Security and Authentication in React Native
Kadi Kraman / Formidable
@kadikraman

Kadi Kraman
Senior React Native Engineer
@kadikraman
Formidable
@kadikraman

Kadi Kraman
Senior Software Engineer
Web Developer
...who writes mobile apps now, because we can do it in JavaScript (thanks, Facebook)
Secrets
How to keep them safe?
If the user shouldn't see it,
1. Do not send it via a network request
2. Do not ship it in the app code
3. Do not save it in Async Storage
3Fun Security Fail
Alternative dating app leaking their members' sensitive info
(August, 2019)
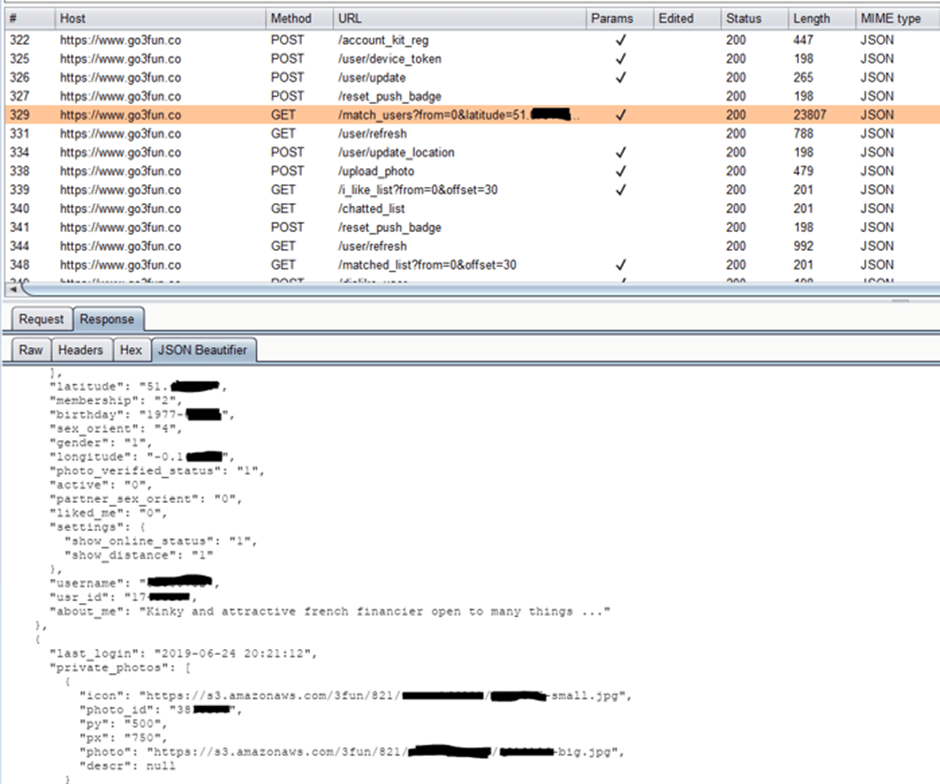
Source: https://securityaffairs.co/
Source: https://www.independent.co.uk
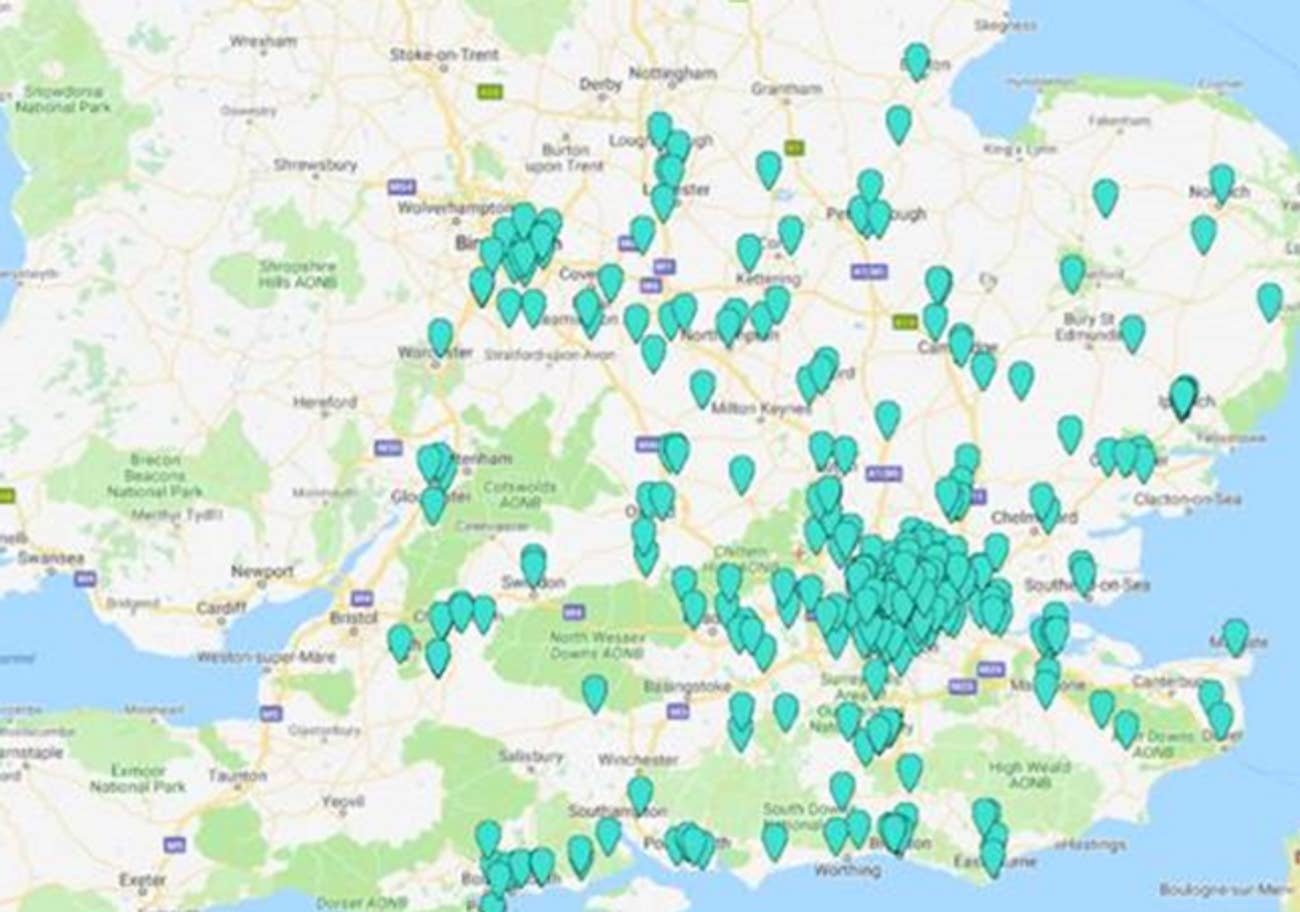
Users' real time location...
