Huntington's Disease
Neuroscience II
Kate Sears
History & Prevalence
- First described by George Huntington in 1872
- Huntington Chorea
- San Luis in Venezuela was discovered by Amerigo Negrette
- Today, 1 in 10,000 have HD
- 250,000 at risk
Symptoms
- Two types: Adult and Juvenile (differ genetically)
- Neurodegenerative: mental processes and physical control
- Psychological symptoms
- Physical symptoms
- Fate
Neurobiology
Basics:
- Nerve Cells
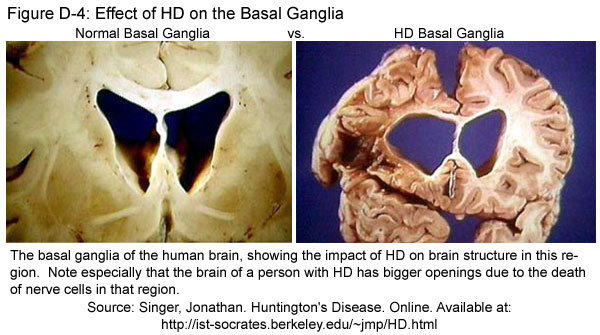
- Basal Ganglia
- Direct pathways
- Indirect pathways
- GABA
Genetics
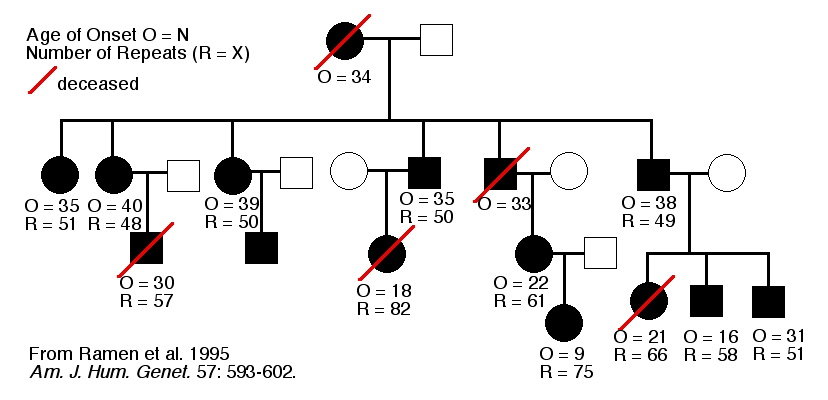
Autosomal Dominant
50% hereditary rate
Chromosome 4
Repetition of CAG
- Normal: 10-28
- At risk: 29-35
- Adult onset: 36-45
- Juvenile onset: 70-120
The Gene
- 20+ years to isolate
- Not a common mutation
- Discovered in 1993
- Isolated IT-15 (Interesting Transcript)
- Repetition of CAG: Glutamine
The Protein
- Huntingtin Protein
- Codes for p53
- Halts progression of cell cycle
- Adding glutamine increases levels
- Tumor Suppressor
Theories?
-
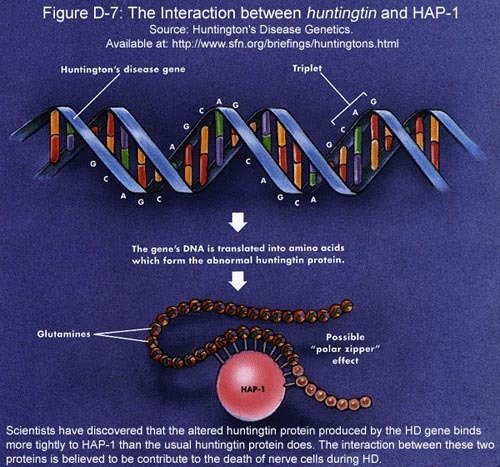
HIP-1 and HAP-1
-
Mitochondria of striatal cells
-
Excitatory?
In Summary
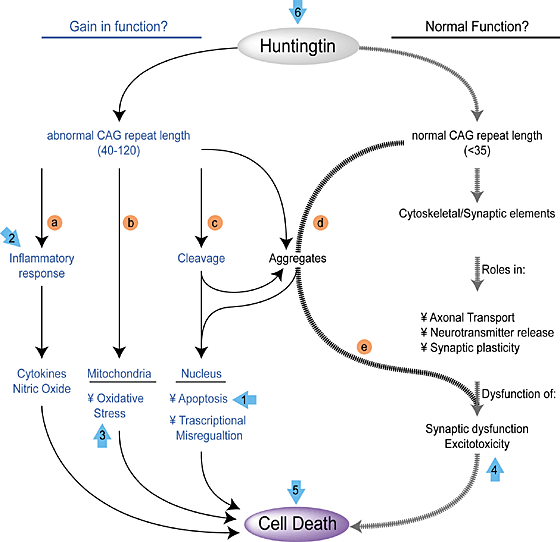
http://www.nature.com/nm/journal/v6/n11/fig_tab/nm1100_1208_F1.html
Research
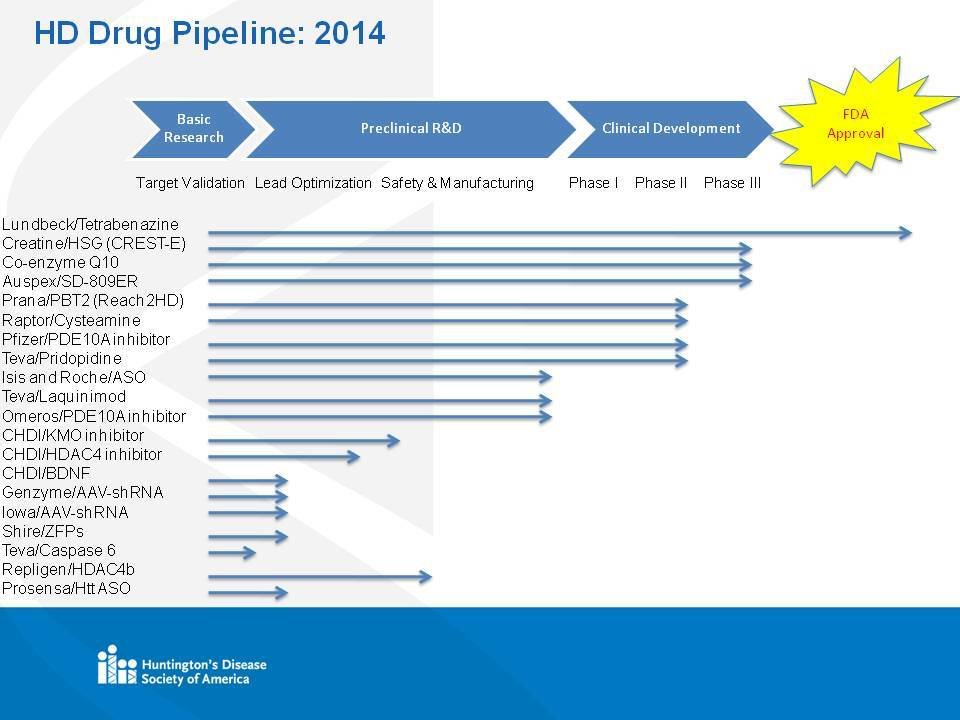
http://www.hdsa.org/research/therapies-in-pipeline.html
Tetrabenazine
- Treatment for Chorea in 2008
- 1st FDA Approved Drug
- Dopamine depleter
- Serotonin and norepinephrine
Therapies
- Physical Therapy
- Psychotropic
- Tetrabenazine
Future?
-
Genetic testing
-
HIP-1 and HAP-1
-
Glutamate
-
p53
-
Pathways