我與 FP 的旅程
緣起:一段程式碼
# 通用語法
request = generate_request()
response = get_response(request)
body = parse_body(response, "html")
html = render(body)# 通用語法
html = render(parse_body(get_response(generate_request()), "html"))緣起:一段程式碼
# Elixir 語法
html =
generate_request()
|> get_response()
|> parse_body(:html)
|> render()管線:函式的組合
# 通用語法
request = generate_request()
response = get_response(request)
body = parse_body(response, "html")
html = render(body)



Initial
request
response
body
html
把函式想像成一條水管
input 經過 function 後,會吐出output
管線:函式的組合
# 通用語法
request = generate_request()
response = get_response(request)
body = parse_body(response, "html")
html = render(body)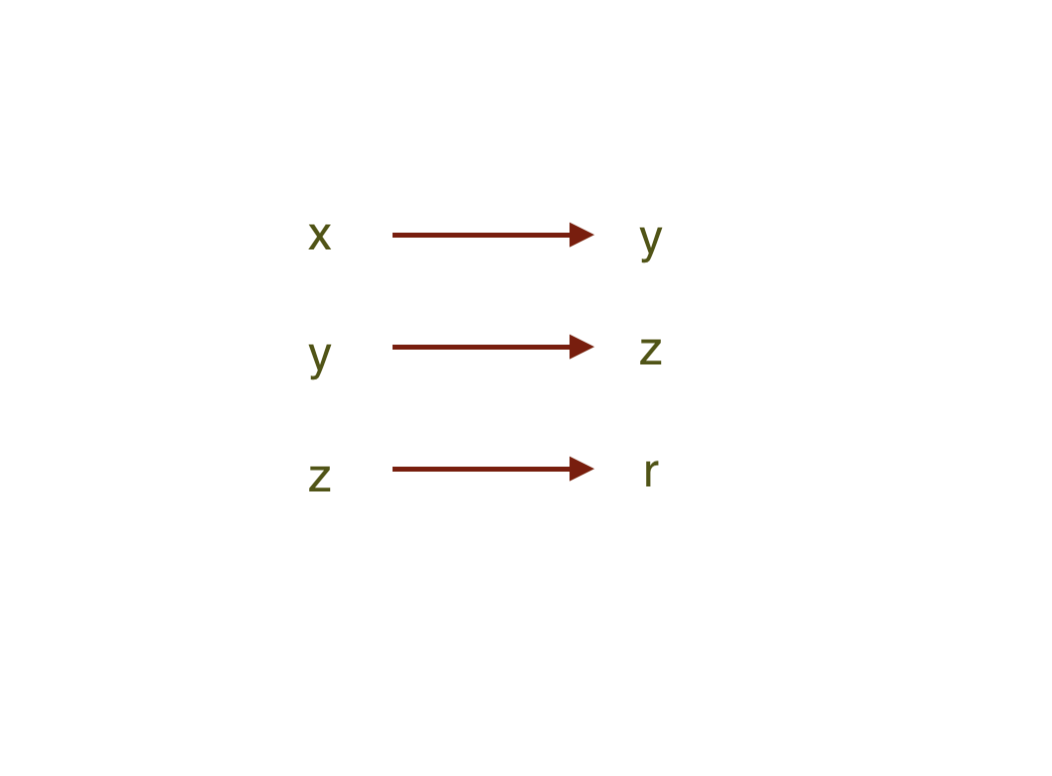