Source: https://securityaffairs.co/
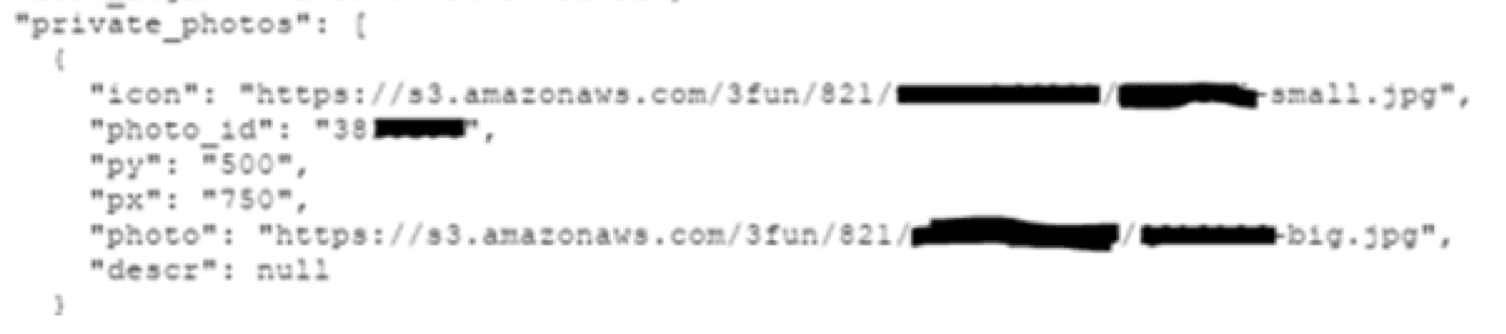
Private photos...

But that will never happen to me!
...right?

Mary Strawberry
react, react native, prosecco
I like long walks on the beach and puppies
Public

Paul Pear
Protected
Private
/api/users
[
{
id: 123,
firstName: "Mary",
lastName: "Strawberry"
avatar: "https://some.url/mary.png",
email: "mary.strawberry@fakemail.com",
phone: "123456789",
interests: ["react", "react native", "prosecco"],
bio: "I like long walks on the beach and puppies"
},
{
id: 234,
firstName: "Paul",
lastName: "Pear",
avatar: "https://some.url/paul.png"
}
]Public, Protected, Private

Sensitive info should always be filtered server-side
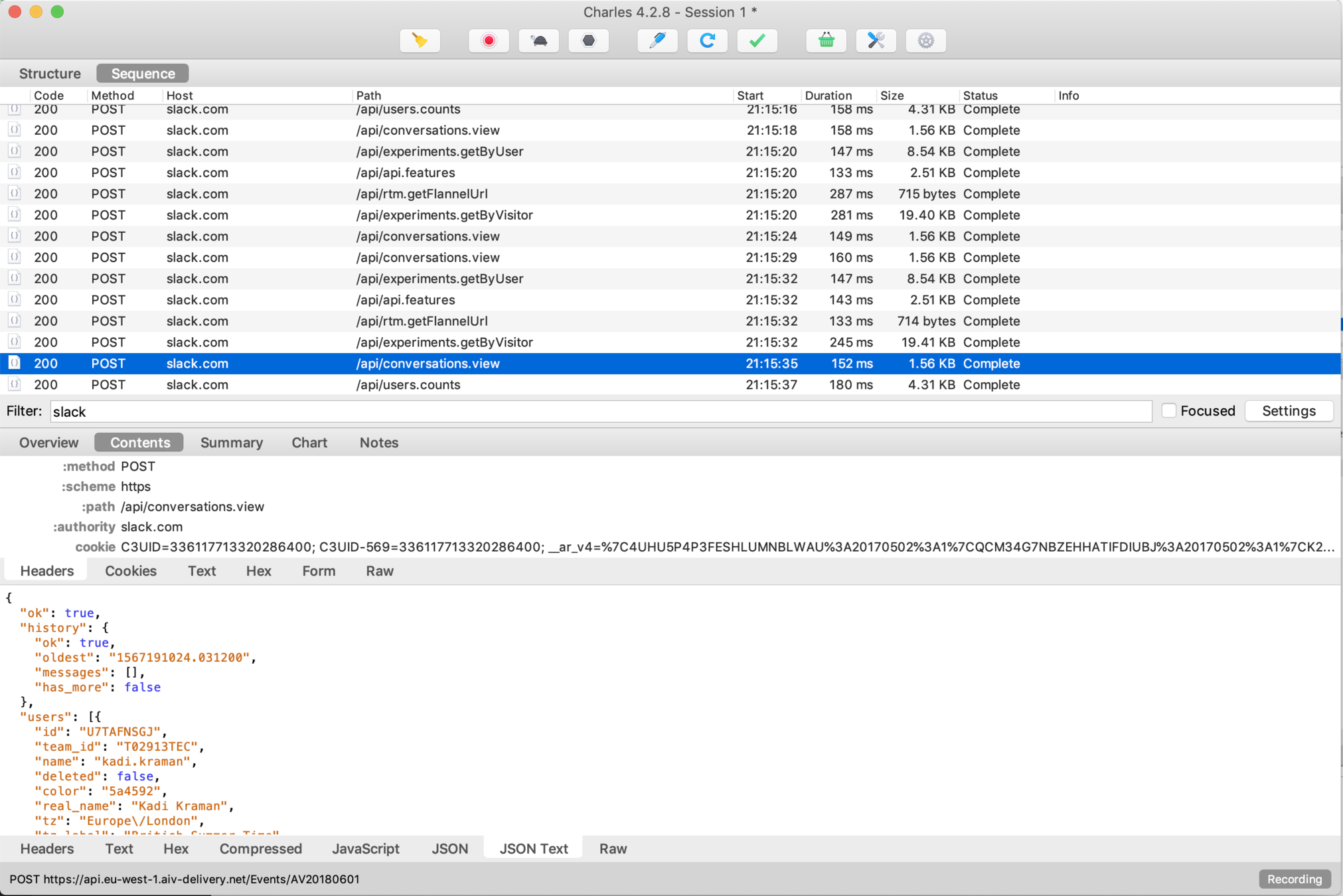
How easy is it really to see your mobile app traffic?
You will need...
