Server Side Rendering
with React & RemixJS

I'm J.D. Nicholls 👋

- Open Source Contributor 👨💻
- Game developer (Hobby) 🎮
- Developer who loves UX 💫
- Chocolate lover 🍫
- Founding Full-Stack Engineer 👷
AT


# WEB DEVS
Web Developers
- Different ways to build websites & web apps (SPA).
- Server/Static rendering is preferred over a full rehydration approach.
- These approaches affect the Performance 🏃
The performance of a site can vary dramatically based on a user's device capabilities and their network conditions.
⬇️
Hydration is hard
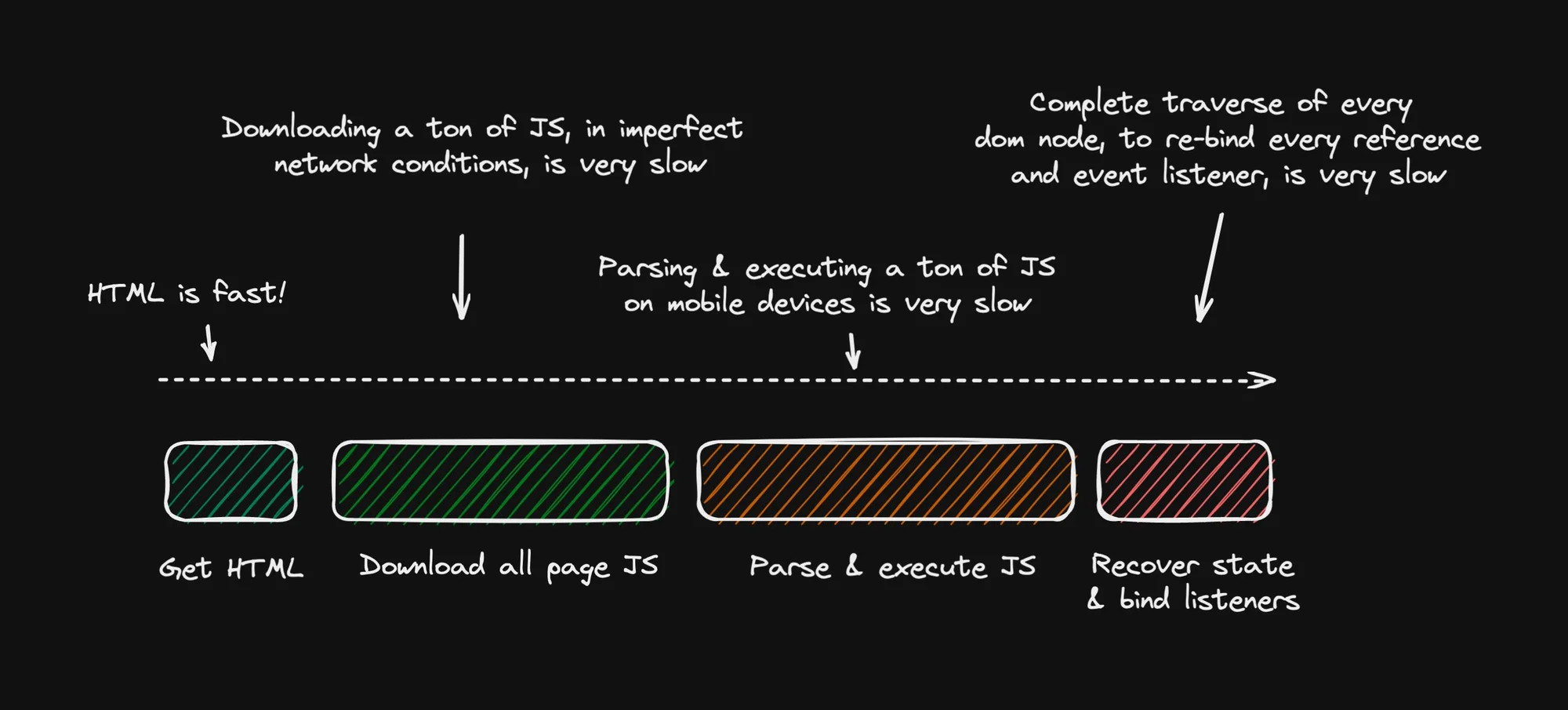
Hydration or rehydration is a technique in which client-side JavaScript converts a static HTML web page, delivered either through static hosting or server-side rendering, into a dynamic web page by attaching event handlers to the HTML elements.
