Research & Science in Spain
10 years (2004-2014)
A personal bird's-eye overview
Jose María Alvarez Rodríguez
10th of September, 2014
Wroclaw, Poland
Disclaimer
The views and opinions expressed in this presentation are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of any public or private institution. Examples of analysis performed within this presentation are only examples. They should not be utilized in real-world analytic products as they are based only on the personal experience of the author and very limited and dated public open source information. Assumptions made within the analysis are not reflective of the position of any Spanish public or private institution.
Context
PhD procedure
Research Career
Academia & Industry
Intellectual property
The Context...
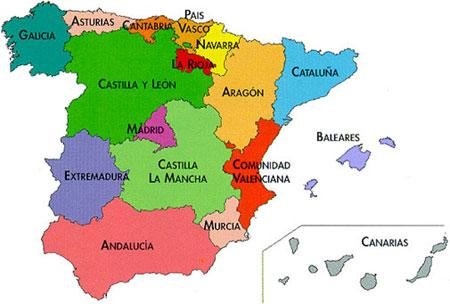
Geographical distribution
...and provinces
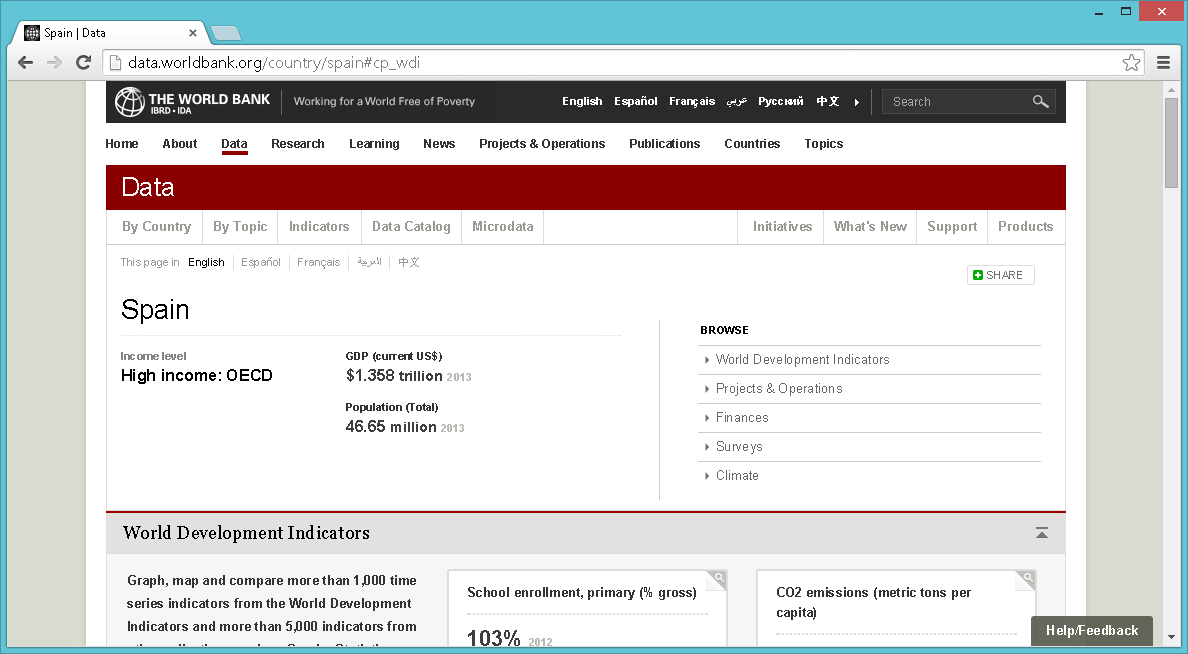
The Worldbank data
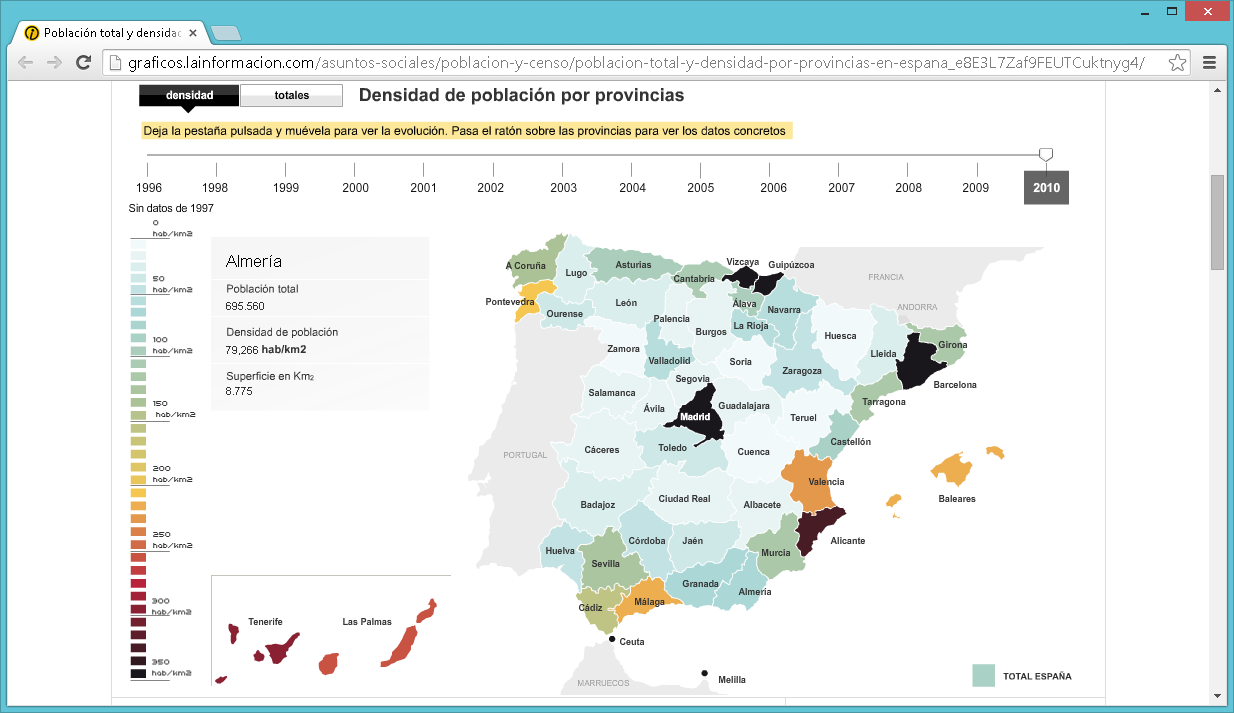
Demography
Summary...
- 17 regions
- 52 provinces + 2 "Autonomous" Cities (Melilla and Ceuta)
- +8000 municipalities...
- Too many governments (politicians)
- Everything everywhere
- Particular interests in every geographical entity
- Different rights and opportunities
- Taxes (e.g. Basque Country)
-
Transfer of:
- Education
- Health
- ...
Before...
- Primary Sector
- Agriculture, fishing, forestry and mining
- Secondary Sector
- Metal sector
- Textile
- Vehicle manufacturing
- Food industry
- Tertiary Sector
- Tourism
- ...
After...
- Primary Sector
- Agriculture & fishing
- Secondary Sector
- Metal sector
- Textile
- Food industry
- Electricity sector
- Construction
- Tertiary Sector
- Tourism
- ...
Join EU and industrial conversions...
Promises...
-
Industrial transformation
- Huge amounts of EU funds were spent...
-
Knowledge society with high...
- Education
- Quality jobs
- Incomes
- ...
but not enough for all Taifa territories


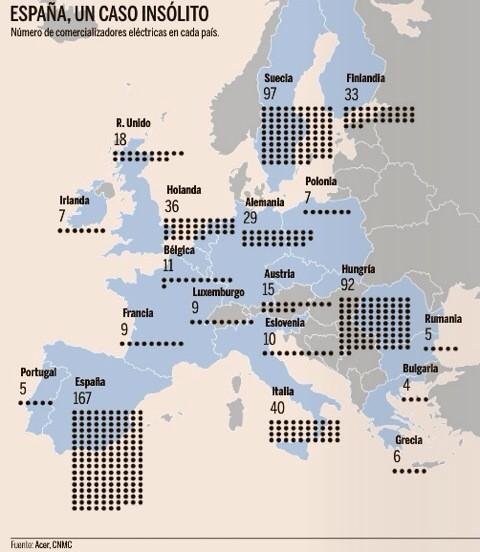

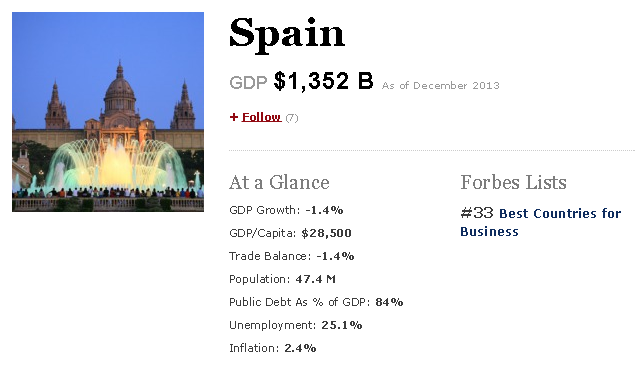
Macroeconomics...
