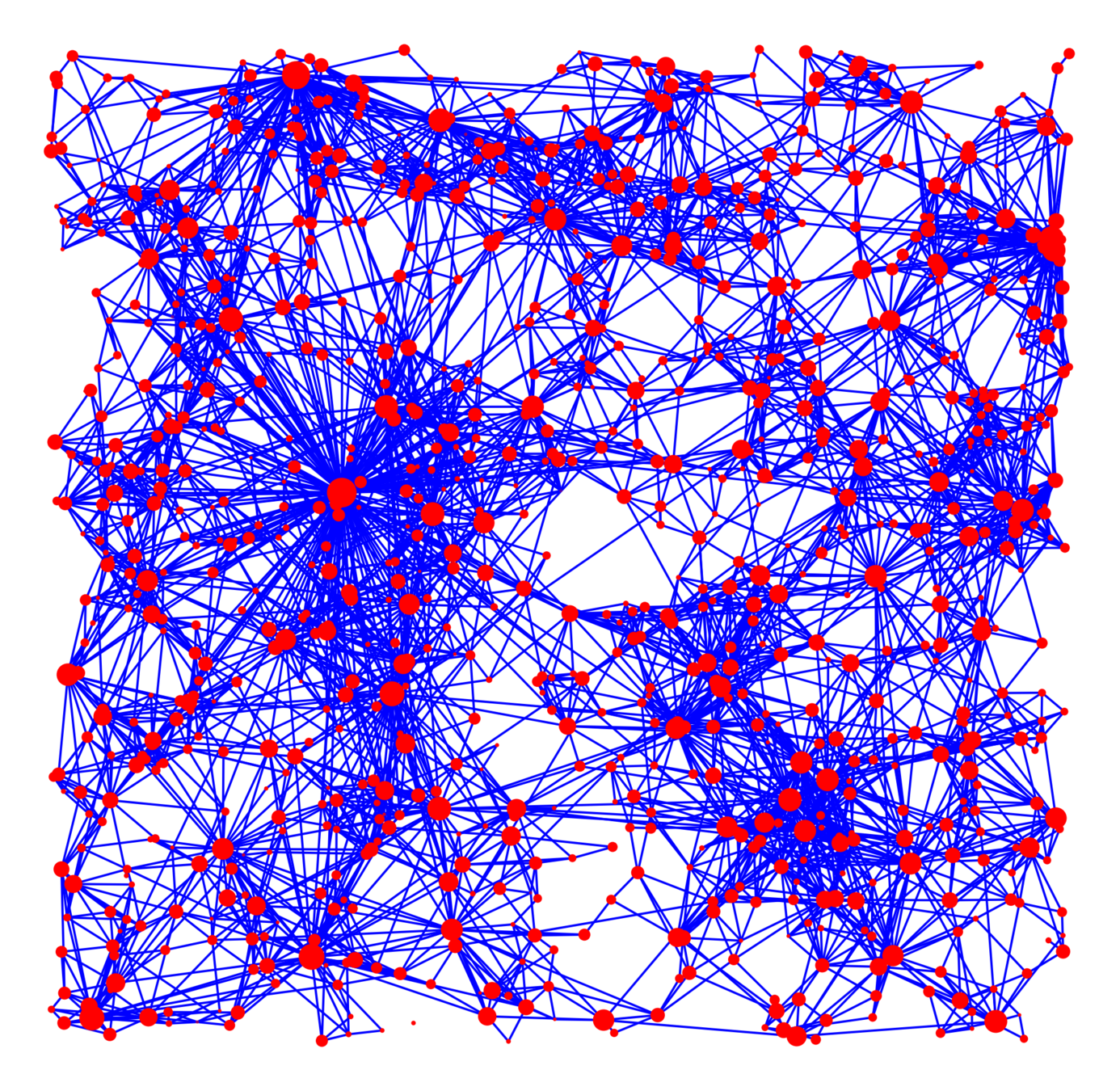
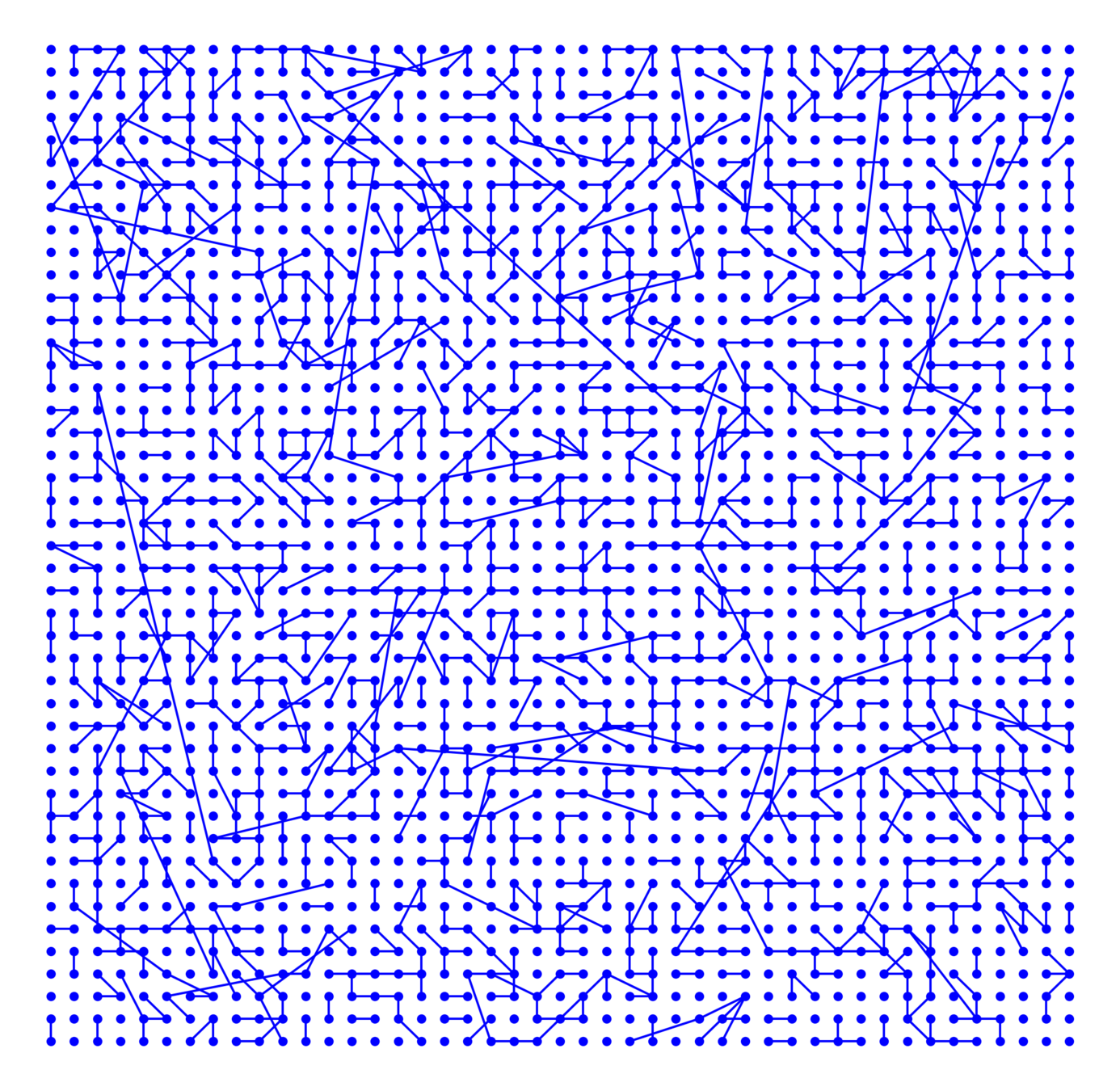
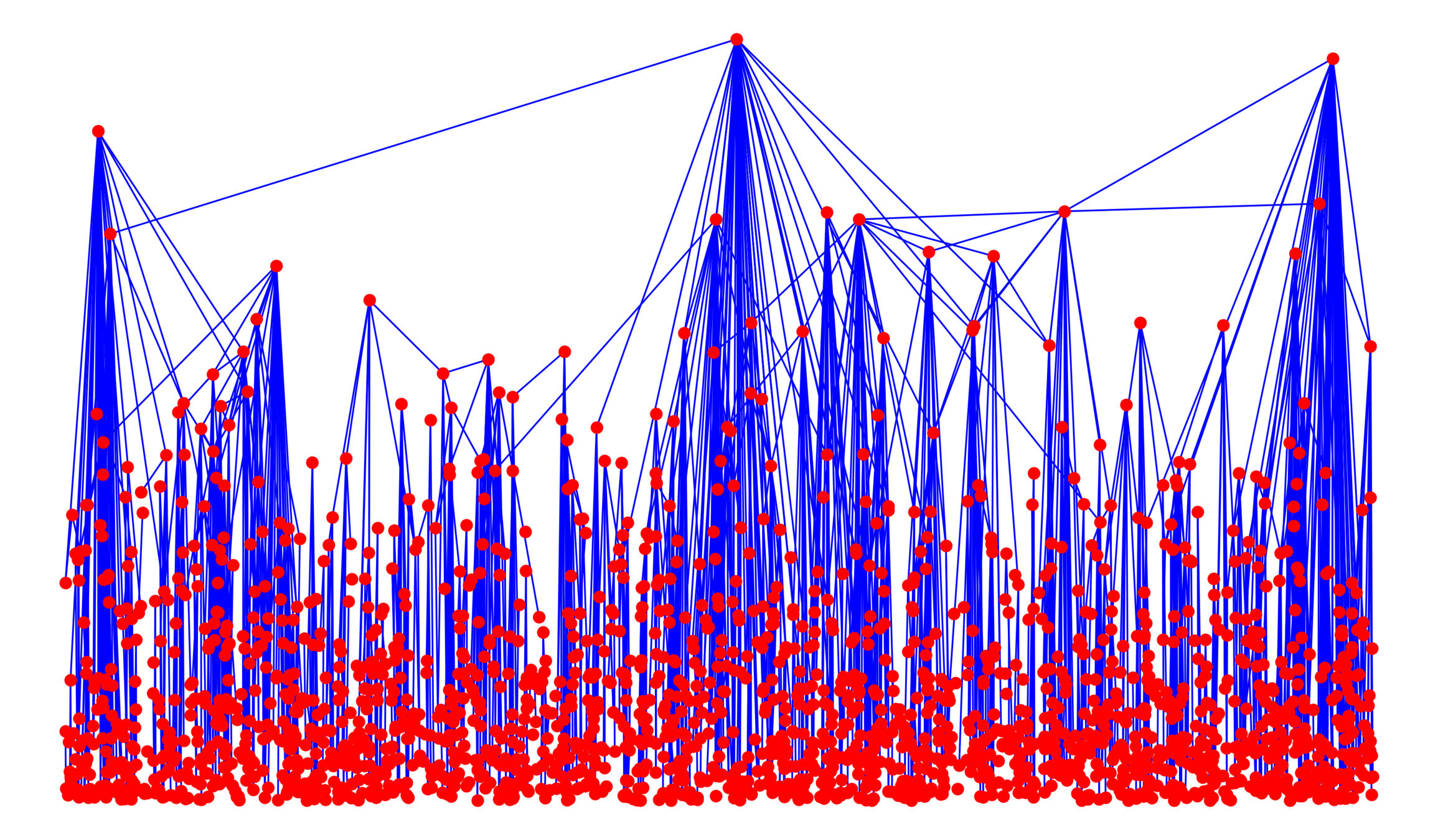
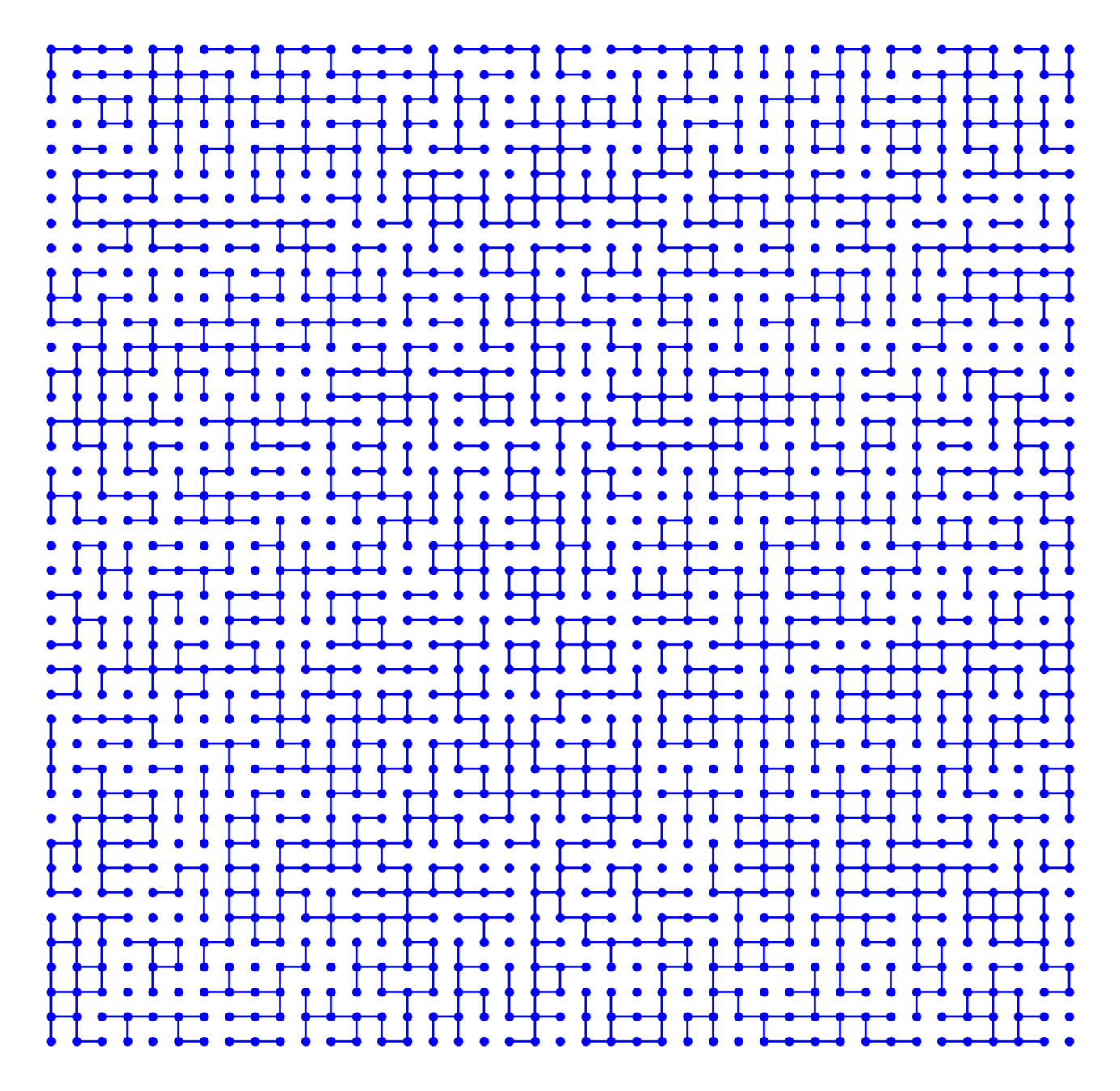
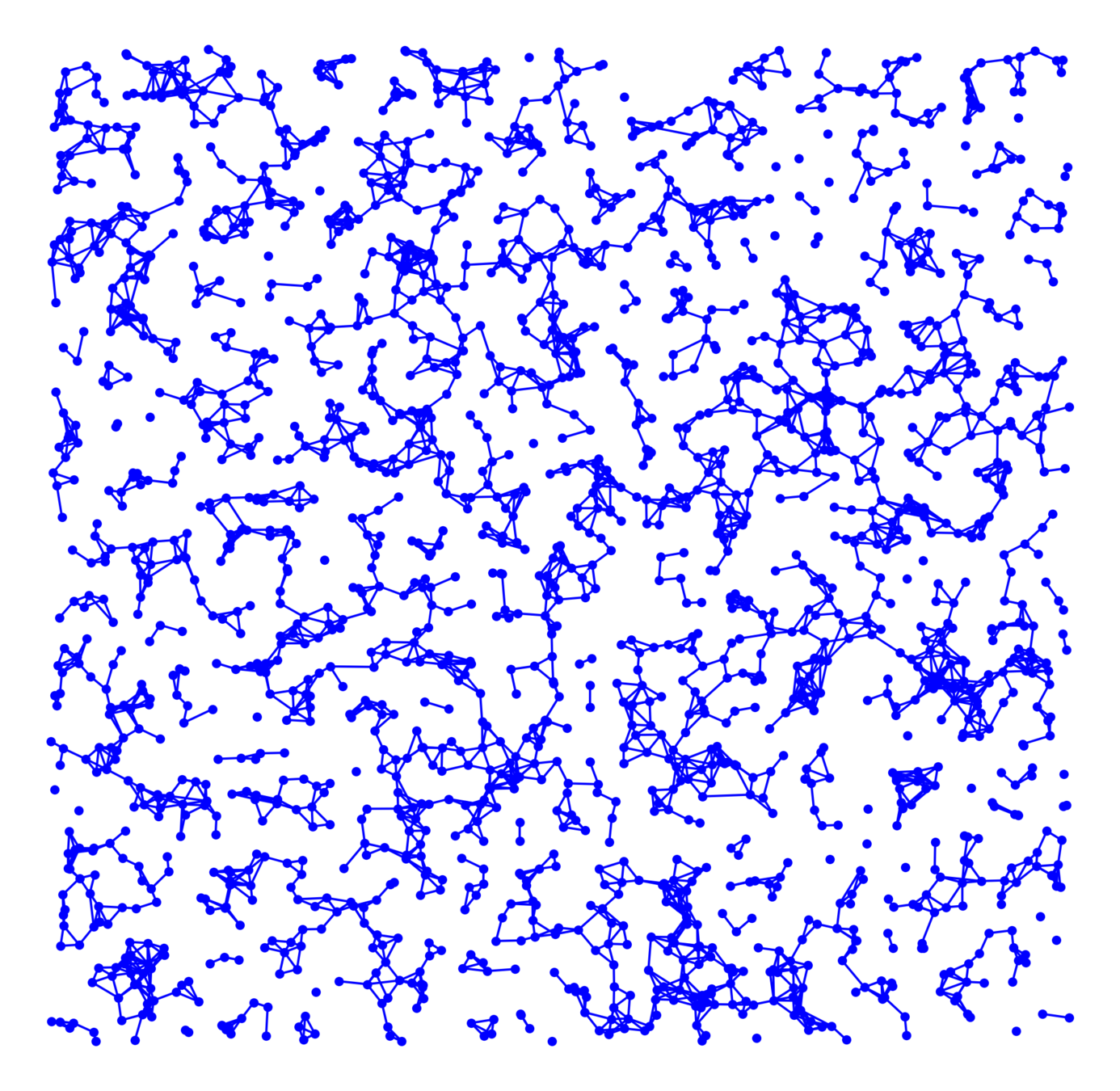
Hyperbolic random graph
Scale-free percolation
Long-range percolation
Age-dependent RCM
Random geom. graph
Nearest-neighbor percolation
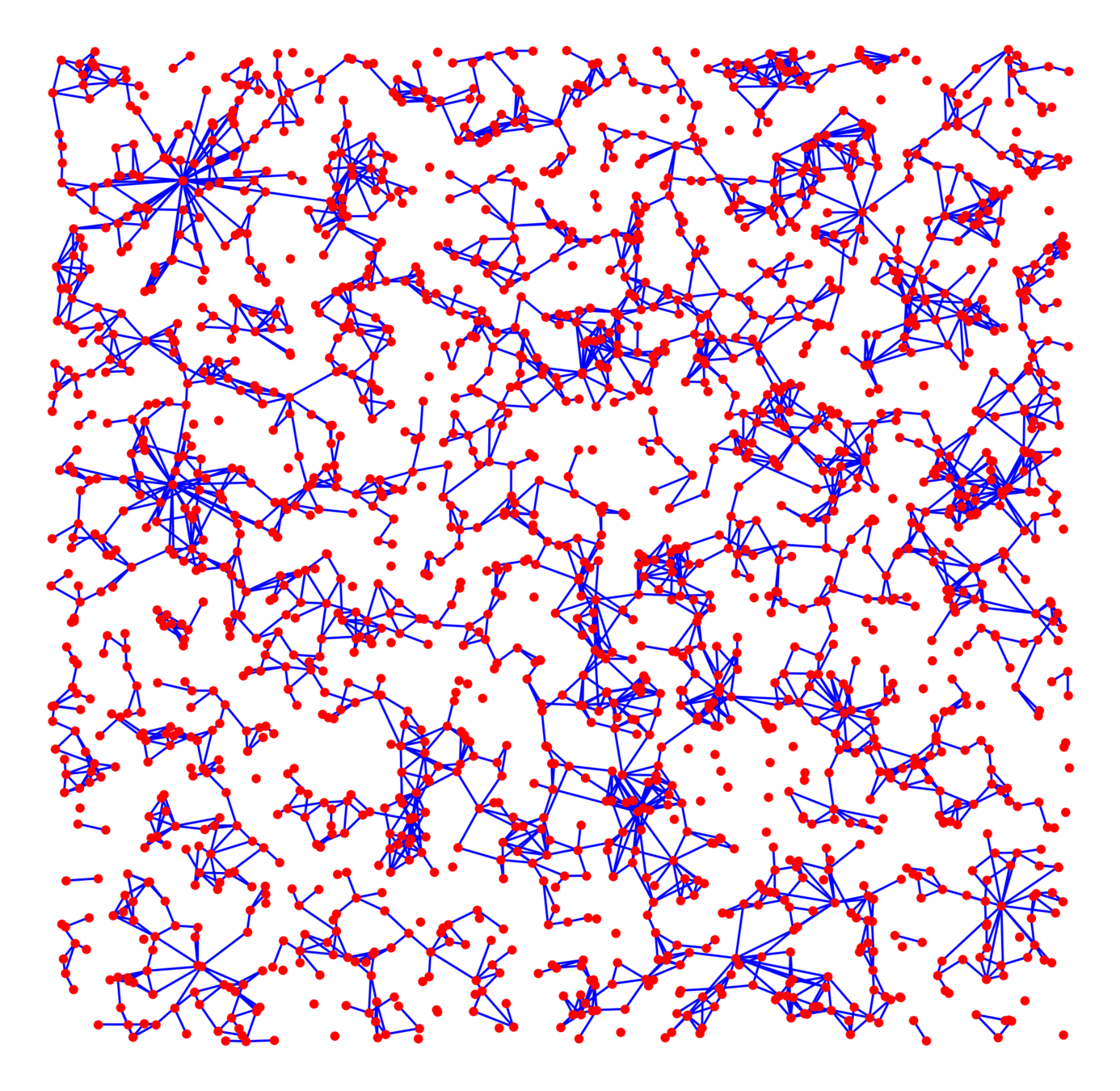
Kernel-based spatial random graphs
Vertex set \(\mathcal{V}_\infty\)
- Spatial locations \(x_v\in\mathbb{R}^d\): PPP(1) or \(\mathbb{Z}^d\),
