ES6 (ES2015) tips


introduction
Mostly for old browsers (<IE10)
ES6+ transpilation to ES5
tip#1
Variables
var x = 5;
const x = 5; // single-assignment
let y = 3; // "let" is the new "var"
ES5
ES6
tip#1
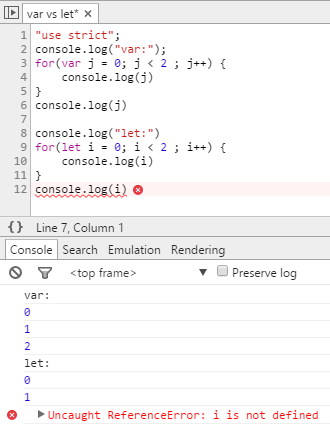
Block scope
function varnish() {
//nish *is* visible out here
for( var nish = 0; nish < 5; nish++ ) {
//nish is visible to the whole function
};
//nish *is* visible out here
};function letuce() {
// tuce is *not* visible out here
for( let tuce = 0; tuce < 5; tuce++ ) {
// tuce is only visible in here (and in the for() parentheses)
};
// tuce is *not* visible out here
};ES5
ES6
tip#1
Block scope
tip#2
Destructuring objects
var obj = {
a: 'a',
b: { foo: 'foo' },
};var a = obj.a; // ==> 'a'
var foo = obj.b.foo; // ==> 'foo'
var undef = obj.c; // ==> undefinedES5
const { a, b } = obj;
const { foo } = obj.b;
const { c } = obj;
console.log(a); // ==> 'a'
console.log(b); // ==> { foo: 'foo' }
console.log(foo); // ==> 'foo'
console.log(c); // ==> undefined [Soft failing]ES6
tip#1
Usage (exemple React)
render() {
const { hasError, type, code } = this.props.currentError;
return (
<Modal isOpen={ hasError }>
<div>
<p>{ code }</p>
<p>{ this.getMessage(code, type) }</p>
</div>
</Modal>
);
}tip#1
Destructuring arrays
var [a, , b] = [1, 2, 3];
console.log(a); // ==> 1
console.log(b); // ==> 3function g({name: x}) {
console.log(x); // ==> 5
}
g({name: 5})Destructuring fn params
tip#1
Switch variables
[a, b] = [b, a];tip#3
Default
function fn(x, y=12) {
// y is 12 if not passed (or passed as undefined)
return x + y;
}function fn(x, y) {
y = y || 12;
// OU:
// if(y === undefined) y = 12;
}ES6
ES5
tip#4
Rest
function fn(x, ...y) {
// y is an Array
return y;
}fn(5, 1) => [1]
fn(5, 2, 1) => [2, 1]
fn(5) => []Usage
tip#4
Spread
function fn(x, y, z) {
return x + y + z;
}fn(1, 1, 1) => 3
fn(...[1, 1, 1]) => 3Usage
tip#4
Spread (apply like)
function f(x, y, z) { }
var args = [0, 1, 2];
f.apply(null, args);
function f(x, y, z) { }
var args = [0, 1, 2];
f(...args);tip#4
Spread into arrays
const colors1 = ['pink', 'green'];
const colors2 = ['red', ...colors1, 'yellow', 'blue'];colors2 ==> ['red', 'pink', 'green', 'yellow', 'blue'] tip#4
Spread and array push
var arr1 = [0, 1, 2];
var arr2 = [3, 4, 5];
arr1.push(...arr2);arr1 ==> [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]tip#5
Prototype (ES5)
function TodoItem(value) {
this.value = value;
}
TodoItem.prototype.validate = function() {
console.log("Validated !");
};
var item = new TodoItem();tip#5
Classes sugar
class TodoItem extends Component {
constructor(props, context) {
super(props, context);
this.state = {
editing: false
};
}
handleDoubleClick() {
super.handleDoubleClick();
this.setState({ editing: true });
}
…
}tip#6
Object assign
Object.assign(target, ...sources)var obj = { a: 1 };
var copie = Object.assign({}, obj)
console.log(copie); // {a: 1}Clone an object
var o1 = { a: 1 };
var o2 = { b: 2 };
var o3 = { c: 3 };
var obj = Object.assign(o1, o2, o3);
console.log(obj); // { a: 1, b: 2, c: 3 }
console.log(o1); // { a: 1, b: 2, c: 3 }Merge objects
tip#7
Object literals
var obj = {
// Shorthand for ‘handler: handler’
handler,
// Methods
toString() {
// Super calls
return "str";
},
// Computed (dynamic) property names
[ 'prop_' + (() => 42)() ]: 42
};ES6
tip#8
Arrow function
var a1 = a.map(function(s){ return s.length });
var a2 = a.map( (s) => s.length );
var a3 = a.map( s => s.length );setInterval(() => {
this.age++;
}, 1000);Optional parenthesis and return
Shorter and scope
tip#9
Template string
const name = 'John';
console.log(`${name} is fun`)
// => 'John is fun'
// Multi-ligne !