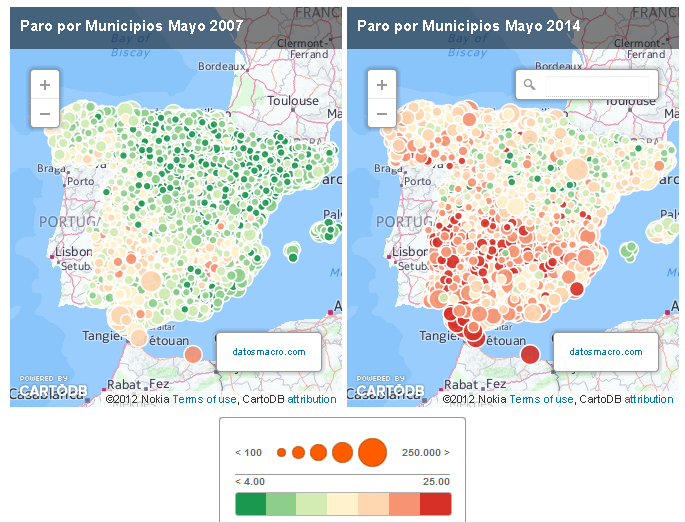
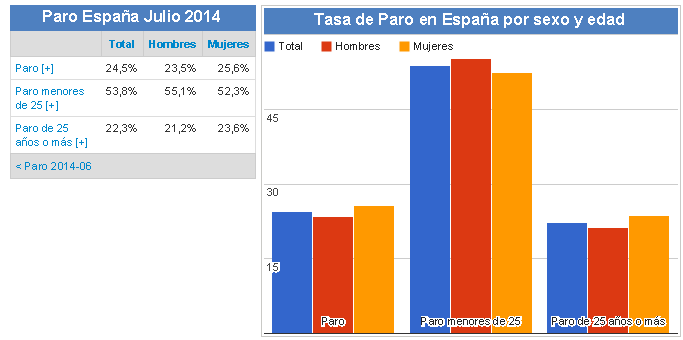
Unemployment
24.5% (July 2014)
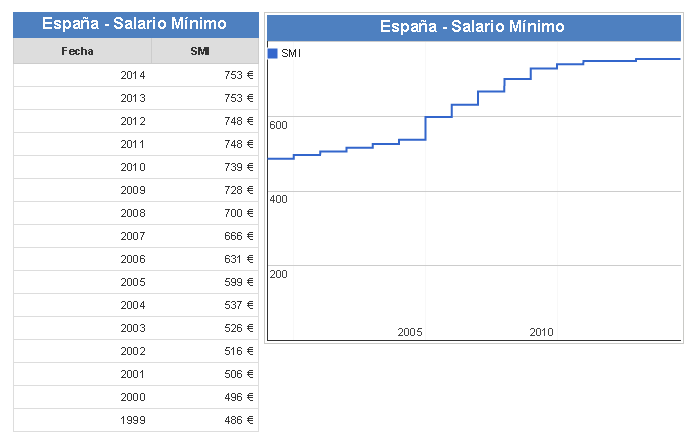
Minimum wage evolution...
The IBEX 35
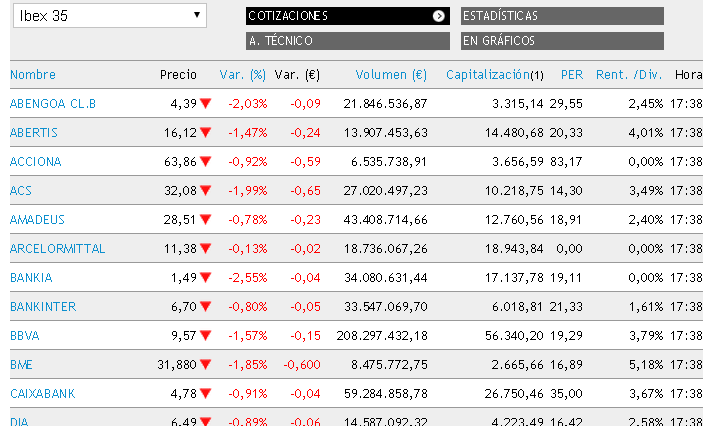
Banks, Construction, Food Industry and Telecommunications...
What Forbes says...

- Banks
- Food industry
- Telecommunications
Let's build a knowledge society
Universities, etc.
Map of Universities (81)...
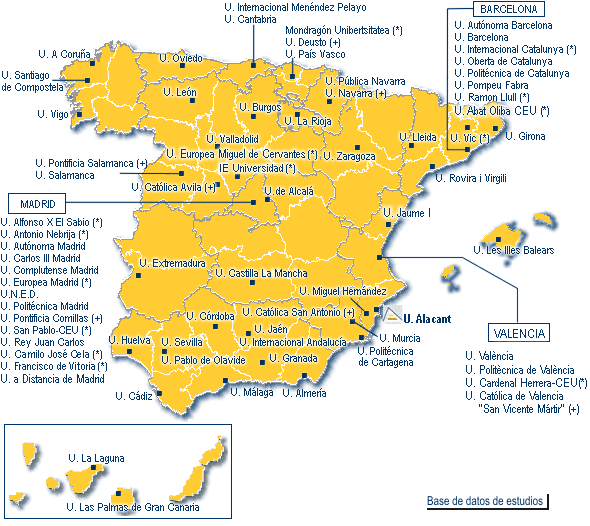
and now we have high-qualified people...
Where to allocate these people?
Strategy (2004-2010)
- Creation of the Ministry of Science
- To manage all research funds
- Creation of:
- Technological centers for every topic: ICT, Energy, Robotics, Bioinformatics, Biology, etc.
- Research infrastructures: HPC, etc.
- Research institutes (new and existing ones)
- Technological platforms...
- Programmes for hiring people with degrees, master or PhD
- Grants for PhD students, etc.
- Programmes for SMEs, LE, etc.
- ...
Some Keypoints
-
Move research to private institutions leaded by public institutions (university and government) and companies in the area
-
From the University to other institutions
-
Avoiding the lack of productivity of "civil servant" researchers
-
- Encourage R&D in companies (mainly SMEs)
- Boost innovation
- ...
CSIC (National Research Council) institutes
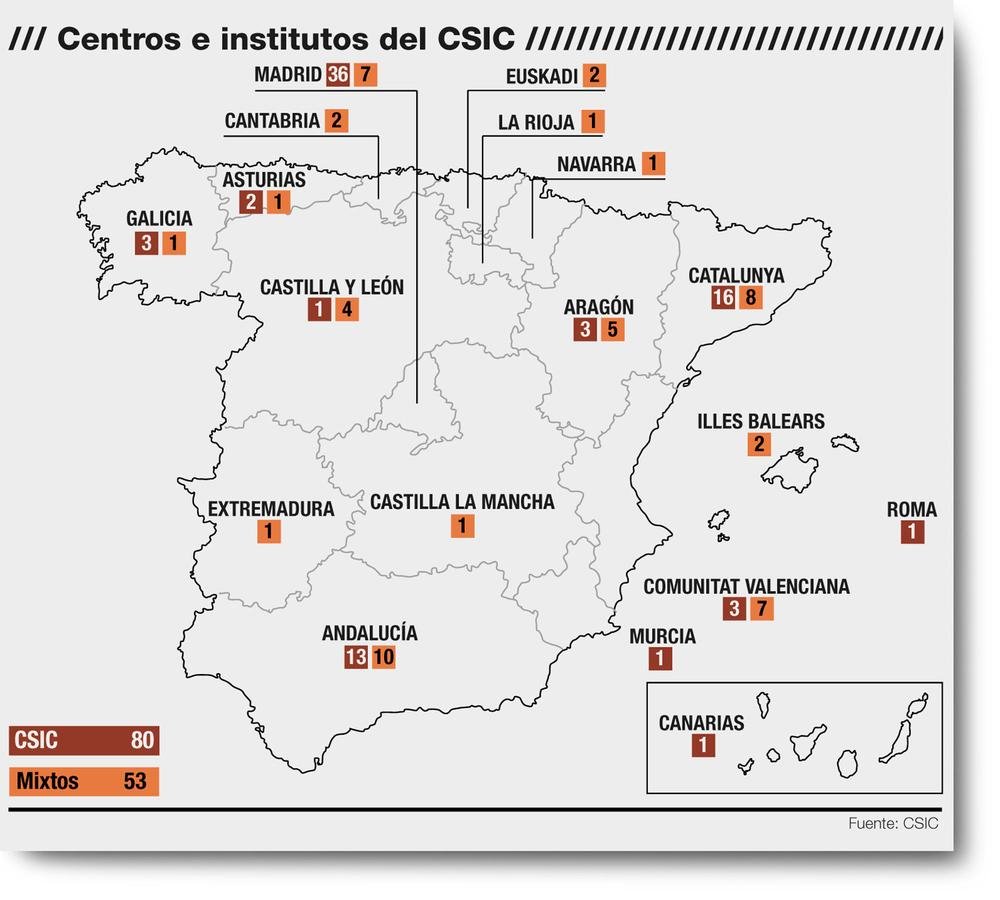
Research Infrastructures

Technological and ScienceParks
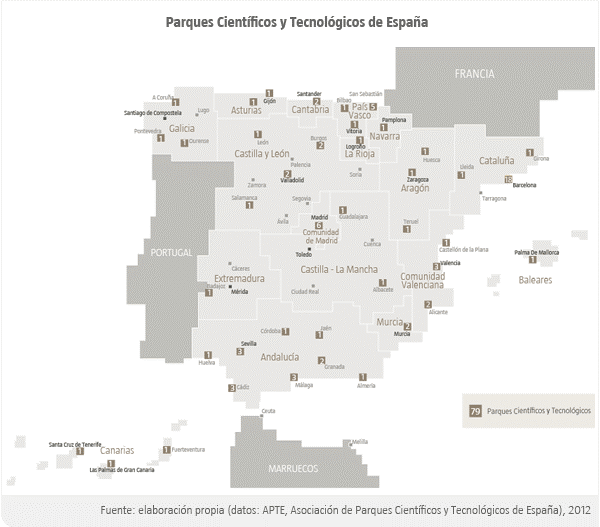
An example...Asturias
1 million people region
Primary and Secondary sectors (mining, industry, etc.)
1 University (old one, more than 400 years)
6 Research Institutes (from the University)
7 Public Research Institutes (CSIC)
3 Research Networks
12 Technological centers
2 Technological Parks
4 Company Incubators
...
At least...
+
- Boost research
- High quality jobs for high-qualified people
- Industry transformation
- Innovation for Companies
- Generation of Know-how, technology and new companies
-
Dissemination
- Publications
- ...
