探討遺傳演算法的種類與效能差異
–以俄羅斯方塊(Tetris)為例
建國中學 賴昭勳
專題簡介
Tetris 簡介
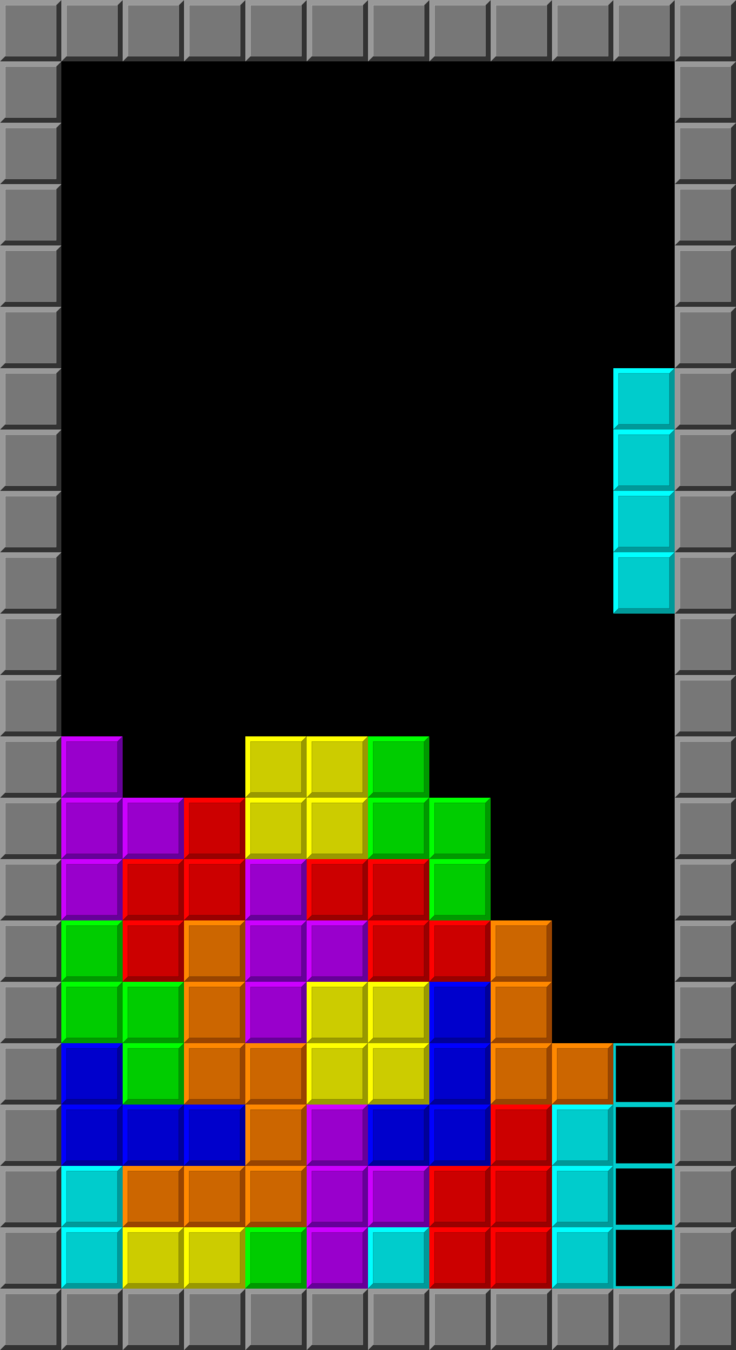
一個 10x20 的遊戲板上,持續有各種「四格骨牌」(Tetromino)掉落,並在一整個橫排都被填滿時可以完全消除,使上面的格子落下。玩家必須要消除橫排以得分,並避免遊戲板被堆到頂端。
From https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tetris
Tetris Ai 好像很多人做過?