# PERFORMANCE
Performance
⬇️
- Avoid regression (business impact).
- Team productivity (faster releases).
- Improves Dev satisfaction (interesting challenges).
- Performance is the art of avoiding work (some tasks are more expensive than others).
- Computational cost (time is money). 💸
- Site speed improvements can increase revenue (Website crawlers indexing sites).
- Better SEO ranking & Engagement (first impressions matter, UX).
- Building a better web, together 🌐
Benefits of adopting a performance culture
⬇️
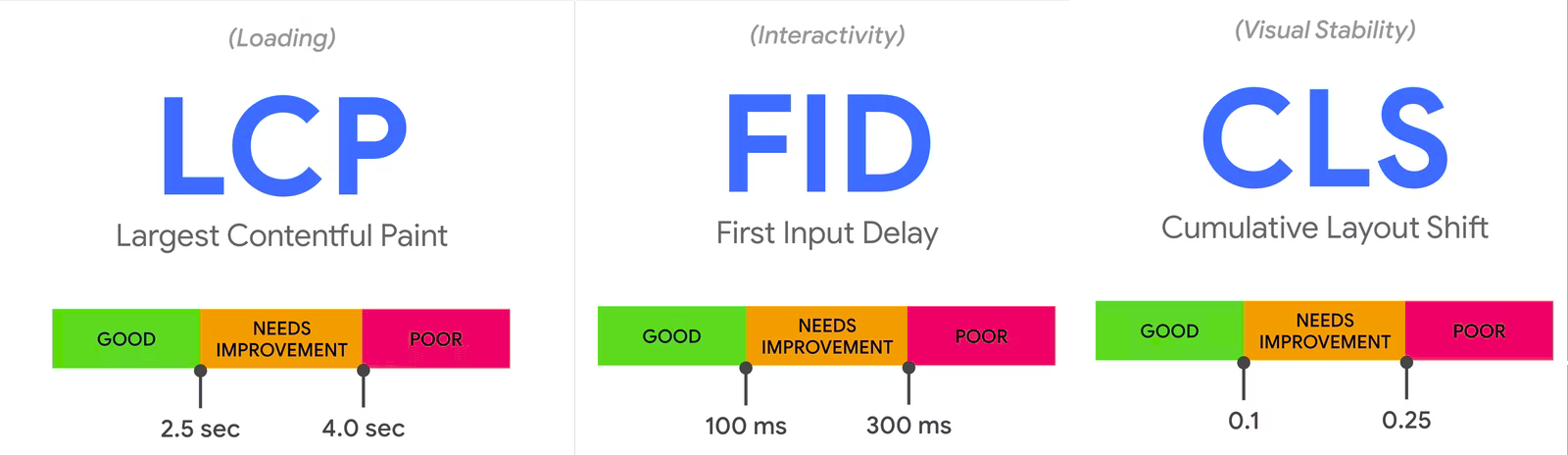
It represents how quickly the main content of a web page is loaded; delivering the initial HTML document as fast as possible. - Optimize LCP by Google
Largest Contentful Paint
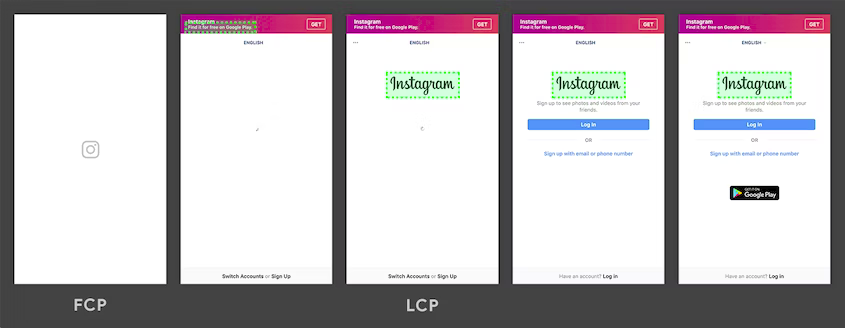
RemixJS
Nested Routes 👀
⬇️
By default all JavaScript is render-blocking. When the browser encounters a script tag that links to an external JS file, it must pause what it's doing and download, parse, compile, and execute that JavaScript. Therefore you should only load the code that's needed for the page - Optimize FID by Google
First Input Delay

⬇️
Avoid inserting new content above existing content, unless in response to a user interaction. This ensures any layout shifts that occur are expected. - Optimize CLS by Google