-
-
Most of managers were politicians
- High salaries out of the government control
- Some Universities lost research capabilities
-
Need of public funding to survive
- No business model behind
- Nº of Patents still low
- Common services replicated over and over
- ...*17 regions
But the crisis just appeared...
Renovation was required
Need of Efficiency
Optimize resources
....
Result 2010-2014
- Most of the research centers/institutes were merged
- Research is already in the public university
- Researchers that were moved to private institutions with high-incomes are again in the public sector
- High-qualified people cannot be allocated (emigration)
- Some European countries are taking advantage of hiring these people without paying the expenses of their education
- EU funds were completely spent
- Those institutions based on public funding were closed
- The Ministry of Science is now part of the Ministry of Economy...
*This is not to explain the high rate of unemployment since most of the current unemployed people are coming from the construction and other industrial sectors.
Strategy in the last 2-3 years...
- Boost entrepreneurship
- To retain high-qualified people
- To create technology-based companies
- To get private funding (business angels)
- To accomplish with the needs of large companies
- Telefónica, BBVA, etc.
-
Public research institutions have faced cuts
- No open (permanent) positions but it is expected to change in the next 2-4 years (I hope)
- Cuts in research programmes for companies
- Look for funding at international level
- Creation of special credit lines for companies
- But not very well-managed (Banks are involved in)
...
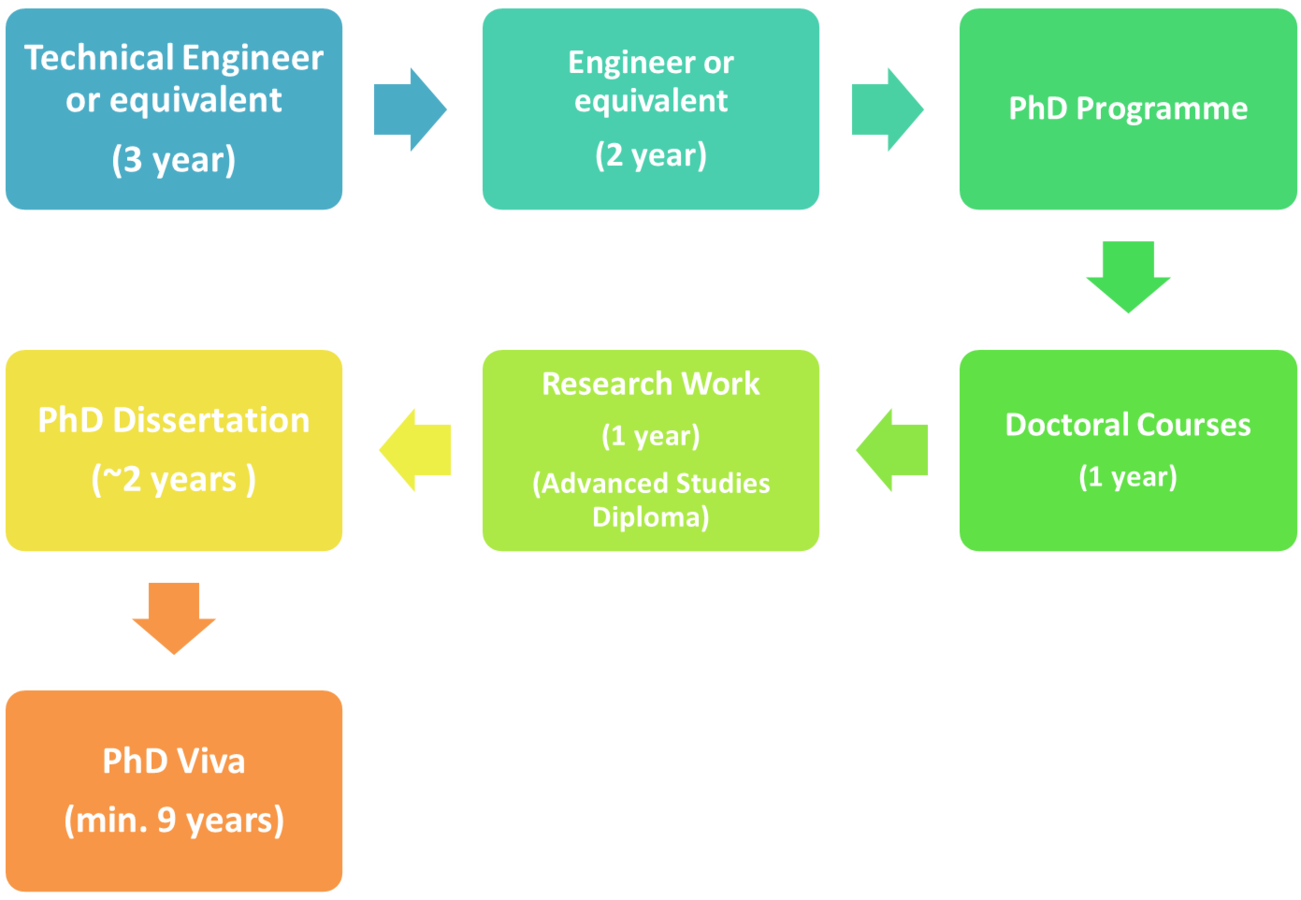
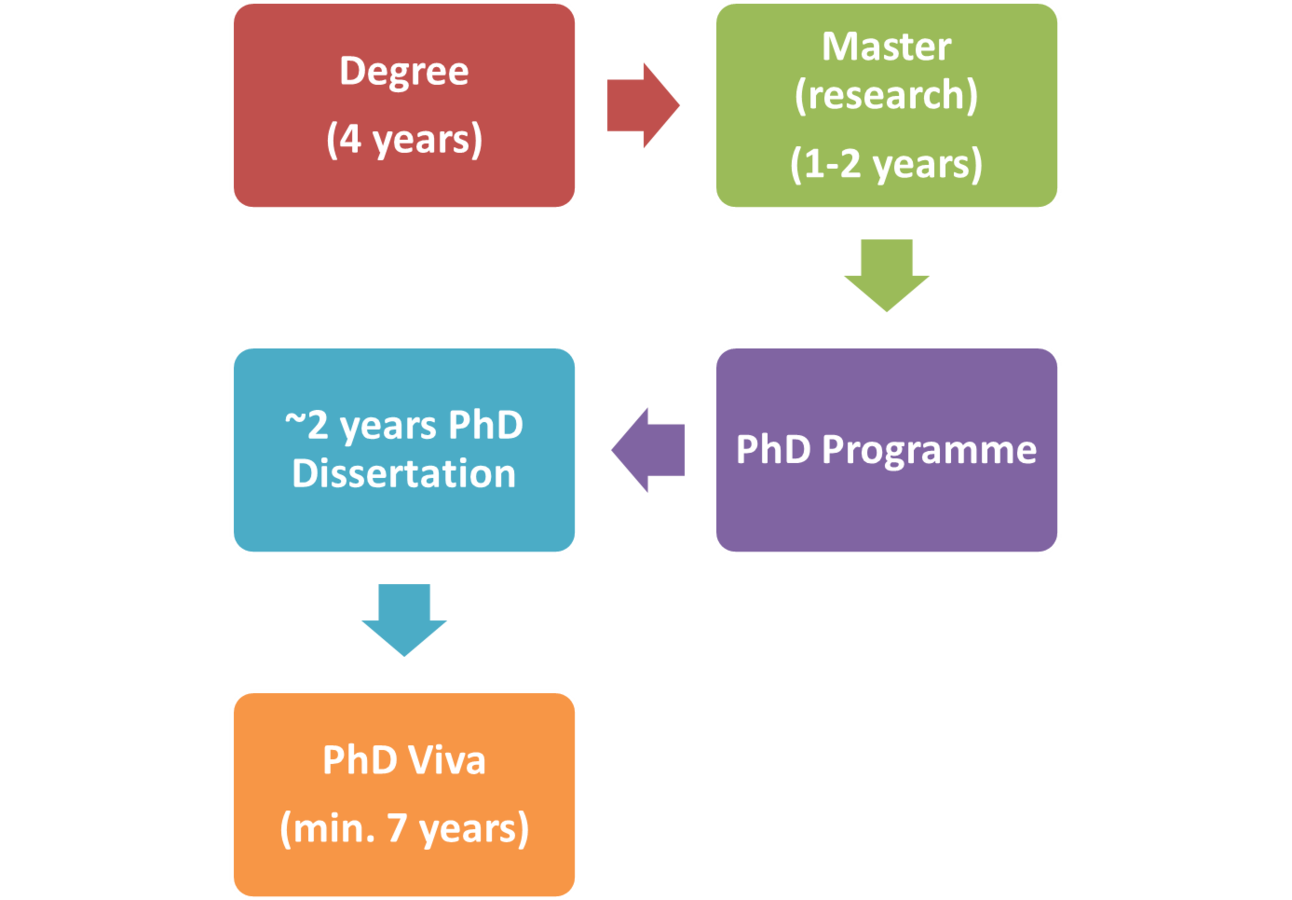
PhD procedure
How to make the PhD in Spain
PhD process and funding
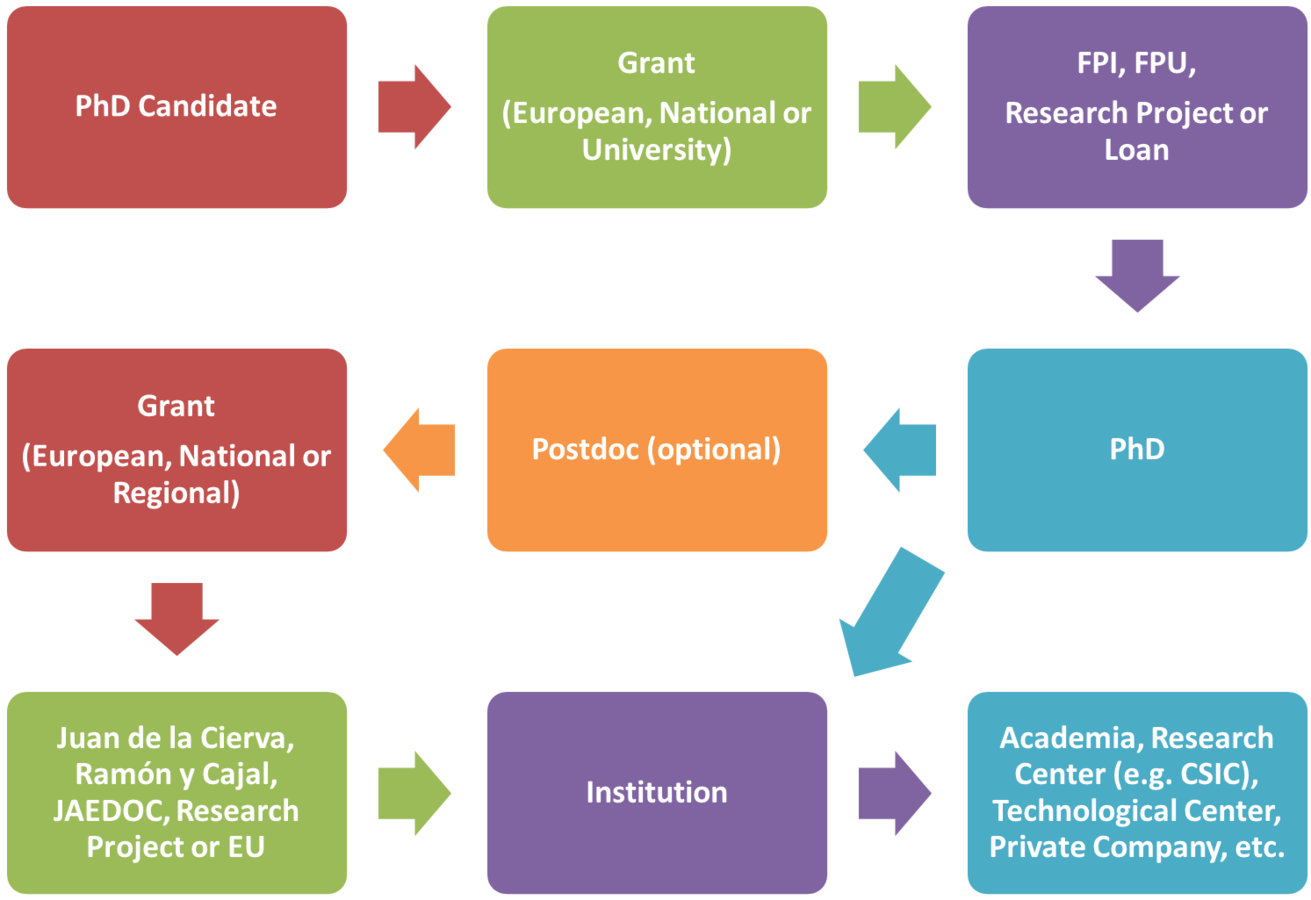
PhD "old" path (RD 1393/2007)
PhD "new" path
PhD process (traditional)...
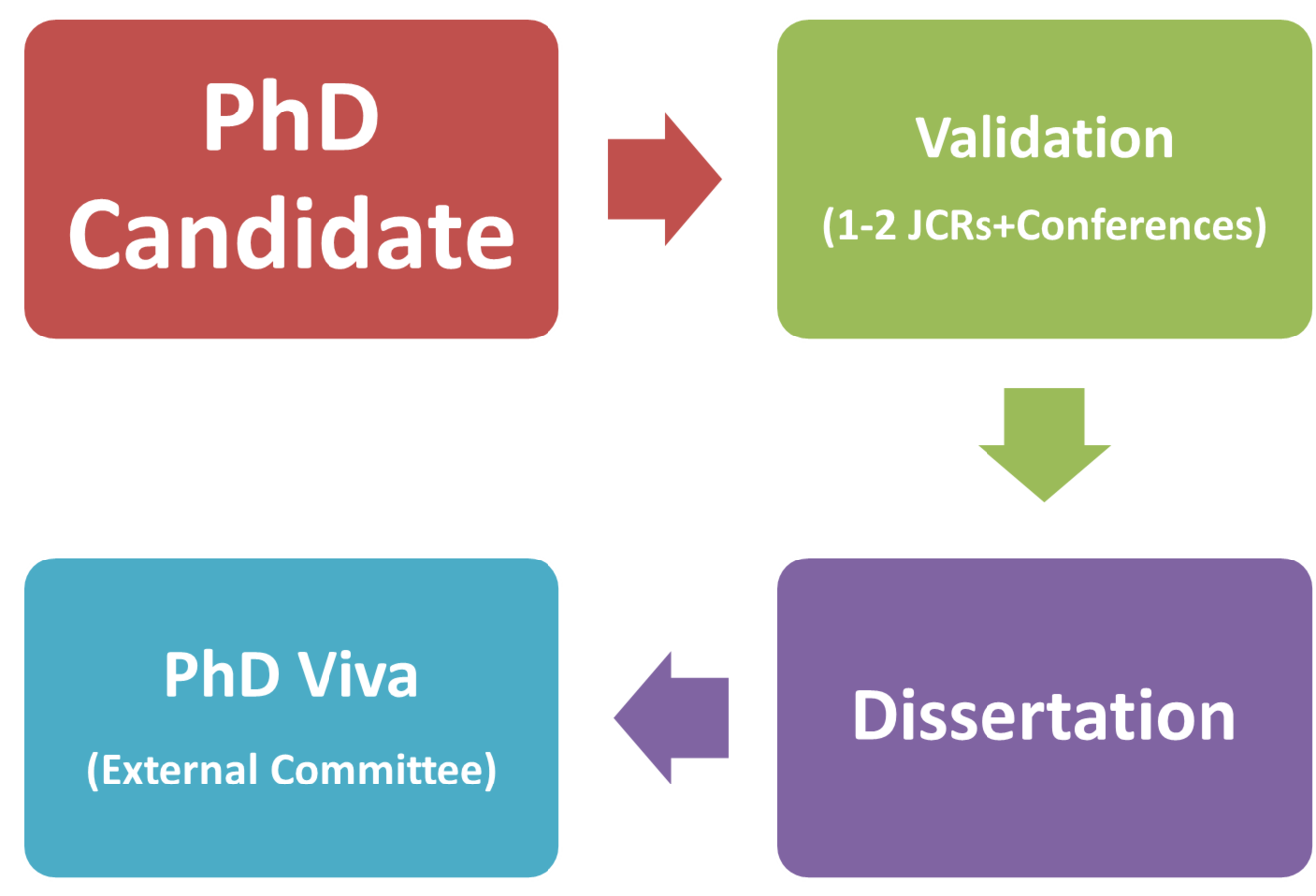
PhD process (alternative)...
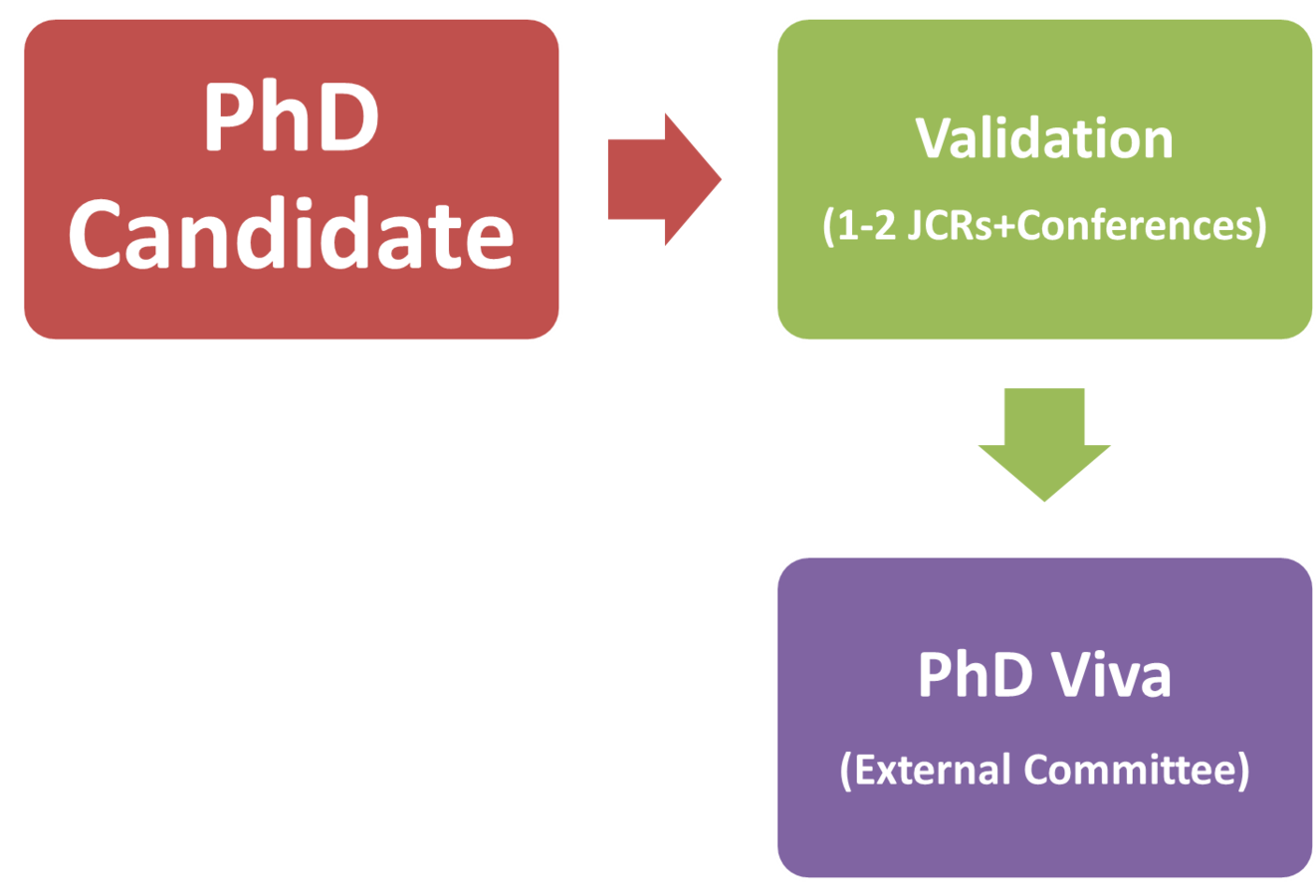
Research Career
Opportunities after the PhD
Possibilities
- Public
- Academia (becoming a Professor in the Public University)
-
Research career at CSIC (National Research Council)
- Research Institutes
- Private
- Technological Research Centers
- Research Institutes
- Companies with R&D departments
- Technology-based companies (entrepreneur)
- ...