- i.i.d. weights \(w_v\ge 1\): \(\mathbb{P}(w_v\ge w)=w^{-(\tau-1)}\),
Edge set \(\mathcal{E}_\infty\)
- Symmetric kernel \(\kappa(w_u, w_v)\),
- Long-range parameter \(\alpha>1\),
- Edge-density \(\beta>0\),
Connection probability
$$\mathbb{P}\big(u\leftrightarrow v\mid \mathcal{V}_\infty\big)=\bigg(\beta\frac{\kappa(w_u, w_v)}{\|x_u-x_v\|^d}\bigg)^\alpha\wedge 1$$
Vertex set \(\mathcal{V}_\infty\)
- Spatial locations \(x_v\in\mathbb{R}^d\): PPP(1) or \(\mathbb{Z}^d\),
- i.i.d. weights \(w_v\ge 1\): \(\mathbb{P}(w_v\ge w)=w^{-(\tau-1)}\),
$$\mathbb{P}\big(u\leftrightarrow v\mid \mathcal{V}_\infty\big)=\bigg(\beta\frac{\kappa(w_u, w_v)}{\|x_u-x_v\|^d}\bigg)^\alpha$$
$$\mathbb{P}\big(u\leftrightarrow v\mid \mathcal{V}_\infty\big)=\phantom{\bigg(\beta}\frac{\kappa(w_u, w_v)}{\phantom{\|x_u-x_v\|^d}}\phantom{\bigg)^\alpha\wedge 1}$$
$$\mathbb{P}\big(u\leftrightarrow v\mid \mathcal{V}_\infty\big)=\phantom{\bigg(\beta}\frac{\kappa(w_u, w_v)}{\|x_u-x_v\|^d}\phantom{\bigg)^\alpha\wedge 1}$$
