MLA-01
1.
Case Study -
A company is building a web-based AI application by using Amazon SageMaker. The application will provide the following capabilities and features: ML experimentation, training, a central model registry, model deployment, and model monitoring.
The application must ensure secure and isolated use of training data during the ML lifecycle. The training data is stored in Amazon S3.
The company needs to use the central model registry to manage different versions of models in the application.
Which action will meet this requirement with the LEAST operational overhead?
A. Create a separate Amazon Elastic Container Registry (Amazon ECR) repository for each model.
B. Use Amazon Elastic Container Registry (Amazon ECR) and unique tags for each model version.
C. Use the SageMaker Model Registry and model groups to catalog the models.
D. Use the SageMaker Model Registry and unique tags for each model version.
2.
Case Study -
A company is building a web-based AI application by using Amazon SageMaker. The application will provide the following capabilities and features: ML experimentation, training, a central model registry, model deployment, and model monitoring.
The application must ensure secure and isolated use of training data during the ML lifecycle. The training data is stored in Amazon S3.
The company is experimenting with consecutive training jobs.
How can the company MINIMIZE infrastructure startup times for these jobs?
A. Use Managed Spot Training.
B. Use SageMaker managed warm pools.
C. Use SageMaker Training Compiler.
D. Use the SageMaker distributed data parallelism (SMDDP) library.
3.
Case Study -
A company is building a web-based AI application by using Amazon SageMaker. The application will provide the following capabilities and features: ML experimentation, training, a central model registry, model deployment, and model monitoring.
The application must ensure secure and isolated use of training data during the ML lifecycle. The training data is stored in Amazon S3.
The company must implement a manual approval-based workflow to ensure that only approved models can be deployed to production endpoints.
Which solution will meet this requirement?
A. Use SageMaker Experiments to facilitate the approval process during model registration.
B. Use SageMaker ML Lineage Tracking on the central model registry. Create tracking entities for the
approval process.
C. Use SageMaker Model Monitor to evaluate the performance of the model and to manage the approval.
D. Use SageMaker Pipelines. When a model version is registered, use the AWS SDK to change the approval
status to "Approved."
4.
Case Study -
A company is building a web-based AI application by using Amazon SageMaker. The application will provide the following capabilities and features: ML experimentation, training, a central model registry, model deployment, and model monitoring.
The application must ensure secure and isolated use of training data during the ML lifecycle. The training data is stored in Amazon S3.
The company needs to run an on-demand workflow to monitor bias drift for models that are deployed to real-time endpoints from the application.
Which action will meet this requirement?
A. Configure the application to invoke an AWS Lambda function that runs a SageMaker Clarify job.
B. Invoke an AWS Lambda function to pull the sagemaker-model-monitor-analyzer built-in SageMaker image.
C. Use AWS Glue Data Quality to monitor bias.
D. Use SageMaker notebooks to compare the bias.
5.
HOTSPOT -
A company stores historical data in .csv files in Amazon S3. Only some of the rows and columns in the .csv files are populated. The columns are not labeled. An ML engineer needs to prepare and store the data so that the company can use the data to train ML models.
Select and order the correct steps from the following list to perform this task. Each step should be selected one time or not at all. (Select and order three.)
• Create an Amazon SageMaker batch transform job for data cleaning and feature engineering.
• Store the resulting data back in Amazon S3.
• Use Amazon Athena to infer the schemas and available columns.
• Use AWS Glue crawlers to infer the schemas and available columns.
• Use AWS Glue DataBrew for data cleaning and feature engineering.
(Continue)
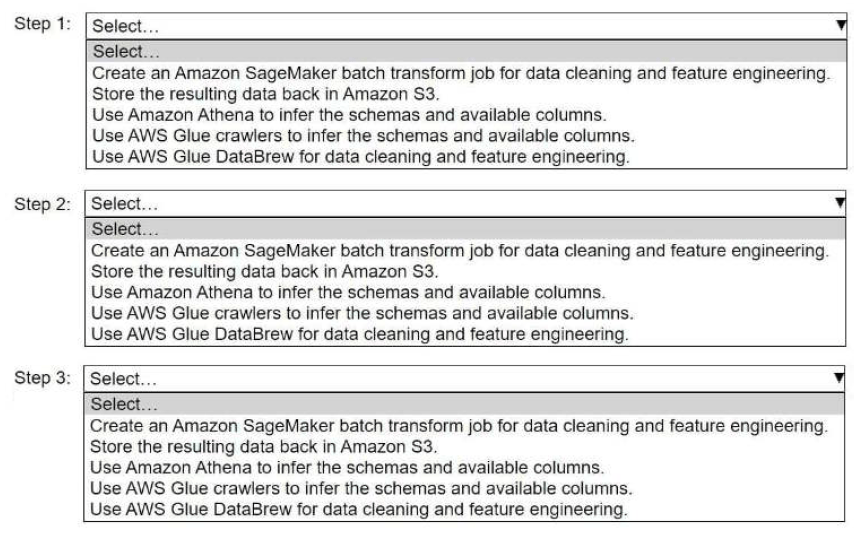
5. (Continued)
6.
HOTSPOT -
An ML engineer needs to use Amazon SageMaker Feature Store to create and manage features to train a model.
Select and order the steps from the following list to create and use the features in Feature Store. Each step should be selected one time. (Select and order three.)
• Access the store to build datasets for training.
• Create a feature group.
• Ingest the records.
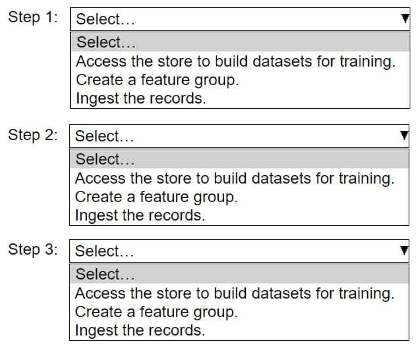
7.
HOTSPOT -
A company wants to host an ML model on Amazon SageMaker. An ML engineer is configuring a continuous integration and continuous delivery (Cl/CD) pipeline in AWS CodePipeline to deploy the model. The pipeline must run automatically when new training data for the model is uploaded to an Amazon S3 bucket.
Select and order the pipeline's correct steps from the following list. Each step should be selected one time or not at all. (Select and order three.)
• An S3 event notification invokes the pipeline when new data is uploaded.
• S3 Lifecycle rule invokes the pipeline when new data is uploaded.
• SageMaker retrains the model by using the data in the S3 bucket.
• The pipeline deploys the model to a SageMaker endpoint.
• The pipeline deploys the model to SageMaker Model Registry.
(Continue)
7. (Continued)
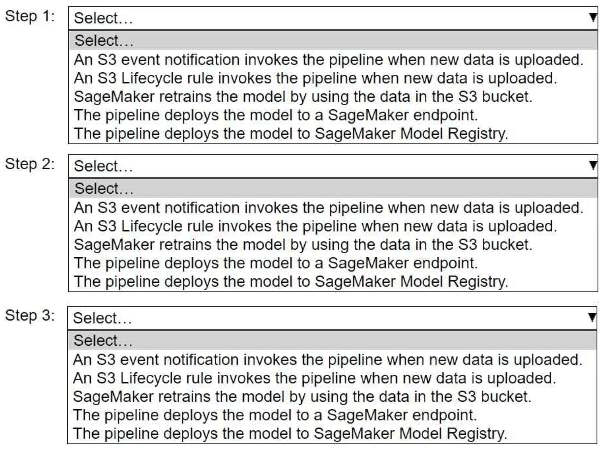
8.
HOTSPOT -
An ML engineer is building a generative AI application on Amazon Bedrock by using large language models (LLMs).
Select the correct generative AI term from the following list for each description. Each term should be selected one time or not at all. (Select three.)
• Embedding
• Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG)
• Temperature
• Token

9.
HOTSPOT -
An ML engineer is working on an ML model to predict the prices of similarly sized homes. The model will base predictions on several features The ML engineer will use the following feature engineering techniques to estimate the prices of the homes:
• Feature splitting
• Logarithmic transformation
• One-hot encoding
• Standardized distribution
Select the correct feature engineering techniques for the following list of features. Each feature engineering technique should be selected one time or not at all (Select three.)
(Continue)

9. (Continued)
10.
Case study -
An ML engineer is developing a fraud detection model on AWS. The training dataset includes transaction logs, customer profiles, and tables from an on-premises MySQL database. The transaction logs and customer profiles are stored in Amazon S3.
The dataset has a class imbalance that affects the learning of the model's algorithm. Additionally, many of the features have interdependencies.
The algorithm is not capturing all the desired underlying patterns in the data.
Which AWS service or feature can aggregate the data from the various data sources?
A. Amazon EMR Spark jobs
B. Amazon Kinesis Data Streams
C. Amazon DynamoDB
D. AWS Lake Formation
11.
Case study -
An ML engineer is developing a fraud detection model on AWS. The training dataset includes transaction logs, customer profiles, and tables from an on-premises MySQL database. The transaction logs and customer profiles are stored in Amazon S3.
The dataset has a class imbalance that affects the learning of the model's algorithm. Additionally, many of the features have interdependencies.
The algorithm is not capturing all the desired underlying patterns in the data.
After the data is aggregated, the ML engineer must implement a solution to automatically detect anomalies in the data and to visualize the result.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
A. Use Amazon Athena to automatically detect the anomalies and to visualize the result.
B. Use Amazon Redshift Spectrum to automatically detect the anomalies. Use Amazon QuickSight to visualize the result.
C. Use Amazon SageMaker Data Wrangler to automatically detect the anomalies and to visualize the result.
D. Use AWS Batch to automatically detect the anomalies. Use Amazon QuickSight to visualize the result.
12.
Case study -
An ML engineer is developing a fraud detection model on AWS. The training dataset includes transaction logs, customer profiles, and tables from an on-premises MySQL database. The transaction logs and customer profiles are stored in Amazon S3.
The dataset has a class imbalance that affects the learning of the model's algorithm. Additionally, many of the features have interdependencies.
The algorithm is not capturing all the desired underlying patterns in the data.