Phone (iPhone 6s)
Laptop (MacBook Pro)
Proxy app (Charles Proxy)
WiFi
DO try this at home! 🏠
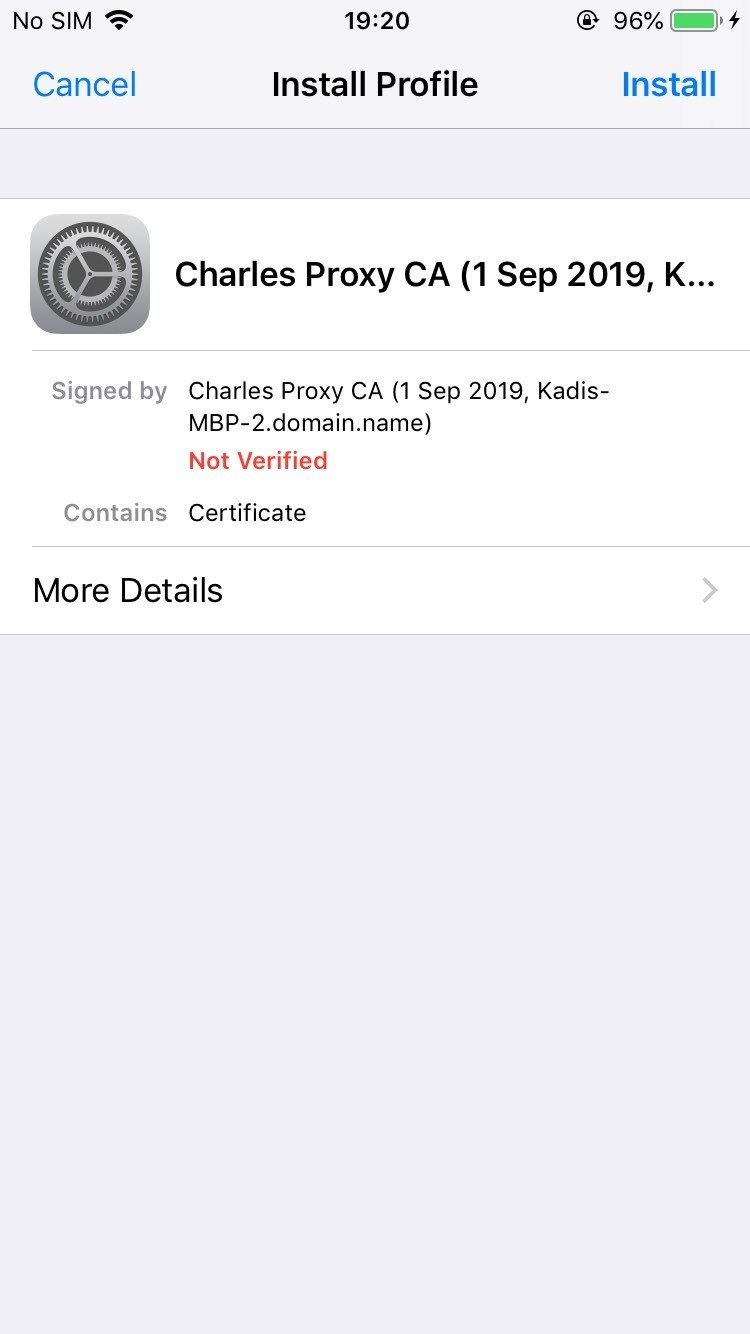
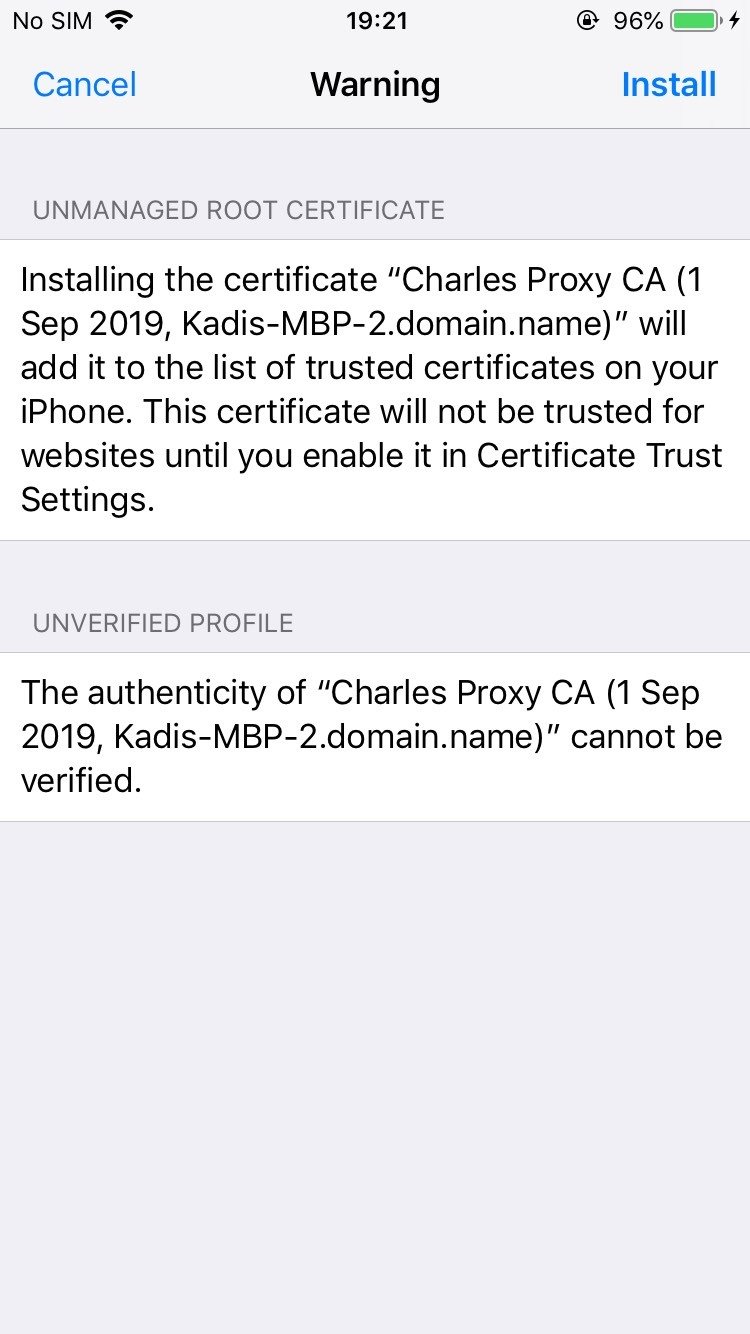
1. Download and install Charles Proxy
2. Configure mobile traffic to go through the proxy
3. Install the Charles Proxy SSL cert on your phone
4. Enable SSL proxying for all hosts
Slack
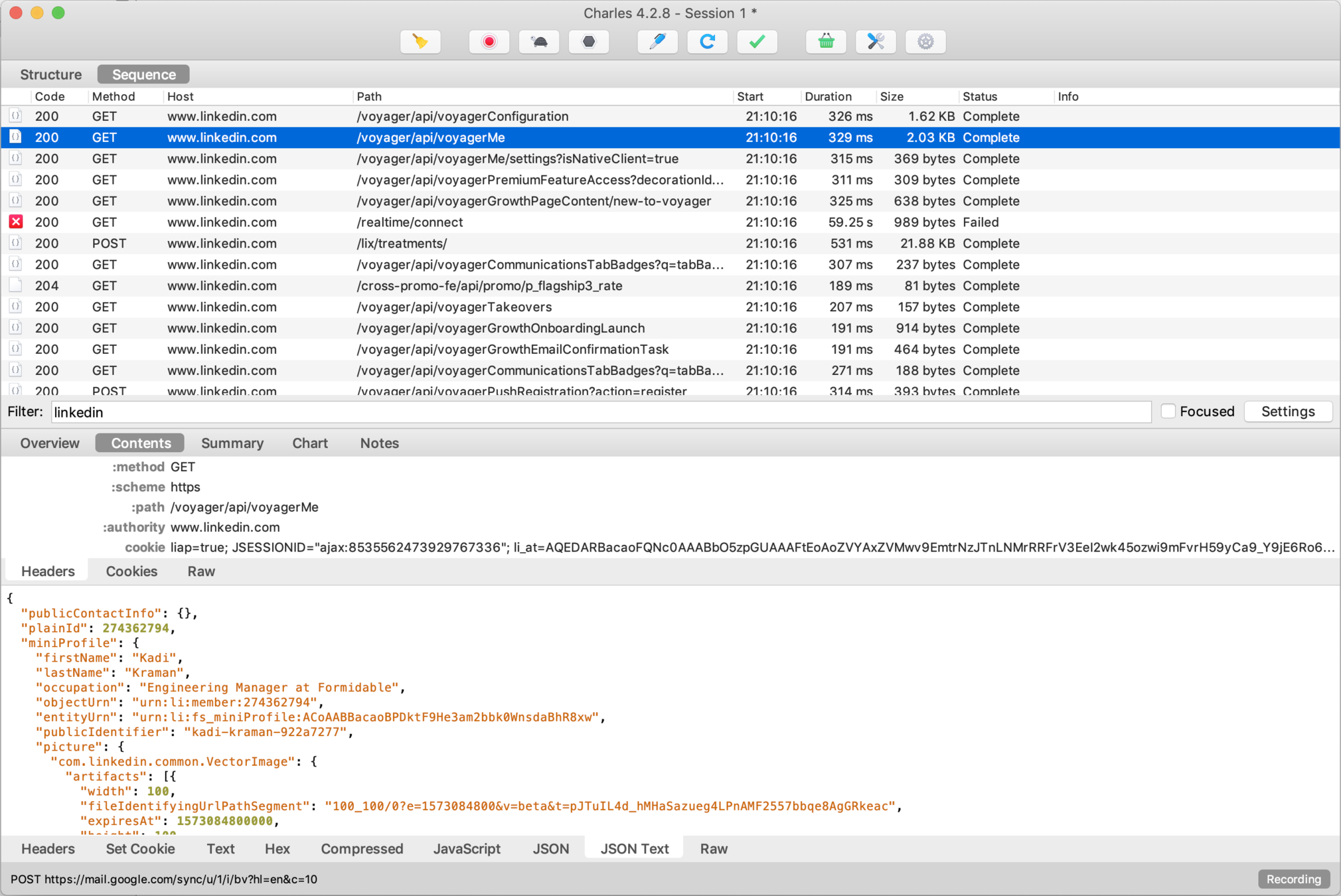
Virgin Active
