C++基礎語法大複習
By Your Dear SENPAIs <3
Adapted from Welly's Slides
❈
❅
❆
❈
❅
❆
-
一定要聽課
-
有問題的話記得問
-
如果之前有學過,覺得不需要聽課,可以課前告知,我們就不會去切你螢幕
-
鐘響5分鐘後開始上課
-
有空記得上機練習,還有填表單
-
在電腦教室吃東西不要被抓到
-
每堂課最後都會玩Kahoot,前三名有小零食
-
會有作業和期末考,讓我們交的出社團成績
課堂規則
表單閒聊~
-
各位想推坑的動漫
-
明日同學的水手服
-
Fate
-
偶像學園
-
古見同學有交流障礙
-
排球少年
-
神奇寶貝XY
-
神奇寶貝超級願望
-
戀上換裝娃娃
-
高木同學
-
吸血鬼馬上死
-
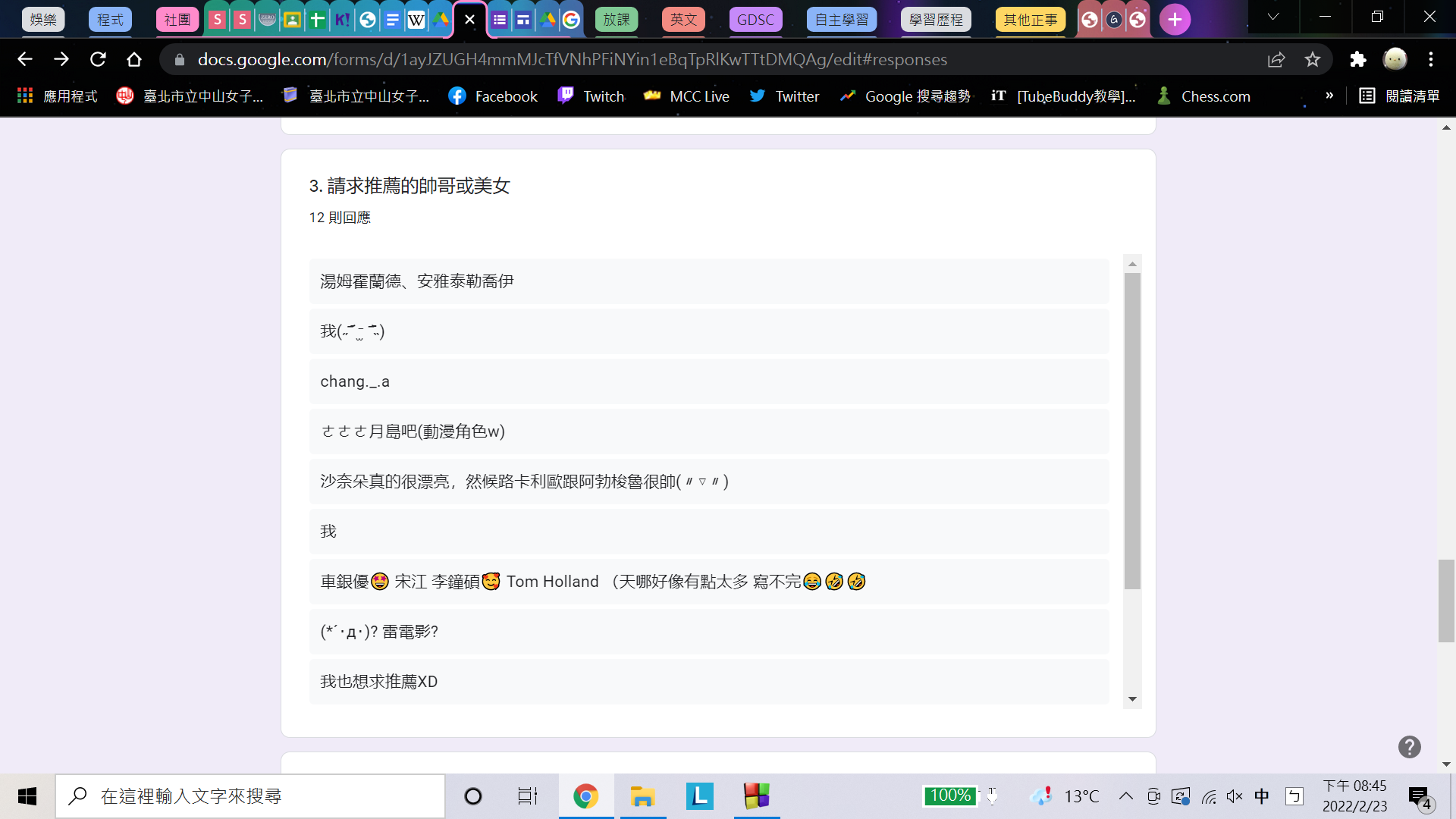
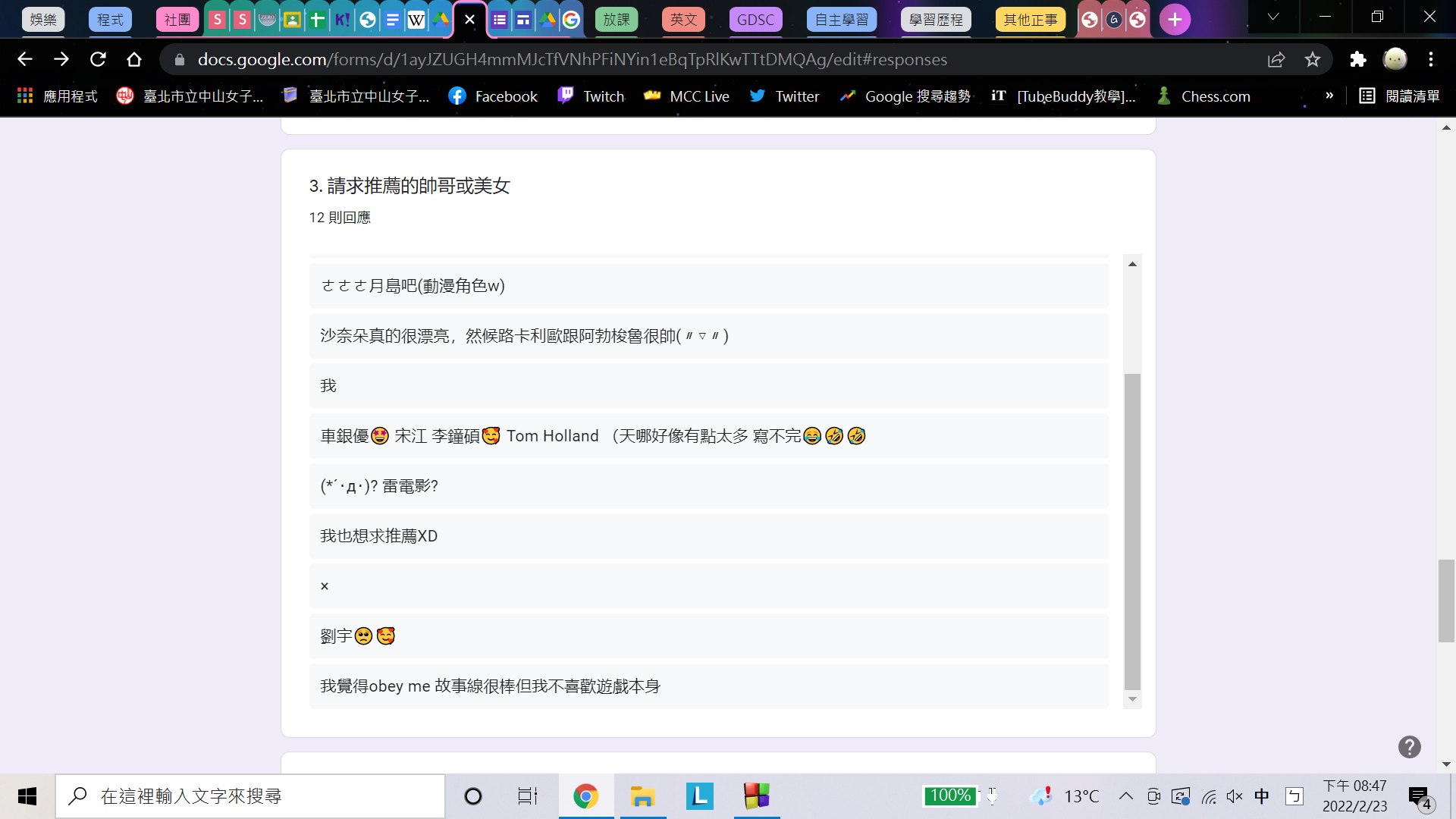
(統計時間:2022/2/23 20:49)
基本環境
development environment
༒
༒
起手式
#include <iostream>
//↑控制輸入輸出的函式庫
using namespace std;
//↑也可以不打,但用到函式庫內的函式時就要加"std::"
int main(){
//↑主函式
//主程式內容
return 0;
//↑回傳值,通常是0,來確保執行正常。因為不是void型別的函式,必須有回傳值
}編譯器——code::blocks
編譯器——Dev C++
線上編譯器
以下略......(其實我只用過第一個www