NES Tetris...很難
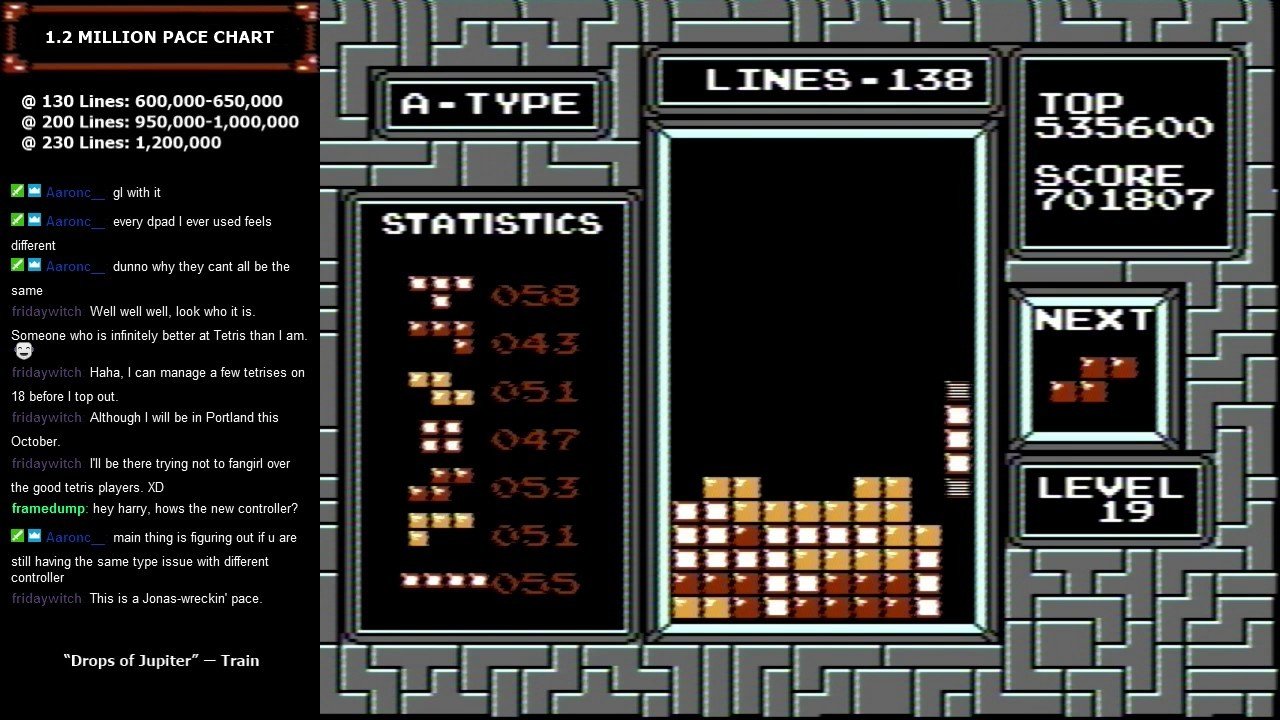
From https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FWqb0G4WBKs
CTWC (Classic Tetris World Championship)

PART ONE: 遊戲的起點
實作遊戲!