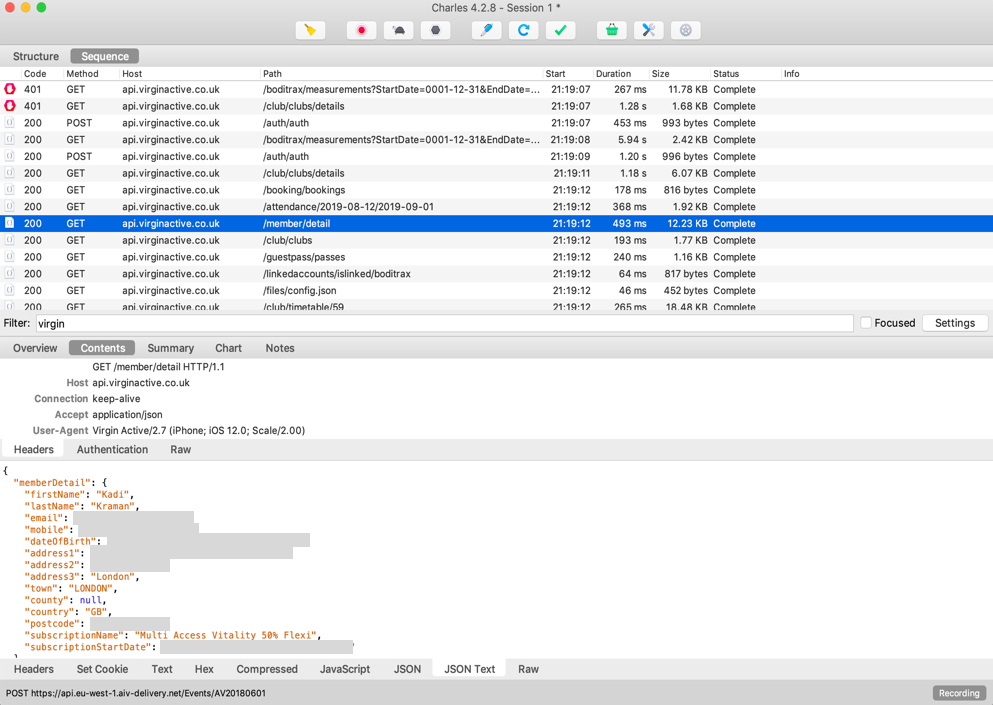
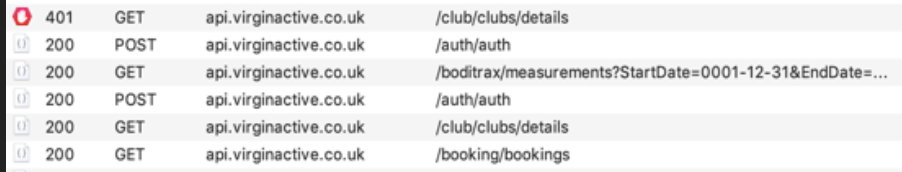
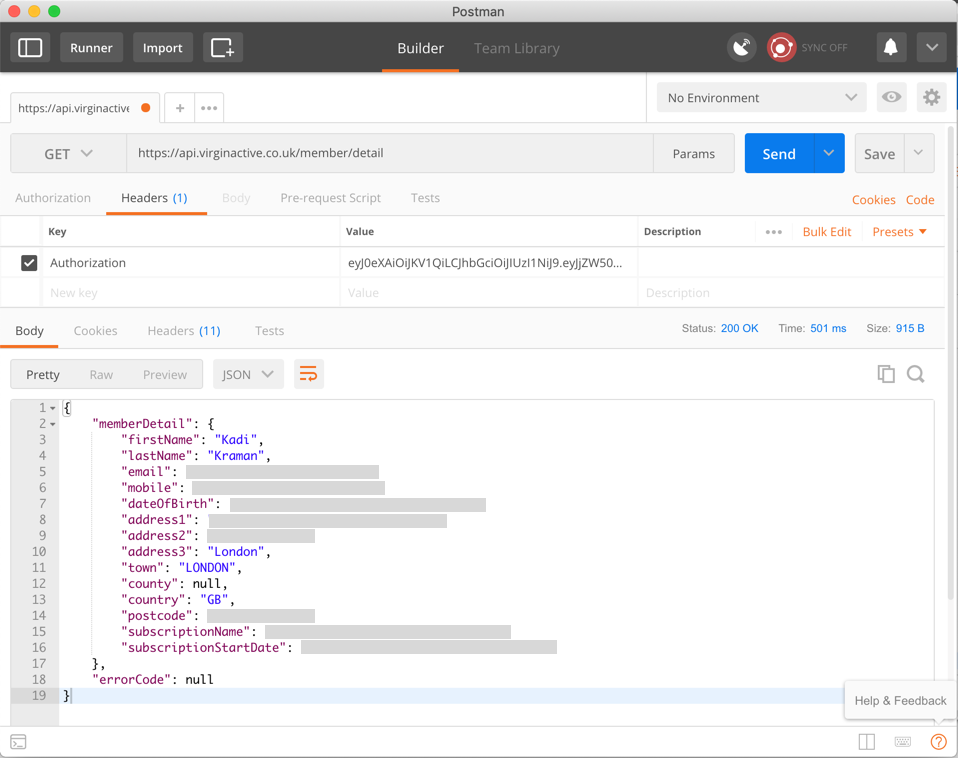
Do not add sensitive info in your app source code
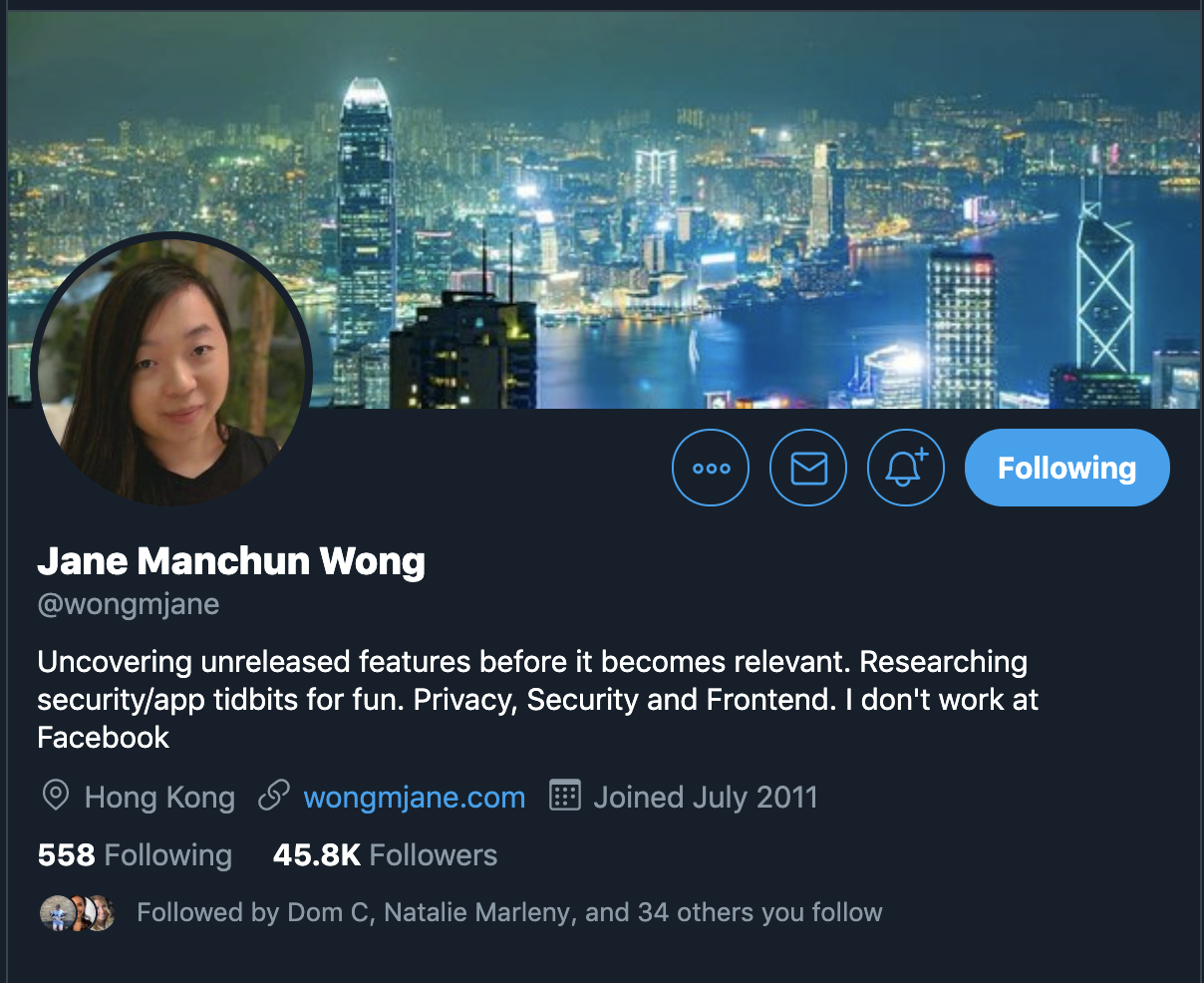
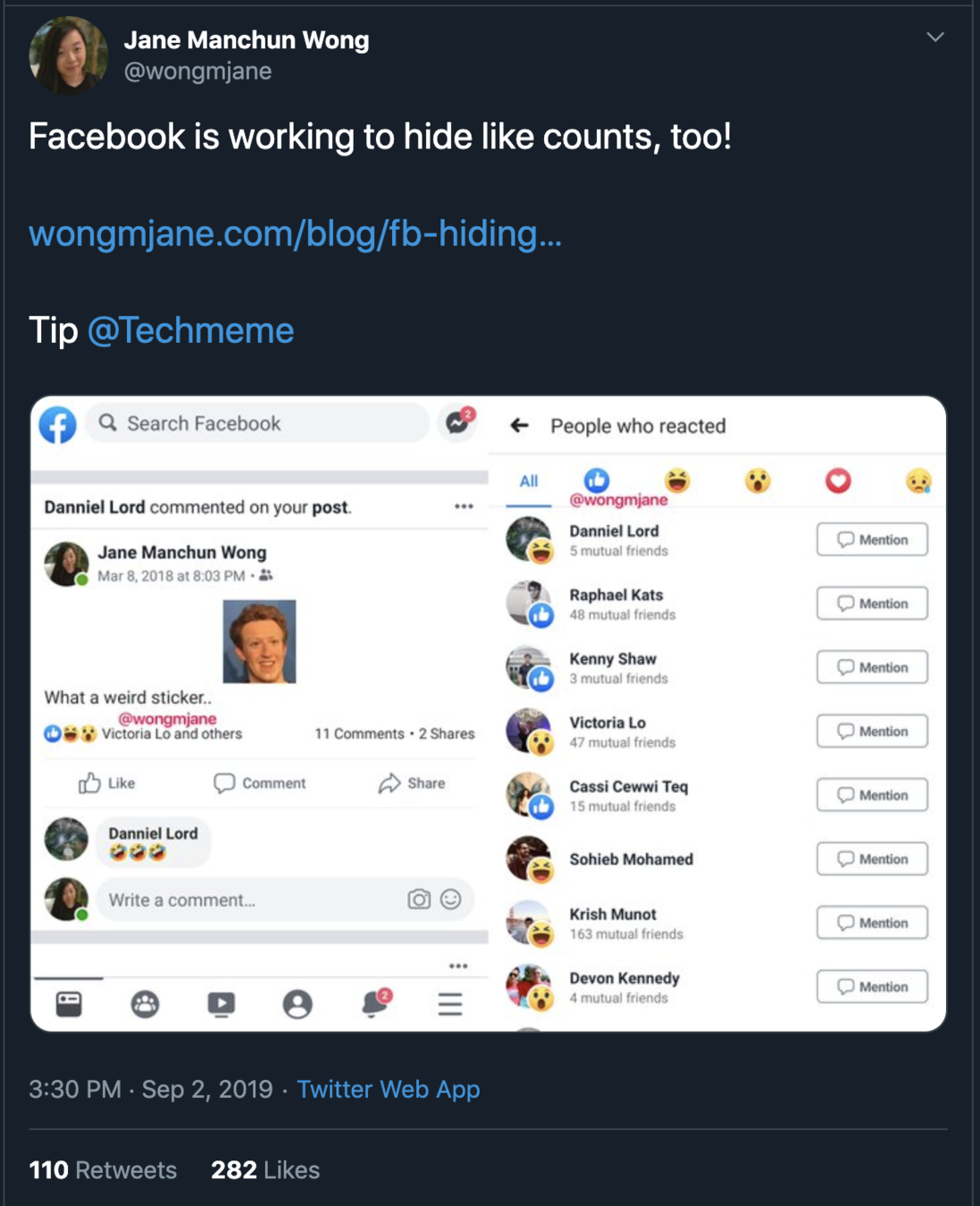
How does she do it?
1. Get the public .apk for each new version of the app
2. Decompile the app code using a publicly available tool (and a custom python script)