輸入/輸出
input / output
༒
༒
cin/cout
在<iostream>裡面
前面需加std::
" "<--空格
endl or '\n'<--換行
字串記得用""!
scanf/printf
cin >> 輸入內容;
cout << 輸出內容;scanf("%輸入型態", &被輸入變數);
printf(內容);講義
變數
variables
༒
༒
變數
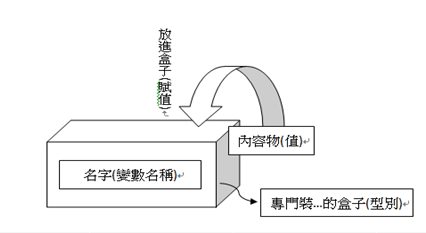
變數型態
| 型態 | 中文意思 | 可儲存的資料 |
|---|---|---|
| int | 整數 | -2,147,483,648 至 2,147,483,647(4個位元組) |
| double | 倍精度浮點數(小數) | 1.7E +/- 308 (15 位數,8個位元組) |
| char | 字元(半形字) | 'a'、'R'、'1'、'@'、'*' ... |
| string | 字串(文句) | "Hello"、"^_^"、"Rock!" ... |
| bool | 布林(是非) | true、false |
| long long | 長長整數(? | -9,223,372,036,854,775,808 至 9,223,372,036,854,775,807(8個位元組) |
declare a variable
C++
型態 名稱;
型態 名稱 = 值;
//ex.
int num = 2;- 宣告時同時指定型態
- 可同時宣告與賦值
Python
名稱 = 值
//ex.