class board:
def __init__(self):
self.pointcalc = [0, 40, 100, 300, 1200]
self.weights = (5.06450279, -0.40483617, 1.14291331, 1.83894321, 0.18530122, 0.35860931, 0.93125075, 0.23497438)
###self.survweights = (1.72746616e+00, 1.18972449e-02, 4.54023544e-01, 4.19517578e-01,1.46628694e-03, -2.19499807e-01, 5.36884577e-01, -4.83240272e-01)
#board data
self.heights = [0] * 10
self.ones = [0] * 10
self.grid = [0] * 24 #each row is an integer
self.rowTrans = [0] * 24
self.alive = 1
#heuristic variables
self.holes = 0
self.avgHeight = 0
self.maxHeight = 0
self.bumpiness = 0
self.newl = 0 #new lines in this move
self.wellCells = 0
self.deepWells = 0
self.blocks = 0
#scoring variables
self.lines = 0
self.pts = 0
def col(self, x, y, piece): #checks collision
def countrowTrans(self, row):
def place (self, x, y, piece, type): #places piece
def checkline(self): #checks for filled lines and updates board position
def put(self, x, piece): #puts piece down according to rotation and position
def printboard(self): #prints current board for debugging
def getstats(self): #completely refreshes stats by checking entire board (only called when lines are cleared)
def getval(self): #the evaluation function
class piece:
def __init__(self, p, num):
self.tile = [] #stores representation of different tile rotations
self.types = num
def getbounds(self):
tet = [piece([[0, 0], [0, 1], [0, 2], [0, 3]], 2),
piece([[0, 0], [0, 1], [1, 1], [1, 0]], 1),
piece([[0, 0], [1, 0], [0, 1], [0, 2]], 4),
piece([[0, 0], [1, 0], [1, 1], [1, 2]], 4),
piece([[0, 0], [1, 0], [1, 1], [2, 1]], 2),