Cumulative Layout Shift
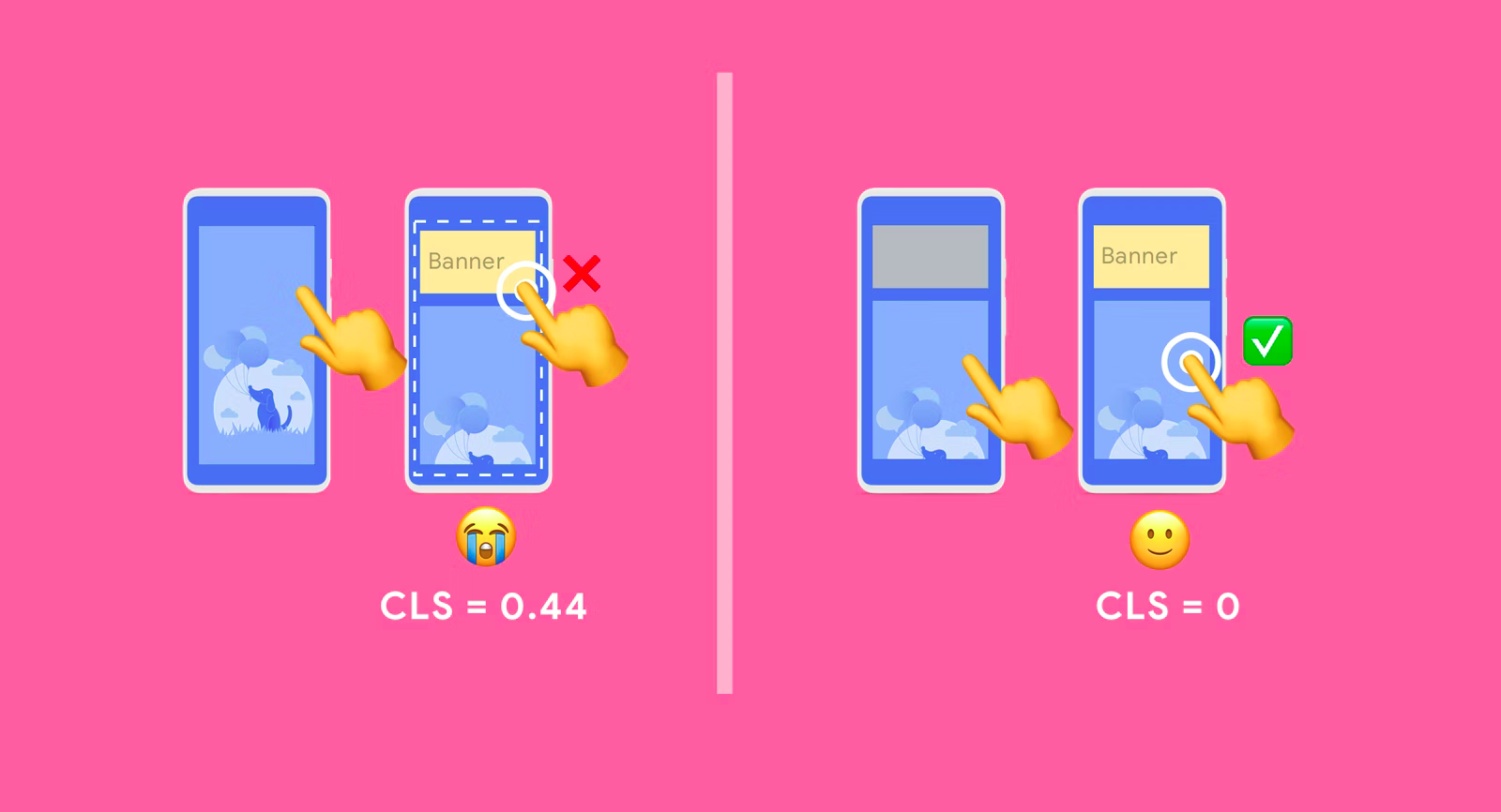
⬇️
# PERFORMANCE METRICS
Important metrics to measure
- TTFB: Time to First Byte - time between clicking a link and the first bit of content coming in. 🔗 ⬇️
- FP: First Paint - the first time any pixel gets becomes visible to the user (It answers the question "Is it happening?"). 🖼️🧐
- FCP: First Contentful Paint - the time when requested content (article body, etc) becomes visible. ⬆️👀
- TTI: Time To Interactive - the time at which a page becomes interactive (events wired up, etc). 👉🖱️
⬇️
Using RUM tools help capture the real world performance metrics in lower tier markets
Measure Performance
Real User Monitoring (RUM) data, also known as field data, captures the performance experienced by a site's actual users. RUM data is what Google uses to determine whether a site meets the recommended Core Web Vitals thresholds.
# MEASURE PERFORMANCE
# RENDERING
⬇️
Rendering on the Web
- Server Side Render the critical HTML.
- Reduce render blocking Javascript.
- Image optimization techniques (compression, WebP, lazy load non-critical images).
- Resize hero image; defer non critical resources.