num = 2- 型態會自動變化
- 沒有宣告詞
- 名稱皆可由字母、數字、底線組成,數字不可為第一個字母,不可使用保留字,會區分大小寫
運算子
operator
༒
༒
運算子優先序
| :: | 範圍解析 |
群組一
| -> | 成員選取 |
| ++ | 後置加1 |
| -- | 後置減1 |
| [] | 陣列註標 |
| () | 函式呼叫 |
| typeid | 類型名稱 |
| const_cast | 常數類型轉換 |
| dynamic_cast | 動態類型轉換 |
群組二
| reinterpret_cast | 重新轉譯的類型轉換 |
| static_cast | 靜態類型轉換 |
| sizeof | 物件或類型的大小 |
| ++ | 前置加1 |
| -- | 前置減1 |
| ~ / compl | 一補數 |
| ! / not | 邏輯not |
| - | 負號 |
| + | 正號 |
群組三
| & | 傳址 |
| * | 傳值 |
| new | 建立動態物件 |
| delete | 刪除動態物件 |
| () | 轉型運算子 |
| + | 加 |
| - | 減 |
群組六
| ->* | 物件指標 |
群組四
| * | 乘 |
| / | 除 |
| % | 取餘數/取模(mod) |
群組五
群組七
| << | 左移 |
| >> | 右移 |
群組八
| < | 小於 |
| > | 大於 |
| <= | 小於等於 |
| >= | 大於等於 |
| == | 等於 |
| != / not_eq | 不等於 |
群組九
| & / bitand | 位元and |
群組十
| | / bitor | 位元包含or |
群組十二
群組十五
| ?: | 三元運算子 |
| = | 指派 |
| *= | 乘等於 |
| /= | 除等於 |
| %= | 取餘數等於 |
| += | 加等於 |
| -= | 減等於 |
| <<= | 左移等於 |
| >>= | 右移等於 |
| &= | 位元and等於 |
群組十一
| ^ / xor | 位元排除or |
| && / and | 邏輯and |
群組十三
| || / or | 邏輯or |
群組十四
| ^= | 位元排除or等於 |
| |= | 位元包含or等於 |
| throw | 擲回運算式 |
| , | 逗號 |
群組十六
算數運算子
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a=1;
int b=2;
cout<<"a+b="<<a+b;//<--加
cout<<"a-b="<<a-b;//<--減
cout<<"a*b="<<a*b;//<--乘
cout<<"a/b="<<a/b;//<--除
cout<<"a%b="<<a%b;//<--取餘數
return 0;
}
//a+b=3
//a-b=-1
//a*b=2
//a/b=0
//a%b=1邏輯運算子
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a=1;
int b=2;
if(a==1||a==2){
cout<<"true"<<endl;
}else{
cout<<"false"<<endl;
}
if(a==1&&a==2){
cout<<"true"<<endl;
}else{
cout<<"false"<<endl;
}
if(a!=b){
cout<<"a!=b"<<endl;
}else{
cout<<"a==b"<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
//true
//false
//a!=b關係運算子
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a=1;
int b=2;
if(a<b){
cout<<"a<b"<<endl;
}
if(a>b){
cout<<"a>b"<<endl;
}
if(a==b){//<--是==1不是=!!!
cout<<"a=b"<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
//a<b偷懶寫法
//前置的場合下會先進行運算再指派到變數,而後置的場合下則是會先指派到變數再進行運算

a = a + 1;
a += 1;
a++; //只有+1時能用
++a;
b = b * 3;
b *= 3;++a/--a
a++/a--
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a,x;
a=1;
x=++a;
cout<<x<<endl;
cout<<a<<endl;
return 0;
}
//2
//2#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a,x;
a=1;
x=a++;
cout<<x<<endl;
cout<<a<<endl;
return 0;
}
//1
//2sizeof
一個會幫你算好你丟進去的東東(ex.型態)有多大(在記憶體中佔幾個byte)的運算子~
#include <iostream>
int is_admin = 0;
int ary[160];
int main(){
std::cout << sizeof(char) << std::endl;
std::cout << sizeof(int) << std::endl;
std::cout << sizeof(long long) << std::endl;
std::cout << sizeof(float) << std::endl;
std::cout << sizeof(int *) << std::endl;
std::cout << sizeof(double *) << std::endl;
}
// 1 4 8 4 8 8條件判斷
if-else / switch-case / ?:
༒
༒
if-else
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a=126;
if(a%2==0){
if(a%3==0){ //巢狀
cout<<"a是6的倍數"<<endl;
}
else if(a%3==0&&a%7==0){
cout<<"a是21的倍數"<<endl;
}
cout<<"a是偶數"<<endl;
}
else{
cout<<"a不是2或3或6的倍數"<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
//a是6的倍數
//a是偶數
-
範例
if(條件式){
陳述句1;
陳述句2;
}else if(條件式){
陳述句1;
陳述句2;
}else{
陳述句1;
陳述句2;
}-
語法
switch(變數){
case 值:
陳述句;
break;
case 值:
陳述句;
break;
default:
陳述句;
break;
}3
9
3
case
case
default
9
8
switch-case
-
語法
-
示意動畫
條件式 ? true的回傳值 : false的回傳值?:
-
語法
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
int main(){
std::string whether;
std::cout << "是否認同「哪裡跌到,就在哪裡躺下」這句話?(y/n)";
std::cin >> whether;
std::cout << (whether=="y" ? "看來我們有同樣的想法" : "好吧,你跟我不一樣");
return 0;
}-
範例
迴圈
for / while / do-while
༒
༒
for
for(起始值; 條件式; 更新值){
陳述句;
}while
while(條件式){
陳述句;
}do-while