var markup = `<li>
${name} is great
</li>`;tip#10
Modules (default)
/* Default export (foo.js) */
class Foo {
// ...
}
export default Foo;/* Import (bar.js) */
import Foo from "foo";
const foo = new Foo();tip#10
Modules (named)
/* Named export (foo.js) */
class Foo {
// ...
}
export default Foo;
export const Bar = 'BAR';/* Import (bar.js) */
import { Bar } from "foo";
// or
import Foo, { Bar } from "foo";
const foo = new Foo();tip#10
Modules
import { unlink as rm } from "fs";
rm(filename);Rename
import * as fs from "fs";
fs.unlink(filename, function(err) { /* check errors */ });Import all named exports
tip#11
Proxies
// Invisible proxy
var target = {};
var p = new Proxy(target, {});
p.a = 37;
console.log(target.a); // 37.tip#11
Proxies
let validator = {
set: function(obj, prop, value) {
if (prop === 'age') {
if (!Number.isInteger(value)) {
throw new TypeError('Not a number !');
}
}
// Default behavior
obj[prop] = value;
}
};
let person = new Proxy({}, validator);
person.age = 100;
console.log(person.age); // 100
person.age = 'jeune'; // ==> Exceptiontip#11
Revocable proxies
let target = {}; // Start with an empty object
let handler = {}; // Don’t intercept anything
let {proxy, revoke} = Proxy.revocable(target, handler);
proxy.foo = 123;
console.log(proxy.foo); // 123
revoke();
console.log(proxy.foo); // TypeError: Revokedtip#12
Collection data structures
var map = new Map()
map.set('contra', { description: 'Asynchronous flow control' })
map.set('dragula', { description: 'Drag and drop' })
map.set('woofmark', { description: 'Markdown and WYSIWYG editor' })
map.get('contra');
map.size // --> 3
for (var [key, val] of map) {
console.log(key + " = " + val);
}ES6 Maps
tip#12
Collection data structures
var map = new WeakMap()
map.set({}, 2)
// set, get, has, delete are possible
// 1) Not iterable, no .entries(), no .keys(), no .values()
// 2) Every key must be an iterable object
// 3) Just like with Map, you can use .has, .get, and .delete too.
==> Weak references : GCES6 Weakmaps
tip#12
Collection data structures
var set = new Set([1, 2, 3, 4, 4]);
set.add(7);
console.log([...set]);
// <- [1, 2, 3, 4, 7]ES6 Sets
tip#12
Collection data structures
var set = new WeakSet()
set.add({})
set.add(new Date())
// No primitive
// No iterability
// You can only .add, .has, and .deleteES6 Weaksets
tip#13
Native promises
var promise = new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
// do an async thing and...
if (/* OK */) {
resolve("It's OK");
}
else {
reject(Error("Erf..."));
}
});promise.then(function(result) {
console.log(result);
}, function(err) {
console.log(err);
});