- Optimizing third-party scripts and building microservices with single responsibility principle significantly reduced TTI and TBT.
- How to lose weight in the browser? - BrowserDiet guide
Techniques for fast load times
- Static Site Generation /
Pre-rendering - Client Side Rendering
- Server Side Rendering
And hybrid rendering techniques 👅
Rendering Options

# SSR
⬇️
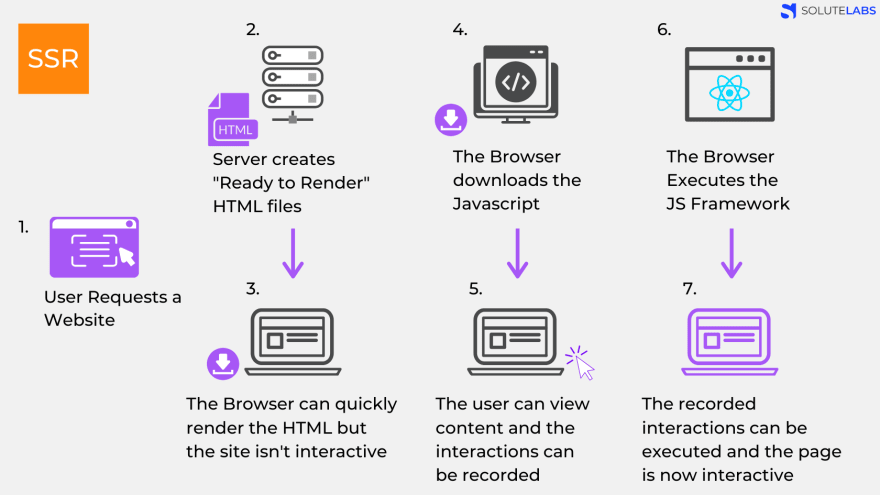
SSR generates the full HTML for a page on the server in response to navigation. This avoids additional round-trips for data fetching and templating on the client, since it’s handled before the browser gets a response.
Server Side Rendering
BTW, it's a joke! ¯\_(ツ)_/¯
React
Angular
BackEnd for
FrontEnd
Server Controls
.NET, Java, etc
REST APIs & JWT Tokens
Progressive Web Apps
AJAX & JSON
SOAP APIs & XML
Serverless & Microservices
Grunt, Gulp, Webpack, Rollup
SPA
Hybrid Apps
Horizontal
Scaling
VueJS
Svelte
Static Site Generation vs Server Side Rendering
SSG was introduced because servers were slow, but this is not the case anymore - Fusebit
# SEO
⬇️
Search engine bots can easily crawl static HTML, but they still tend to have problems with indexing JavaScript-generated content.