do{
陳述句;
}while(條件式);for vs while
for(int i=0;i<5;i++){
std::cout << i << ' ';
}
//0 1 2 3 4 宣告變數 條件(為true時才會跑迴圈) 改變變數值
int i=0
while(i<5){
std::cout << i << ' ';
i += 1;
}
//0 1 2 3 4 條件(為true時才會跑迴圈)
break
跳出這個迴圈
continue
跳過此次迴圈
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a=10;
for(int i=0;i<a;i++){
if(i==5){
break;
}
cout<<i<<" ";
}
return 0;
}
//0 1 2 3 4#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a=10;
for(int i=0;i<a;i++){
if(i==5){
continue;
}
cout<<i<<" ";
}
return 0;
}
//0 1 2 3 4 6 7 8 9例子——十十乘法表
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a=10;
for(int i=0;i<a;i++){
for(int j=0;j<a;j++){ //巢狀
cout<<a<<"*"<<b<<'='<<a*b<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a=1;
int b=1;
while(a<11){
while(b<11){ //巢狀
cout<<a<<'*'<<b<<'='<<a*b<<endl;
b+=1;
}
b=1;
a+=1;
}
return 0;
}
陣列
array
༒
༒
int arr[3] = {6, 8, 9};陣列型態 陣列名稱 空間格數 初始值



0
1
2
6
8
9
一維陣列
一維陣列
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a[10]={1,6,5,2,8,4,3,5,2,89};
int b[10];
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
cin>>b[i];
}
for(int j=0;j<10;j++){
cout<<a[j]<<" ";
cout<<b[j]<<" ";
}
return 0;
}
-
範例
-
語法
型態 名稱[空間格數];
型態 名稱[空間格數] = {值1, 值2, ...};int a[2][3] = {{0, 1, 2}, {3, 4, 5}};
int b[2][3] = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
//二維陣列(2*3)
int c[2][3][2] = {{{0, 1}, {2, 3}, {4, 5}}, {{6, 7}, {8, 9}, {10, 11}}};
//三維陣列(2*3*2)| a[0][0] | a[0][1] | a[0][2] |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 |
| a[1][0] | a[1][1] | a[1][2] |
|---|---|---|
| 3 | 4 | 5 |
多維陣列
//更多維度的陣列我懶的畫也畫不出來,請自行想像:D
二維陣列
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a[3][3];
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
for(int j=0;j<3;j++)
cin>>a[i][j];
}
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
for(int j=0;j<3;j++)
cout<<a[i][j]<<" ";
cout << '\n';
}
return 0;
}函式
function
༒
༒
函式庫的函式
| 函式庫 | 函式 | 功能 | 回傳值型態 |
|---|---|---|---|
| math.h | sqrt( float x ) | 回傳 x 的開根號值 | float |
| pow( float x, float y ) | 回傳 x 的 y 次方 | float | |
| ctype.h | isalpha( char c ) | 回傳 c 是不是英文字母 | bool |
| isdigit( char c ) | 回傳 c 是不是數字 | bool | |
| string.h | strlen( char s[] ) | 回傳 s 的長度 | int |
自定義函式
回傳值型態 函式名稱(參數1型態 參數名稱1, 參數2型態 參數名稱2, ... ){
Do anything you want...
return 回傳值; //void型態沒有回傳值
} //函式大括號後沒有分號!- 可沒有參數或回傳值(但只有void)
- 回傳值可能為數值(int、double)、字元(char)或是/非(bool)
- 若用void記得用還是要加小括號
- 參數間用逗號分開
- 回傳值型態要和當初定義的相同
- 每個參數都要定義型態
Example
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int calculate(int a,char b,int c){
if(b=='+'){
return a+c;
}
else if(b=='-'){
return a-c;
}
else if(b=='*'){
return a*c;
}
else if(b=='/'){
return a/c;
}
}
int main()
{
int A,B;
char cal;
cin>>A>>cal>>B;
cout<<calculate(A,cal,B);
return 0;
}
Example(void)
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void bird()
{
cout << " .-." << endl;
cout << " /'v'\\" << endl;
cout << " (/ \\)" << endl;
cout << "='=\"=\"===< " << endl;
cout << "mrf|_|" << endl;
}
void cat()
{
cout << " /\\_/\\" << endl;
cout << " ____/ o o \\" << endl;
cout << " /~____ =o= /" << endl;
cout << " (______)__m_m)" << endl;
}
int main()
{
bird();
cout << "麻雀:早安~" << endl;
cat();
cout << "貓:我要吃掉你!" << endl;
bird();
cout << "麻雀:不要><" << endl;
return 0;
}
/*
.-.
/'v'\
(/ \)
='="="===<
mrf|_|
麻雀:早安~
/\_/\
____/ o o \
/~____ =o= /
(______)__m_m)
貓:我要吃掉你!
.-.
/'v'\
(/ \)
='="="===<
mrf|_|
麻雀:不要><
*/遞迴
recursion
༒
༒
介紹
int who_am_i(int now){
if(now == 1)
return 1;
else
return who_am_i(now-1) + 1;
}- 函式自己呼叫自己
- 如果你想知道排在你前面有多少人,除了慢慢數外,還有什麼方法?