The training dataset includes categorical data and numerical data. The ML engineer must prepare the training dataset to maximize the accuracy of the model.
Which action will meet this requirement with the LEAST operational overhead?
A. Use AWS Glue to transform the categorical data into numerical data.
B. Use AWS Glue to transform the numerical data into categorical data.
C. Use Amazon SageMaker Data Wrangler to transform the categorical data into numerical data.
D. Use Amazon SageMaker Data Wrangler to transform the numerical data into categorical data.
13.
Case study -
An ML engineer is developing a fraud detection model on AWS. The training dataset includes transaction logs, customer pro«les, and tables from an on-premises MySQL database. The transaction logs and customer profiles are stored in Amazon S3.
The dataset has a class imbalance that affects the learning of the model's algorithm. Additionally, many of the features have interdependencies.
The algorithm is not capturing all the desired underlying patterns in the data.
Before the ML engineer trains the model, the ML engineer must resolve the issue of the imbalanced data.
Which solution will meet this requirement with the LEAST operational effort?
A. Use Amazon Athena to identify patterns that contribute to the imbalance. Adjust the dataset accordingly.
B. Use Amazon SageMaker Studio Classic built-in algorithms to process the imbalanced dataset.
C. Use AWS Glue DataBrew built-in features to oversample the minority class.
D. Use the Amazon SageMaker Data Wrangler balance data operation to oversample the minority class.
14.
Case study -
An ML engineer is developing a fraud detection model on AWS. The training dataset includes transaction logs, customer profiles, and tables from an on-premises MySQL database. The transaction logs and customer profiles are stored in Amazon S3.
The dataset has a class imbalance that affects the learning of the model's algorithm. Additionally, many of the features have interdependencies.
The algorithm is not capturing all the desired underlying patterns in the data.
The ML engineer needs to use an Amazon SageMaker built-in algorithm to train the model.
Which algorithm should the ML engineer use to meet this requirement?
A. LightGBM
B. Linear learner
C. К-means clustering
D. Neural Topic Model (NTM)
15.
A company has deployed an XGBoost prediction model in production to predict if a customer is likely to cancel a subscription. The company uses Amazon SageMaker Model Monitor to detect deviations in the F1 score.
During a baseline analysis of model quality, the company recorded a threshold for the F1 score. After several months of no change, the model's F1 score decreases significantly.
What could be the reason for the reduced F1 score?
A. Concept drift occurred in the underlying customer data that was used for predictions.
B. The model was not suciently complex to capture all the patterns in the original baseline data.
C. The original baseline data had a data quality issue of missing values.
D. Incorrect ground truth labels were provided to Model Monitor during the calculation of the baseline.
16.
A company has a team of data scientists who use Amazon SageMaker notebook instances to test ML models. When the data scientists need new permissions, the company attaches the permissions to each individual role that was created during the creation of the SageMaker notebook instance.
The company needs to centralize management of the team's permissions.
Which solution will meet this requirement?
A. Create a single IAM role that has the necessary permissions. Attach the role to each notebook instance that the team uses.
B. Create a single IAM group. Add the data scientists to the group. Associate the group with each notebook instance that the team uses.
C. Create a single IAM user. Attach the AdministratorAccess AWS managed IAM policy to the user. Configure each notebook instance to use the IAM user.
D. Create a single IAM group. Add the data scientists to the group. Create an IAM role. Attach the AdministratorAccess AWS managed IAM policy to the role. Associate the role with the group. Associate the group with each notebook instance that the team uses.
17.
An ML engineer needs to use an ML model to predict the price of apartments in a specific location.
Which metric should the ML engineer use to evaluate the model's performance?
A. Accuracy
B. Area Under the ROC Curve (AUC)
C. F1 score
D. Mean absolute error (MAE)
18.
An ML engineer has trained a neural network by using stochastic gradient descent (SGD). The neural network performs poorly on the test set. The values for training loss and validation loss remain high and show an oscillating pattern. The values decrease for a few epochs and then increase for a few epochs before repeating the same cycle.
What should the ML engineer do to improve the training process?
A. Introduce early stopping.
B. Increase the size of the test set.
C. Increase the learning rate.
D. Decrease the learning rate.
19.
An ML engineer needs to process thousands of existing CSV objects and new CSV objects that are uploaded. The CSV objects are stored in a central Amazon S3 bucket and have the same number of columns. One of the columns is a transaction date. The ML engineer must query the data based on the transaction date.
Which solution will meet these requirements with the LEAST operational overhead?
A. Use an Amazon Athena CREATE TABLE AS SELECT (CTAS) statement to create a table based on the transaction date from data in the central S3 bucket. Query the objects from the table.
B. Create a new S3 bucket for processed data. Set up S3 replication from the central S3 bucket to the new S3 bucket. Use S3 Object Lambda to query the objects based on transaction date.
C. Create a new S3 bucket for processed data. Use AWS Glue for Apache Spark to create a job to query the CSV objects based on transaction date. Con«gure the job to store the results in the new S3 bucket. Query the objects from the new S3 bucket.
D. Create a new S3 bucket for processed data. Use Amazon Data Firehose to transfer the data from the central S3 bucket to the new S3 bucket. Con«gure Firehose to run an AWS Lambda function to query the data based on transaction date.
20.
A company has a large, unstructured dataset. The dataset includes many duplicate records across several key attributes.
Which solution on AWS will detect duplicates in the dataset with the LEAST code development?
A. Use Amazon Mechanical Turk jobs to detect duplicates.
B. Use Amazon QuickSight ML Insights to build a custom deduplication model.
C. Use Amazon SageMaker Data Wrangler to pre-process and detect duplicates.
D. Use the AWS Glue FindMatches transform to detect duplicates.
21.
A company needs to run a batch data-processing job on Amazon EC2 instances. The job will run during the weekend and will take 90 minutes to finish running. The processing can handle interruptions. The company will run the job every weekend for the next 6 months.
Which EC2 instance purchasing option will meet these requirements MOST cost-effectively?
A. Spot Instances
B. Reserved Instances
C. On-Demand Instances
D. Dedicated Instances
22.
An ML engineer has an Amazon Comprehend custom model in Account A in the us-east-1 Region. The ML engineer needs to copy the model to Account В in the same Region.
Which solution will meet this requirement with the LEAST development effort?
A. Use Amazon S3 to make a copy of the model. Transfer the copy to Account B.
B. Create a resource-based IAM policy. Use the Amazon Comprehend ImportModel API operation to copy the model to Account B.
C. Use AWS DataSync to replicate the model from Account A to Account B.
D. Create an AWS Site-to-Site VPN connection between Account A and Account В to transfer the model.
23.
An ML engineer is training a simple neural network model. The ML engineer tracks the performance of the model over time on a validation dataset. The model's performance improves substantially at first and then degrades after a specific number of epochs.
Which solutions will mitigate this problem? (Choose two.)
A. Enable early stopping on the model.
B. Increase dropout in the layers.
C. Increase the number of layers.
D. Increase the number of neurons.
E. Investigate and reduce the sources of model bias.
24.
A company has a Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) application that uses a vector database to store embeddings of documents. The company must migrate the application to AWS and must implement a solution that provides semantic search of text files. The company has already migrated the text repository to an Amazon S3 bucket.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
A. Use an AWS Batch job to process the «les and generate embeddings. Use AWS Glue to store the embeddings. Use SQL queries to perform the semantic searches.
B. Use a custom Amazon SageMaker notebook to run a custom script to generate embeddings. Use SageMaker Feature Store to store the embeddings. Use SQL queries to perform the semantic searches.
C. Use the Amazon Kendra S3 connector to ingest the documents from the S3 bucket into Amazon Kendra. Query Amazon Kendra to perform the semantic searches.
D. Use an Amazon Textract asynchronous job to ingest the documents from the S3 bucket. Query Amazon Textract to perform the semantic searches.
25.
A company uses Amazon Athena to query a dataset in Amazon S3. The dataset has a target variable that the company wants to predict.
The company needs to use the dataset in a solution to determine if a model can predict the target variable.
Which solution will provide this information with the LEAST development effort?
A. Create a new model by using Amazon SageMaker Autopilot. Report the model's achieved performance.
B. Implement custom scripts to perform data pre-processing, multiple linear regression, and performance evaluation. Run the scripts on Amazon EC2 instances.
C. Configure Amazon Macie to analyze the dataset and to create a model. Report the model's achieved performance.
D. Select a model from Amazon Bedrock. Tune the model with the data. Report the model's achieved performance.
26.
A company wants to predict the success of advertising campaigns by considering the color scheme of each advertisement. An ML engineer is preparing data for a neural network model. The dataset includes color information as categorical data.
Which technique for feature engineering should the ML engineer use for the model?
A. Apply label encoding to the color categories. Automatically assign each color a unique integer.
B. Implement padding to ensure that all color feature vectors have the same length.
C. Perform dimensionality reduction on the color categories.
D. One-hot encode the color categories to transform the color scheme feature into a binary matrix.
27.
A company uses a hybrid cloud environment. A model that is deployed on premises uses data in Amazon 53 to provide customers with a live conversational engine.
The model is using sensitive data. An ML engineer needs to implement a solution to identify and remove the sensitive data.
Which solution will meet these requirements with the LEAST operational overhead?
A. Deploy the model on Amazon SageMaker. Create a set of AWS Lambda functions to identify and remove the sensitive data.
B. Deploy the model on an Amazon Elastic Container Service (Amazon ECS) cluster that uses AWS Fargate. Create an AWS Batch job to identify and remove the sensitive data.
C. Use Amazon Macie to identify the sensitive data. Create a set of AWS Lambda functions to remove the sensitive data.
D. Use Amazon Comprehend to identify the sensitive data. Launch Amazon EC2 instances to remove the sensitive data.
28.
An ML engineer needs to create data ingestion pipelines and ML model deployment pipelines on AWS. All the raw data is stored in Amazon S3 buckets.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
A. Use Amazon Data Firehose to create the data ingestion pipelines. Use Amazon SageMaker Studio Classic to create the model deployment pipelines.