Initial
request
response
body
html
管線:函式的組合




Initial
request
response
body
html

x
y
z
r


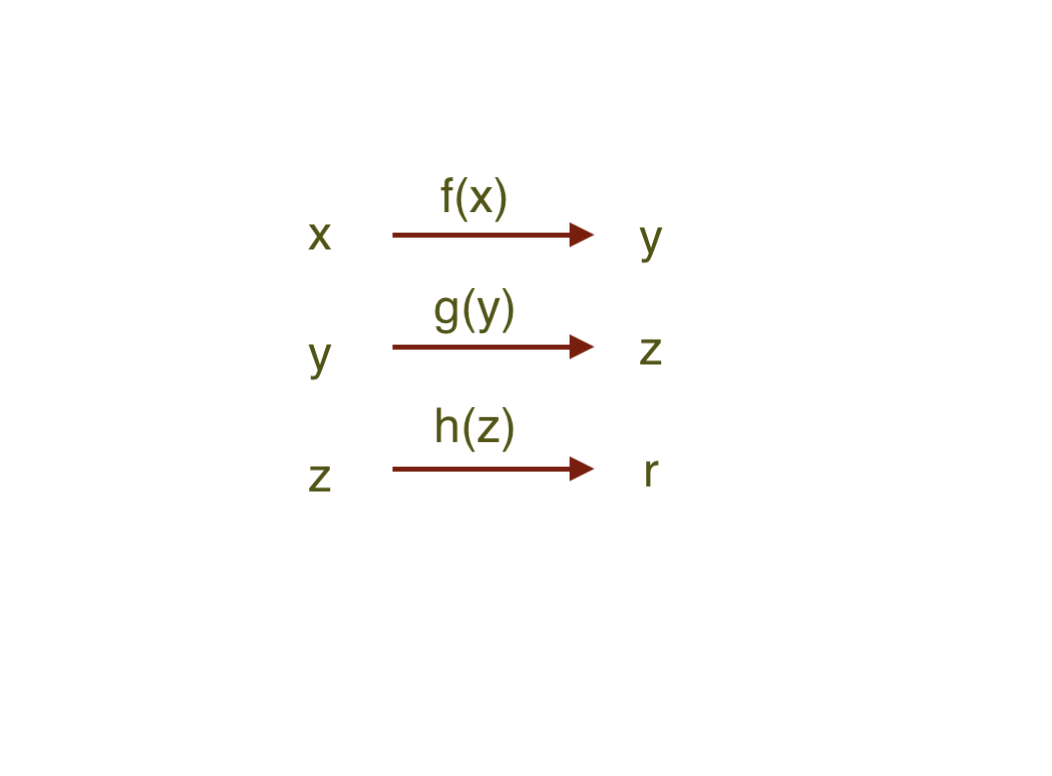
管線:函式的組合

x
y
z
r


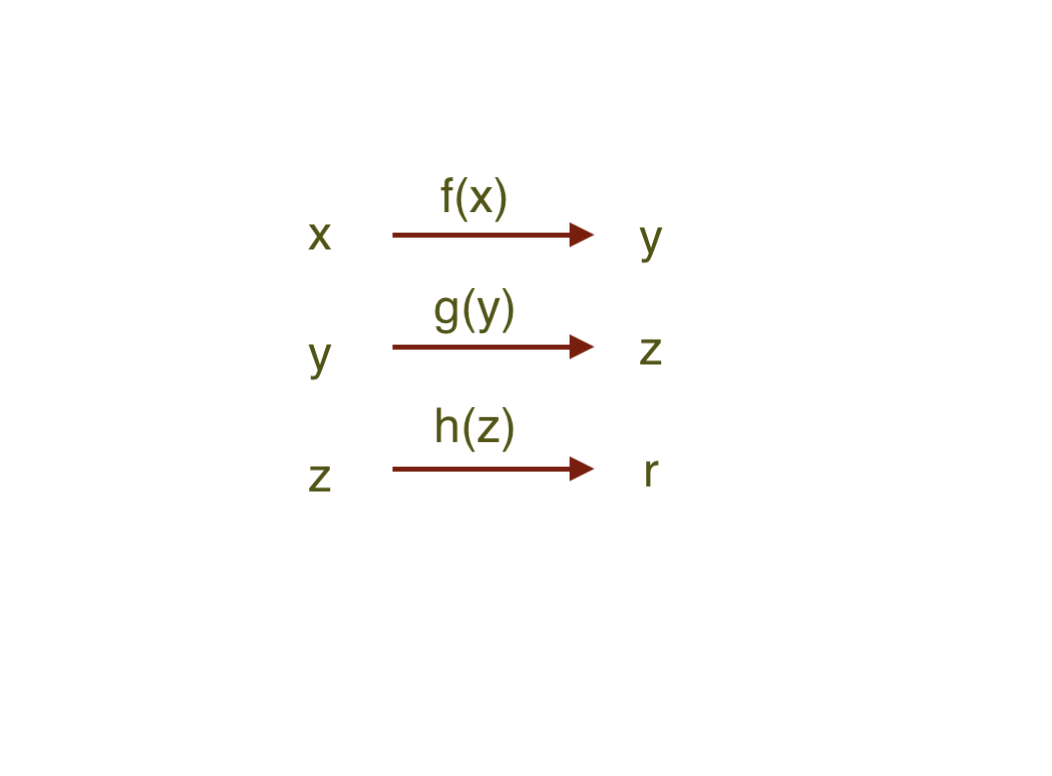
r = h( g ( f ( x ) ) )