piece([[0, 0], [0, 1], [1, 1], [1, 2]], 2),
piece([[0, 0], [0, 1], [0, 2], [1, 1]], 4), ] #I, O, L, J, S, Z, T
for i in tet:
i.getbounds()gui: 看得到結果


PART TWO: AI 的誕生
AI 做選擇的方法
枚舉所有旋轉,放置位置
計算放下後的評估分數
更新目前找到
最好的放法
做出最終選擇
扣的
cur = tet[x[cnt]]
best = 1000
bestrot, bestpos = 0, 0
for i in range(cur.types): # for each rotation
for j in range(cur.minx[i], cur.maxx[i] + 1): # possible placements
result = board()
result.copyboard(gameboard)
result.put(j, cur.tile[i])
resval = result.getval()
if resval < best:
best = resval
bestrot, bestpos = i, j等等,那評估分數怎麼算的?
盤面中很多不同的啟發因子(heuristic)
作為判斷依據

平均高度:5.6
最高高度:9
洞:2個
凹凸度:31
可消行數:2
...還有更多!
self.weights = (5.06450279, -0.40483617, 1.14291331, 1.83894321, 0.18530122, 0.35860931, 0.93125075, 0.23497438)
def getval(self):
return self.weights[0] * self.holes + self.weights[1] * self.bumpiness + self.weights[2] * (max(7, self.maxHeight) - 7) \
+ self.weights[3] * (-self.newl) + self.weights[4] * self.wellCells + self.weights[5] * self.deepWells + \
self.weights[6] * totalrowtrans + self.weights[7] * -self.blocks + 0.1 * self.avgHeight所以,上面的 self.weights 要怎麼找呢?
這就是基因演算法派上場的時候了!
PART THREE: 適者生存
學長,我會基因演算法了!
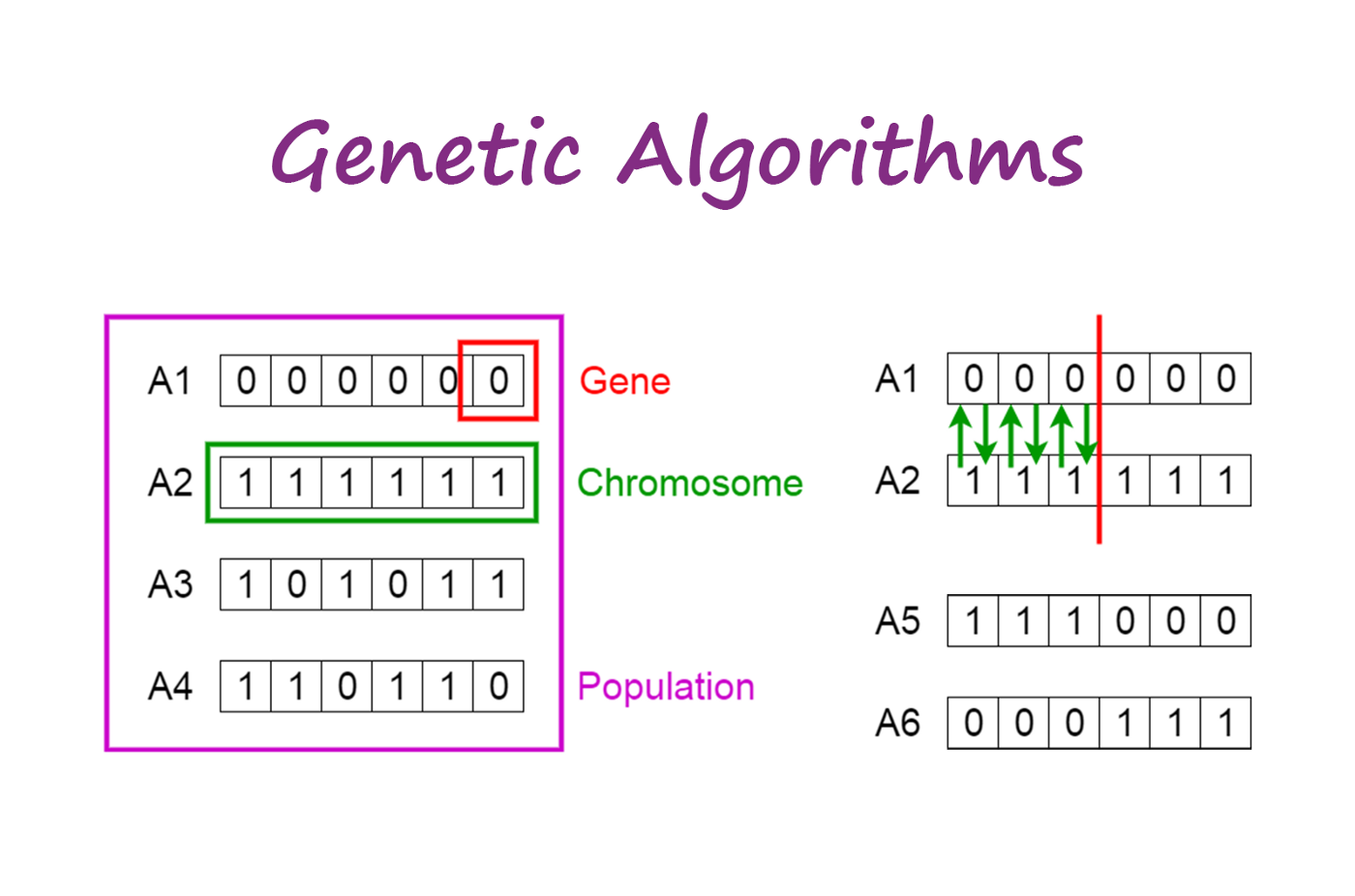
基因
個體
族群
From https://towardsdatascience.com/introduction-to-genetic-algorithms-including-example-code-e396e98d8bf3
適應度:玩20場Tetris 之後的平均分數
個體的基因代表啟發因子的權重
\Crossover/
- 帶權選擇親代父母
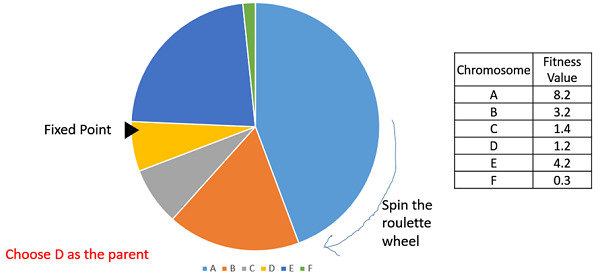
- 隨機選擇要從哪個親代遺傳
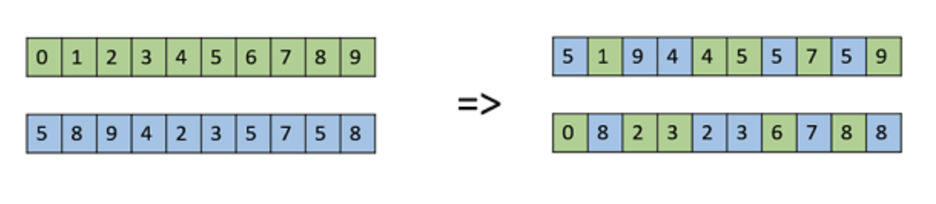
From https://www.tutorialspoint.com/genetic_algorithms/genetic_algorithms_parent_selection.htm
突...突變了?!