B. Use AWS Glue to create the data ingestion pipelines. Use Amazon SageMaker Studio Classic to create the model deployment pipelines.
C. Use Amazon Redshift ML to create the data ingestion pipelines. Use Amazon SageMaker Studio Classic to create the model deployment pipelines.
D. Use Amazon Athena to create the data ingestion pipelines. Use an Amazon SageMaker notebook to create the model deployment pipelines.
29.
A company that has hundreds of data scientists is using Amazon SageMaker to create ML models. The models are in model groups in the SageMaker Model Registry.
The data scientists are grouped into three categories: computer vision, natural language processing (NLP), and speech recognition. An ML engineer needs to implement a solution to organize the existing models into these groups to improve model discoverability at scale. The solution must not affect the integrity of the model artifacts and their existing groupings.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
A. Create a custom tag for each of the three categories. Add the tags to the model packages in the SageMaker Model Registry.
B. Create a model group for each category. Move the existing models into these category model groups.
C. Use SageMaker ML Lineage Tracking to automatically identify and tag which model groups should contain the models.
D. Create a Model Registry collection for each of the three categories. Move the existing model groups into the collections.
30.
A company runs an Amazon SageMaker domain in a public subnet of a newly created VPC. The network is configured properly, and ML engineers can access the SageMaker domain.
Recently, the company discovered suspicious trac to the domain from a speci«c IP address. The company needs to block trac from the specific IP address.
Which update to the network configuration will meet this requirement?
A. Create a security group inbound rule to deny trac from the specific IP address. Assign the security group to the domain.
B. Create a network ACL inbound rule to deny trac from the specific IP address. Assign the rule to the default network Ad for the subnet where the domain is located.
C. Create a shadow variant for the domain. Configure SageMaker Inference Recommender to send traffic from the specific IP address to the shadow endpoint.
D. Create a VPC route table to deny inbound trac from the specific IP address. Assign the route table to the domain.
31.
A company is gathering audio, video, and text data in various languages. The company needs to use a large language model (LLM) to summarize the gathered data that is in Spanish.
Which solution will meet these requirements in the LEAST amount of time?
A. Train and deploy a model in Amazon SageMaker to convert the data into English text. Train and deploy an LLM in SageMaker to summarize the text.
B. Use Amazon Transcribe and Amazon Translate to convert the data into English text. Use Amazon Bedrock with the Jurassic model to summarize the text.
C. Use Amazon Rekognition and Amazon Translate to convert the data into English text. Use Amazon Bedrock with the Anthropic Claude model to summarize the text.
D. Use Amazon Comprehend and Amazon Translate to convert the data into English text. Use Amazon Bedrock with the Stable Diffusion model to summarize the text.
32.
A financial company receives a high volume of real-time market data streams from an external provider. The streams consist of thousands of JSON records every second.
The company needs to implement a scalable solution on AWS to identify anomalous data points.
Which solution will meet these requirements with the LEAST operational overhead?
A. Ingest real-time data into Amazon Kinesis data streams. Use the built-in RANDOM_CUT_FOREST function in Amazon Managed Service for Apache Flink to process the data streams and to detect data anomalies.
B. Ingest real-time data into Amazon Kinesis data streams. Deploy an Amazon SageMaker endpoint for real-time outlier detection. Create an AWS Lambda function to detect anomalies. Use the data streams to invoke the Lambda function.
C. Ingest real-time data into Apache Kafka on Amazon EC2 instances. Deploy an Amazon SageMaker endpoint for real-time outlier detection. Create an AWS Lambda function to detect anomalies. Use the data streams to invoke the Lambda function.
D. Send real-time data to an Amazon Simple Queue Service (Amazon SQS) FIFO queue. Create an AWS Lambda function to consume the queue messages. Program the Lambda function to start an AWS Glue extract, transform, and load (ETL) job for batch processing and anomaly detection.
33.
A company has a large collection of chat recordings from customer interactions after a product release. An ML engineer needs to create an ML model to analyze the chat data. The ML engineer needs to determine the success of the product by reviewing customer sentiments about the product.
Which action should the ML engineer take to complete the evaluation in the LEAST amount of time?
A. Use Amazon Rekognition to analyze sentiments of the chat conversations.
B. Train a Naive Bayes classifier to analyze sentiments of the chat conversations.
C. Use Amazon Comprehend to analyze sentiments of the chat conversations.
D. Use random forests to classify sentiments of the chat conversations.
34.
A company has a conversational AI assistant that sends requests through Amazon Bedrock to an Anthropic Claude large language model (LLM). Users report that when they ask similar questions multiple times, they sometimes receive different answers. An ML engineer needs to improve the responses to be more consistent and less random.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
A. Increase the temperature parameter and the top_k parameter.
B. Increase the temperature parameter. Decrease the top_k parameter.
C. Decrease the temperature parameter. Increase the top_k parameter.
D. Decrease the temperature parameter and the top_k parameter.
35.
A company is using ML to predict the presence of a specific weed in a farmer's field. The company is using the Amazon SageMaker linear learner built-in algorithm with a value of multiclass_dassi«er for the predictorjype hyperparameter.
What should the company do to MINIMIZE false positives?
A. Set the value of the weight decay hyperparameter to zero.
B. Increase the number of training epochs.
C. Increase the value of the target_precision hyperparameter.
D. Change the value of the predictorjype hyperparameter to regressor.
36.
A company has implemented a data ingestion pipeline for sales transactions from its ecommerce website. The company uses Amazon Data Firehose to ingest data into Amazon OpenSearch Service. The buffer interval of the Firehose stream is set for 60 seconds. An OpenSearch linear model generates real-time sales forecasts based on the data and presents the data in an OpenSearch dashboard.
The company needs to optimize the data ingestion pipeline to support sub-second latency for the real-time dashboard.
Which change to the architecture will meet these requirements?
A. Use zero buffering in the Firehose stream. Tune the batch size that is used in the PutRecordBatch operation.
B. Replace the Firehose stream with an AWS DataSync task. Con«gure the task with enhanced fan-out consumers.
C. Increase the buffer interval of the Firehose stream from 60 seconds to 120 seconds.
D. Replace the Firehose stream with an Amazon Simple Queue Service (Amazon SQS) queue.
37.
A company has trained an ML model in Amazon SageMaker. The company needs to host the model to provide inferences in a production environment.
The model must be highly available and must respond with minimum latency. The size of each request will be between 1 KB and 3 MB. The model will receive unpredictable bursts of requests during the day. The inferences must adapt proportionally to the changes in demand.
How should the company deploy the model into production to meet these requirements?
A. Create a SageMaker real-time inference endpoint. Con«gure auto scaling. Con«gure the endpoint to present the existing model.
B. Deploy the model on an Amazon Elastic Container Service (Amazon ECS) cluster. Use ECS scheduled scaling that is based on the CPU of the ECS cluster.
C. Install SageMaker Operator on an Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (Amazon EKS) cluster. Deploy the model in Amazon EKS. Set horizontal pod auto scaling to scale replicas based on the memory metric.
D. Use Spot Instances with a Spot Fleet behind an Application Load Balancer (ALB) for inferences. Use the ALBRequestCountPerTarget metric as the metric for auto scaling.
38.
An ML engineer needs to use an Amazon EMR cluster to process large volumes of data in batches. Any data loss is unacceptable.
Which instance purchasing option will meet these requirements MOST cost-effectively?
A. Run the primary node, core nodes, and task nodes on On-Demand Instances.
B. Run the primary node, core nodes, and task nodes on Spot Instances.
C. Run the primary node on an On-Demand Instance. Run the core nodes and task nodes on Spot Instances.
D. Run the primary node and core nodes on On-Demand Instances. Run the task nodes on Spot Instances.
39.
A company wants to improve the sustainability of its ML operations.
Which actions will reduce the energy usage and computational resources that are associated with the company's training jobs? (Choose two.)
A. Use Amazon SageMaker Debugger to stop training jobs when non-converging conditions are detected.
B. Use Amazon SageMaker Ground Truth for data labeling.
C. Deploy models by using AWS Lambda functions.
D. Use AWS Trainium instances for training.
E. Use PyTorch or TensorFlow with the distributed training option.
40.
A company is planning to create several ML prediction models. The training data is stored in Amazon S3. The entire dataset is more than 5 ТВ in size and consists of CSV, JSON, Apache Parquet, and simple text files.
The data must be processed in several consecutive steps. The steps include complex manipulations that can take hours to finish running. Some of the processing involves natural language processing (NLP) transformations. The entire process must be automated.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
A. Process data at each step by using Amazon SageMaker Data Wrangler. Automate the process by using Data Wrangler jobs.
B. Use Amazon SageMaker notebooks for each data processing step. Automate the process by using Amazon EventBridge.
C. Process data at each step by using AWS Lambda functions. Automate the process by using AWS Step Functions and Amazon EventBridge.
D. Use Amazon SageMaker Pipelines to create a pipeline of data processing steps. Automate the pipeline by using Amazon EventBridge.
41.
An ML engineer needs to use AWS CloudFormation to create an ML model that an Amazon SageMaker endpoint will host.
Which resource should the ML engineer declare in the CloudFormation template to meet this requirement?
A. AWS::SageMaker::Model
B. AWS::SageMaker::Endpoint
C. AWS::SageMaker::NotebookInstance
D. AWS::SageMaker::Pipeline
42.
An advertising company uses AWS Lake Formation to manage a data lake. The data lake contains structured data and unstructured data. The company's ML engineers are assigned to speci«c advertisement campaigns.
The ML engineers must interact with the data through Amazon Athena and by browsing the data directly in an Amazon S3 bucket. The ML engineers must have access to only the resources that are specific to their assigned advertisement campaigns.
Which solution will meet these requirements in the MOST operationally ecient way?
A. Configure IAM policies on an AWS Glue Data Catalog to restrict access to Athena based on the ML engineers' campaigns.
B. Store users and campaign information in an Amazon DynamoDB table. Con«gure DynamoDB Streams to invoke an AWS Lambda function to update S3 bucket policies.