3. Read through the code to see what's changed
Source: https://finance.yahoo.com/news/
Async Storage
Simple, unencrypted, asynchronous, persistent, key-value storage system that is global to the app
It should be used instead of LocalStorage
Async Storage
Use for non-sensitive app info
Persisted app state - YES
Auth tokens - NO
Async Storage is sandboxed for each app
However this is an OS restriction, which can be overcome
Rooting/Jailbreaking devices
Rooting (Android)
obtaining root access to device
Jailbreaking (iOS)
privilege escalation of an Apple device for the purpose of removing software restrictions imposed by Apple
If the user shouldn't see it,
1. Do not send it via a network request
2. Do not ship it in the app code
3. Do not save it in Async Storage
Recap!
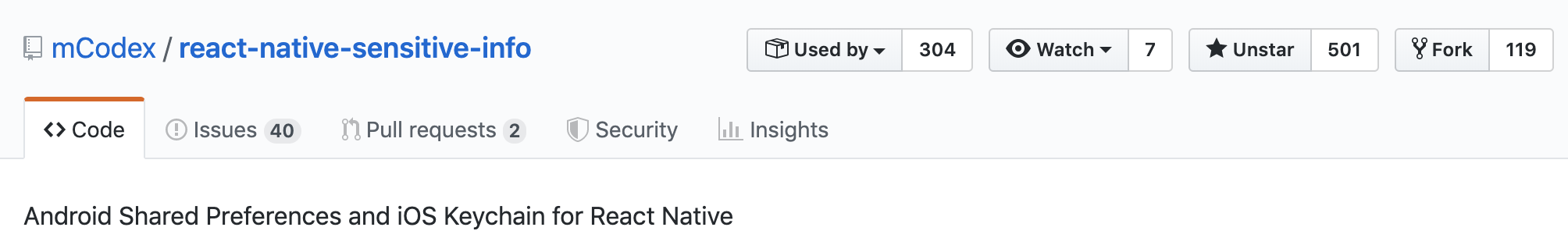
So where can you store tokens?