- 範例
for迴圈
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Proin urna odio, aliquam vulputate faucibus id, elementum lobortis felis. Mauris urna dolor, placerat ac sagittis quis.
遞迴
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Proin urna odio, aliquam vulputate faucibus id, elementum lobortis felis. Mauris urna dolor, placerat ac sagittis quis.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a=0;
for(int i=0;i<11;i++){
a=a+i;
}
cout<<a;
return 0;
}
//55#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int sum(int a){
if(a==1){
return 1;
}
else{
return sum(a-1)+a;
}
}
int main()
{
cout<<sum(10);
return 0;
}
//55經典題型
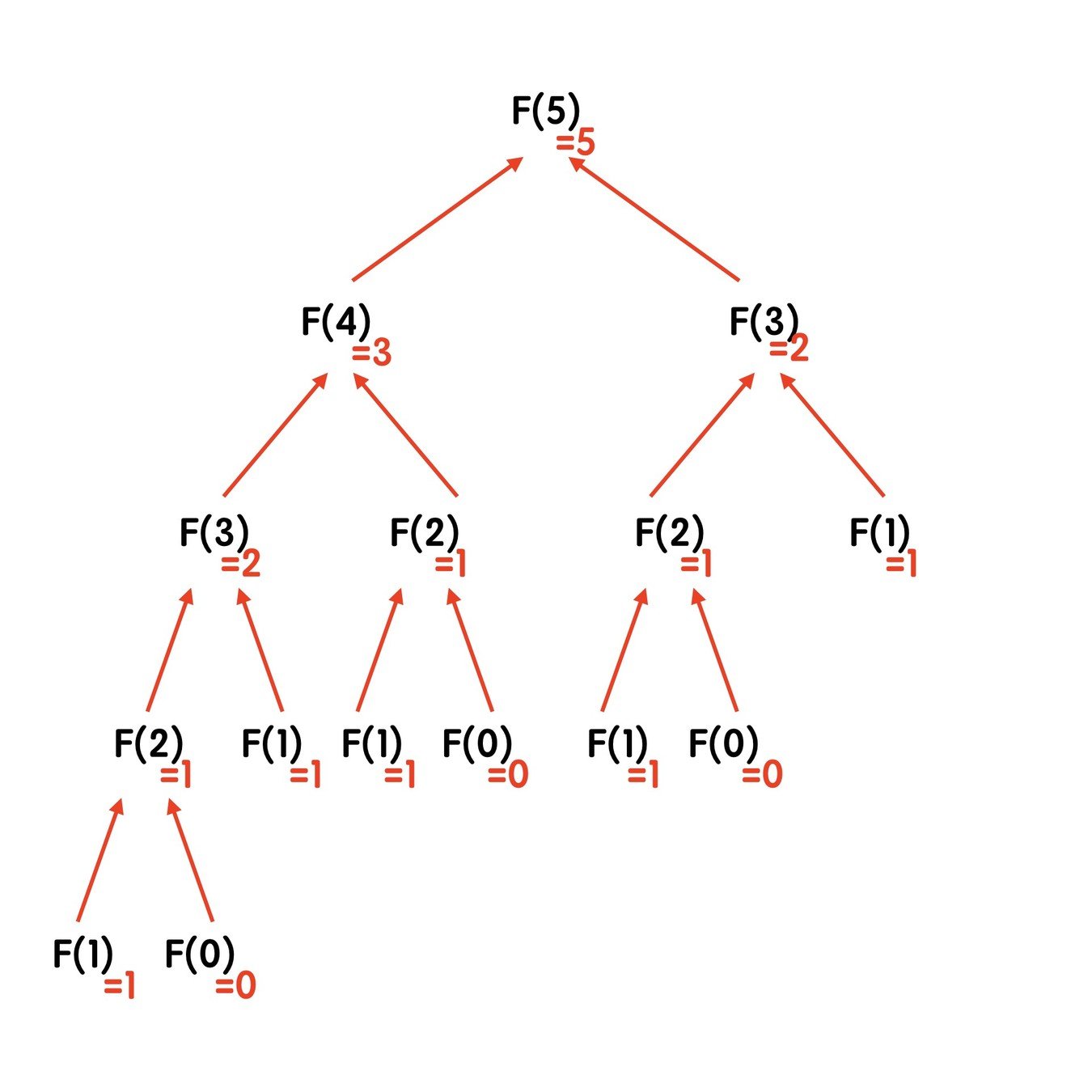
費氏數列
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int fibonacci(int a){
if(a==0){