ANECA
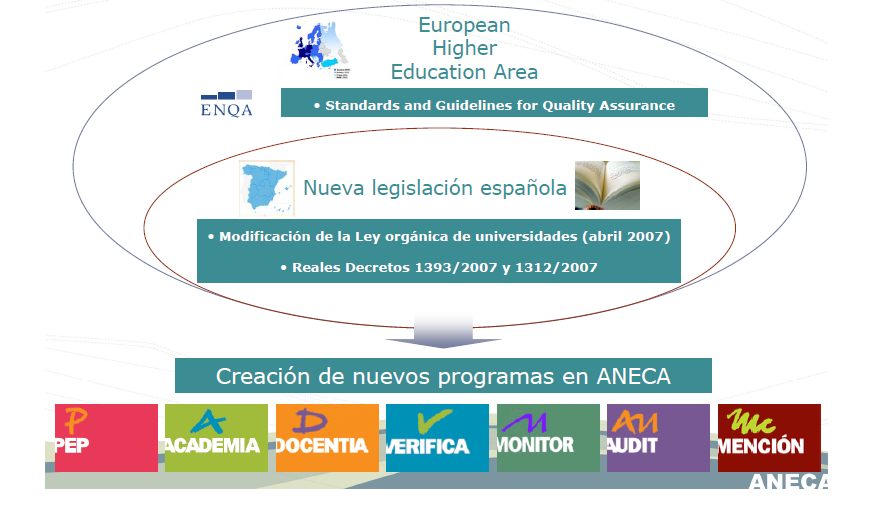
National Agency for Quality Assessement
Professor (categories)

How to become Professor...
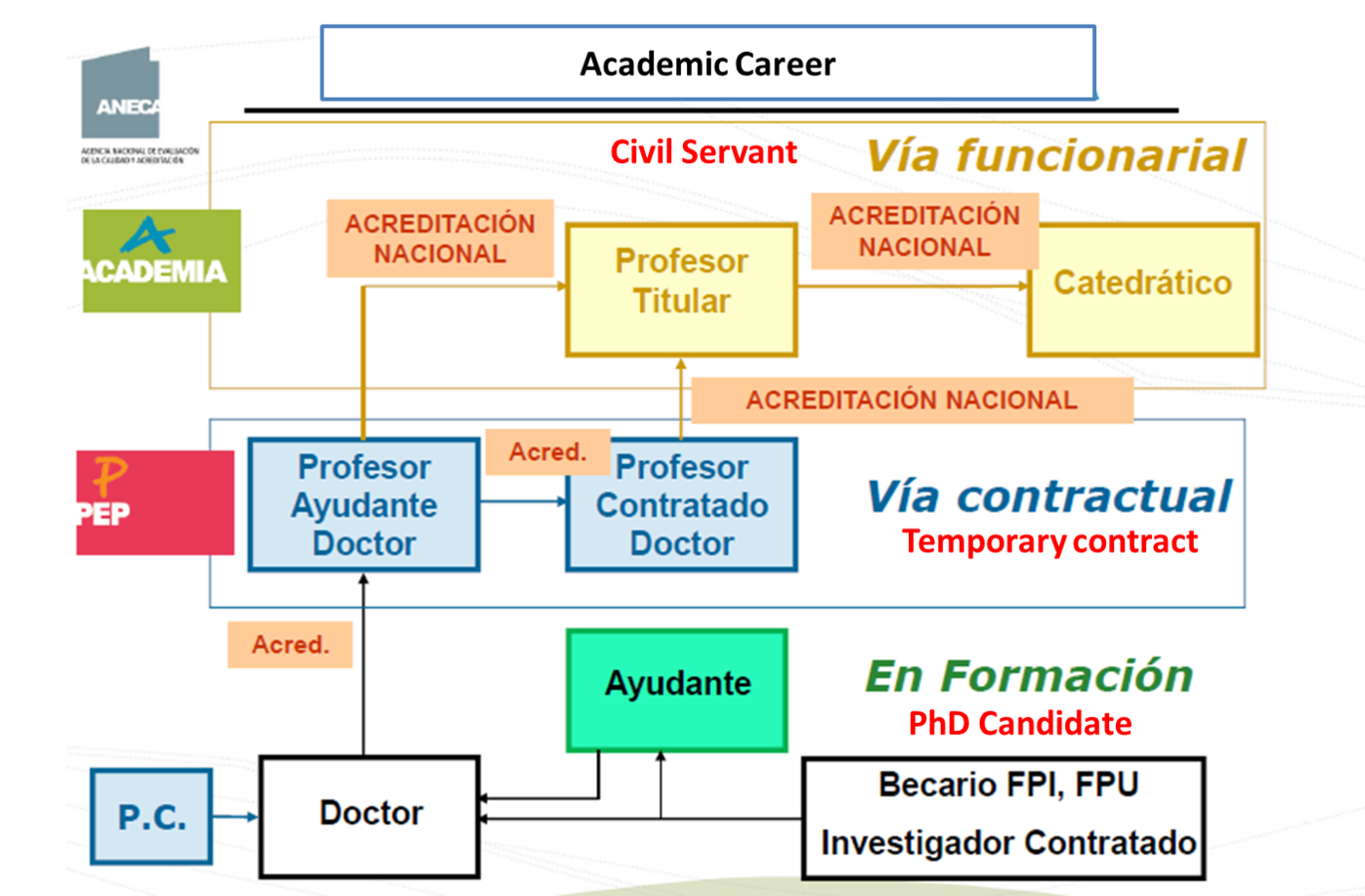
ANECA Process
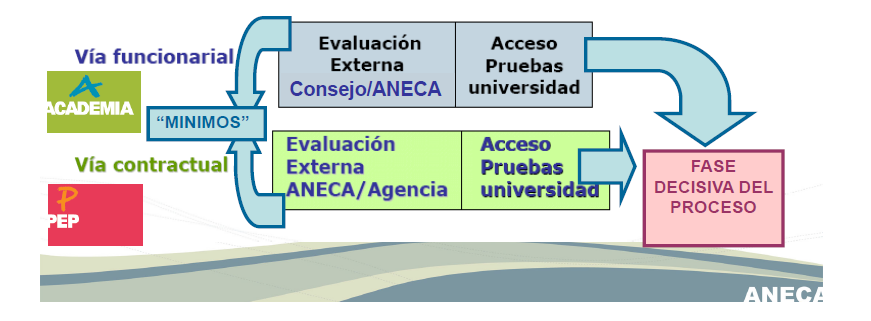
2 Ways
- Civil Servant (paid by the National Government)
- Temporary Contract (paid by the Regional Government)
2 Steps
-
Positive evaluation by ANECA
- Committee of experts, renew each 2 years
- Non-positive->penalty of 6 or 18 months
- Open positions and contest (managed by each university)
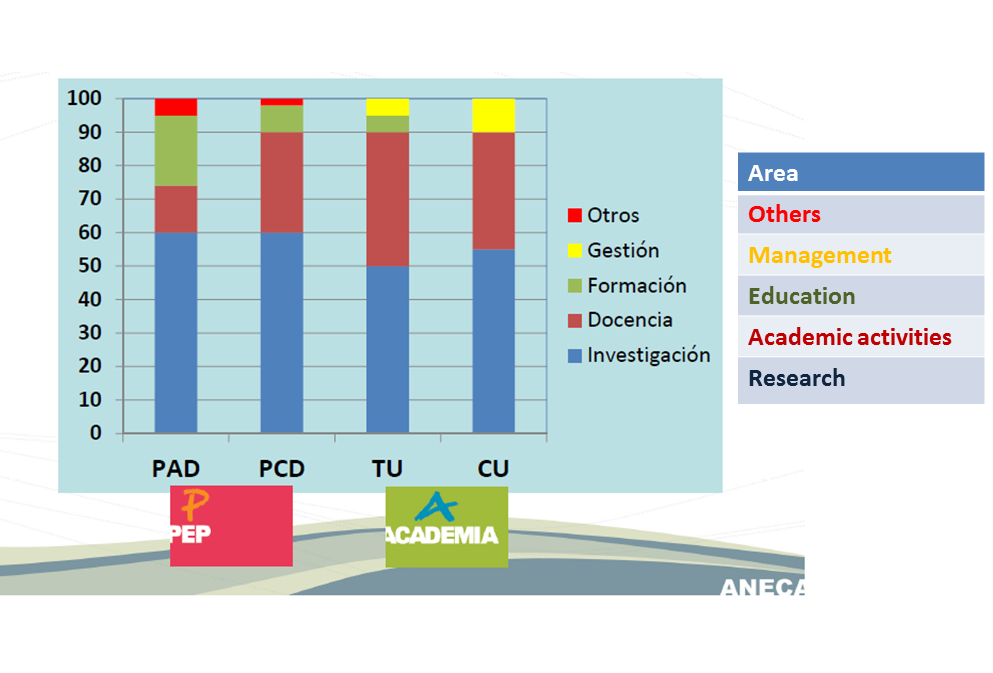
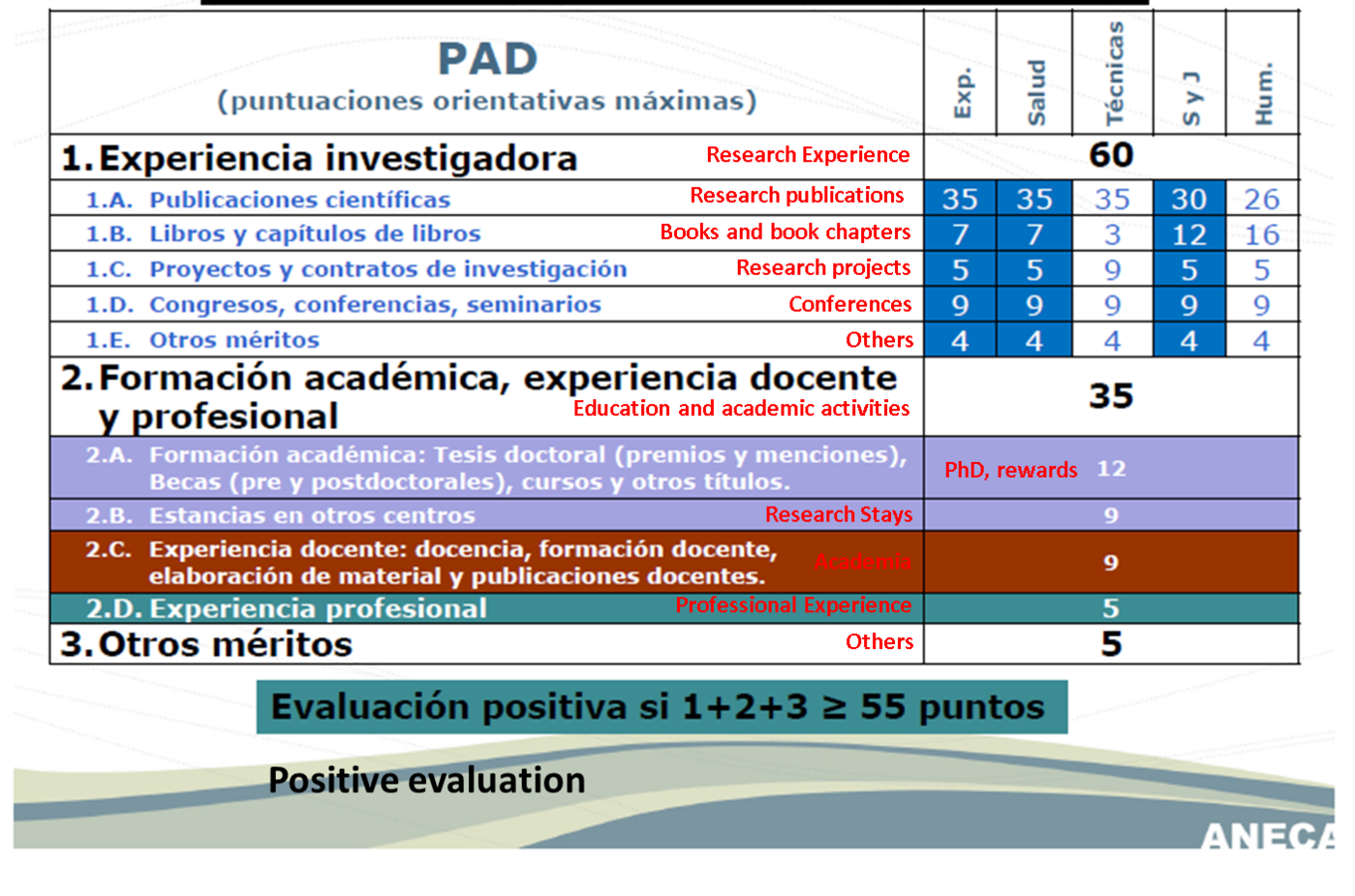
Criteria: Score per Category (I)
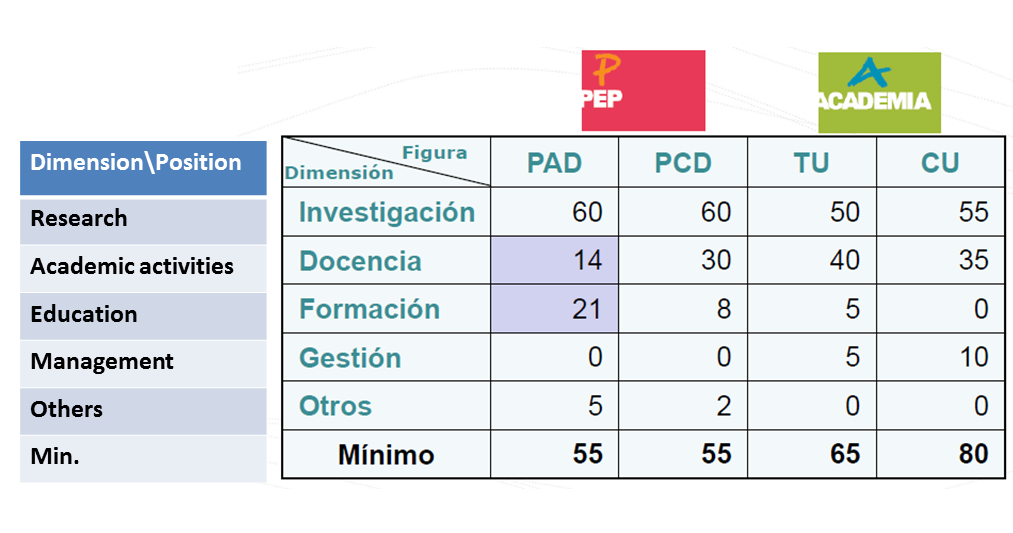
Criteria: Score per Category (II)
Assistant Professor
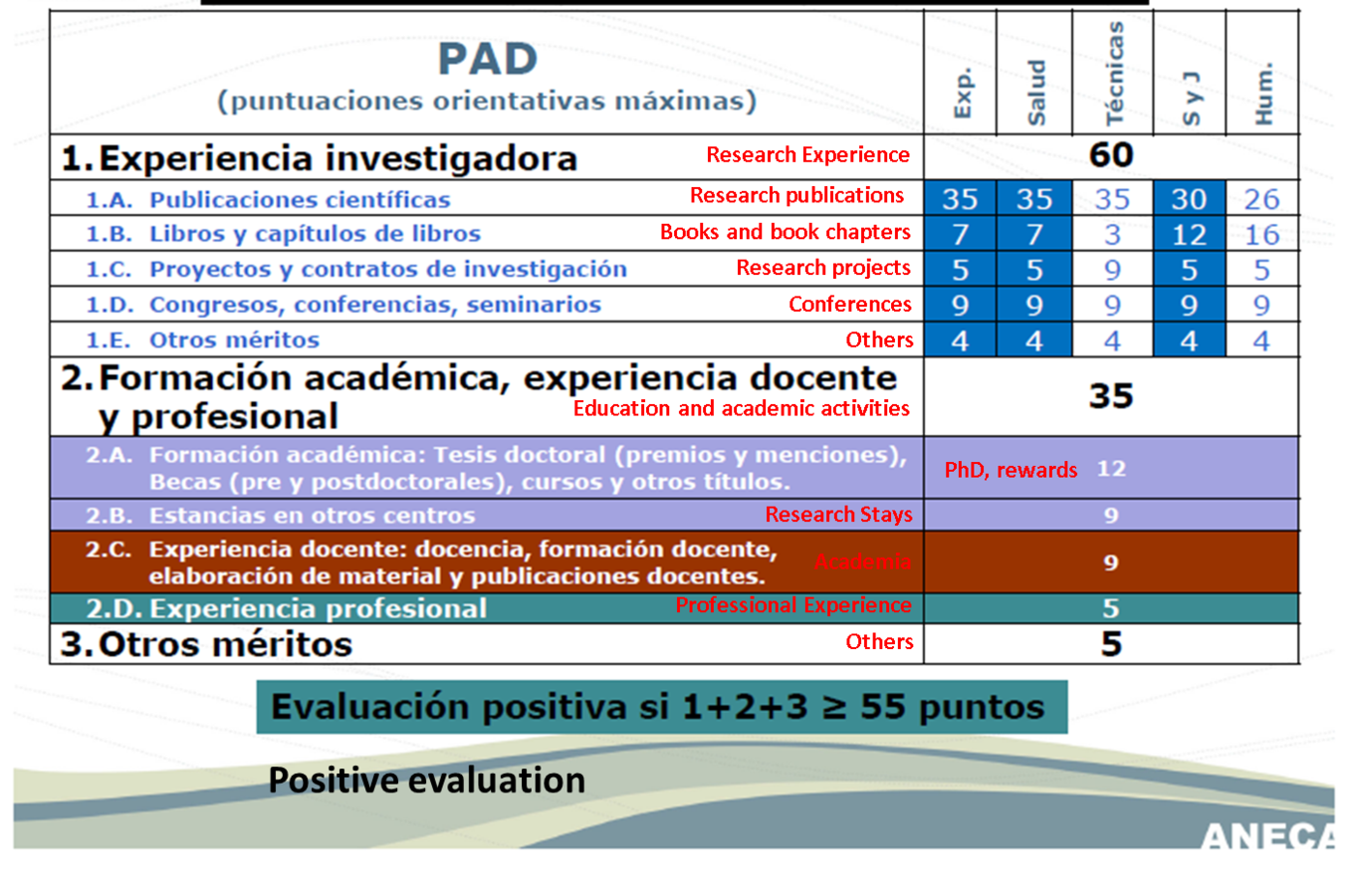
