Tech and Human Rights
OSF Learning Initiative
Dr. Jun-E Tan
https://slides.com/jun-e/osflearninginitiative
| Paradigm | Digital (1) | Digital (2) |
Developmental (1) |
Developmental (2) |
| Sphere | Conventional rights in digital spaces | Data-centred rights | Access to the digital | Governance of the digital |
| Description of sphere | Rights of individuals in digital spaces / on the Internet | Digital data that represent physical entities | Access to digital spaces and meaningful participation | Digital and Internet governance |
| Examples of rights | ✅ Rights to freedom of expression, association and assembly online ✅ Right to consumer protection ✅ Right to seek joy and pleasure ✅ Right to exist free from violence, hateful speech, and harassment ✅ Right to not be discriminated ✅ Right to have informed consent on participation |
✅ Right to data privacy ✅ Right to freedom from digital surveillance ✅ Right to data ownership and control ✅ Right to data security and protection |
✅ Right to access state and other services online ✅ Right to access the Internet ✅ Right to access information and content ✅ Right to access hardware/software |
✅ Right to participate in digital governance processes or be consulted on Internet policy issues |
A Framework for Digital Rights
4 Waves of AI Development
- Internet AI
- Business AI
- Perception AI
- Autonomous AI
Lee (2018)
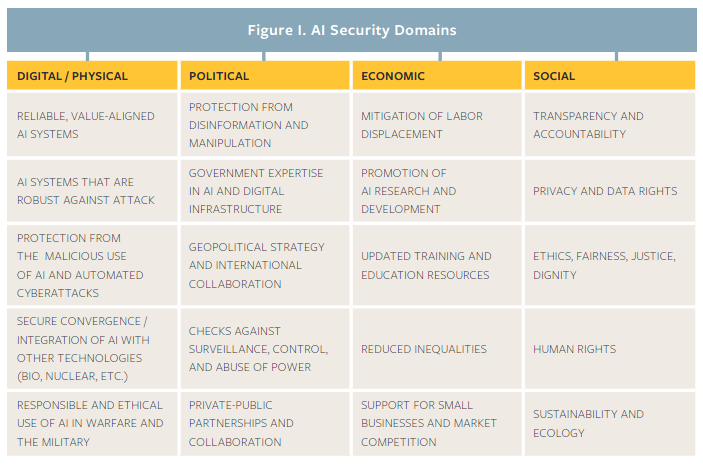
Newman (2019)

Type 1: the risks or opportunity costs of not implementing AI, missing out on potential benefits

Type 2: the risks of unintended consequences or unsafe outcomes of AI

Type 3: the risks of AI being used for malicious purposes
References
- Tan, J.-E. (2019). "Digital Rights in Southeast Asia: Conceptual Framework and Movement Building". In Y.H. Khoo & D. Simanjundtak (Eds.), Exploring the Nexus between Technologies and Human Rights: Opportunities and Challenges for Southeast Asia. Bangkok: SHAPE-SEA (Download)
- Lee, K.-F. (2018). AI Superpowers: China, Silicon Valley, and the New World Order. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Company.
-
Newman, J. C. (2019). Toward AI Security: Global Aspirations for a More Resilient Future (CLTC White Paper Series). Centre for Long-term Cybersecurity. https://cltc.berkeley.edu/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/CLTC_Cussins_Toward_AI_Security.pdf