$$\mathbb{P}\big(u\leftrightarrow v\mid \mathcal{V}_\infty\big)=\bigg(\phantom{\beta}\frac{\kappa(w_u, w_v)}{\|x_u-x_v\|^d}\bigg)^\alpha\phantom{\wedge 1}$$
$$\mathbb{P}\big(u\leftrightarrow v\mid \mathcal{V}_\infty\big)$$
Kernel-based spatial random graphs
Vertex set \(\mathcal{V}_\infty\)
- Spatial locations \(x_v\in\mathbb{R}^d\): PPP(1),
- i.i.d. weights \(w_v\ge 1\): Pareto(\(\tau\)),
Edge set \(\mathcal{E}_\infty\)
- Symmetric kernel \(\kappa(w_1, w_2)\),
- Edge-density \(\beta>0\),
- Long-range parameter \(\alpha>1\),
Connection probability
$$\mathbb{P}\big(u\leftrightarrow v\mid \mathcal{V}_\infty\big)=\bigg(\beta\frac{\kappa(w_u, w_v)}{\|x_u-x_v\|^d}\bigg)^\alpha\wedge 1$$
Vertex set \(\mathcal{V}_\infty\)
- Spatial locations \(x_v\in\mathbb{R}^d\): PPP(1), or \(\mathbb{Z}^d\),
- i.i.d. weights \(w_v\ge 1\): \(\mathbb{P}(w_v\ge w)=w^{-(\tau-1)}\),
Edge set \(\mathcal{E}_\infty\)
- Symmetric kernel \(\kappa(w_1, w_2)\),
- Edge-density \(\beta>0\),
- Long-range parameter \(\alpha>1\),