Android Shared Preferences
iOS Keychain
The info should still be encrypted, because jailbroken devices will be able to access it in plaintext
Security tips
1. Do calculate permissions server-side
2. Do only send the user data they're allowed to see
3. Do use secure storage, e.g.
- react-native-sensitive-info or
- react-native-keychain
for tokens and other sensitive info
Authentication
OAuth 2 !== OpenID
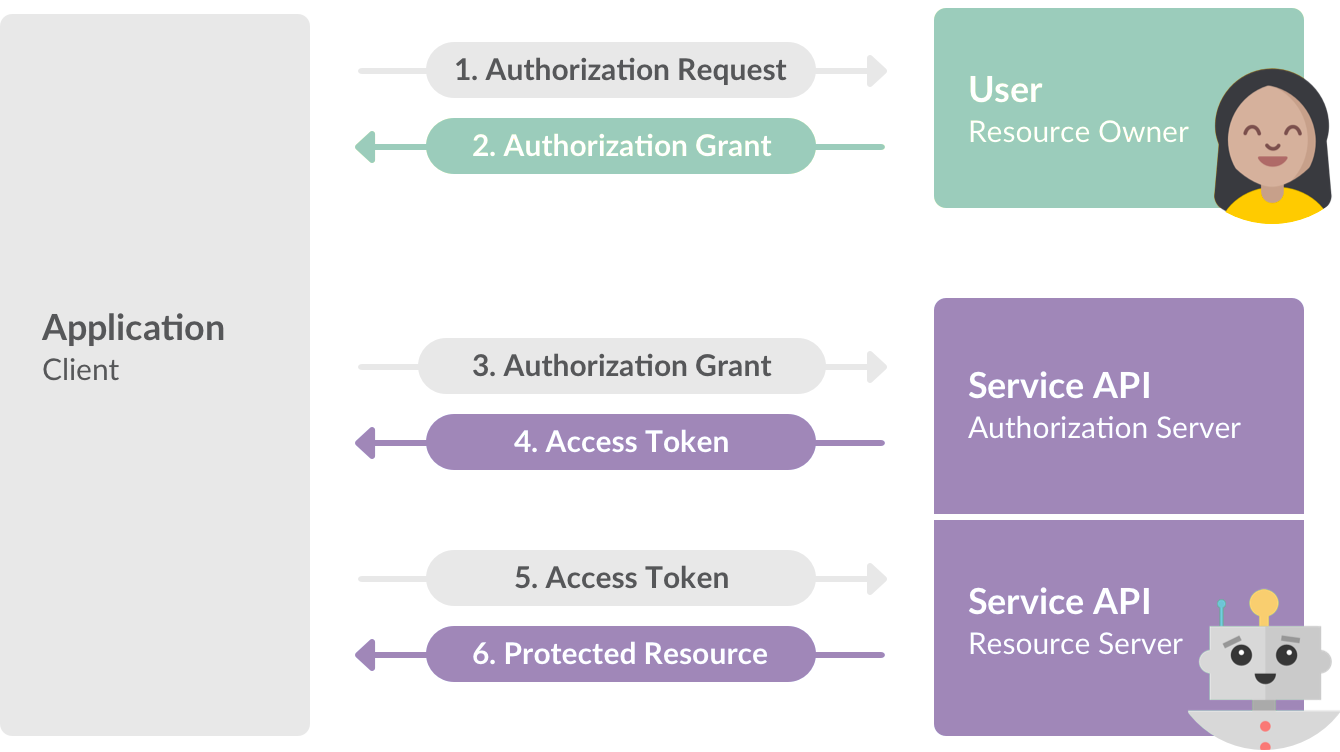
Source: https://api.slack.com/docs/oauth
OAuth 2
OpenID
Open standard and decentralized authentication protocol
Allows users to be authenticated by co-operating sites
OpenID Connect - authentication layer that sits on top of the OAuth 2.0 authorization framework
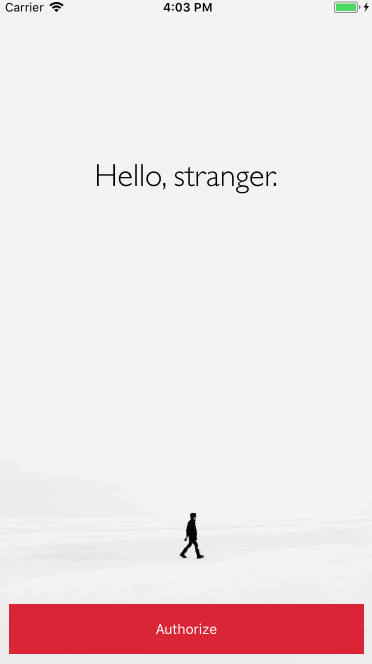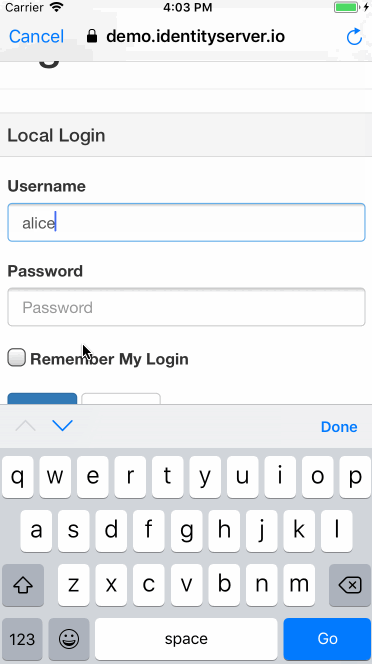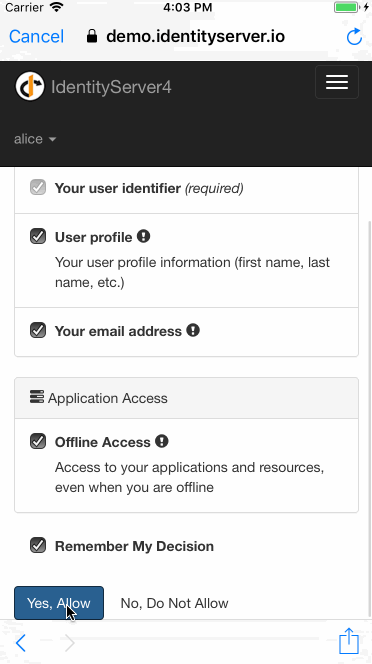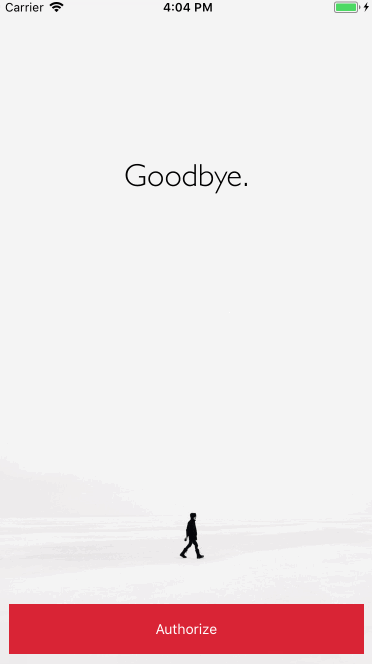
Potential Security concerns with OAuth2 on Native Apps
POST
/authorize?
