week 06
Representation Learning on Graphs
Social Network Analysis
Network Embeddings
Graphs representation
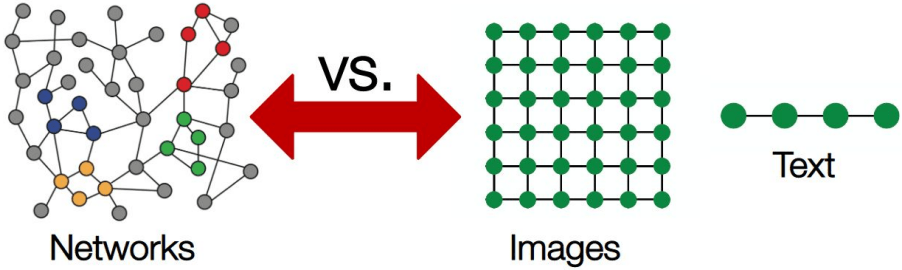
In many fields the data have a graph structure
- social: friendship graph in social networks, graph of scientific citations
- man-made: internet, web, road networks, air communication networks
- In biology: protein interactions, complex molecules.
Graph representation
- supervised, semi-supervised
- node classification
- Is the account a bot
- Predicting user age, gender, profession in a social network
- Predicting the function of a new protein based on its interaction with others
- article topic prediction on the basis of citations
- link prediction
- content recommendation in an online platform
- forecasting drug side effects
- community detection
- searching for users with similar interests
- Revealing functional groups of proteins
- node classification
Objective: extract features from the graph in a form suitable for machine learning algorithms
Machine learning tasks on graphs and their applications
Approaches to learning graph representations
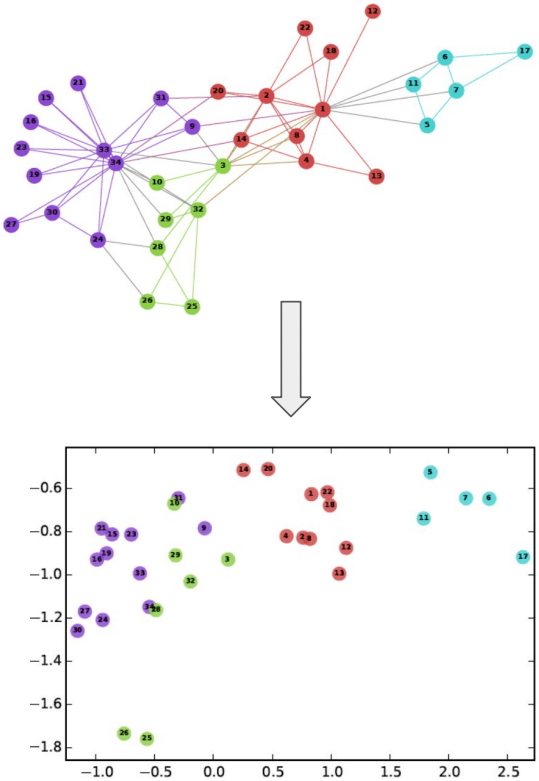
Task: find a representation of graph vertices as vectors of (low-dimensional) space that preserve useful information. Normally, vectors are close in space if the vertices are close in the graph
graph embedding ~ representation learning
Approaches:
- Naive methods;
- Based on matrix decompositions;
- Based on random walks;
- Graph neural networks.
- Other (edge probability)
Naive Approaches
Simple graph representations
-
Graphlets
-
Centralities
-
Layout Based
Matrix Decomposition
Node representation as a dimensionality reduction problem with information preservation.
General idea: represent the graph as a matrix and decompose it.