The interpolating kernel
Connection probability
$${\color{grey}\mathbb{P}\big(u\leftrightarrow v\mid \mathcal{V}_\infty\big)=\bigg(\beta}\frac{\kappa(w_u, w_v)}{\color{grey}\|x_u-x_v\|^d}{\color{grey}\bigg)^\alpha\wedge 1}$$
A parameterized kernel: \(\sigma\ge 0\)
$$\kappa_{\sigma}(w_u, w_v):=\max\{w_u, w_v\}\min\{w_u, w_v\}^\sigma$$
- \(\sigma\): assortativity
- \(\sigma\): interpolation

SFP/GIRG

Hyperbolic RG

Age-dep. RCM
Scale-free Gilbert



Long-range percolation
Random geom. graph
Nearest-neighbor percolation
Degree distribution
Theorem. When \(\tau>2\):
Theorem. When \(\tau<2\):
- Infinite degrees
- Bounded diameter
$$\mathbb{P}(\mathrm{deg}(0)\ge k)\sim k^{-(\tau_\mathrm{deg}-1)}.$$
[Deijfen, v.d. Hofstad, Hooghiemstra '13]
[Gracar, Grauer, Lüchtrath, Mörters '18]
[Heydenreich, Hulshof, J. '17]
[Hirsch '17]
[v.d. Hofstad, v.d. Hoorn, Maitra, '22]
[J., Komjáthy, Mitsche, '22+]
[Lüchtrath '22]
Theorem. When \(\tau<2\):
Theorem. When \(\tau>2\):
$${\color{grey}\mathbb{P}(\mathrm{deg}(0)\ge k)\sim k^{-(\tau_\mathrm{deg}-1)}.}$$
Small components
- \(\mathcal{C}_\infty\) : unique infinite component
(exists by assumption). - \(\mathcal{C}(0)\): component containing 0
- \(\mathcal{C}_n^{(2)}\) : second-largest component in \(\mathcal{G}_n\)
(graph in volume-\(n\) box)
Definition
- Cluster-size decay: $$\mathbb{P}\big(k\le |\mathcal{C}(0)|<\infty\big)= $$
- Second-largest component: $$|\mathcal{C}_n^{(2)}|=\Theta\big(\phantom{what}\big)$$
Questions
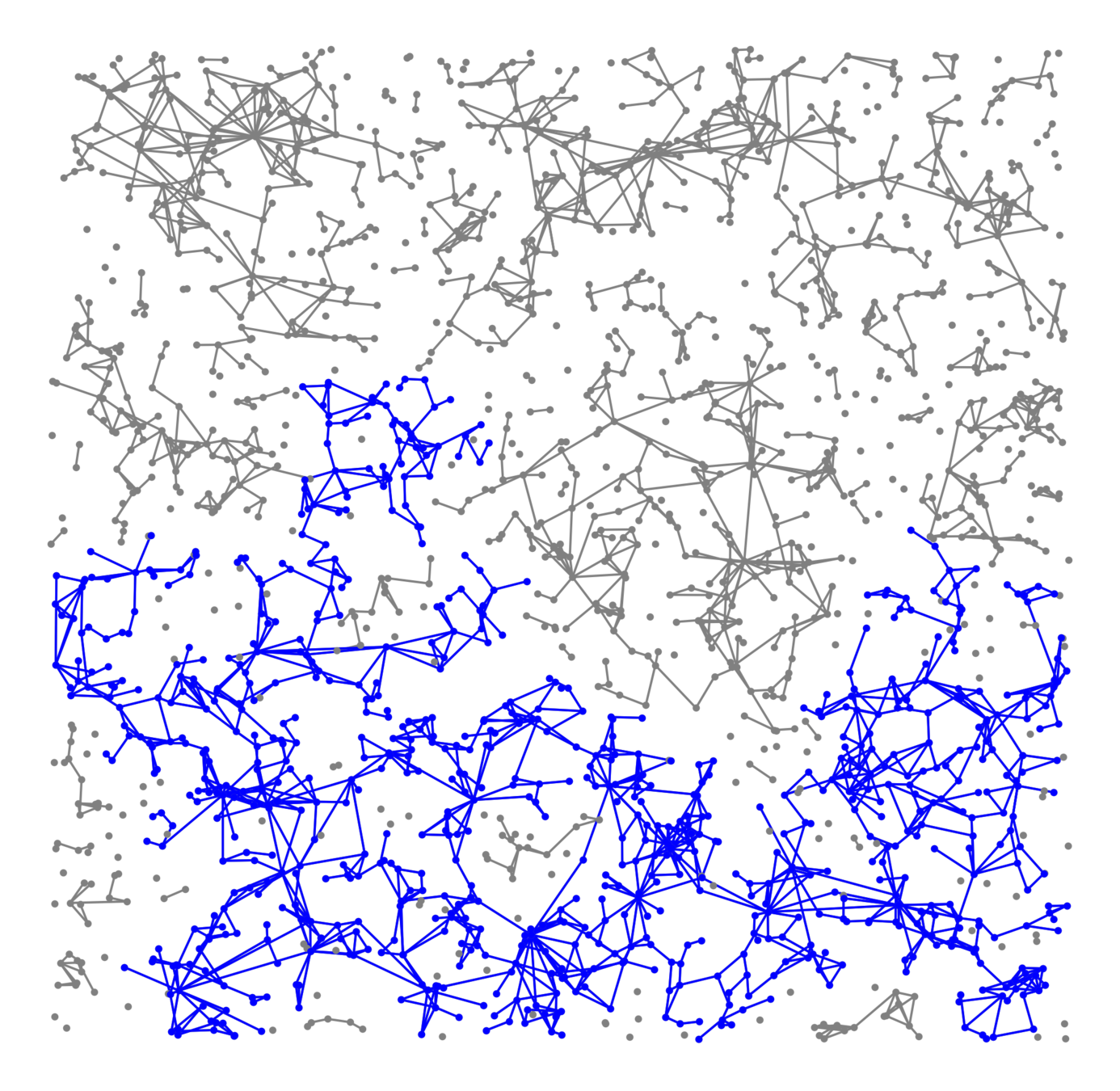