-
有一定機率在某個基因上發生
-
會把原本的數值在一定範圍內改變
-
突變量隨世代增加會變小
if random.random() < 0.07122: #mutation
if random.randint(0, 1) == 0:
child1[0][j] += random.uniform(-0.5/(gen + 1), 0.5/(gen + 1))
else:
child2[0][j] += random.uniform(-0.5/(gen + 1), 0.5/(gen + 1))鰣(ㄕˊ)糳(ㄗㄨㄛˋ)
pop = []
size = 50
tabugen = 3
clancnt = 0
for i in range(size): #隨機產生族群
pop.append([numpy.array(list(random.uniform(-1, 1) for i in range(8))), clancnt, [], numpy.array(list(random.uniform(-1, 1) for i in range(8))), 1])
# individual: weights forming a chromosome, the clan number, tabu list, memetic vector for local optimization, memetic scalar
clancnt += 1
for gen in range(100):
print("Generation ", gen + 1, sep='')
print(pop)
gettestdata(10)
res = []
c = 0
for individual in pop: #取得適應度
val = score(individual[0], 0)
res.append((val, individual))
print(val, end=" ")
c += 1
res = sorted(res, key= lambda x: x[0])
res.reverse()
print()
print(res[0])
s = sum(list(a[0] for a in res))
pop = []
valid = 0
count = 0
while valid < size - 1: #交配
count += 1
p1, p2 = [], [] #selects p1 and p2 as parents
s1, s2 = 0, 0
r = random.uniform(0, s - 0.01)
n = 0
for j in range(len(res)):
n += res[j][0]
if n > r:
p1 = res[j][1]
s1 = res[j][0]
break
r = random.uniform(0, s - 0.01)
n = 0
for j in range(len(res)):
n += res[j][0]
if n > r:
p2 = res[j][1]
s2 = res[j][0]
break
#print(p1, p2)
child1, child2 = [numpy.array([0.0] * 8), p1[1], copy.deepcopy(p1[2])], [numpy.array([0.0] * 8), p2[1], copy.deepcopy(p2[2])]
for j in range(8):
if random.random() < 0.5:
child1[0][j] = p1[0][j]
child2[0][j] = p2[0][j]
else:
child1[0][j] = p2[0][j]
child2[0][j] = p1[0][j]
if random.random() < 0.07122: #mutation 突變
if random.randint(0, 1) == 0:
child1[0][j] += random.uniform(-0.5/(gen + 1), 0.5/(gen + 1))
else:
child2[0][j] += random.uniform(-0.5/(gen + 1), 0.5/(gen + 1))
child1[2].append(child2[1]) #adds each other to tabu list
child2[2].append(child1[1])
pop.append(child1)
if valid < size - 1:
pop.append(child2)
pop.append(res[0][1])PART FOUR: 部落的禁忌
等等...好像不太對?
是不是...會近親通婚?!
這樣生出來的小孩不是都...
禁忌的力量
禁忌搜索(tabu search) 是一種搜尋演算法,可以避免搜尋結果停在區域極值(local minima)
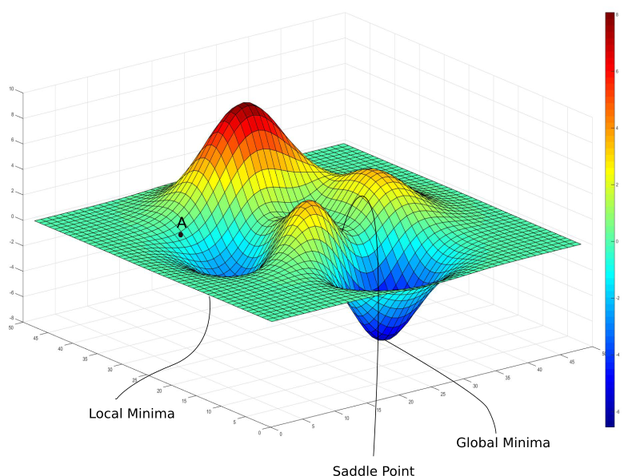
From https://bdtechtalks.com/2020/04/27/deep-learning-mode-connectivity-adversarial-attacks/gradient-descent-local-minima/
你是誰家的?