Notation:
- \( G(V,E) \) - graph with vertices \( V \) and edges \( E \)
- \( W \) - adjacency matrix with weights
- \( D \) - diagonal degree matrix
- \( L = D - W \) - Laplacian of the graph
- \( Y_i \) is the vector representation of a vertex \( i \) of dimension \( d \ll |V| \)
- \( I \) is a unary matrix
- \( \phi(Y) \) - loss function
≈
d
d
|V|
|V|
\( d \ll|V| \)
Locally Linear Embedding
is reduced to finding the smallest eigenvectors of the sparse matrix \( (I-W)^T(I-W) \)
K. Saul, T. Roweis: An Introduction to Locally Linear Embedding (2000) [pdf]
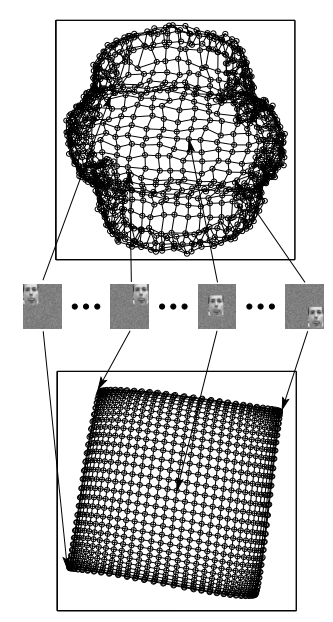
Laplacian Eigenmaps
M. Belkin, P. Niyogi: Laplacian Eigenmaps for Dimensionality Reduction and Data Representation (NIPS, 2002) [pdf]
