Desarrollando Drones
UAVS
- Intro
- Regulaciones
- Componentes de un UAVs
- Arquitecturas/Protocolos de comunicacion
-
Programacion
- Configuracion del entorno
- Librerias / SDKS / Apps
- Ejemplos
Agenda
Drones
Unmaned Aerial Vehicle
Un dron es un vehículo aéreo que vuela sin tripulación.
Pueden ser controlados via Software o volar de forma autonoma con sistemas embebidos y GPS.
Tienen aplicaciones militares, vigilancia, rescate, monitoreo de trafico, agricultura, incendios, investigacion, geografia.
Drones
Regulacion en Colombia Circular 002 del 2015 Aerocivil
-
Los drones que se pueden operar en Colombia son aquellos que pesen hasta 25Kg. La operación civil de drones de un peso mayor queda prohibida en Colombia.
-
La operación del dron únicamente podrá hacerse en horario diurno y en condiciones meteorológicas de vuelo visual.
-
Los drones no podrán volar sobre un área congestionada, edificaciones, público o aglomeración de personas, [....] Tampoco podrán volar desde un aeródromo o en sus proximidades dentro de un radio de 5Km.
Drones
Regulacion en Colombia Circular 002 del 2015 Aerocivil
-
La altura máxima a la que pueden volar es 152 metros y no podrán alejarse más de 750 metros del operador o del lugar de su lanzamiento o despegue.
-
Si el dron se va a utilizar en labores de fotografía, vídeo, telemetría, datos, sensores, scanner, etc. (sic), se requiere permiso de la Fuerza Aérea Colombiana.
Conceptos Basicos
Componentes
Componentes
Controladora de Vuelo APM
- ArduCopter – open source autopilot Stabilizes the drone
- Navigates the drone (uses barometer, GPS and compass)
- A battery monitoring unit allows for failsafe landings on low battery.
- Power module measures voltage, current, and powers the APM at the odd voltage of 5.3V
Componentes
Controladora de Vuelo APM

Componentes
Controladora de Vuelo APM - API
Stabilize (manual control)
Alt(itude) hold (fixed Z)
Loiter aka stationkeep (keep fixed X,Y,Z)
Land (reduce Z until barometer detects descending rate <20cm/s and disarm)
Return to Launch (RTL) – first climb to a prespecified altitude (RTL_ALTITUDE), then return to the arming position (HOME)
Guided Mode (GOTO position)
Auto Mode: Execute a script including waypoints, ending in Land, RTL or Loiter.
Arquitecturas
Protocolos de comunicacion (software)

Arquitecturas
Protocolos de comunicacion (software)
Command line GCS
Also proxies and multiplexes commands to/from several GCSs (designed for GSC redundancy):
Each MAVLink from a GCS/App forwarded to Autopilot (master)
Each MAVLink from autopilot forwarded to GCS/App
Written in Python

Arquitecturas
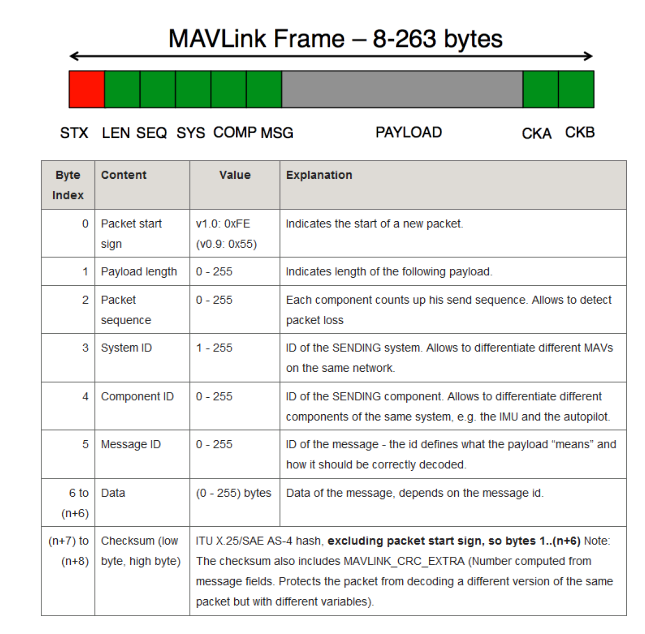
Protocolos de comunicacion MAVLink
MAVLink is the only way to talk to the Autopilot.
MAVLink is a very lightweight, header-only message marshalling library for micro air vehicles.
Authoritative source of information: http://qgroundcontrol.org/mavlink/start
Library support for C/C++/C#, Python, WLua, JavaScript
Two versions defined: v0.9 and v1.0. We use v1.0.
Arquitecturas
Protocolos de comunicacion MAVLink
Arquitecturas
Protocolos de comunicacion AR Drone 2/AT Commands