Assistant Professor
(Tenure Track)
Comparison
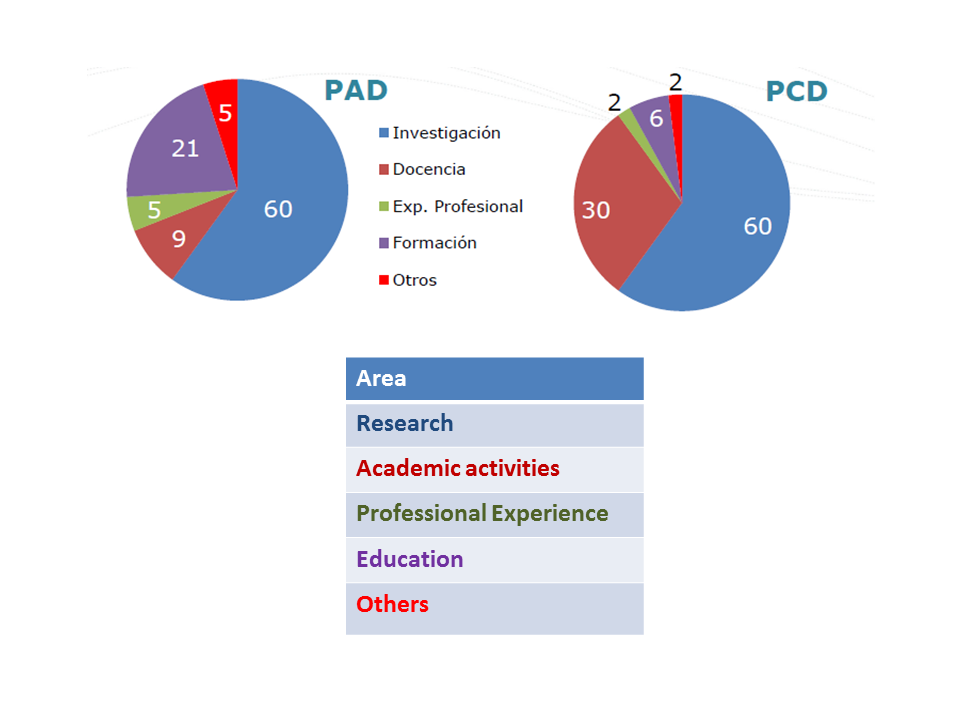
Non-Tenure
Tenure
Associate Professor vs
Full Professor
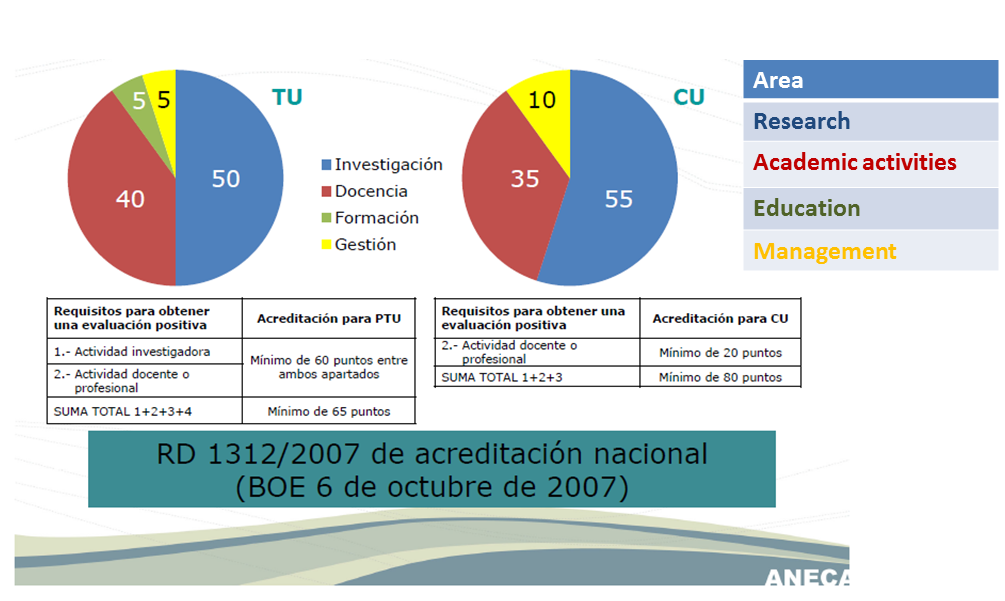
*6-year performance evaluation to get new rewards. E.g. less lectures, etc.
What others say...
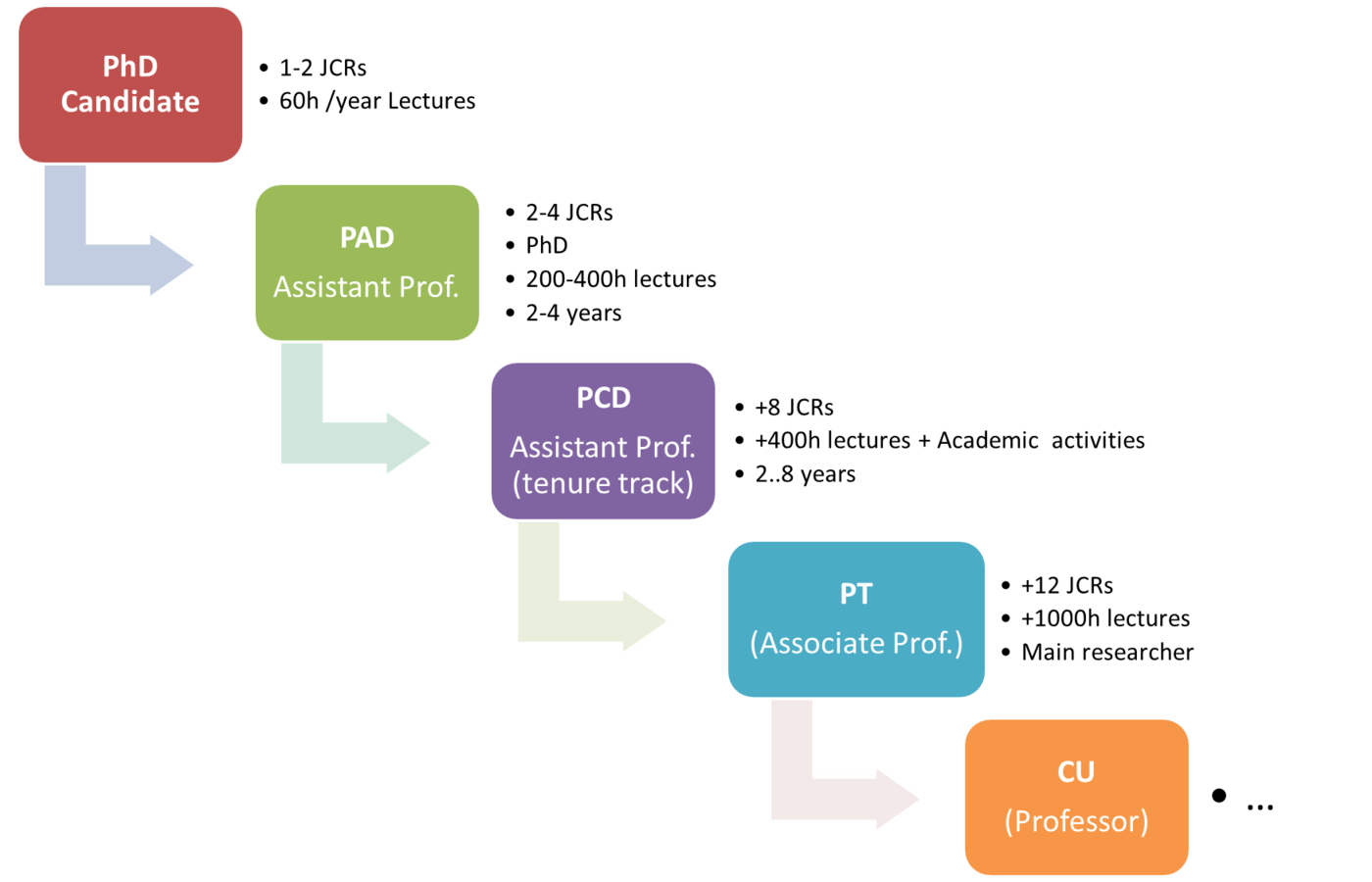
+ PhD Supervision
Some conclusions...
- ANECA is an intermediary organism to evaluate your performance
- Some criteria have been somehow hacked
- E.g. Research stays must be now about 3 months and with results (publications, etc.)
- The responsibility of hiring depends on each University
- Different criteria according to region, budget, etc.
- It is a long way to become Associate Professor...Be patient!