C. Use Lake Formation to authorize AWS Glue to access the S3 bucket. Con«gure Lake Formation tags to map ML engineers to their campaigns.
D. Configure S3 bucket policies to restrict access to the S3 bucket based on the ML engineers' campaigns.
43.
An ML engineer needs to use data with Amazon SageMaker Canvas to train an ML model. The data is stored in Amazon S3 and is complex in structure. The ML engineer must use a file format that minimizes processing time for the data.
Which file format will meet these requirements?
A. CSV files compressed with Snappy
B. JSON objects in JSONL format
C. JSON files compressed with gzip
D. Apache Parquet files
44.
An ML engineer is evaluating several ML models and must choose one model to use in production. The cost of false negative predictions by the models is much higher than the cost of false positive predictions.
Which metric finding should the ML engineer prioritize the MOST when choosing the model?
A. Low precision
B. High precision
C. Low recall
D. High recall
45.
A company has trained and deployed an ML model by using Amazon SageMaker. The company needs to implement a solution to record and monitor all the API call events for the SageMaker endpoint. The solution also must provide a notification when the number of API call events breaches a threshold.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
A. Use SageMaker Debugger to track the inferences and to report metrics. Create a custom rule to provide a noti«cation when the threshold is breached.
B. Use SageMaker Debugger to track the inferences and to report metrics. Use the tensor_variance built-in rule to provide a notification when the threshold is breached.
C. Log all the endpoint invocation API events by using AWS CloudTrail. Use an Amazon CloudWatch dashboard for monitoring. Set up a CloudWatch alarm to provide notification when the threshold is breached.
D. Add the Invocations metric to an Amazon CloudWatch dashboard for monitoring. Set up a CloudWatch alarm to provide notification when the threshold is breached.
46.
A company has AWS Glue data processing jobs that are orchestrated by an AWS Glue work¬ow. The AWS Glue jobs can run on a schedule or can be launched manually.
The company is developing pipelines in Amazon SageMaker Pipelines for ML model development. The pipelines will use the output of the AWS Glue jobs during the data processing phase of model development. An ML engineer needs to implement a solution that integrates the AWS Glue jobs with the pipelines.
Which solution will meet these requirements with the LEAST operational overhead?
A. Use AWS Step Functions for orchestration of the pipelines and the AWS Glue jobs.
B. Use processing steps in SageMaker Pipelines. Con«gure inputs that point to the Amazon Resource Names (ARNs) of the AWS Glue jobs.
C. Use Callback steps in SageMaker Pipelines to start the AWS Glue work¬ow and to stop the pipelines until the AWS Glue jobs «nish running.
D. Use Amazon EventBridge to invoke the pipelines and the AWS Glue jobs in the desired order.
47.
A company is using an Amazon Redshift database as its single data source. Some of the data is sensitive.
A data scientist needs to use some of the sensitive data from the database. An ML engineer must give the data scientist access to the data without transforming the source data and without storing anonymized data in the database.
Which solution will meet these requirements with the LEAST implementation effort?
A. Configure dynamic data masking policies to control how sensitive data is shared with the data scientist at query time.
B. Create a materialized view with masking logic on top of the database. Grant the necessary read permissions to the data scientist.
C. Unload the Amazon Redshift data to Amazon S3. Use Amazon Athena to create schema-on-read with masking logic. Share the view with the data scientist.
D. Unload the Amazon Redshift data to Amazon S3. Create an AWS Glue job to anonymize the data. Share the dataset with the data scientist.
48.
An ML engineer is using a training job to fine-tune a deep learning model in Amazon SageMaker Studio. The ML engineer previously used the same
pre-trained model with a similar dataset. The ML engineer expects vanishing gradient, underutilized GPU, and over«tting problems.
The ML engineer needs to implement a solution to detect these issues and to react in predefined ways when the issues occur. The solution also must provide comprehensive real-time metrics during the training.
Which solution will meet these requirements with the LEAST operational overhead?
A. Use TensorBoard to monitor the training job. Publish the findings to an Amazon Simple Noti«cation Service (Amazon SNS) topic. Create an AWS Lambda function to consume the findings and to initiate the predefined actions.
B. Use Amazon CloudWatch default metrics to gain insights about the training job. Use the metrics to invoke an AWS Lambda function to initiate the predefined actions.
C. Expand the metrics in Amazon CloudWatch to include the gradients in each training step. Use the metrics to invoke an AWS Lambda function to initiate the predefined actions.
D. Use SageMaker Debugger built-in rules to monitor the training job. Configure the rules to initiate the predefined actions.
49.
A credit card company has a fraud detection model in production on an Amazon SageMaker endpoint. The company develops a new version of the model. The company needs to assess the new model's performance by using live data and without affecting production end users.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
A. Set up SageMaker Debugger and create a custom rule.
B. Set up blue/green deployments with all-at-once trac shifting.
C. Set up blue/green deployments with canary trac shifting.
D. Set up shadow testing with a shadow variant of the new model.
50.
A company stores time-series data about user clicks in an Amazon S3 bucket. The raw data consists of millions of rows of user activity every day. ML engineers access the data to develop their ML models.
The ML engineers need to generate daily reports and analyze click trends over the past 3 days by using Amazon Athena. The company must retain the data for 30 days before archiving the data.
Which solution will provide the HIGHEST performance for data retrieval?
A. Keep all the time-series data without partitioning in the S3 bucket. Manually move data that is older than 30 days to separate S3 buckets.
B. Create AWS Lambda functions to copy the time-series data into separate S3 buckets. Apply S3 Lifecycle policies to archive data that is older than 30 days to S3 Glacier Flexible Retrieval.
C. Organize the time-series data into partitions by date prefix in the S3 bucket. Apply S3 Lifecycle policies to archive partitions that are older than 30 days to S3 Glacier Flexible Retrieval.
D. Put each day's time-series data into its own S3 bucket. Use S3 Lifecycle policies to archive S3 buckets that hold data that is older than 30 days to S3 Glacier Flexible Retrieval.
51.
A company has deployed an ML model that detects fraudulent credit card transactions in real time in a banking application. The model uses Amazon SageMaker Asynchronous Inference. Consumers are reporting delays in receiving the inference results.
An ML engineer needs to implement a solution to improve the inference performance. The solution also must provide a notification when a deviation in model quality occurs.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
A. Use SageMaker real-time inference for inference. Use SageMaker Model Monitor for notifications about model quality.
B. Use SageMaker batch transform for inference. Use SageMaker Model Monitor for notifications about model quality.
C. Use SageMaker Serverless Inference for inference. Use SageMaker Inference Recommender for notifications about model quality.
D. Keep using SageMaker Asynchronous Inference for inference. Use SageMaker Inference Recommender for notifications about model quality.
52.
An ML engineer needs to implement a solution to host a trained ML model. The rate of requests to the model will be inconsistent throughout the day.
The ML engineer needs a scalable solution that minimizes costs when the model is not in use. The solution also must maintain the model's capacity to respond to requests during times of peak usage.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
A. Create AWS Lambda functions that have fixed concurrency to host the model. Configure the Lambda functions to automatically scale based on the number of requests to the model.
B. Deploy the model on an Amazon Elastic Container Service (Amazon ECS) cluster that uses AWS Fargate. Set a static number of tasks to handle requests during times of peak usage.
C. Deploy the model to an Amazon SageMaker endpoint. Deploy multiple copies of the model to the endpoint. Create an Application Load Balancer to route trac between the different copies of the model at the endpoint.
D. Deploy the model to an Amazon SageMaker endpoint. Create SageMaker endpoint auto scaling policies that are based on Amazon CloudWatch metrics to adjust the number of instances dynamically.
53.
A company uses Amazon SageMaker Studio to develop an ML model. The company has a single SageMaker Studio domain. An ML engineer needs to implement a solution that provides an automated alert when SageMaker compute costs reach a specific threshold.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
A. Add resource tagging by editing the SageMaker user profile in the SageMaker domain. Configure AWS Cost Explorer to send an alert when the threshold is reached.
B. Add resource tagging by editing the SageMaker user profile in the SageMaker domain. Configure AWS Budgets to send an alert when the threshold is reached.
C. Add resource tagging by editing each user's IAM profile. Configure AWS Cost Explorer to send an alert when the threshold is reached.
D. Add resource tagging by editing each user's IAM profile. Configure AWS Budgets to send an alert when the threshold is reached.
54.
A company uses Amazon SageMaker for its ML workloads. The company's ML engineer receives a 50 MB Apache Parquet data file to build a fraud detection model. The file includes several correlated columns that are not required.
What should the ML engineer do to drop the unnecessary columns in the file with the LEAST effort?
A. Download the file to a local workstation. Perform one-hot encoding by using a custom Python script.
B. Create an Apache Spark job that uses a custom processing script on Amazon EMR.
C. Create a SageMaker processing job by calling the SageMaker Python SDK.
D. Create a data flow in SageMaker Data Wrangler. Con«gure a transform step.
55.
A company is creating an application that will recommend products for customers to purchase. The application will make API calls to Amazon Q Business. The company must ensure that responses from Amazon Q Business do not include the name of the company's main competitor.
Which solution will meet this requirement?
A. Configure the competitor's name as a blocked phrase in Amazon Q Business.
B. Configure an Amazon Q Business retriever to exclude the competitor’s name.
C. Configure an Amazon Kendra retriever for Amazon Q Business to build indexes that exclude the competitor's name.
D. Configure document attribute boosting in Amazon Q Business to deprioritize the competitor's name.
56.
An ML engineer needs to use Amazon SageMaker to fine-tune a large language model (LLM) for text summarization. The ML engineer must follow a low-code no-code (LCNC) approach.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
A. Use SageMaker Studio to fine-tune an LLM that is deployed on Amazon EC2 instances.
B. Use SageMaker Autopilot to fine-tune an LLM that is deployed by a custom API endpoint.
C. Use SageMaker Autopilot to fine-tune an LLM that is deployed on Amazon EC2 instances.
D. Use SageMaker Autopilot to fine-tune an LLM that is deployed by SageMaker JumpStart.
57.