return 0;
}
else if(a==1){
return 1;
}
else{
return fibonacci(a-1)+fibonacci(a-2);
}
}
int main()
{
int N;
cin>>N;
cout<<fibonacci(N);
return 0;
}//用文字來說,就是費氏數列由0和1開始,之後的費波那契數就是由之前的兩數相加而得出。輾轉相除法
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int euclidean_algorithm(int a,int b){
if(b==0){
return a;
}
else{
return euclidean_algorithm(b,a%b);
}
}
int main()
{
int M,N;
cin>>M>>N;
cout<<euclidean_algorithm(M,N);
return 0;
}
指標
pointer
༒
༒
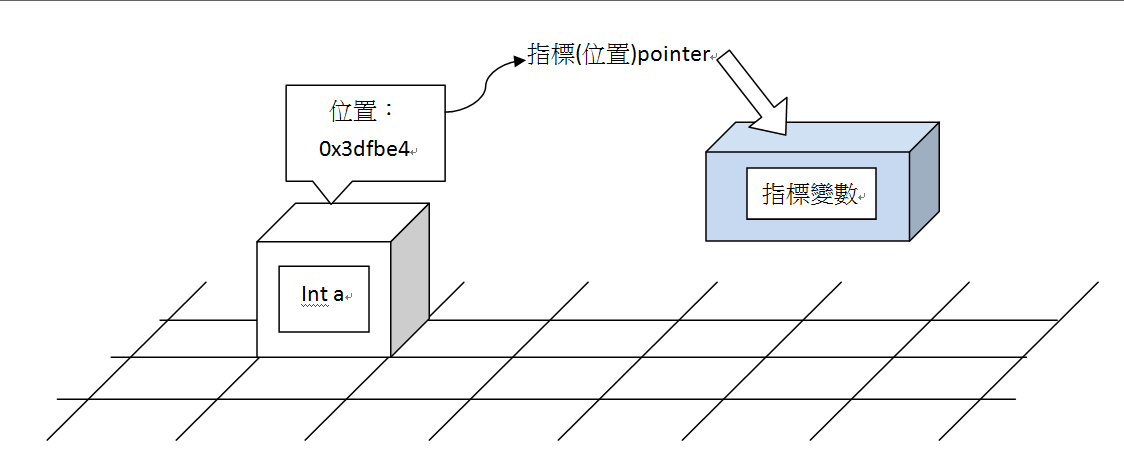
指標

存放盒子的地址
指標變數(指標)
符號整理
-
取值符號:*
-
取址符號:&
-
宣告指標變數:*
-
宣告參考(reference):&

記憶體位址:0x+十六進位的一串數字 ex.0x40f7d8
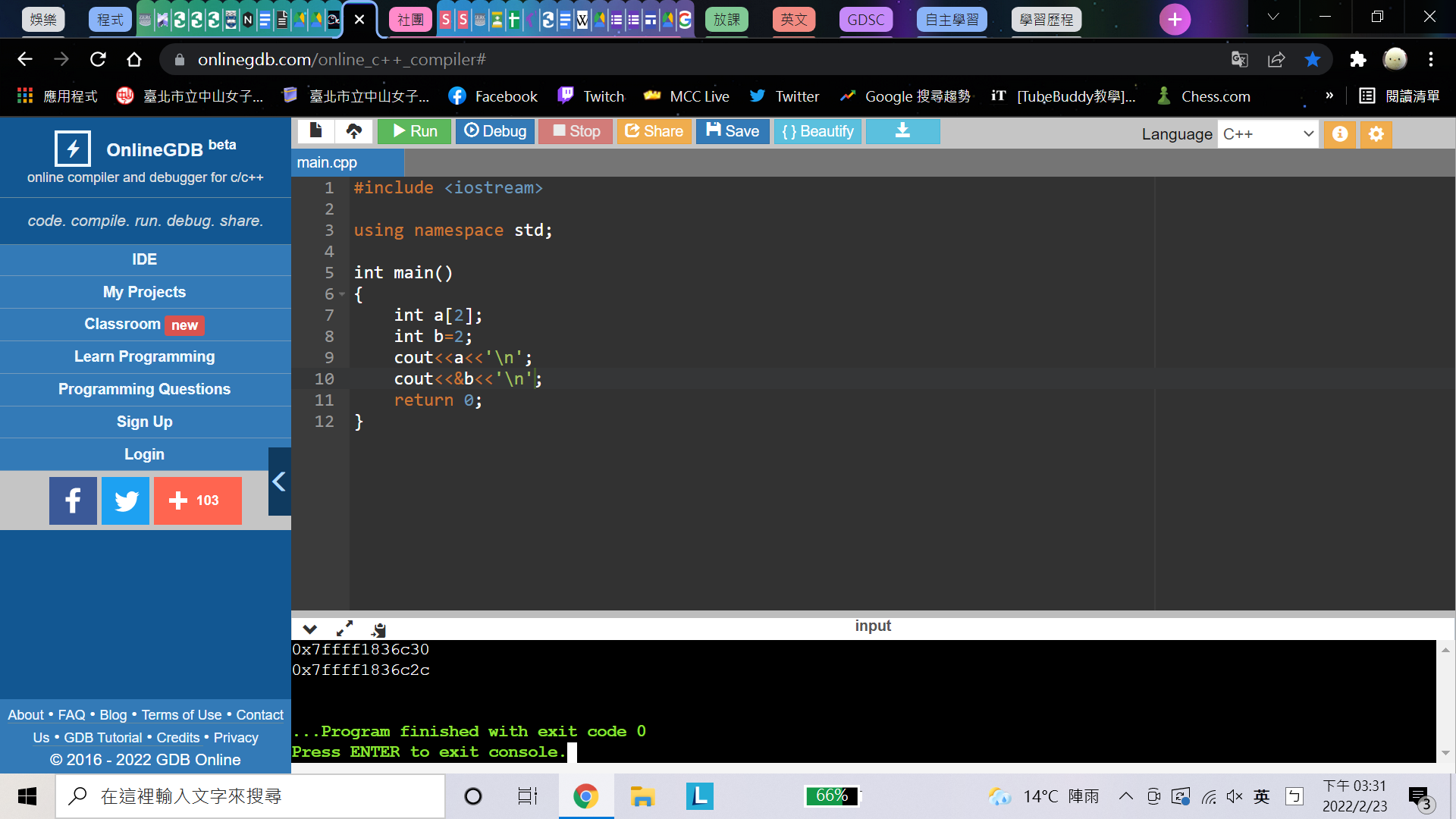
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a[2];
int b=2;
cout<<a;
cout<<&b;
return 0;
}範例——取址符號
記憶體位址
指標變數:一種存址的變數型態