is reduced to finding the smallest eigenvectors of the normalized Laplassian
Idea: vertex representation is close if the vertices are connected
Cauchy Graph Embeddings
Another distance function \( distance = \frac{|Y_i - Y_j|^2}{|Y_i - Y_j|^2+\sigma^2} \)
D. Luo, C. Ding, F. Nie, H. Huang: Cauchy Graph Embedding (ICML 2011) [pdf]
Matrix Decomposition
Naive method problems
The main problem is maintaining only 1st order proximity
Definitions:
First-order proximity between vertices \( i \) and \( j \) = edge weight \( W_{ij} \)
Let be the \(k\)-order closeness. Then the \( (k+1) \) order closeness between vertices \( i \) and \( j \) = the similarity measure of vectors \( s_i \) and \( s_j \) .
≈
d
d
|V|
|V|
\( d \ll|V| \)
GraRep (CIKM, 2015)
The representations for all k are concatenated. The disadvantage is the complexity of the algorithm \( O(|V|^3) \).
Normalized transition matrix \( X^k_{i,j}=log\frac{A^k_i,j}{\sum\limits_iA^k_{i,j}}-\log\beta \)
S. Cao, W. Lu, Q. Xu: GraRep (CIKM, 2015) [link]
HOPE
Take S proximity matrix instead of adjacency matrix (Katz Index, Rooted Page Rank, Common Neighbors, Adamic-Adar score)
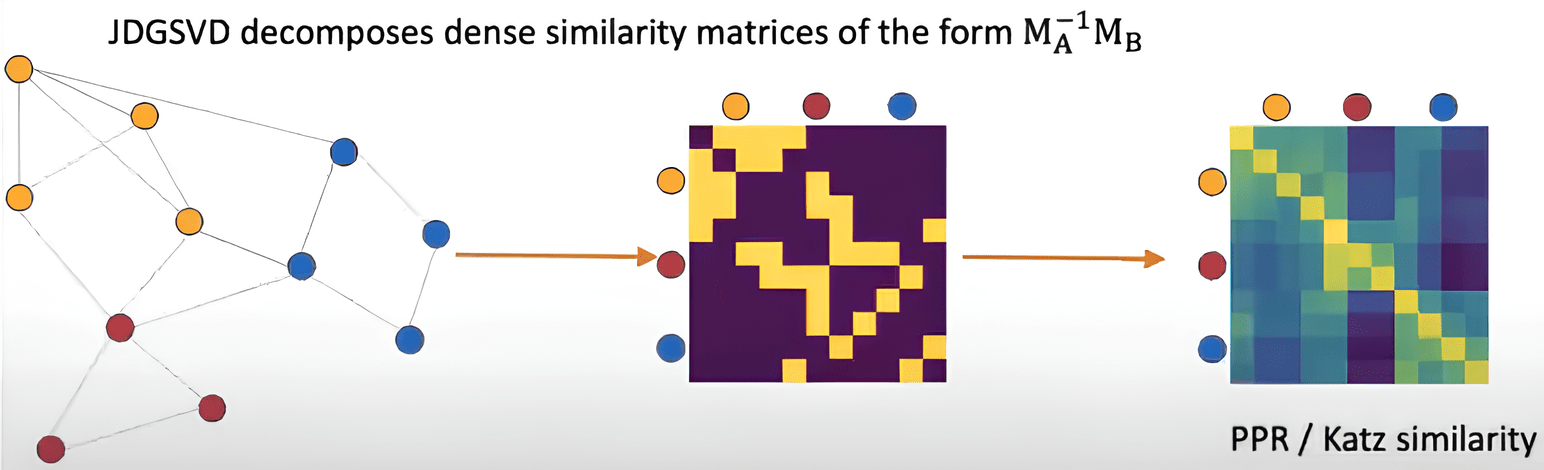
The main disadvantages of matrix decomposition algorithms: only the 1st order closeness and/or high complexity of the algorithm
D. Zhu, et all: High-order Proximity Preserved Embedding For Dynamic Networks , KDD 2016
AROPE
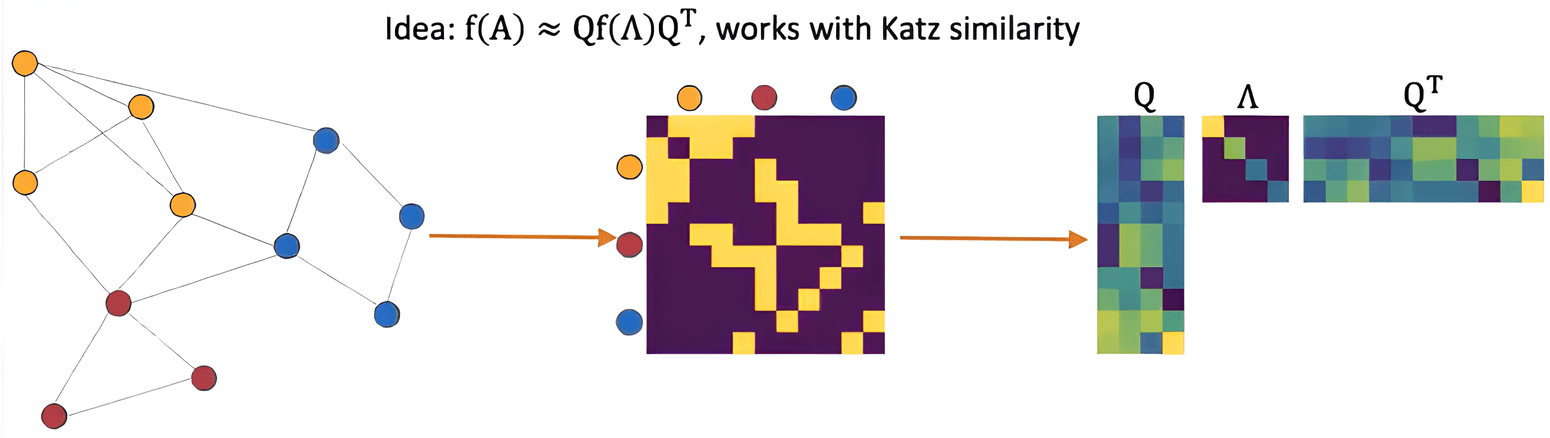
M. Ou, P. Cui, J. Pei, Z. Zhang, W. Zhu: Asymmetric Transitivity Preserving Graph Embedding [pdf]