SEO
export type LoaderData = {
url: string;
requestInfo?: {
title?: string;
description?: string;
};
};
// Be called on the server before rendering
export const loader: LoaderFunction = async ({ request }) => {
return json<LoaderData>({
url: request.url,
});
};
export const meta: MetaFunction = ({ data }) => {
const requestInfo = (data as LoaderData | undefined)?.requestInfo;
return {
...getSocialMetas({
url: data?.url,
title: requestInfo?.title,
description: requestInfo?.description,
}),
};
};# PRESENTING CODE
Meta tags for SEO
import { MY_ICON } from '@company/shared';
export function getSocialMetas({
image = MY_ICON,
url = 'https://my.company.com',
title = 'My Company',
description = 'We are a great company',
charset = 'utf-8',
viewport = 'width=device-width,initial-scale=1,viewport-fit=cover',
keywords = 'Web, Mobile, Services, APIs, Games, WebSites',
}: {
url: string
image?: string
title?: string
description?: string
keywords?: string,
charset?: 'utf-8',
viewport?: string,
}) {
return {
charset,
viewport,
title,
description,
keywords,
image,
'og:url': url,
'og:title': title,
'og:description': description,
'twitter:creator': '@jdnichollsc',
'twitter:title': title,
'twitter:description': description,
}
}# PRESENTING CODE
Utils for SEO
How well can search engines understand your content?

# ROUTES
How to write a proxy with Remix:
— Kent C. Dodds 💿 (@kentcdodds) August 18, 2022
// app/routes/my-wat-proxy.js
export const loader = () => fetch('https://t.co/sunQQNdEZZ')
That's it.
- Render Nested Routes in Remix.
- Handle 404s in Remix with CatchBoundaries.
- Handle Unexpected Errors With Error Boundaries in Remix.
Routes
Back to the web standards.
# ENV VARS
Environment Variables
// constants.server.ts
declare global {
interface Window {
ENV: Record<string, unknown>;
}
}
export const CDN_URL = typeof document !== 'undefined'
? window.ENV?.CDN_URL
: process.env.CDN_URL;
export const LOGO_ICON = `${CDN_URL}/logo_icon.svg`;⬇️
Environment Variables are values that live on the server that your application can use. Using these from Browser is easy to accidentally leak secrets into publicly accessible files!
# ENV VARS
Load Env. Variables
export type LoaderData = {
ENV: Record<string, unknown>;
};
export const loader = () => {
return json<LoaderData>({
ENV: {
CDN_URL: process.env.CDN_URL,
},
});
};
export default function App() {
const { ENV } = useLoaderData<LoaderData>();
// window.ENV = ENV using dangerouslySetInnerHTML
}# CACHING
Caching
- Strategies for service worker caching (Optional)
⬇️
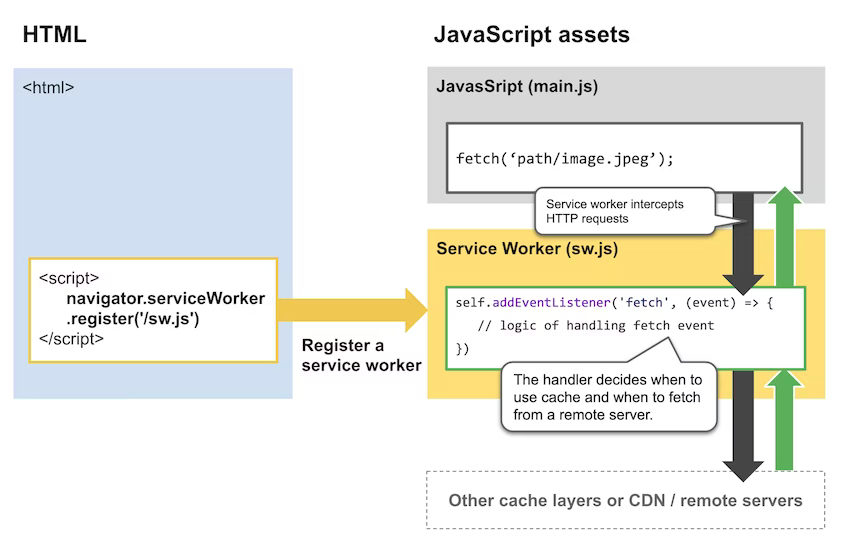
Caching web content helps improve upon the responsiveness of your websites by reducing the load on backend resources and network congestion.