A company has an ML model that needs to run one time each night to predict stock values. The model input is 3 MB of data that is collected during the current day. The model produces the predictions for the next day. The prediction process takes less than 1 minute to finish running.
How should the company deploy the model on Amazon SageMaker to meet these requirements?
A. Use a multi-model serverless endpoint. Enable caching.
B. Use an asynchronous inference endpoint. Set the InitialInstanceCount parameter to 0.
C. Use a real-time endpoint. Configure an auto scaling policy to scale the model to 0 when the model is not in use.
D. Use a serverless inference endpoint. Set the MaxConcurrency parameter to 1.
58.
An ML engineer trained an ML model on Amazon SageMaker to detect automobile accidents from dosed-circuit TV footage. The ML engineer used SageMaker Data Wrangler to create a training dataset of images of accidents and non-accidents.
The model performed well during training and validation. However, the model is underperforming in production because of variations in the quality of the images from various cameras.
Which solution will improve the model's accuracy in the LEAST amount of time?
A. Collect more images from all the cameras. Use Data Wrangler to prepare a new training dataset.
B. Recreate the training dataset by using the Data Wrangler corrupt image transform. Specify the impulse noise option.
C. Recreate the training dataset by using the Data Wrangler enhance image contrast transform. Specify the Gamma contrast option.
D. Recreate the training dataset by using the Data Wrangler resize image transform. Crop all images to the same size.
59.
A company has an application that uses different APIs to generate embeddings for input text. The company needs to implement a solution to automatically rotate the API tokens every 3 months.
Which solution will meet this requirement?
A. Store the tokens in AWS Secrets Manager. Create an AWS Lambda function to perform the rotation.
B. Store the tokens in AWS Systems Manager Parameter Store. Create an AWS Lambda function to perform the rotation.
C. Store the tokens in AWS Key Management Service (AWS KMS). Use an AWS managed key to perform the rotation.
D. Store the tokens in AWS Key Management Service (AWS KMS). Use an AWS owned key to perform the rotation.
60.
An ML engineer receives datasets that contain missing values, duplicates, and extreme outliers. The ML engineer must consolidate these
datasets into a single data frame and must prepare the data for ML.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
A. Use Amazon SageMaker Data Wrangler to import the datasets and to consolidate them into a single data frame. Use the cleansing and enrichment functionalities to prepare the data.
B. Use Amazon SageMaker Ground Truth to import the datasets and to consolidate them into a single data frame. Use the human-in-the-loop capability to prepare the data.
C. Manually import and merge the datasets. Consolidate the datasets into a single data frame. Use Amazon Q Developer to generate code snippets that will prepare the data.
D. Manually import and merge the datasets. Consolidate the datasets into a single data frame. Use Amazon SageMaker data labeling to prepare the data.
61.
A company has historical data that shows whether customers needed long-term support from company staff. The company needs to develop an ML model to predict whether new customers will require long-term support.
Which modeling approach should the company use to meet this requirement?
A. Anomaly detection
B. Linear regression
C. Logistic regression
D. Semantic segmentation
62.
An ML engineer has developed a binary classi«cation model outside of Amazon SageMaker. The ML engineer needs to make the model accessible to a SageMaker Canvas user for additional tuning.
The model artifacts are stored in an Amazon S3 bucket. The ML engineer and the Canvas user are part of the same SageMaker domain.
Which combination of requirements must be met so that the ML engineer can share the model with the Canvas user? (Choose two.)
A. The ML engineer and the Canvas user must be in separate SageMaker domains.
B. The Canvas user must have permissions to access the S3 bucket where the model artifacts are stored.
C. The model must be registered in the SageMaker Model Registry.
D. The ML engineer must host the model on AWS Marketplace.
E. The ML engineer must deploy the model to a SageMaker endpoint.
63.
A company is building a deep learning model on Amazon SageMaker. The company uses a large amount of data as the training dataset. The company needs to optimize the model's hyperparameters to minimize the loss function on the validation dataset.
Which hyperparameter tuning strategy will accomplish this goal with the LEAST computation time?
A. Hyperband
B. Grid search
C. Bayesian optimization
D. Random search
64.
A company is planning to use Amazon Redshift ML in its primary AWS account. The source data is in an Amazon S3 bucket in a secondary account.
An ML engineer needs to set up an ML pipeline in the primary account to access the S3 bucket in the secondary account. The solution must not require public IPv4 addresses.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
A. Provision a Redshift cluster and Amazon SageMaker Studio in a VPC with no public access enabled in the primary account. Create a VPC peering connection between the accounts. Update the VPC route tables to remove the route to 0.0.0.0/0.
B. Provision a Redshift cluster and Amazon SageMaker Studio in a VPC with no public access enabled in the primary account. Create an AWS Direct Connect connection and a transit gateway. Associate the VPCs from both accounts with the transit gateway. Update the VPC route tables to remove the route to 0.0.0.0/0.
C. Provision a Redshift cluster and Amazon SageMaker Studio in a VPC in the primary account. Create an AWS Site-to-Site VPN connection with two encrypted IPsec tunnels between the accounts. Set up interface VPC endpoints for Amazon S3.
D. Provision a Redshift cluster and Amazon SageMaker Studio in a VPC in the primary account. Create an S3 gateway endpoint. Update the S3 bucket policy to allow IAM principals from the primary account. Set up interface VPC endpoints for SageMaker and Amazon Redshift.
65.
A company is using an AWS Lambda function to monitor the metrics from an ML model. An ML engineer needs to implement a solution to send an
email message when the metrics breach a threshold.
Which solution will meet this requirement?
A. Log the metrics from the Lambda function to AWS CloudTrail. Con«gure a CloudTrail trail to send the email message.
B. Log the metrics from the Lambda function to Amazon CloudFront. Con«gure an Amazon CloudWatch alarm to send the email message.
C. Log the metrics from the Lambda function to Amazon CloudWatch. Con«gure a CloudWatch alarm to send the email message.
D. Log the metrics from the Lambda function to Amazon CloudWatch. Con«gure an Amazon CloudFront rule to send the email message.
66.
A company has used Amazon SageMaker to deploy a predictive ML model in production. The company is using SageMaker Model Monitor on the model. After a model update, an ML engineer notices data quality issues in the Model Monitor checks.
What should the ML engineer do to mitigate the data quality issues that Model Monitor has identified?
A. Adjust the model's parameters and hyperparameters.
B. Initiate a manual Model Monitor job that uses the most recent production data.
C. Create a new baseline from the latest dataset. Update Model Monitor to use the new baseline for evaluations.
D. Include additional data in the existing training set for the model. Retrain and redeploy the model.
67.
A company has an ML model that generates text descriptions based on images that customers upload to the company's website. The images can be up to 50 MB in total size.
An ML engineer decides to store the images in an Amazon S3 bucket. The ML engineer must implement a processing solution that can scale to accommodate changes in demand.
Which solution will meet these requirements with the LEAST operational overhead?
A. Create an Amazon SageMaker batch transform job to process all the images in the S3 bucket.
B. Create an Amazon SageMaker Asynchronous Inference endpoint and a scaling policy. Run a script to make an inference request for each image.
C. Create an Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (Amazon EKS) cluster that uses Karpenter for auto scaling. Host the model on the EKS cluster. Run a script to make an inference request for each image.
D. Create an AWS Batch job that uses an Amazon Elastic Container Service (Amazon ECS) cluster. Specify a list of images to process for each AWS Batch job.
68.
An ML engineer needs to use AWS services to identify and extract meaningful unique keywords from documents.
Which solution will meet these requirements with the LEAST operational overhead?
A. Use the Natural Language Toolkit (NLTK) library on Amazon EC2 instances for text pre-processing. Use the Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) algorithm to identify and extract relevant keywords.
B. Use Amazon SageMaker and the BlazingText algorithm. Apply custom pre-processing steps for stemming and removal of stop words. Calculate term frequency-inverse document frequency (TF-IDF) scores to identify and extract relevant keywords.
C. Store the documents in an Amazon S3 bucket. Create AWS Lambda functions to process the documents and to run Python scripts for stemming and removal of stop words. Use bigram and trigram techniques to identify and extract relevant keywords.
D. Use Amazon Comprehend custom entity recognition and key phrase extraction to identify and extract relevant keywords.
69.
A company needs to give its ML engineers appropriate access to training data. The ML engineers must access training data from only their own business group. The ML engineers must not be allowed to access training data from other business groups.
The company uses a single AWS account and stores all the training data in Amazon S3 buckets. All ML model training occurs in Amazon SageMaker.
Which solution will provide the ML engineers with the appropriate access?
A. Enable S3 bucket versioning.
B. Con«gure S3 Object Lock settings for each user.
C. Add cross-origin resource sharing (CORS) policies to the S3 buckets.
D. Create IAM policies. Attach the policies to IAM users or IAM roles.
70.
A company needs to host a custom ML model to perform forecast analysis. The forecast analysis will occur with predictable and sustained load during the same 2-hour period every day.
Multiple invocations during the analysis period will require quick responses. The company needs AWS to manage the underlying infrastructure and any auto scaling activities.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
A. Schedule an Amazon SageMaker batch transform job by using AWS Lambda.
B. Configure an Auto Scaling group of Amazon EC2 instances to use scheduled scaling.
C. Use Amazon SageMaker Serverless Inference with provisioned concurrency.
D. Run the model on an Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (Amazon EKS) cluster on Amazon EC2 with pod auto scaling.
71.
A company's ML engineer has deployed an ML model for sentiment analysis to an Amazon SageMaker endpoint. The ML engineer needs to explain to company stakeholders how the model makes predictions.
Which solution will provide an explanation for the model's predictions?
A. Use SageMaker Model Monitor on the deployed model.
B. Use SageMaker Clarify on the deployed model.
C. Show the distribution of inferences from A/В testing in Amazon CloudWatch.
D. Add a shadow endpoint. Analyze prediction differences on samples.
72.
An ML engineer is using Amazon SageMaker to train a deep learning model that requires distributed training. After some training attempts, the ML engineer observes that the instances are not performing as expected. The ML engineer identifies communication overhead between the training instances.