authors’ code (MATLAB) [link]
Z. Zhang, P. Cui, X. Wang, J. Pei, X. Yao, W. Zhu: Arbitrary-Order Proximity Preserved Network Embedding [pdf]
authors’ code (MATLAB + Python) [link]
HOPE
AROPE
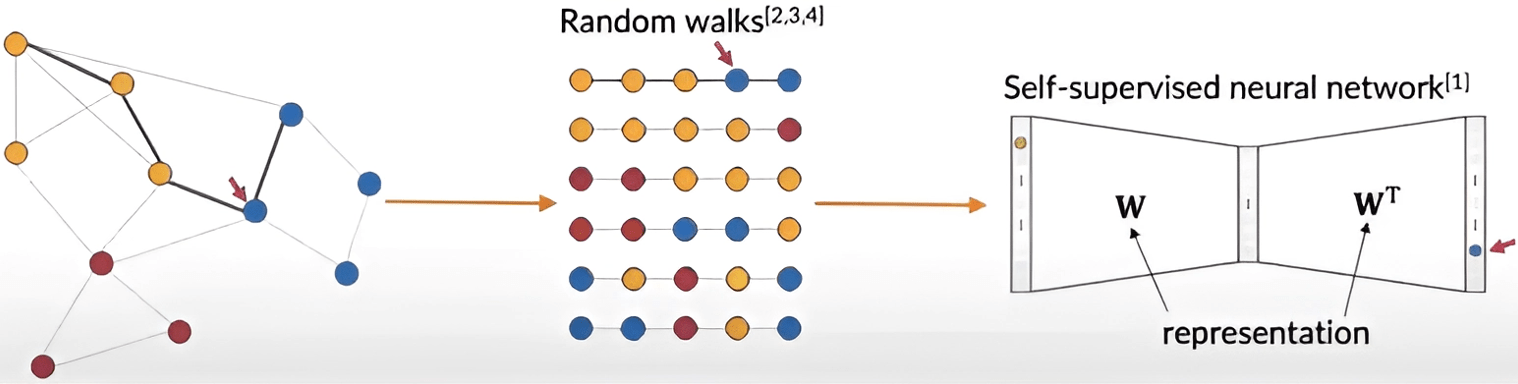
Random Walk
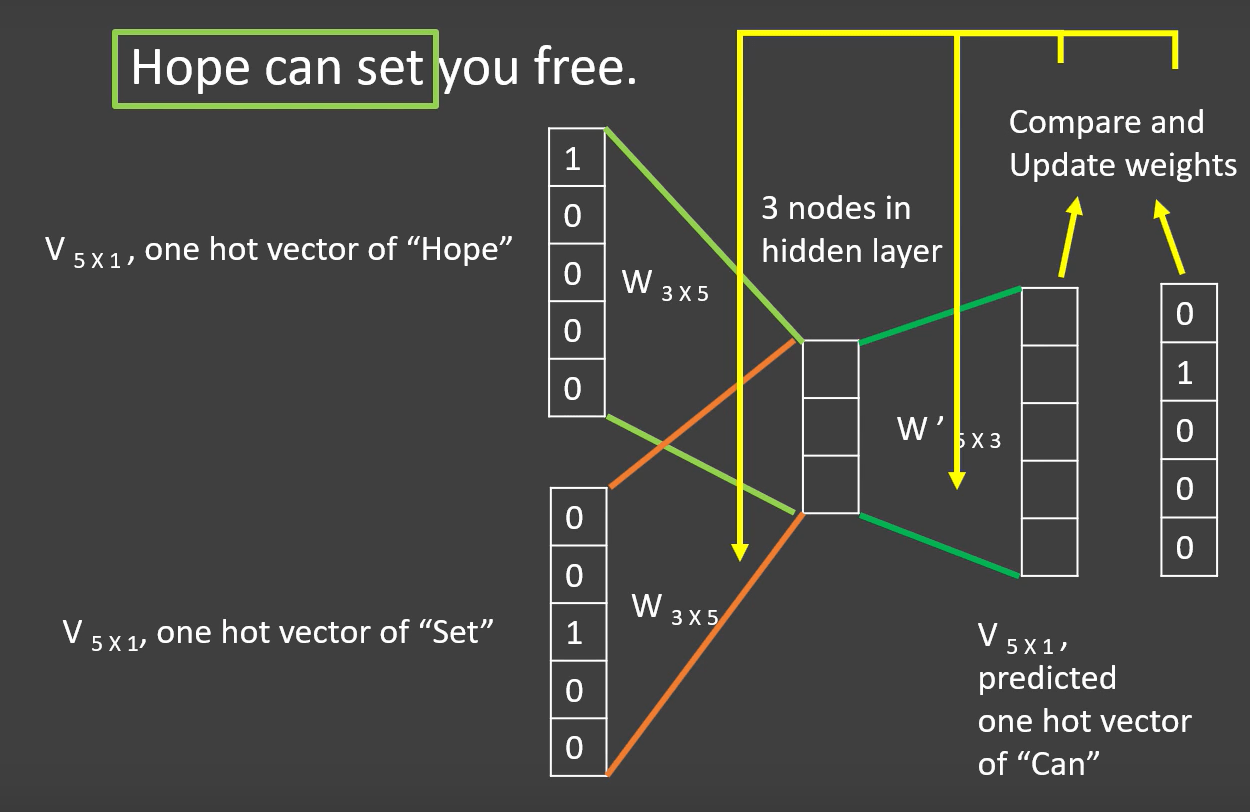
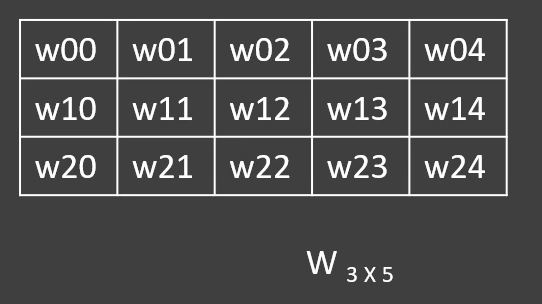
Word2vec
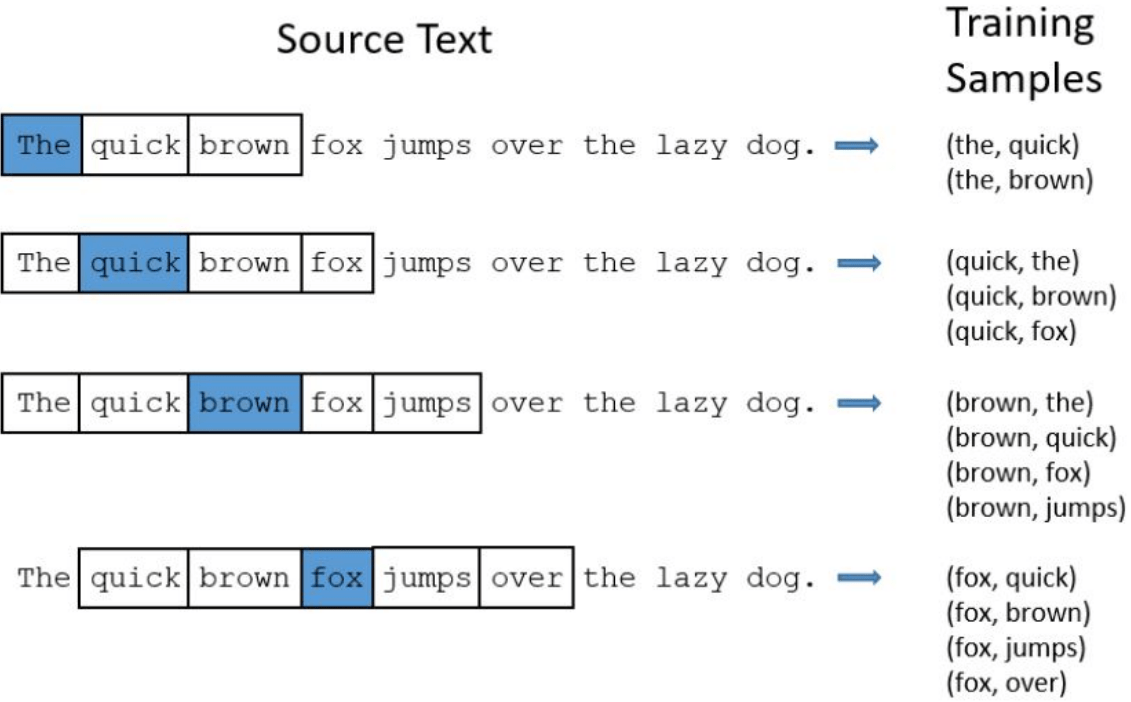
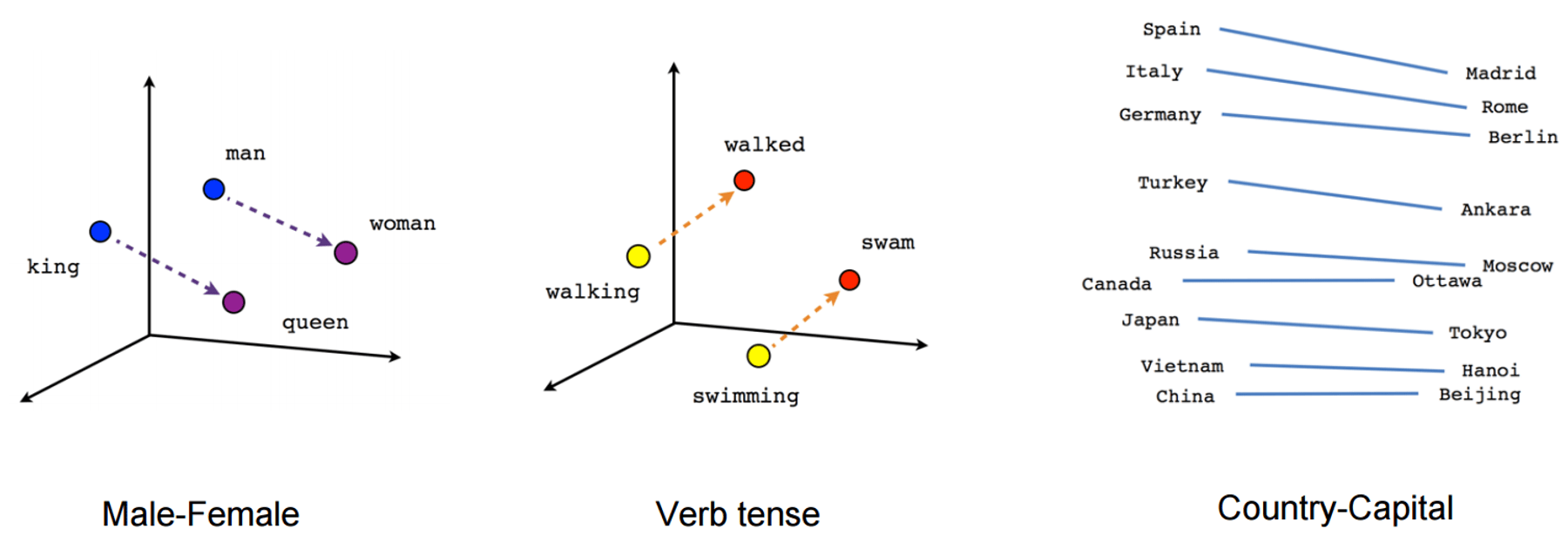
word2vec learns vector representations of words, useful in application tasks. Vectors show interesting semantic properties. For example:
- king: male = queen: female ⇒
- king - man + woman = queen
Word2vec
Random walks
Key Idea: Nodes in random walks \( \approx \) words in sentences -> use word2vec.

Deepwalk
- Parameters