# CACHE STRATEGIES
Cache Strategies using SW
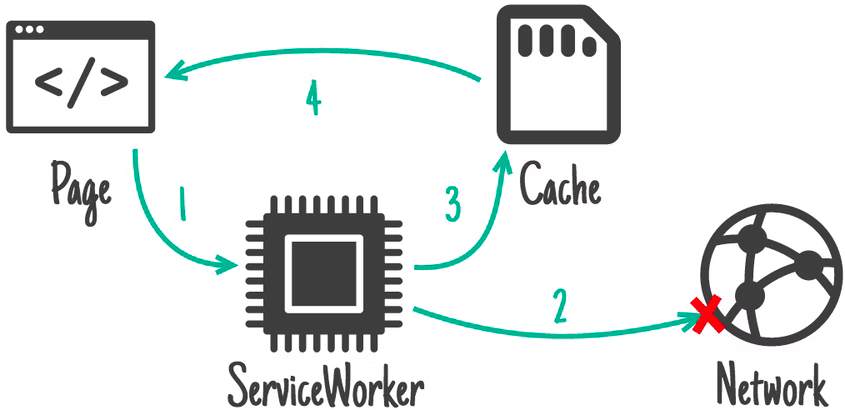
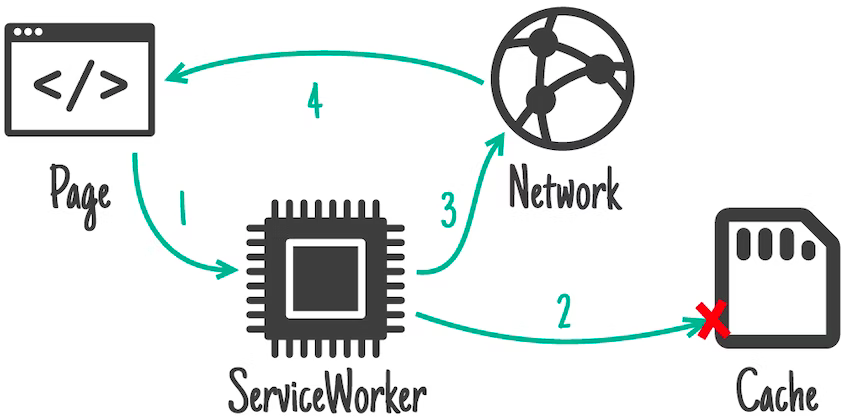
Cache First, falling back to network
- images
- fonts
- styles
- video/audio
Network First, falling back to cache
- routes (SSR)
// Imports Workbox from the CDN. Note that "6.2.0" of the URL
// is the version of the Workbox runtime.
importScripts('https://storage.googleapis.com/workbox-cdn/releases/6.2.0/workbox-sw.js');
if (workbox) {
console.log(`Yay! Workbox is loaded 🎉`);
initializeWorkbox();
} else {
console.log(`Boo! Workbox didn't load 😬`);
}
function initializeWorkbox() {
// Automatically adds an activate event listener to service worker
workbox.core.clientsClaim();
// registerRoutes here!