What should the ML engineer do to MINIMIZE the communication overhead between the instances?
A. Place the instances in the same VPC subnet. Store the data in a different AWS Region from where the instances are deployed.
B. Place the instances in the same VPC subnet but in different Availability Zones. Store the data in a different AWS Region from where the instances are deployed.
C. Place the instances in the same VPC subnet. Store the data in the same AWS Region and Availability Zone where the instances are deployed.
D. Place the instances in the same VPC subnet. Store the data in the same AWS Region but in a different Availability Zone from where the instances are deployed.
73.
A company is running ML models on premises by using custom Python scripts and proprietary datasets. The company is using PyTorch. The model building requires unique domain knowledge. The company needs to move the models to AWS.
Which solution will meet these requirements with the LEAST effort?
A. Use SageMaker built-in algorithms to train the proprietary datasets.
B. Use SageMaker script mode and premade images for ML frameworks.
C. Build a container on AWS that includes custom packages and a choice of ML frameworks.
D. Purchase similar production models through AWS Marketplace.
74.
A company is using Amazon SageMaker and millions of files to train an ML model. Each file is several megabytes in size. The files are stored in an
Amazon S3 bucket. The company needs to improve training performance.
Which solution will meet these requirements in the LEAST amount of time?
A. Transfer the data to a new S3 bucket that provides S3 Express One Zone storage. Adjust the training job to use the new S3 bucket.
B. Create an Amazon FSx for Lustre file system. Link the file system to the existing S3 bucket. Adjust the training job to read from the file system.
C. Create an Amazon Elastic File System (Amazon EFS) file system. Transfer the existing data to the file system. Adjust the training job to read from the file system.
D. Create an Amazon ElastiCache (Redis OSS) cluster. Link the Redis OSS cluster to the existing S3 bucket. Stream the data from the Redis OSS cluster directly to the training job.
75.
A company wants to develop an ML model by using tabular data from its customers. The data contains meaningful ordered features with sensitive
information that should not be discarded. An ML engineer must ensure that the sensitive data is masked before another team starts to build the model.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
A. Use Amazon Made to categorize the sensitive data.
B. Prepare the data by using AWS Glue DataBrew.
C. Run an AWS Batch job to change the sensitive data to random values.
D. Run an Amazon EMR job to change the sensitive data to random values.
76.
An ML engineer needs to deploy ML models to get inferences from large datasets in an asynchronous manner. The ML engineer also needs to implement scheduled monitoring of the data quality of the models. The ML engineer must receive alerts when changes in data quality occur.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
A. Deploy the models by using scheduled AWS Glue jobs. Use Amazon CloudWatch alarms to monitor the data quality and to send alerts.
B. Deploy the models by using scheduled AWS Batch jobs. Use AWS CloudTrail to monitor the data quality and to send alerts.
C. Deploy the models by using Amazon Elastic Container Service (Amazon ECS) on AWS Fargate. Use Amazon EventBridge to monitor the data quality and to send alerts.
D. Deploy the models by using Amazon SageMaker batch transform. Use SageMaker Model Monitor to monitor the data quality and to send alerts.
77.
An ML engineer normalized training data by using min-max normalization in AWS Glue DataBrew. The ML engineer must normalize the production inference data in the same way as the training data before passing the production inference data to the model for predictions.
Which solution will meet this requirement?
A. Apply statistics from a well-known dataset to normalize the production samples.
B. Keep the min-max normalization statistics from the training set. Use these values to normalize the production samples.
C. Calculate a new set of min-max normalization statistics from a batch of production samples. Use these values to normalize all the production samples.
D. Calculate a new set of min-max normalization statistics from each production sample. Use these values to normalize all the production samples.
78.
A company is planning to use Amazon SageMaker to make classification ratings that are based on images. The company has 6 ТВ of training data that is stored on an Amazon FSx for NetApp ONTAP system virtual machine (SVM). The SVM is in the same VPC as SageMaker.
An ML engineer must make the training data accessible for ML models that are in the SageMaker environment.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
A. Mount the FSx for ONTAP file system as a volume to the SageMaker Instance.
B. Create an Amazon S3 bucket. Use Mountpoint for Amazon S3 to link the S3 bucket to the FSx for ONTAP file system.
C. Create a catalog connection from SageMaker Data Wrangler to the FSx for ONTAP file system.
D. Create a direct connection from SageMaker Data Wrangler to the FSx for ONTAP file system.
79.
A company regularly receives new training data from the vendor of an ML model. The vendor delivers cleaned and prepared data to the company's Amazon S3 bucket every 3-4 days.
The company has an Amazon SageMaker pipeline to retrain the model. An ML engineer needs to implement a solution to run the pipeline when new data is uploaded to the S3 bucket.
Which solution will meet these requirements with the LEAST operational effort?
A. Create an S3 Lifecycle rule to transfer the data to the SageMaker training instance and to initiate training.
B. Create an AWS Lambda function that scans the S3 bucket. Program the Lambda function to initiate the pipeline when new data is uploaded.
C. Create an Amazon EventBridge rule that has an event pattern that matches the S3 upload. Configure the pipeline as the target of the rule.
D. Use Amazon Managed Work¬ows for Apache Air¬ow (Amazon MWAA) to orchestrate the pipeline when new data is uploaded.
80.
An ML engineer is developing a fraud detection model by using the Amazon SageMaker XGBoost algorithm. The model classi«es transactions as either fraudulent or legitimate.
During testing, the model excels at identifying fraud in the training dataset. However, the model is inecient at identifying fraud in new and unseen transactions.
What should the ML engineer do to improve the fraud detection for new transactions?
A. Increase the learning rate.
B. Remove some irrelevant features from the training dataset.
C. Increase the value of the max_depth hyperparameter.
D. Decrease the value of the max_depth hyperparameter.
81.
A company has a binary classi«cation model in production. An ML engineer needs to develop a new version of the model.
The new model version must maximize correct predictions of positive labels and negative labels. The ML engineer must use a metric to recalibrate the model to meet these requirements.
Which metric should the ML engineer use for the model recalibration?
A. Accuracy
B. Precision
C. Recall
D. Speci«city
82.
A company is using Amazon SageMaker to create ML models. The company's data scientists need fine-grained control of the ML workflows that they orchestrate. The data scientists also need the ability to visualize SageMaker jobs and workflows as a directed acyclic graph (DAG). The data scientists must keep a running history of model discovery experiments and must establish model governance for auditing and compliance verifications.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
A. Use AWS CodePipeline and its integration with SageMaker Studio to manage the entire ML workflows. Use SageMaker ML Lineage Tracking for the running history of experiments and for auditing and compliance verifications.
B. Use AWS CodePipeline and its integration with SageMaker Experiments to manage the entire ML workflows. Use SageMaker Experiments for the running history of experiments and for auditing and compliance verifications.
C. Use SageMaker Pipelines and its integration with SageMaker Studio to manage the entire ML workflows. Use SageMaker ML Lineage Tracking for the running history of experiments and for auditing and compliance verifications.
D. Use SageMaker Pipelines and its integration with SageMaker Experiments to manage the entire ML workflows. Use SageMaker Experiments for the running history of experiments and for auditing and compliance verifications.
83.
A company wants to reduce the cost of its containerized ML applications. The applications use ML models that run on Amazon EC2 instances, AWS Lambda functions, and an Amazon Elastic Container Service (Amazon ECS) cluster. The EC2 workloads and ECS workloads use Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS) volumes to save predictions and artifacts.
An ML engineer must identify resources that are being used ineciently. The ML engineer also must generate recommendations to reduce the cost of these resources.
Which solution will meet these requirements with the LEAST development effort?
A. Create code to evaluate each instance's memory and compute usage.
B. Add cost allocation tags to the resources. Activate the tags in AWS Billing and Cost Management.
C. Check AWS CloudTrail event history for the creation of the resources.
D. Run AWS Compute Optimizer.
84.
A company needs to create a central catalog for all the company's ML models. The models are in AWS accounts where the company developed the models initially. The models are hosted in Amazon Elastic Container Registry (Amazon ECR) repositories.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
A. Configure ECR cross-account replication for each existing ECR repository. Ensure that each model is visible in each AWS account.
B. Create a new AWS account with a new ECR repository as the central catalog. Configure ECR cross-account replication between the initial ECR repositories and the central catalog.
C. Use the Amazon SageMaker Model Registry to create a model group for models hosted in Amazon ECR. Create a new AWS account. In the new account, use the SageMaker Model Registry as the central catalog. Attach a cross-account resource policy to each model group in the initial AWS accounts.
D. Use an AWS Glue Data Catalog to store the models. Run an AWS Glue crawler to migrate the models from the ECR repositories to the Data Catalog. Configure cross-account access to the Data Catalog.
85.
A company has developed a new ML model. The company requires online model validation on 10% of the trac before the company fully releases the model in production. The company uses an Amazon SageMaker endpoint behind an Application Load Balancer (ALB) to serve the model.
Which solution will set up the required online validation with the LEAST operational overhead?
A. Use production variants to add the new model to the existing SageMaker endpoint. Set the variant weight to 0.1 for the new model. Monitor the number of invocations by using Amazon CloudWatch.
B. Use production variants to add the new model to the existing SageMaker endpoint. Set the variant weight to 1 for the new model. Monitor the number of invocations by using Amazon CloudWatch.
C. Create a new SageMaker endpoint. Use production variants to add the new model to the new endpoint. Monitor the number of invocations by using Amazon CloudWatch.
D. Configure the ALB to route 10% of the trac to the new model at the existing SageMaker endpoint. Monitor the number of invocations by using AWS CloudTrail.
86.
A company needs to develop an ML model. The model must identify an item in an image and must provide the location of the item.
Which Amazon SageMaker algorithm will meet these requirements?
A. Image classification
B. XGBoost
C. Object detection
D. K-nearest neighbors (k-NN)
87.
A company has an Amazon S3 bucket that contains 1 ТВ of files from different sources. The S3 bucket contains the following file types in the same S3 folder: CSV, JSON, XLSX, and Apache Parquet.