- In practical tasks \( w = 10 \), \( \gamma=80 \), \( t=80 \)
- newer change \( w \)
- If you lower \( w \), increase \( \gamma \), \( t \)
B. Perozzi, R. Al-Rfou, S. Skiena: DeepWalk: Online Learning of Social Representations (KDD, 2014) [pdf]
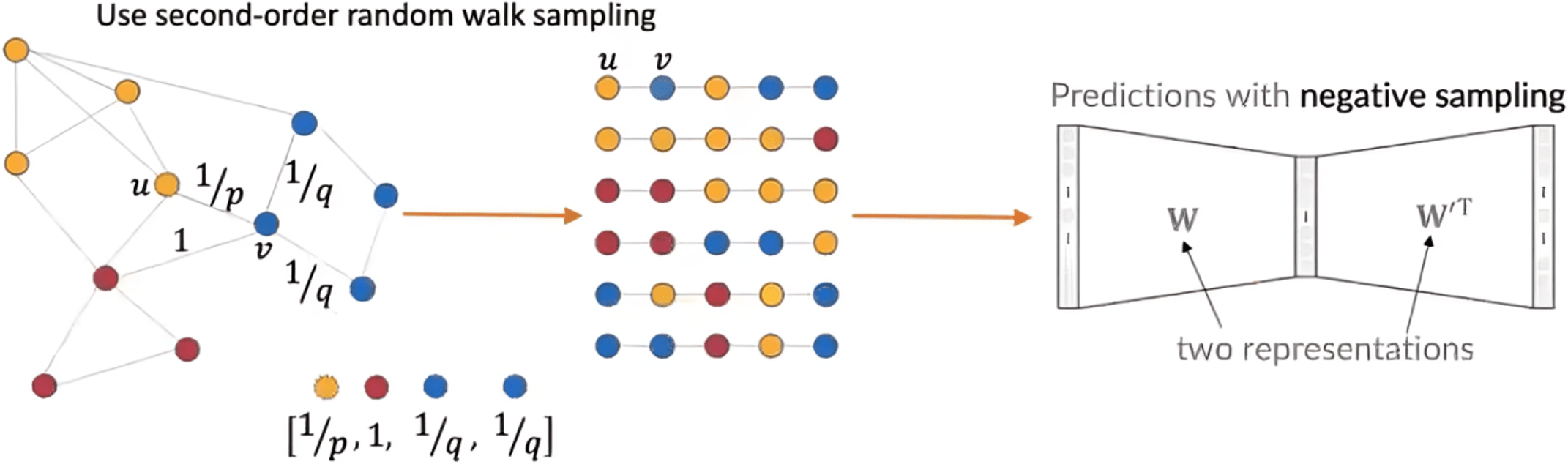
Node2vec
Low q - explore intra-cluster information
High q - explore inter-cluster information
Large-scale Information Network Embedding (LINE)
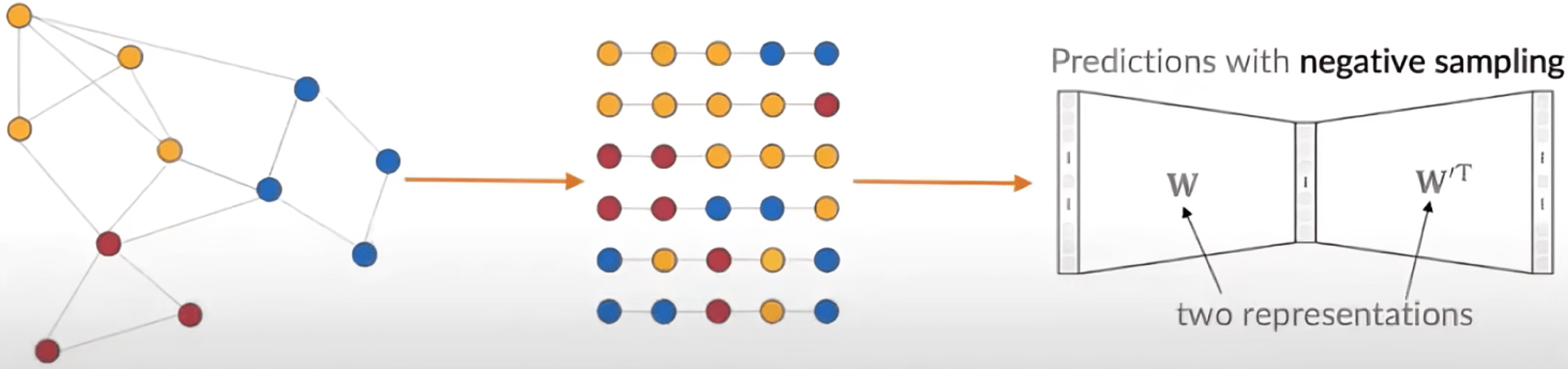
Key Idea: - don't generate random walks
J. Tang, M. Qu, M. Wang, M. Zhang, J. Yan, Q. Mei: LINE: Large-scale Information Network Embedding, WWW, 2015 [pdf]
code (C++) [link]
VERSE
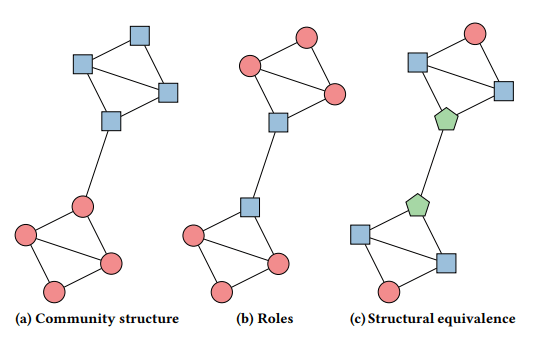
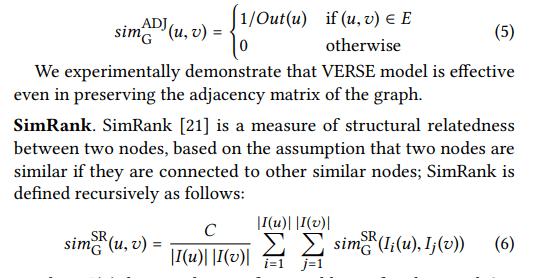
Useful Links
I. Makarov, D. Kiselev1, N. Nikitinsky, L. Subelj: Survey on graph embeddings and their applications to machine learning problems on graphs [link]
J. Qiu, Y. Dong, H. Ma, J. Li, K. Wang, J. Tang: Unifying DeepWalk, LINE, PTE, and node2vec [pdf]
authors’ code (Python) [link]
- NetMF
Z. Zhang, P. Cui, H. Li, X. Wang, W. Zhu: Billion-scale Network Embedding with Iterative Random Projection [pdf]
authors’ code (Python) [link]
- RandNE
H. Chen, S. Fahad Sultan, Y. Tian, M. Chen, S. Skiena: Fast and Accurate Network Embeddings via Very Sparse Random Projection [pdf]
authors’ code (Python) [link]
- FastRP
D. Yang, P. Rosso1, B. Li and P. Cudre-Mauroux: Highly Efficient Graph Embeddings via Recursive Sketching [pdf]
authors’ code (C++ & Python) [link]
- NodeSketch