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a=2;
int *p = &a;
cout<<p<<endl;
cout<<*p<<endl;
cout<<&p<<endl;
cout<<a<<endl;
//cout<<*a<<endl; 編譯錯誤
cout<<&a<<endl;
return 0;
}範例——指標變數&取值符號
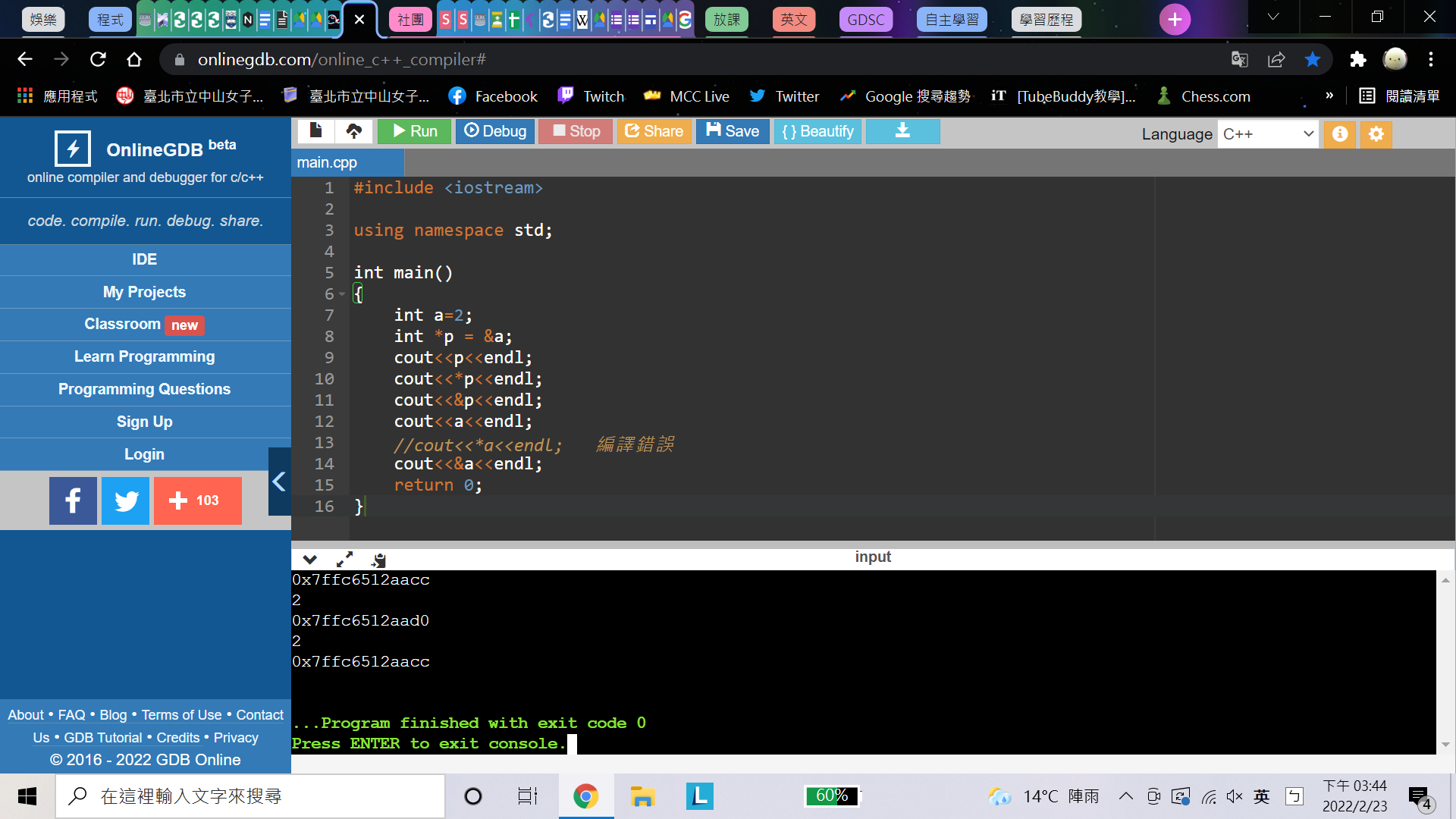
p的值(a的位址)
p所指向變數的值(a的值)
p的位址
a的值
a的位址
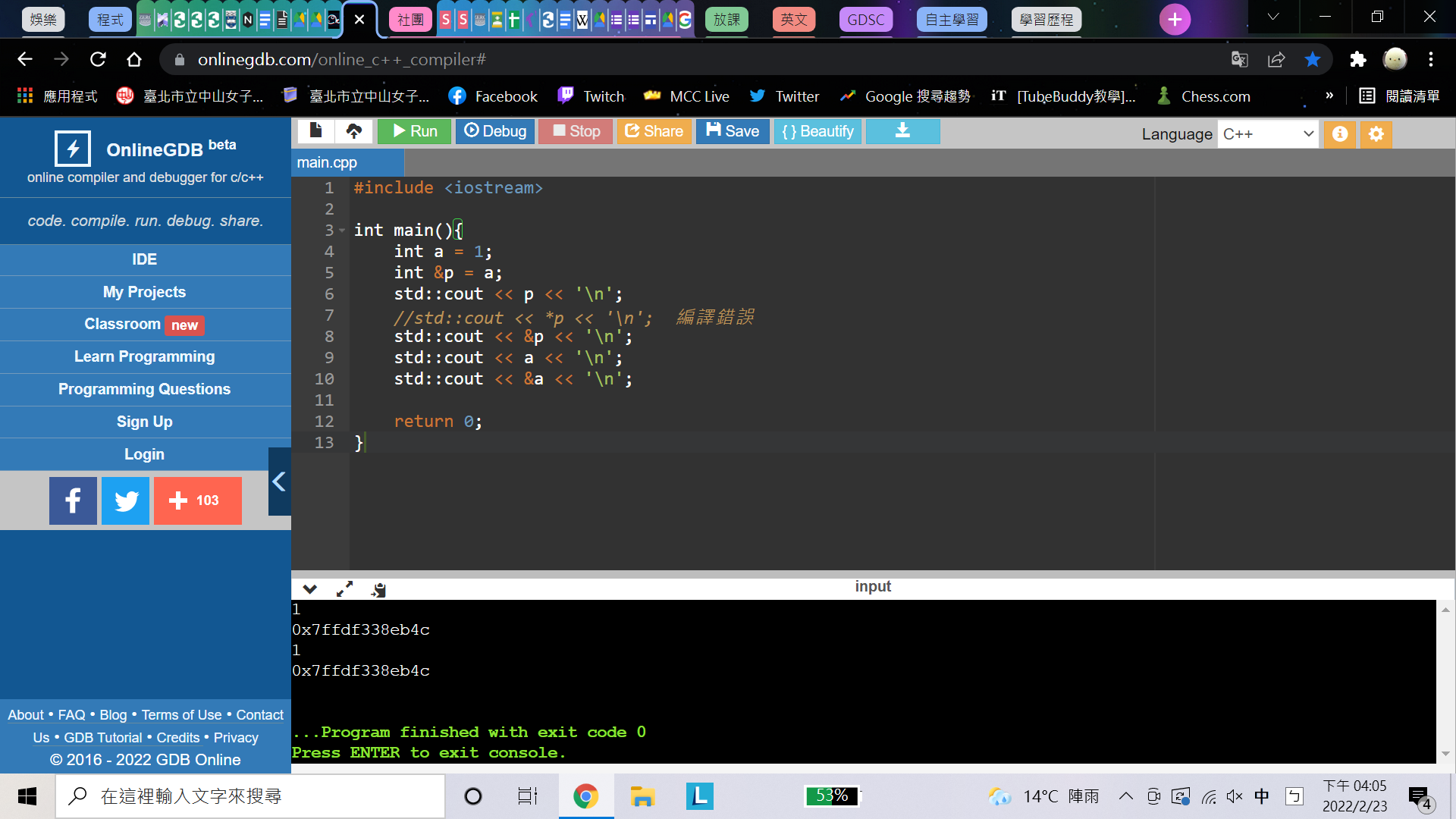
參考(reference):就像是取個小名,使呼叫原本的變數或者其參考(reference),都可以得到該值:D
ps.與其叫它參考,不如把它想像成標籤或貼紙吧,比較好理解
#include <iostream>
int main(){
int a = 1;
int &p = a;
std::cout << p << '\n';
//std::cout << *p << '\n'; 編譯錯誤
std::cout << &p << '\n';
std::cout << a << '\n';
std::cout << &a << '\n';
return 0;
}範例——參考(reference)
a的值
a的位址
a的值
a的位址
常用於函式的參數,因為可以直接修改到填入變數的值!
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void f(int &A, int &B) {
int tmp = A;
A = B;
B = tmp;
cout << A << " " << B <<endl;
}
int main(){
int a = 1, b = 2;
f(a, b);
cout << a << " " << b;
return 0;
}範例——參考(reference)
範例——一維指標陣列
#include <iostream>
int main(){
int r[5] = {2, 4, 6, 8, 10};
int *p[5]; //只是宣告5格存址的空間
for(int i=0;i<5;i++) //賦值
p[i] = r+i;
for(int i=0;i<5;i++) //輸出
std::cout << *p[i] << ' ';
std::cout << '\n';
int (*q)[5]; //記憶體空間連續
q = &r; //賦值
for(int i=0;i<5;i++) //輸出
std::cout << (*q)[i] << ' ';
std::cout << '\n';
return 0;
}
//2 4 6 8 10
//2 4 6 8 10#include <iostream>
int main(){
int arr[3][4] = {
3, 6, 2, 7,
3, 6, 4, 5,
2, 6, 8, 9
};
int (*q)[3][4] = &arr;
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
for(int j=0;j<4;j++)
std::cout << (*q)[i][j] << ' ';
std::cout << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
//3 6 2 7
//3 6 4 5
//2 6 8 9範例——二維指標陣列
Kahoot!
༒
༒