An ML engineer must implement a solution that uses AWS Glue DataBrew to process the data. The ML engineer also must store the final output in Amazon S3 so that AWS Glue can consume the output in the future.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
A. Use DataBrew to process the existing S3 folder. Store the output in Apache Parquet format.
B. Use DataBrew to process the existing S3 folder. Store the output in AWS Glue Parquet format.
C. Separate the data into a different folder for each file type. Use DataBrew to process each folder individually. Store the output in Apache Parquet format.
D. Separate the data into a different folder for each file type. Use DataBrew to process each folder individually. Store the output in AWS Glue Parquet format.
88.
A manufacturing company uses an ML model to determine whether products meet a standard for quality. The model produces an output of "Passed" or "Failed." Robots separate the products into the two categories by using the model to analyze photos on the assembly line.
Which metrics should the company use to evaluate the model's performance? (Choose two.)
A. Precision and recall
B. Root mean square error (RMSE) and mean absolute percentage error (MAPE)
C. Accuracy and F1 score
D. Bilingual Evaluation Understudy (BLEU) score
E. Perplexity
89.
An ML engineer needs to encrypt all data in transit when an ML training job runs. The ML engineer must ensure that encryption in transit is applied to processes that Amazon SageMaker uses during the training job.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
A. Encrypt communication between nodes for batch processing.
B. Encrypt communication between nodes in a training cluster.
C. Specify an AWS Key Management Service (AWS KMS) key during creation of the training job request.
D. Specify an AWS Key Management Service (AWS KMS) key during creation of the SageMaker domain.
90.
An ML engineer needs to use metrics to assess the quality of a time-series forecasting model.
Which metrics apply to this model? (Choose two.)
A. Recall
B. LogLoss
C. Root mean square error (RMSE)
D. InferenceLatency
E. Average weighted quantile loss (wQL)
91.
A company runs Amazon SageMaker ML models that use accelerated instances. The models require real-time responses. Each model has different scaling requirements. The company must not allow a cold start for the models.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
A. Create a SageMaker Serverless Inference endpoint for each model. Use provisioned concurrency for the endpoints.
B. Create a SageMaker Asynchronous Inference endpoint for each model. Create an auto scaling policy for each endpoint.
C. Create a SageMaker endpoint. Create an inference component for each model. In the inference component settings, specify the newly created endpoint. Create an auto scaling policy for each inference component. Set the parameter for the minimum number of copies to at least 1.
D. Create an Amazon S3 bucket. Store all the model artifacts in the S3 bucket. Create a SageMaker multi-model endpoint. Point the endpoint to the S3 bucket. Create an auto scaling policy for the endpoint. Set the parameter for the minimum number of copies to at least 1.
92.
A company uses Amazon SageMaker for its ML process. A compliance audit discovers that an Amazon S3 bucket for training data uses serverside encryption with S3 managed keys (SSE-S3).
The company requires customer managed keys. An ML engineer changes the S3 bucket to use server-side encryption with AWS KMS keys (SSEKMS).
The ML engineer makes no other con«guration changes.
After the change to the encryption settings, SageMaker training jobs start to fail with AccessDenied errors.
What should the ML engineer do to resolve this problem?
A. Update the IAM policy that is attached to the execution role for the training jobs. Include the s3:ListBucket and s3:GetObject permissions.
B. Update the S3 bucket policy that is attached to the S3 bucket. Set the value of the aws:SecureTransport condition key to True.
C. Update the IAM policy that is attached to the execution role for the training jobs. Include the kms:Encrypt and kms:Decrypt permissions.
D. Update the IAM policy that is attached to the user that created the training jobs. Include the kms:CreateGrant permission.
93.
A company runs training jobs on Amazon SageMaker by using a compute optimized instance. Demand for training runs will remain constant for the next 55 weeks. The instance needs to run for 35 hours each week. The company needs to reduce its model training costs.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
A. Use a serverless endpoint with a provisioned concurrency of 35 hours for each week. Run the training on the endpoint.
B. Use SageMaker Edge Manager for the training. Specify the instance requirement in the edge device configuration. Run the training.
C. Use the heterogeneous cluster feature of SageMaker Training. Configure the instance_type, instance_count, and instance_groups arguments to run training jobs.
D. Opt in to a SageMaker Savings Plan with a 1-year term and an All Upfront payment. Run a SageMaker Training job on the instance.
94.
HOTSPOT
-
A company needs to train an ML model that will use historical transaction data to predict customer behavior.
Select the correct AWS service from the following list to perform each task on the data. Each service should be selected one time or not at all.
(Select three.)
• Amazon Athena
• AWS Glue
• Amazon Kinesis Data Streams
• Amazon S3
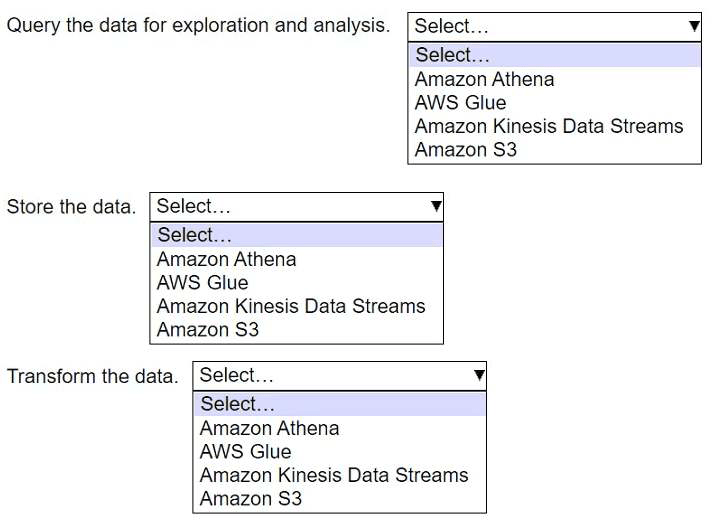
95.
A company deployed an ML model that uses the XGBoost algorithm to predict product failures. The model is hosted on an Amazon SageMaker endpoint and is trained on normal operating data. An AWS Lambda function provides the predictions to the company's application.
An ML engineer must implement a solution that uses incoming live data to detect decreased model accuracy over time.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
A. Use Amazon CloudWatch to create a dashboard that monitors real-time inference data and model predictions. Use the dashboard to detect drift.
B. Modify the Lambda function to calculate model drift by using real-time inference data and model predictions. Program the Lambda function to send alerts.
C. Schedule a monitoring job in SageMaker Model Monitor. Use the job to detect drift by analyzing the live data against a baseline of the training data statistics and constraints.
D. Schedule a monitoring job in SageMaker Debugger. Use the job to detect drift by analyzing the live data against a baseline of the training data statistics and constraints.
96.
A company has an ML model that uses historical transaction data to predict customer behavior. An ML engineer is optimizing the model in Amazon SageMaker to enhance the model's predictive accuracy. The ML engineer must examine the input data and the resulting predictions to identify trends that could skew the model's performance across different demographics.
Which solution will provide this level of analysis?
A. Use Amazon CloudWatch to monitor network metrics and CPU metrics for resource optimization during model training.
B. Create AWS Glue DataBrew recipes to correct the data based on statistics from the model output.
C. Use SageMaker Clarify to evaluate the model and training data for underlying patterns that might affect accuracy.
D. Create AWS Lambda functions to automate data pre-processing and to ensure consistent quality of input data for the model.
97.
A company uses 10 Reserved Instances of accelerated instance types to serve the current version of an ML model. An ML engineer needs to deploy a new version of the model to an Amazon SageMaker real-time inference endpoint.
The solution must use the original 10 instances to serve both versions of the model. The solution also must include one additional Reserved Instance that is available to use in the deployment process. The transition between versions must occur with no downtime or service interruptions.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
A. Configure a blue/green deployment with all-at-once trac shifting.
B. Configure a blue/green deployment with canary trac shifting and a size of 10%.
C. Configure a shadow test with a trac sampling percentage of 10%.
D. Configure a rolling deployment with a rolling batch size of 1.
98.
An IoT company uses Amazon SageMaker to train and test an XGBoost model for object detection. ML engineers need to monitor performance metrics when they train the model with variants in hyperparameters. The ML engineers also need to send Short Message Service (SMS) text messages after training is complete.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
A. Use Amazon CloudWatch to monitor performance metrics. Use Amazon Simple Queue Service (Amazon SQS) for message delivery.
B. Use Amazon CloudWatch to monitor performance metrics. Use Amazon Simple Noti«cation Service (Amazon SNS) for message delivery.
C. Use AWS CloudTrail to monitor performance metrics. Use Amazon Simple Queue Service (Amazon SQS) for message delivery.
D. Use AWS CloudTrail to monitor performance metrics. Use Amazon Simple Noti«cation Service (Amazon SNS) for message delivery.
99.
A company is working on an ML project that will include Amazon SageMaker notebook instances. An ML engineer must ensure that the SageMaker notebook instances do not allow root access.
Which solution will prevent the deployment of notebook instances that allow root access?
A. Use IAM condition keys to stop deployments of SageMaker notebook instances that allow root access.
B. Use AWS Key Management Service (AWS KMS) keys to stop deployments of SageMaker notebook instances that allow root access.
C. Monitor resource creation by using Amazon EventBridge events. Create an AWS Lambda function that deletes all deployed SageMaker notebook instances that allow root access.
D. Monitor resource creation by using AWS CloudFormation events. Create an AWS Lambda function that deletes all deployed SageMaker notebook instances that allow root access.
100.
A company is using Amazon SageMaker to develop ML models. The company stores sensitive training data in an Amazon S3 bucket. The model training must have network isolation from the internet.
Which solution will meet this requirement?
A. Run the SageMaker training jobs in private subnets. Create a NAT gateway. Route traffic for training through the NAT gateway.
B. Run the SageMaker training jobs in private subnets. Create an S3 gateway VPC endpoint. Route traffic for training through the S3 gateway VPC endpoint.
C. Run the SageMaker training jobs in public subnets that have an attached security group. In the security group, use inbound rules to limit trafficc from the internet. Encrypt SageMaker instance storage by using server-side encryption with AWS KMS keys (SSE-KMS).