Supercritical scaling exponent \(\zeta\)
- Cluster-size decay: $$\mathbb{P}\big(k\le |\mathcal{C}(0)|<\infty\big)= \exp\big(-\Theta(k^{\mathbf{\zeta}})\big);$$
- Second-largest component: $$|\mathcal{C}_n^{(2)}|=\Theta\big((\log(n))^{1/\zeta}\big).$$




[Alexander & Chayes & Chayes '90, Grimmett (& Marstrand),
Kesten & Zhang '90,
...,
Lichev, Lodewijks, Mitsche, Schapira '22,
Penrose '05]
[Sly & Crawford'12]
[Kiwi & Mitsche '17]
When \(\tau>2\), there exists \(\zeta\in(0,1)\) s.t.



Supercritical scaling exponent \(\zeta\)
- Cluster-size decay: $$\mathbb{P}\big(k\le |\mathcal{C}(0)|<\infty\big)= \exp\big(-\Theta(k^{\mathbf{\zeta}})\big);$$
- Second-largest component: $$|\mathcal{C}_n^{(2)}|=\Theta\big((\log(n))^{1/\zeta}\big).$$
When \(\tau>2\), there exists \(\zeta\in(0,1)\) s.t.


Only four possible values




Phase diagram of \(\zeta\)
- Cluster-size decay: $$\mathbb{P}\big(k\le |\mathcal{C}(0)|<\infty\big)= \exp\big(-\Theta(k^{\mathbf{\zeta}})\big);$$
- Second-largest component: $$|\mathcal{C}_n^{(2)}|=\Theta\big((\log(n))^{1/\zeta}\big).$$
When \(\tau>2\), there exists \(\zeta\in(0,1)\) s.t.


Only four possible values
Conjecture "almost" proven [JKM'22+]
\(d=1\): \(\qquad\zeta_\mathrm{nn}>\max\{\zeta_\mathrm{ll}, \zeta_\mathrm{lh}, \zeta_\mathrm{hh}\}\quad \Longrightarrow\quad \)subcritical
If \(\zeta_\mathrm{nn}\) is the unique maximum of \(Z\), \(d>1\):
[Gracar, Mönch, Lüchtrath '22]
Consider supercritical interpolating model, \(\sigma\le\tau-1\).
- Cluster-size decay: $$\mathbb{P}\big(k\le |\mathcal{C}(0)|<\infty\big)\sim \exp\big(-\Theta(k^{\max(Z)})\big);$$
- Second-largest component: $$|\mathcal{C}_n^{(2)}|\sim\Theta\big((\log(n))^{1/\max(Z)}\big).$$
If \(\zeta_\mathrm{nn}\) is not the unique maximum of \(Z:=\{\zeta_\mathrm{ll}, \zeta_\mathrm{lh}, \zeta_\mathrm{hh}, \zeta_\mathrm{nn}\}\):
- Always lower bound;
- Upper bound: no weights, high edge-density \(\beta\gg\beta_c\).
Gap: Monotonicity of \(\zeta\)