- Many people has now positive evaluation but positions are closed.
- ...
Academia & Industry
Collaboration and types of relationships
Typical relationship
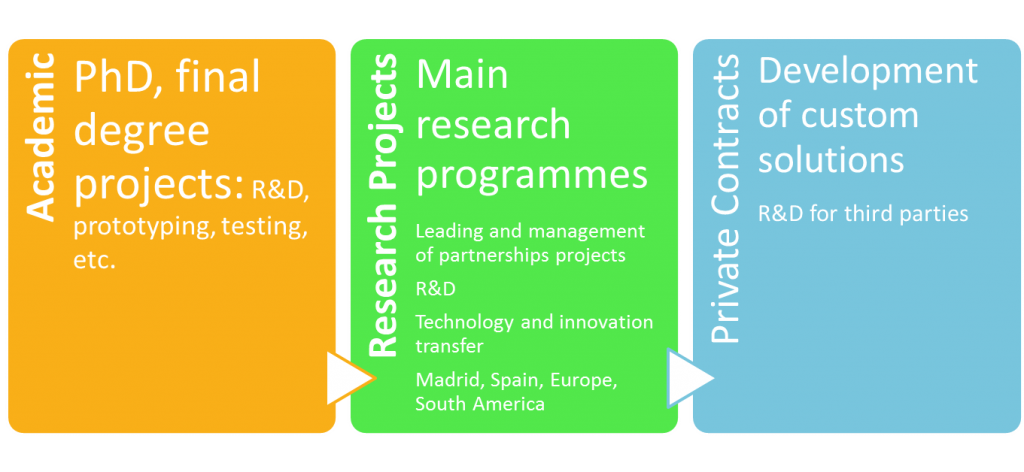
Keypoints
-
Most universities have created a particular service to support research activities
-
Technology transfer office (OTRI)
-
Preparation of project proposals
-
Intellectual and industrial rights management
-
Creation of technology-based companies (Incubators)
-
-
-
Most universities have also created an associated foundation (non-profit)
- to speed up the contracts without too much bureaucracy
-
Legal framework for making contracts
- A professor/university/foundation can sign a private contract
- Indirect costs (~20%) are preventing a more competitive public university
- ...