D. Encrypt traffic to Amazon S3 by using a bucket policy that includes a value of True for the aws:SecureTransport condition key. Use default at-rest encryption for Amazon S3. Encrypt SageMaker instance storage by using server-side encryption with AWS KMS keys (SSE-KMS).
101.
A company needs an AWS solution that will automatically create versions of ML models as the models are created.
Which solution will meet this requirement?
A. Amazon Elastic Container Registry (Amazon ECR)
B. Model packages from Amazon SageMaker Marketplace
C. Amazon SageMaker ML Lineage Tracking
D. Amazon SageMaker Model Registry
102.
A company needs to use Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) to supplement an open source large language model (LLM) that runs on Amazon Bedrock. The company's data for RAG is a set of documents in an Amazon S3 bucket. The documents consist of .csv files and .docx files.
Which solution will meet these requirements with the LEAST operational overhead?
A. Create a pipeline in Amazon SageMaker Pipelines to generate a new model. Call the new model from Amazon Bedrock to perform RAG queries.
B. Convert the data into vectors. Store the data in an Amazon Neptune database. Connect the database to Amazon Bedrock. Call the Amazon Bedrock API to perform RAG queries.
C. Fine-tune an existing LLM by using an AutoML job in Amazon SageMaker. Configure the S3 bucket as a data source for the AutoML job.
Deploy the LLM to a SageMaker endpoint. Use the endpoint to perform RAG queries.
D. Create a knowledge base for Amazon Bedrock. Configure a data source that references the S3 bucket. Use the Amazon Bedrock API to perform RAG queries.
103.
A company plans to deploy an ML model for production inference on an Amazon SageMaker endpoint. The average inference payload size will vary from 100 MB to 300 MB. Inference requests must be processed in 60 minutes or less.
Which SageMaker inference option will meet these requirements?
A. Serverless inference
B. Asynchronous inference
C. Real-time inference
D. Batch transform
104.
An ML engineer notices class imbalance in an image classification training job.
What should the ML engineer do to resolve this issue?
A. Reduce the size of the dataset.
B. Transform some of the images in the dataset.
C. Apply random oversampling on the dataset.
D. Apply random data splitting on the dataset.
105.
A company receives daily .csv files about customer interactions with its ML model. The company stores the files in Amazon S3 and uses the files to retrain the model. An ML engineer needs to implement a solution to mask credit card numbers in the files before the model is retrained.
Which solution will meet this requirement with the LEAST development effort?
A. Create a discovery job in Amazon Macie. Configure the job to find and mask sensitive data.
B. Create Apache Spark code to run on an AWS Glue job. Use the Sensitive Data Detection functionality in AWS Glue to find and mask sensitive data.
C. Create Apache Spark code to run on an AWS Glue job. Program the code to perform a regex operation to find and mask sensitive data.
D. Create Apache Spark code to run on an Amazon EC2 instance. Program the code to perform an operation to find and mask sensitive data.
106.
A medical company is using AWS to build a tool to recommend treatments for patients. The company has obtained health records and selfreported
textual information in English from patients. The company needs to use this information to gain insight about the patients.
Which solution will meet this requirement with the LEAST development effort?
A. Use Amazon SageMaker to build a recurrent neural network (RNN) to summarize the data.
B. Use Amazon Comprehend Medical to summarize the data.
C. Use Amazon Kendra to create a quick-search tool to query the data.
D. Use the Amazon SageMaker Sequence-to-Sequence (seq2seq) algorithm to create a text summary from the data.
107.
A company needs to extract entities from a PDF document to build a classi«er model.
Which solution will extract and store the entities in the LEAST amount of time?
A. Use Amazon Comprehend to extract the entities. Store the output in Amazon S3.
B. Use an open source AI optical character recognition (OCR) tool on Amazon SageMaker to extract the entities. Store the output in Amazon S3.
C. Use Amazon Textract to extract the entities. Use Amazon Comprehend to convert the entities to text. Store the output in Amazon S3.
D. Use Amazon Textract integrated with Amazon Augmented AI (Amazon A2I) to extract the entities. Store the output in Amazon S3.
108.
A company shares Amazon SageMaker Studio notebooks that are accessible through a VPN. The company must enforce access controls to prevent malicious actors from exploiting presigned URLs to access the notebooks.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
A. Set up Studio client IP validation by using the aws:sourceIp IAM policy condition.
B. Set up Studio client VPC validation by using the aws:sourceVpc IAM policy condition.
C. Set up Studio client role endpoint validation by using the aws:PrimaryTag IAM policy condition.
D. Set up Studio client user endpoint validation by using the aws:PrincipalTag IAM policy condition.
109.
An ML engineer needs to merge and transform data from two sources to retrain an existing ML model. One data source consists of .csv files that are stored in an Amazon S3 bucket. Each .csv file consists of millions of records. The other data source is an Amazon Aurora DB cluster.
The result of the merge process must be written to a second S3 bucket. The ML engineer needs to perform this merge-and-transform task every week.
Which solution will meet these requirements with the LEAST operational overhead?
A. Create a transient Amazon EMR cluster every week. Use the cluster to run an Apache Spark job to merge and transform the data.
B. Create a weekly AWS Glue job that uses the Apache Spark engine. Use DynamicFrame native operations to merge and transform the data.
C. Create an AWS Lambda function that runs Apache Spark code every week to merge and transform the data. Configure the Lambda function to connect to the initial S3 bucket and the DB cluster.
D. Create an AWS Batch job that runs Apache Spark code on Amazon EC2 instances every week. Configure the Spark code to save the data from the EC2 instances to the second S3 bucket.
110.
An ML engineer has deployed an Amazon SageMaker model to a serverless endpoint in production. The model is invoked by the InvokeEndpoint API operation.
The model's latency in production is higher than the baseline latency in the test environment. The ML engineer thinks that the increase in latency is because of model startup time.
What should the ML engineer do to con«rm or deny this hypothesis?
A. Schedule a SageMaker Model Monitor job. Observe metrics about model quality.
B. Schedule a SageMaker Model Monitor job with Amazon CloudWatch metrics enabled.
C. Enable Amazon CloudWatch metrics. Observe the ModelSetupTime metric in the SageMaker namespace.
D. Enable Amazon CloudWatch metrics. Observe the ModelLoadingWaitTime metric in the SageMaker namespace.
111.
An ML engineer needs to ensure that a dataset complies with regulations for personally identifiable information (PII). The ML engineer will use the data to train an ML model on Amazon SageMaker instances. SageMaker must not use any of the PII.
Which solution will meet these requirements in the MOST operationally ecient way?
A. Use the Amazon Comprehend DetectPiiEntities API call to redact the PII from the data. Store the data in an Amazon S3 bucket. Access the S3 bucket from the SageMaker instances for model training.
B. Use the Amazon Comprehend DetectPiiEntities API call to redact the PII from the data. Store the data in an Amazon Elastic File System (Amazon EFS) file system. Mount the EFS file system to the SageMaker instances for model training.
C. Use AWS Glue DataBrew to cleanse the dataset of PII. Store the data in an Amazon Elastic File System (Amazon EFS) file system. Mount the EFS file system to the SageMaker instances for model training.
D. Use Amazon Macie for automatic discovery of PII in the data. Remove the PII. Store the data in an Amazon S3 bucket. Mount the S3 bucket to the SageMaker instances for model training.
112.
A company must install a custom script on any newly created Amazon SageMaker notebook instances.
Which solution will meet this requirement with the LEAST operational overhead?
A. Create a lifecycle configuration script to install the custom script when a new SageMaker notebook is created. Attach the lifecycle configuration to every new SageMaker notebook as part of the creation steps.
B. Create a custom Amazon Elastic Container Registry (Amazon ECR) image that contains the custom script. Push the ECR image to a Docker registry. Attach the Docker image to a SageMaker Studio domain. Select the kernel to run as part of the SageMaker notebook.
C. Create a custom package index repository. Use AWS CodeArtifact to manage the installation of the custom script. Set up AWS PrivateLink endpoints to connect CodeArtifact to the SageMaker instance. Install the script.
D. Store the custom script in Amazon S3. Create an AWS Lambda function to install the custom script on new SageMaker notebooks. Configure Amazon EventBridge to invoke the Lambda function when a new SageMaker notebook is initialized.
113.
A company is building a real-time data processing pipeline for an ecommerce application. The application generates a high volume of clickstream data that must be ingested, processed, and visualized in near real time. The company needs a solution that supports SQL for data processing and Jupyter notebooks for interactive analysis.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
A. Use Amazon Data Firehose to ingest the data. Create an AWS Lambda function to process the data. Store the processed data in Amazon S3. Use Amazon QuickSight to visualize the data.
B. Use Amazon Kinesis Data Streams to ingest the data. Use Amazon Data Firehose to transform the data. Use Amazon Athena to process the data. Use Amazon QuickSight to visualize the data.
C. Use Amazon Managed Streaming for Apache Kafka (Amazon MSK) to ingest the data. Use AWS Glue with PySpark to process the data. Store the processed data in Amazon S3. Use Amazon QuickSight to visualize the data.
D. Use Amazon Managed Streaming for Apache Kafka (Amazon MSK) to ingest the data. Use Amazon Managed Service for Apache Flink to process the data. Use the built-in Flink dashboard to visualize the data.
114.
A medical company needs to store clinical data. The data includes personally identifiable information (PII) and protected health information (PHI).
An ML engineer needs to implement a solution to ensure that the PII and PHI are not used to train ML models.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
A. Store the clinical data in Amazon S3 buckets. Use AWS Glue DataBrew to mask the PII and PHI before the data is used for model training.
B. Upload the clinical data to an Amazon Redshift database. Use built-in SQL stored procedures to automatically classify and mask the PII and PHI before the data is used for model training.
C. Use Amazon Comprehend to detect and mask the PII before the data is used for model training. Use Amazon Comprehend Medical to detect and mask the PHI before the data is used for model training.
D. Create an AWS Lambda function to encrypt the PII and PHI. Program the Lambda function to save the encrypted data to an Amazon S3 bucket for model training.