Arquitecturas
Protocolos de comunicacion AR Drone 2/AT Commands
The AR.Drone 2 AT command protocol is used to control the AR.Drone 2 over wifi
Arquitecturas
Protocolos de comunicacion AR Drone 2/AT Commands
The AT commands are encoded as 8-bit ASCII characters with a carriage return "<CR>" as a newline delimeter. All AT commands start with "AT*" followed by a command name, a equals sign, a sequence number(starting with 1, which also resets the sequence number), and optionally a list of comma-seperated arguments for the command.
Arquitecturas
Protocolos de comunicacion AR Drone 2/AT Commands
- AT*REF (input) - Takeoff/Landing/Emergency stop command
- AT*PCMD (flag, roll, pitch, gaz, yaw) - Move the drone
- AT*PCMD_MAG (flag, roll, pitch, gaz, yaw, psi, psi accuracy) - Move the drone (With Absolute Control support)
- AT*FTRIM - Sets the reference for the horizontal plane (The drone must be on the ground)
- AT*CONFIG (key, value) - Configuration of the AR.Drone 2
- AT*CONFIG_IDS (session, user, application ids) - Identifiers for AT*CONFIG commands
- AT*COMWDG - Reset the communication watchdog
- AT*CALIB (device number) - Aks the drone to calibrate the magneto meter (The drone must be flying)
Programacion
Configuracion del entorno APM
curl -sL https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_8.x | sudo -E bash -
sudo apt-get install -y nodejsInstalar NodeJS
sudo apt-get install python-pip python-dev build-essentialInstalar Python y pip
Programacion
Configuracion del entorno APM
sudo apt-get install python-dev python-opencv python-wxgtk3.0
python-pip python-matplotlib python-pygame python-lxml
Instalar dependencias
pip install MAVProxy
pip install future
pip install pymavlink
pip install dronekitInstalar protocolo y proxy Mavlink
Programacion
Configuracion del entorno AR
npm install ar-drone
npm install ardrone-autonomyInstalar cliente para comandos AT con nodejs y librerias
Programacion
Ejemplos
vehicle = connect('/dev/ttyACM0', wait_ready=True)
vehicle.mode = VehicleMode("GUIDED")
vehicle.armed = True
vehicle.simple_takeoff(aTargetAltitude) # Altitud en metrosUso de Dronekit con python Mavlink
Programacion
Ejemplos
var autonomy = require('ardrone-autonomy');
var mission = autonomy.createMission();
mission.takeoff()
.zero()
.altitude(1)
.forward(1)
.right(1)
.left(1)
.backward(1)
.hover(1000) // for 1 second
.land();Uso de AR drone con Nodejs
¿ Como hacer un proyecto con todo esto ?
Explicacion del Proyecto WEB Voyager2.0
- Conexion en tiempo real con Sockets
- Uso de Python y Nodejs en conjunto
- Uso de raspberry pi como servidor
- Recebir datos de sensores en la web (Ej: Lidar)
- Accionar Componentes (Ej: Servo motor)
- Comunicacion a Mavlink desde la web
- Comunicacion a AR Drone desde la web
< Coding time >
El Stack





Compartimos el codigo