Research Project flow
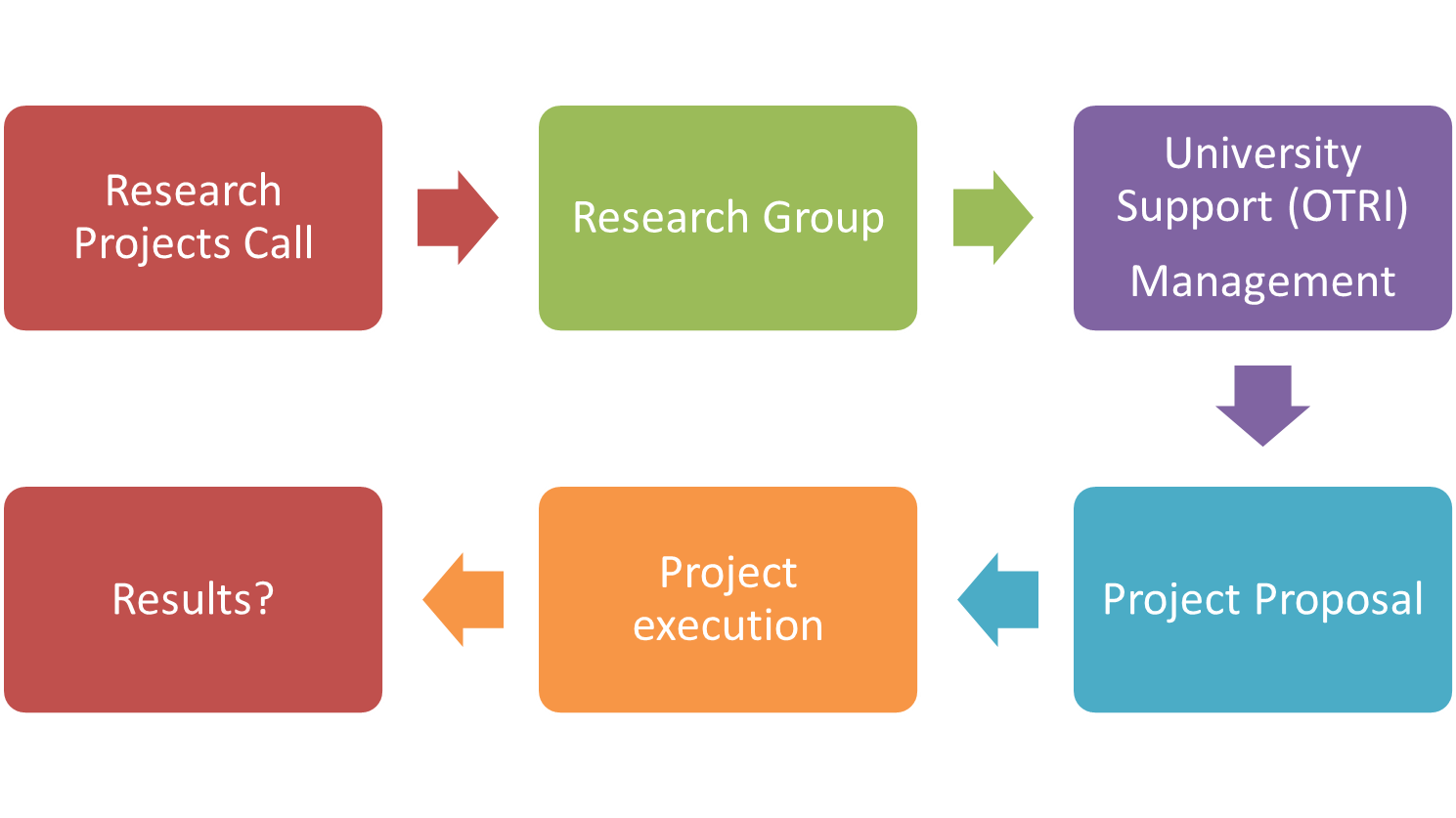
Some remarks...
- Some companies have emerged to carry out similar activities to the OTRI but for private companies
- Make project proposals
- Management of the succeed proposals
- Companies can apply for funding to make international project proposals
- Only submission is required
- E.g FP7 and H2020
- ...
Intellectual property
Generation of know-how
technology-based companies
General Framework
- Spanish Office for patents and trademarks (OEPM)
-
Complete Legal Framework for intellectual property and industrial rights
- Transposed from the European Union
-
http://noticias.juridicas.com/base_datos/Admin/rdleg1-1996.html
- Patents
- Industry models
- Utility models
- ...
Some comments...
- The university holds partial intellectual and industrial rights in everything that is generated at the university...
- Final degree projects, PhD results, Research projects results, etc.
- A Professor can lead the creation of a company (spin-off) but can only hold a part of it (10%)
- Due to the legal framework for civil servants
- Compatibility between private and public sector
- Start-ups or technology-based companies are now boosted in technological parks through incubators...
Start-ups...(Wayra Telefónica)

A technology-based company
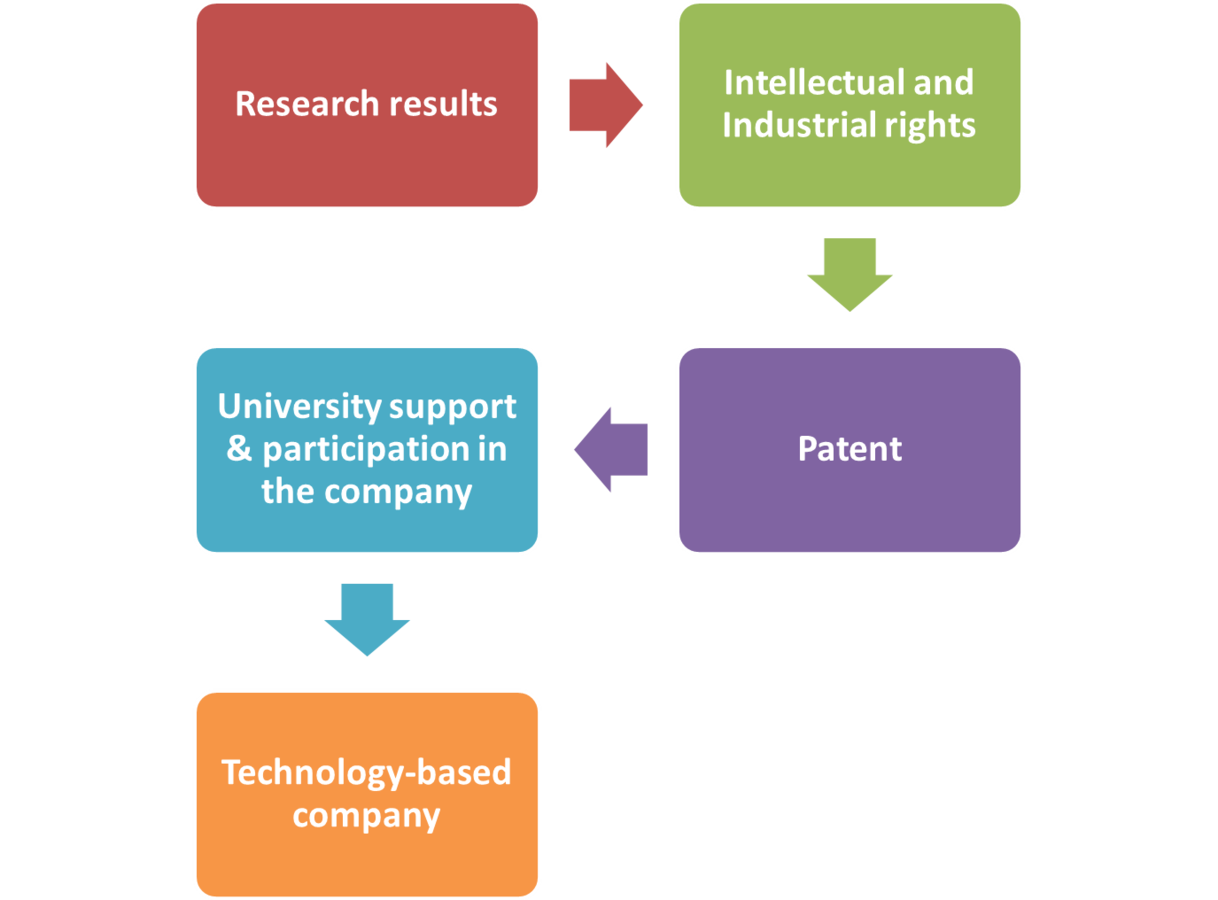
Some researchers avoid this model:
- The university is part of the company
- Legal restrictions
UC3M
-
OTRI-
Management of research
-
Help with patents
-
...
-
-
Technological and Science Park-
Incubator
-
Contests for launching ideas
-
Legal support
- http://www.uc3m.es/ss/Satellite/UC3MInstitucional/en/PortadaMiniSiteA/1371207248804/Science_Park
-
- ...

Other type of
commercial exploitation...
A company created by 9 universities to find clients for their research results...
Some Conclusions...
- The industrial sector in Spain is evolving...
- Support for technology-based companies
- Retain high-qualified people and create know-how
- Focus on products/services not just projects
- Hold a PhD is becoming more relevant
- Many things are turning to an American style...
-
Private Universities are becoming more competitive
- Higher salaries (best professionals?), cost-efficient to develop research ideas, etc.
- Private funding is required but still far from the American ones (risk/return perception)
-
Private Universities are becoming more competitive
- Academic or research career within a permanent position is now complicated
- ...
Q & A?