clientId=<my_id>&
redirectUri=<my_redirect_uri>&
scope=<access_scope>1. Ask the user to authenticate
2. After a successful login, the provided redirect uri is called together with an verification code
3. verification code is exchanged for an auth token
POST
/token?
clientId=<my_id>&
code=<code>POST
/authorize?
clientId=<my_id>&
redirectUri=<my_redirect_uri>&
scope=<access_scope>
1. Ask the user to authenticate
2. After a successful login, the provided redirect uri is called together with an verification code
3. verification code is exchanged for an auth token
POST
/token?
clientId=<my_id>&
code=<code>&
clientSecret=<secret>POST
/authorize?
clientId=<my_id>&
redirectUri=<my_redirect_uri>&
scope=<access_scope>
1. Ask the user to authenticate
2. After a successful login, the provided redirect uri is called together with an verification code
3. Verification code is exchanged for an auth token
POST
/token?
clientId=<my_id>&
code=<code>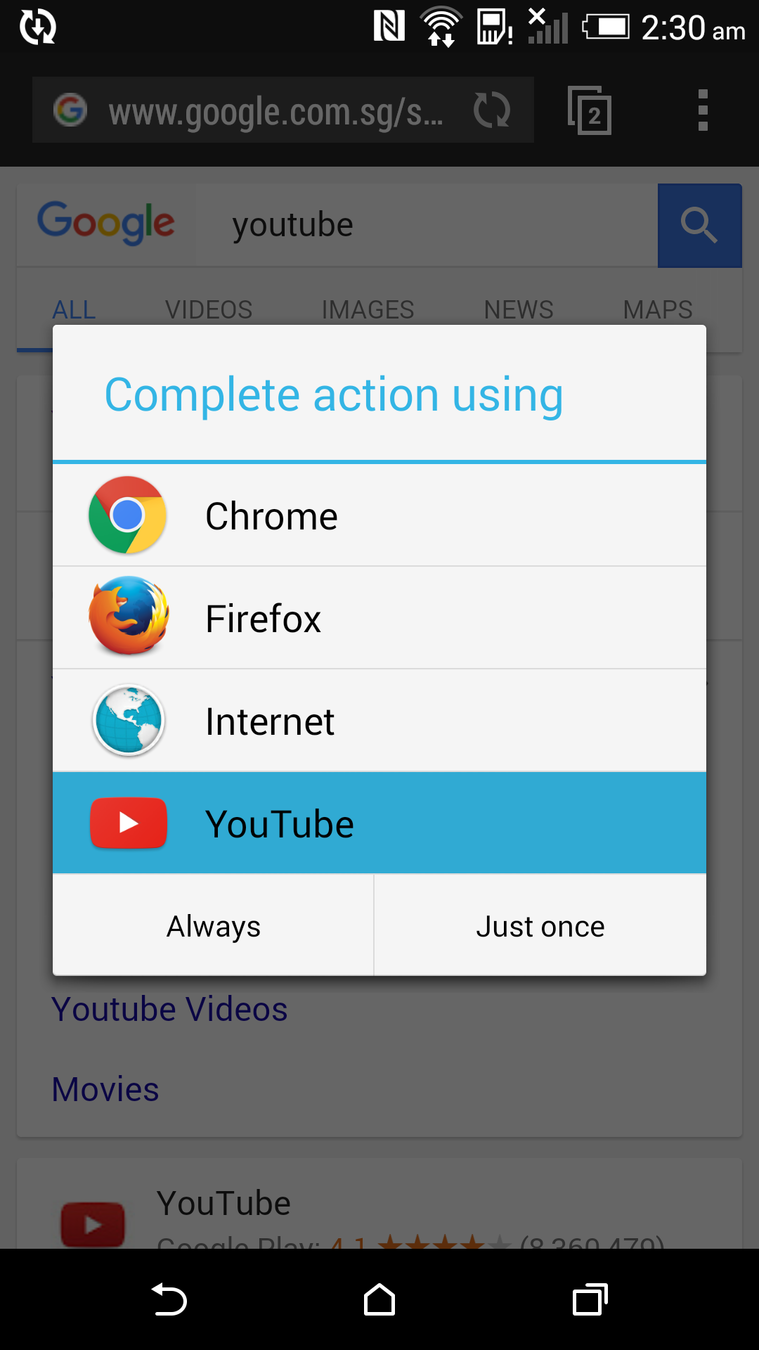
Web addresses are unique, app schemes are not
The attacker can intercept the verification code and use it to obtain the auth token
PKCE ("pixy") to the rescue!
Security extension to OAuth 2.0 for public clients on mobile devices
Designed to prevent interception of the authorisation code by a malicious application that has sneaked into the same device
Proof Key for Code Exchange
POST
/authorize?
clientId=<my_id>&
redirectUri=<my_redirect_uri>&
scope=<access_scope>&
code_challenge=<generated_code_challenge>&
code_challenge_method=<method_used>1. Ask the user to authenticate
2. After a successful login, the provided redirect uri is called together with an verification code
3. verification code is exchanged for an auth token
POST
/token?
clientId=<my_id>&
code=<code>&
code_verifier=<generated_code_verifier>POST
/authorize?
clientId=<my_id>&
redirectUri=<my_redirect_uri>&
scope=<access_scope>&
code_challenge=<generated_code_challenge>&
code_challenge_method=<method_used>1. Ask the user to authenticate
2. After a successful login, the provided redirect uri is called together with an verification code
3. verification code is exchanged for an auth token
POST
/token?
clientId=<my_id>&
code=<code>&
code_verifier=<generated_code_verifier>const sha256 = (buffer) =>
crypto
.createHash('sha256')
.update(buffer)
.digest();
const challenge = base64URLEncode(sha256(verifier));POST
/authorize?
clientId=<my_id>&
redirectUri=<my_redirect_uri>&
scope=<access_scope>&
code_challenge=<generated_code_challenge>&
code_challenge_method=<method_used>1. Ask the user to authenticate
2. After a successful login, the provided redirect uri is called together with an verification code
3. Verification code is exchanged for an auth token
POST
/token?
clientId=<my_id>&
code=<code>&
code_verifier=<generated_code_verifier>Cryptographically random key that was used to generate the code_challenge passed to /authorize.
const sha256 = (buffer) =>
crypto
.createHash('sha256')
.update(buffer)
.digest();
const challenge = base64URLEncode(sha256(verifier));


React Native App Auth
Thank you!
Unsplash photos by @wflwong @jonah_jpg @jonaselia @markusspiske