- 部落編號:這個個體屬於哪個家族(ex.姓氏)
- 禁忌名單:個體的祖先有哪些家族(ex.親戚)
在交配時,父母親部落編號相同或編號在對方禁忌名單內,就不會生下子代!
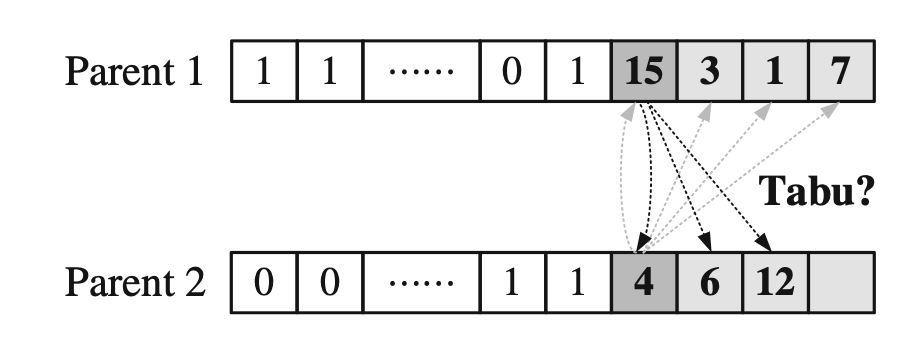
埕(ㄔㄥˊ)氏(ㄕˋ)
pop = []
size = 50
tabugen = 3 #禁忌名單存幾個世代
clancnt = 0
for i in range(size):
pop.append([numpy.array(list(random.uniform(-1, 1) for i in range(8))), clancnt, [], numpy.array(list(random.uniform(-1, 1) for i in range(8))), 1])
# individual: weights forming a chromosome, the clan number, tabu list, memetic vector for local optimization, memetic scalar
clancnt += 1
for gen in range(100):
#...和前面一樣
while valid < size - 1:
count += 1
p1, p2 = [], [] #selects p1 and p2 as parents
s1, s2 = 0, 0
r = random.uniform(0, s - 0.01)
n = 0
for j in range(len(res)):
n += res[j][0]
if n > r:
p1 = res[j][1]
s1 = res[j][0]
break
r = random.uniform(0, s - 0.01)
n = 0
for j in range(len(res)):
n += res[j][0]
if n > r:
p2 = res[j][1]
s2 = res[j][0]
break
#print(p1, p2)
#判斷禁忌
tabu = False #checks if match is tabu/
if p1[1] == p2[1]:
tabu = True
for clan in p1[2]:
if p2[1] == clan:
tabu = True
for clan in p2[2]:
if p1[1] == clan:
tabu = True
#print(tabu)
if tabu:
continue
else:
valid += 2
child1, child2 = [numpy.array([0.0] * 8), p1[1], copy.deepcopy(p1[2])], [numpy.array([0.0] * 8), p2[1], copy.deepcopy(p2[2])]
for j in range(8):
if random.random() < 0.5:
child1[0][j] = p1[0][j]
child2[0][j] = p2[0][j]
else:
child1[0][j] = p2[0][j]
child2[0][j] = p1[0][j]
if random.random() < 0.07122: #mutation
if random.randint(0, 1) == 0:
child1[0][j] += random.uniform(-0.5/(gen + 1), 0.5/(gen + 1))
else:
child2[0][j] += random.uniform(-0.5/(gen + 1), 0.5/(gen + 1))
child1[2].append(child2[1]) #adds each other to tabu list
child2[2].append(child1[1])
while len(child1[2]) > tabugen:
child1[2].pop(0)
while len(child2[2]) > tabugen:
child2[2].pop(0)
pop.append(child1)
if valid < size - 1:
pop.append(child2)
pop.append(res[0][1])
clancnt += 1PART FIVE: 文化衝突
但是,
基因演算法搜尋到的範圍太少了!
因此,有一個演算法出現了...
迷因演算法!!!

From https://www.reddit.com/r/memes/comments/eq2pe6/google_image_meme_man_meme/

From https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Amu-4_mH0no
迷因:文化的遺傳單位
那這跟演算法有什麼關係?
