Python Programming
Class 5
NumPy (short for Numerical Python) provides an efficient interface to store and operate on dense data buffers.

-
Benefits:
- Efficient storage
- Data operations
Arrays from Scratch
Note: unlike Python lists, NumPy is constrained to arrays that all contain the same type. If types do not match, NumPy will upcast if possible (here, integers are upcast to floating point):
#Creating Arrays from Python Lists
array1 = np.array([1, 4, 2, 5, 3])
array2 = np.array([3.14, 4, 2, 3])
array3 = np.array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]])
array4 = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4], dtype='float32')Functions to create arrays
#Numpy also provides many functions to create arrays:
a = np.zeros((2,2)) # Array of all zeros
b = np.ones((1,2)) # Array of all ones
c = np.full((2,2), 7) # Constant array
d = np.eye(2) # Create a 2x2 identity matrix
e = np.random.random((2,2)) # Array filled with random values
Attributes of arrays
np.random.seed(0) # seed for reproducibility
x1 = np.random.randint(10, size=6) # One-dimensional array
x2 = np.random.randint(10, size=(3, 4)) # Two-dimensional array
x3 = np.random.randint(10, size=(3, 4, 5)) # Three-dimensional array
print("x3 ndim: ", x3.ndim)
print("x3 shape:", x3.shape)
print("x3 size: ", x3.size)Indexing of arrays
Getting and setting the value of individual array elements
x[start:stop:step]
- If any of these are unspecified, they default to the values start=0, stop=size of dimension, step=1.
-
see examples
One-dimensional subarrays
#One dimentional
x1
x1[0]
x1[4]
x2[0, 0] = 12
#Note
x1[0] = 3.14159 # this will be truncated!x1
x1[:5] # first five elements
x1[5:] # elements after index 5
x1[4:7] # middle subarray
x1[::2]
x1[::]
Multidimensional subarrays
#Multi dimentional
x2
x2[:2, :3] # two rows, three column
x2[:3, ::2] # all rows, every other column
x2[0, :] # first row of x2
x2[0, :]
x2[0, ::]
x2[0, 0:4:1]Accessing array rows and columns
x2[:, 0] #first column of x2
One commonly needed routine is accessing single rows or columns of an array. You can do this by combining indexing and slicing, using an empty slice marked by a single colon (:):
Subarrays as no-copy views