}
// This allows the web app to trigger skipWaiting via
// registration.waiting.postMessage({type: 'SKIP_WAITING'})
self.addEventListener('message', (event) => {
if (event.data && event.data.type === 'SKIP_WAITING') {
self.skipWaiting();
}
});# PRESENTING CODE
Using Workbox
function initializeWorkbox() {
// registerRoutes here!
const staticAssetsRoute = new workbox.routing.Route(({request}) => {
return [
'image',
'font',
'style',
].includes(request.destination);
}, new workbox.strategies.CacheFirst({
cacheName: 'static-assets'
}));
workbox.routing.registerRoute(staticAssetsRoute);
}# PRESENTING CODE
Cache First for static assets
function initializeWorkbox() {
// registerRoutes here!
const mediaAssetsRoute = new workbox.routing.Route(({request}) => {
return [
'video',
'audio',
].includes(request.destination);
}, new workbox.strategies.CacheFirst({
cacheName: 'media-assets',
plugins: [
new workbox.cacheableResponse.CacheableResponsePlugin({
statuses: [200]
}),
new workbox.rangeRequests.RangeRequestsPlugin(),
],
}));
workbox.routing.registerRoute(mediaAssetsRoute);
}# PRESENTING CODE
Cache First for media assets
function initializeWorkbox() {
// registerRoutes here!
const navigationRoute = new workbox.routing.NavigationRoute(
new workbox.strategies.NetworkFirst({
networkTimeoutSeconds: 3,
cacheName: 'navigations'
})
);
workbox.routing.registerRoute(navigationRoute);
}# PRESENTING CODE
Network First for navigation (SSR)
self.addEventListener('install', event => {
self.skipWaiting();
event.waitUntil(
// caching etc
);
});# COOKIES
Creating Cookies
import { createCookie } from "@remix-run/node"; // or cloudflare/deno
const userPrefs = createCookie("user-prefs", {
expires: new Date("2021-01-01"),
});This technique is a fundamental building block of many interactive websites that adds state so you can build authentication, shopping carts, user preferences, and many other features that require remembering who is "logged in".
A cookie is a small piece of information that your server sends someone in a HTTP response that their browser will send back on subsequent requests.

# COOKIES
Using Cookies
import { userPrefs } from '~/cookies';
const getUserPrefsCookie = (request) => userPrefs.parse(
request.headers.get("Cookie"),
);
// Loading a cookie
export async function loader({ request }) {
const cookie = (await getUserPrefsCookie(request)) || {};
return json({ showBanner: cookie.showBanner });
}
// Updating a cookie
export async function action({ request }) {
const cookie = (await getUserPrefsCookie(request)) || {};
cookie.showBanner = false;
return redirect("/", {
headers: {
"Set-Cookie": await userPrefs.serialize(cookie),
},
});
}# COOKIES
Creating Session Cookies
import { createCookieSessionStorage } from '@remix-run/node';
export const globalSession = createCookieSessionStorage({
cookie: {
name: '__session',
secure: true,
secrets: [process.env.SESSION_SECRET],
sameSite: 'lax',
path: '/',
maxAge: 60 * 60 * 24 * 30, // 30 days
httpOnly: true,
},
});Sessions are an important part of websites that allow the server to identify requests coming from the same person, especially when it comes to server-side form validation or when JavaScript is not on the page.
# COOKIES
Using Session Cookies
import { globalSession } from '~/cookies';
const ERROR_KEY = 'error';
const MESSAGE_KEY = 'message';
async function getGlobalSession(request: Request) {
const session = await globalSession.getSession(
request.headers.get('Cookie')
);
return {
getError: () => session.get(ERROR_KEY) as string | undefined,
flashError: (error: string) => session.flash(ERROR_KEY, error),
getMessage: () => session.get(MESSAGE_KEY) as string | undefined,
flashMessage: (message: string) => session.flash(MESSAGE_KEY, message),
commitSession: () => globalSession.commitSession(session),
destroySession: () => globalSession.destroySession(session),
};
}
export const action = async ({ request }) => {
const { flashMessage, commitSession } = await getGlobalSession(request);
flashMessage('Email verification code sent successfully');
return redirect('/login', {
headers: {
'Set-Cookie': await commitSession(),
},
});
};Resources
- Browser Rendering Optimization course - Building 60 FPS Web Apps.
- Up and Running with Remix - Free course by Kent Dodds.
- Frontend Performance Checklist 2021 - Performance has to be measured, monitored and refined continually.
- RemixJS examples.