迷因演算法(Memetic algorithm)
-
結合區域搜尋和基因演算法
-
個體在評估適應度前會先自己嘗試進步
-
迷因的選擇可以透過「傳承」
我們的「迷因」
一個隨機產生的向量!
每次測試現在的權重向量加上迷因之後成績會不會變高,如果會就更新(類似模擬退火)
pop = []
size = 50
tabugen = 3
clancnt = 0
for i in range(size):
pop.append([numpy.array(list(random.uniform(-1, 1) for i in range(8))), clancnt, [], numpy.array(list(random.uniform(-1, 1) for i in range(8))), 1])
# individual: weights forming a chromosome, the clan number, tabu list, memetic vector for local optimization, memetic scalar
clancnt += 1
for individual in pop:
val = score(individual[0], 0)
# print(individual[0], individual[3], individual[4])
for step in range(5):
newparam = numpy.add(individual[0],
numpy.multiply(numpy.divide(individual[3], numpy.linalg.norm(individual[3])),
individual[4]))
localval = score(newparam, 0)
if localval > val:
val = localval
individual[0] = newparam
individual[4] *= 0.9
else:
if step == 0:
individual[3] = numpy.array(list(random.random() for i in range(8)))
break
# print(individual[0])
res.append((val, individual))
print(val, end=" ")
c += 1迷因的傳承
爸:欸欸兒子,這個迷因我覺得很讚,看完之後整個人都變強了,你要不要試試看XD
媽:我也有一個迷因,但是你爸比較強所以你就 用他的吧
你:(使用那個迷因搜尋)
你:這什麼爛梗啊88888
你:(重新作一個迷因)
大概就是這樣(講師寫到這裡已經不行了)
PART SIX: 結局
演算法的表現到底如何?
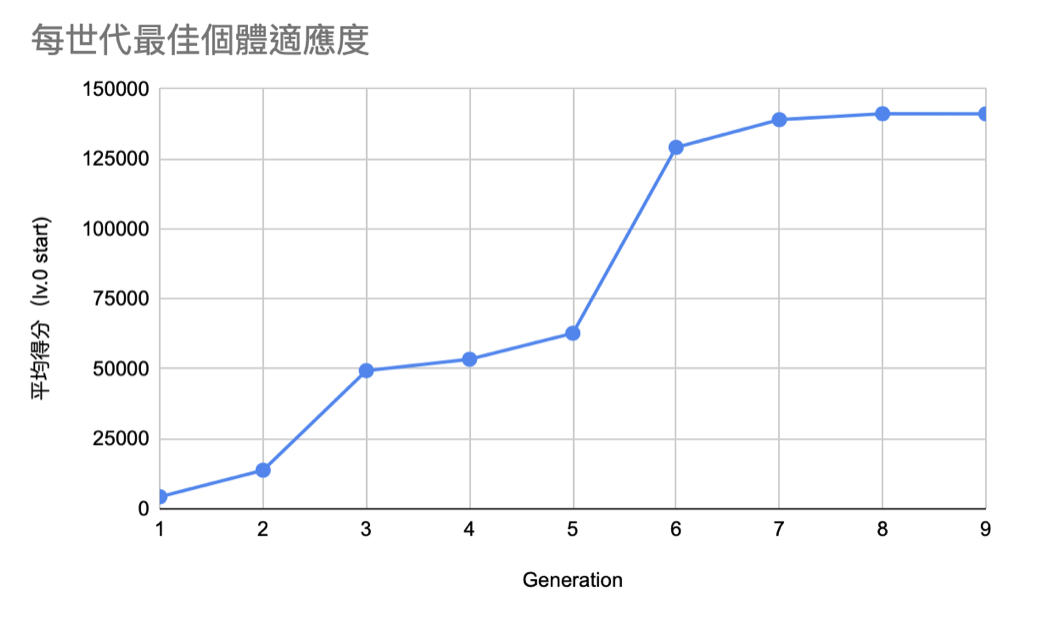
最後分數
- 平均行數:230.4行 (最多也只到230行)
- 平均分數(Lv. 0 Start):290251.6分
- 平均分數(Lv. 18 Start):486000分