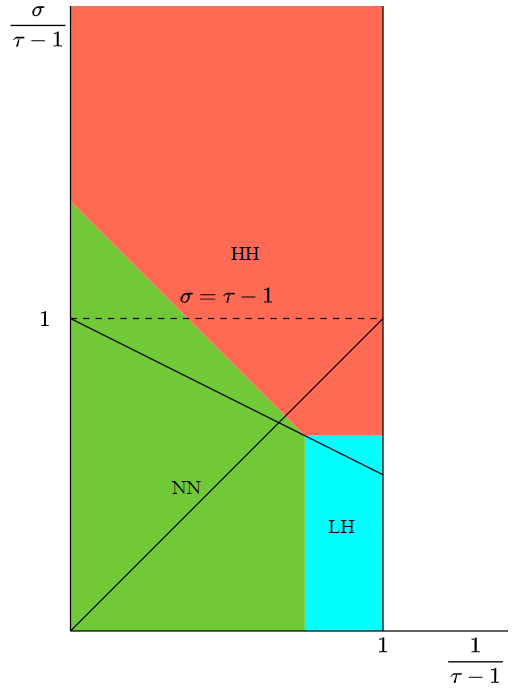
$$d=2\\\alpha=1.6$$
Proof strategy: 4 steps
(2)
(4)
(1)
(3)
(1)
(3)
Lower bounds
Upper bounds
Lower bounds: an isolated component
Aim: Find minimal \(\zeta\) s.t.
Isolation events
- \(\mathcal{C}(0)\ge k\) in \(\Theta(k)\)-volume box,
-
\(\Theta(k)\)-volume box disconnected:
- Empty boundary
- High-weight vertices are dangerous
- Especially close to boundary
- No edges
- Trade-off \(\gamma\)








Lower bounds: an isolated component
Aim: Find minimal \(\zeta\) s.t.
Isolation costs (vertices)



Lower bounds: an isolated component
Aim: Find minimal \(\zeta\) s.t.
Isolation costs (edges)



Isolation costs (edges)
Possible optimizers




Minimizing \(\zeta\)



Edges, vertices

Aim: Find minimal \(\zeta\) s.t.
Lower bound wrap-up

Conclusion:
Aim: Find minimal \(\zeta\) s.t.







nn
ll
lh
hh
Thank you!

Consider supercritical interpolating model, \(\sigma\le\tau-1\).
If \(\zeta_\mathrm{nn}\) is not the unique maximum of \(Z:=\{\zeta_\mathrm{ll}, \zeta_\mathrm{lh}, \zeta_\mathrm{hh}, \zeta_\mathrm{nn}\}\)
- Cluster-size decay: $$\mathbb{P}\big(k\le |\mathcal{C}(0)|<\infty\big)\sim \exp\big(-\Theta(k^{\max(Z)})\big);$$
- Second-largest component: $$|\mathcal{C}_n^{(2)}|\sim\Theta\big((\log(n))^{1/\max(Z)}\big).$$
If \(\zeta_\mathrm{nn}\) is the unique maximum of \(Z\), \(d>1\):
- Always lower bound;
- Upper bound: no weights, high edge-density \(\beta\gg\beta_c\).
Upper bound: second-largest component
Reveal graph in stages.
-
Form "backbone"
with "\((k^{\gamma_1}, k^{\gamma_2})\)"-edges of length \(k^{1/d}\). - Merge all large components with backbone with edges of length \(k^{1/d}\).




Three techniques: \(\zeta_\mathrm{ll}, \zeta_\mathrm{lh}\), and \(\zeta_\mathrm{hh}\):
No control short edges/local geometry:
no upper bound (nn)
Prevent too large components
Consider supercritical interpolating model, \(\sigma\le\tau-1\).
If \(\zeta_\mathrm{nn}\) is not the unique maximum of \(Z:=\{\zeta_\mathrm{ll}, \zeta_\mathrm{lh}, \zeta_\mathrm{hh}, \zeta_\mathrm{nn}\}\)
- Cluster-size decay: $$\mathbb{P}\big(k\le |\mathcal{C}(0)|<\infty\big)\sim \exp\big(-\Theta(k^{\max(Z)})\big);$$
- Second-largest component: $$|\mathcal{C}_n^{(2)}|\sim\Theta\big((\log(n))^{1/\max(Z)}\big).$$
If \(\zeta_\mathrm{nn}\) is the unique maximum of \(Z\), \(d>1\):
- Always lower bound;
- Upper bound: no weights, high edge-density \(\beta\gg\beta_c\).

\(\zeta_\mathrm{ll}=2-\alpha, \qquad \zeta_\mathrm{lh}=\frac{\tau-1}{\alpha}-(\tau-2), \qquad \zeta_\mathrm{hh}=\frac{3-\tau}{2-(\tau-1)/\alpha}, \qquad \zeta_\mathrm{nn}=\frac{d-1}d\)
Upper bounds
Aim: Maximize \(\zeta\) s.t.
When \(n\le\exp\big(-\tfrac12k^{\zeta}\big)\)
When \(k=k_n=(2\log(n))^{1/\zeta}\)
Upper bound: second-largest component
Reveal graph in stages.
-
Form "backbone"
with "\((k^{\gamma_1}, k^{\gamma_2})\)"-edges of length \(k^{1/d}\). - Merge all large components with backbone.




Three techniques: \(\zeta_\mathrm{ll}, \zeta_\mathrm{lh}\), and \(\zeta_\mathrm{hh}\):
No control short edges/local geometry:
no upper bound (nn)
Lower bounds: an isolated component
Aim: Find minimal \(\zeta\) s.t.
Isolation costs (edges)



Isolation costs (edges)
Possible optimizers