One important —and extremely useful— thing to know about array slices is that they return views rather than copies of the array data.
This is one area in which NumPy array slicing differs from Python list slicing: in lists, slices will be copies.
x2
x2_sub = x2[:2, :2]
x2_sub[0, 0] = 99Creating copies of arrays
x2_sub_copy = x2[:2, :2].copy()
x2_sub_copy[0, 0] = 42
x2Joining arrays
x = np.array([1, 2, 3])
y = np.array([3, 2, 1])
z = np.concatenate([x, y]) #concatenate
z = np.hstack([x, y]) #hstack
z = np.vstack([x, y]) #vstackVectorized operations
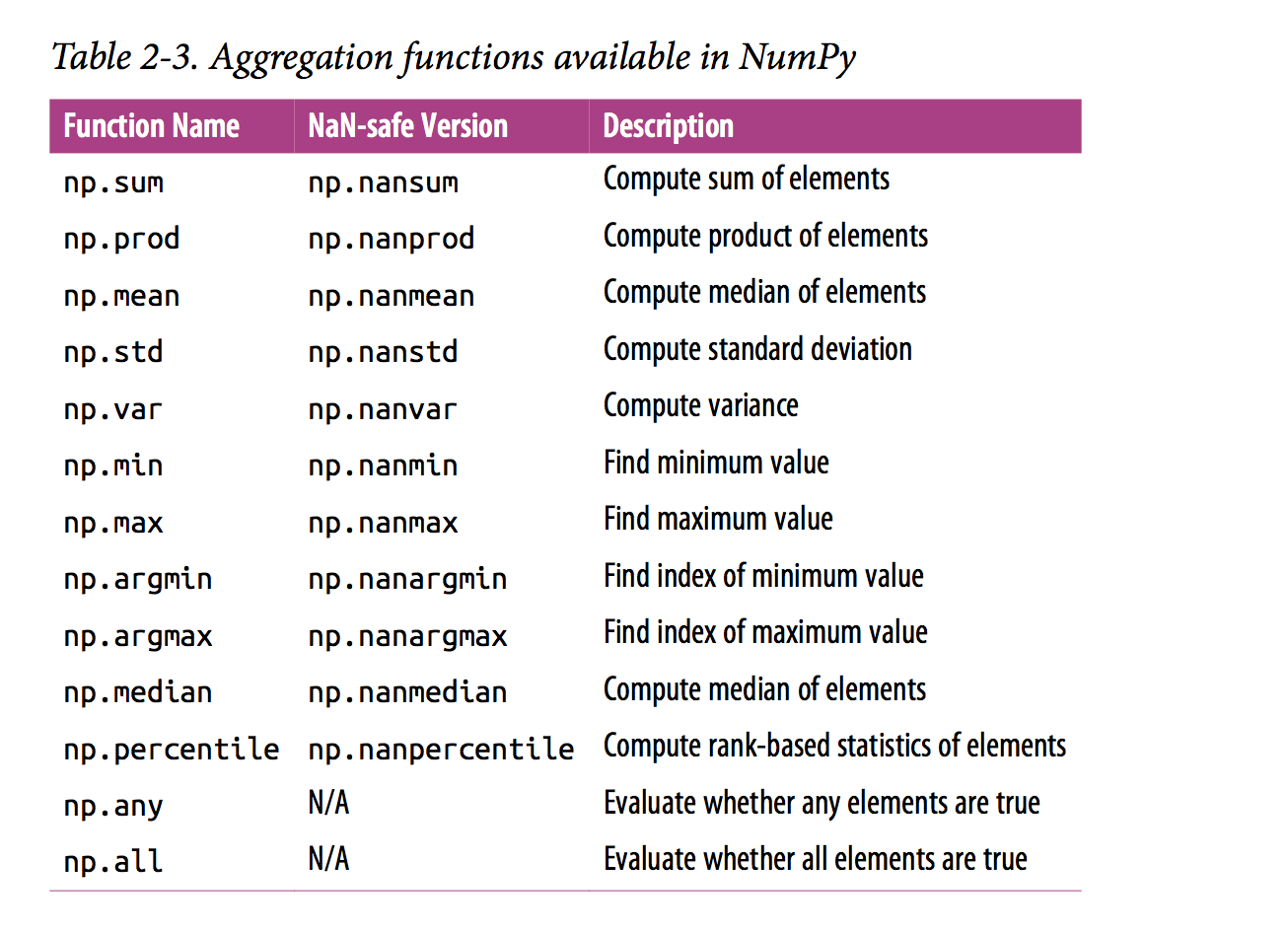
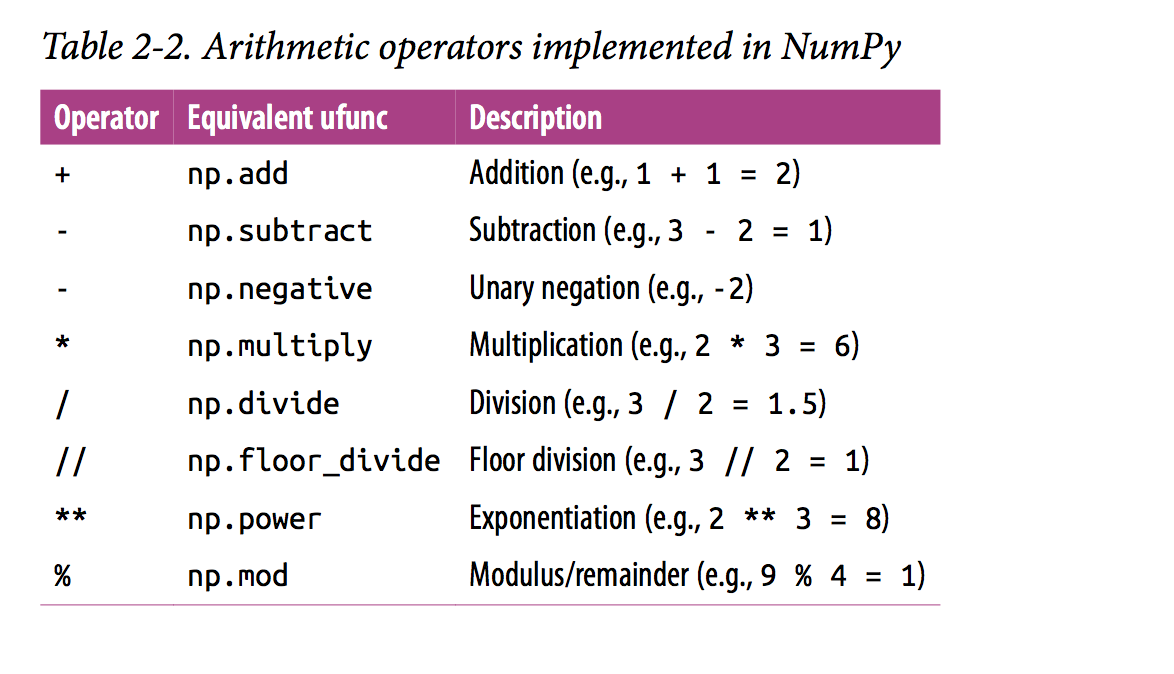
-
see examples
Challenge 1
Average is 4.413
Variance is 8.216431
Standard deviation is 2.86643175394Write a Python script to create a random array with 1000 elements (each element in range [0,10) ) and
compute the average, variance, standard deviation of the array elements.
Note: use 1 as random seed.
Documentation: https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy-1.13.0/reference/generated/numpy.random.randint.html
Answer 1
import numpy as np
np.random.seed(1)
random_array = np.random.randint(10, size=(1000,1))
print('Average is ' + str(np.average(random_array)))
print('Variance is ' + str(np.var(random_array)))
print('Standard deviation is '+ str(np.std(random_array)))Challenge 2
Maximum value is: 97
Index of Maximum value is: 3Write a Python script that:
- Create two random matrices of integers (each element in range [0,10), size =(3,4))
- Multiply matrices element wise and save result in new variable
- Sum each column and save array in new variable.
- Find maximum value of array
- Find maximum value index
Note: use 1 as random seed.
Answer 2
import numpy as np
#Create two random matrices of integers (max posible value 10, size = (3,4))
np.random.seed(1) # seed for reproducibility
a = np.random.randint(10, size=(3, 4)) # Two-dimensional array
c = np.random.randint(10, size=(3, 4))
#Multiply matrices element wise
d = np.multiply(a, c)
#Sum Columns
e = np.sum(d,axis=0)
#Fin maximum value
print('Maximum value is: '+str(np.max(e)))
#Find Maximun value index
print('Index of Maximum value is: '+str(np.argmax(e)))