管線:函式的組合

x
r


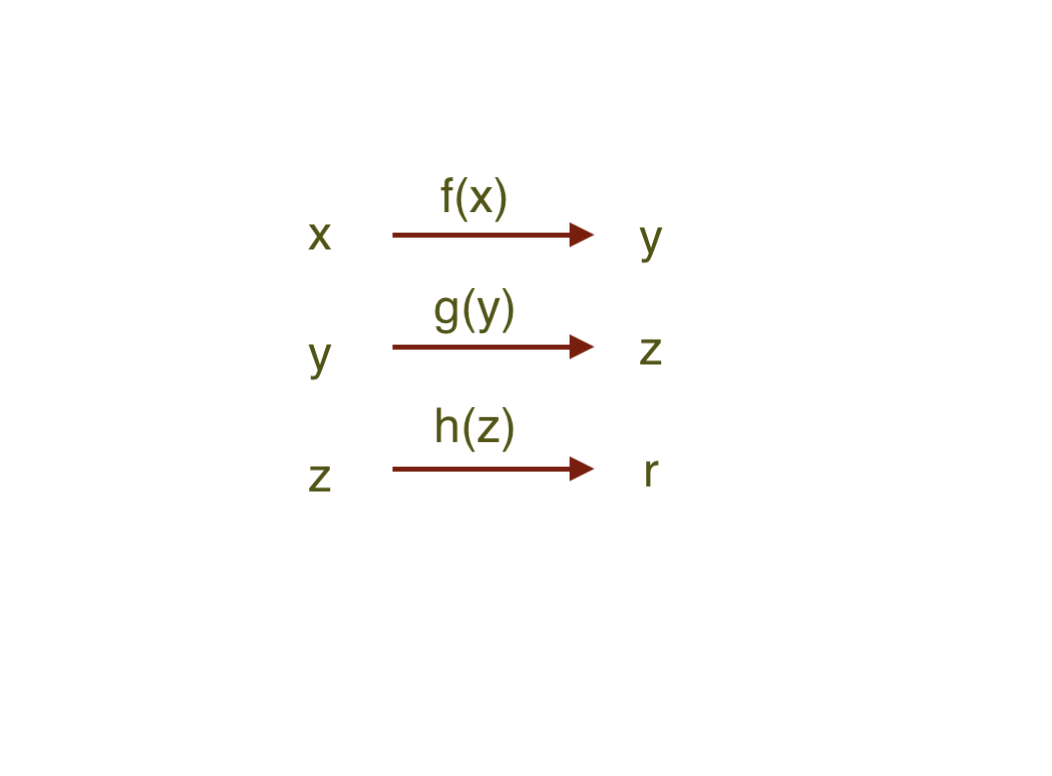
r = h( g ( f ( x ) ) )
r = compose( h, g , f ) (x)
r = compose( h, g , f ) (x)
f
g
h
管線:函式的組合
r = compose( h, g , f ) (x)
r = compose( h, g , f ) (x)



x
r
f
g
h
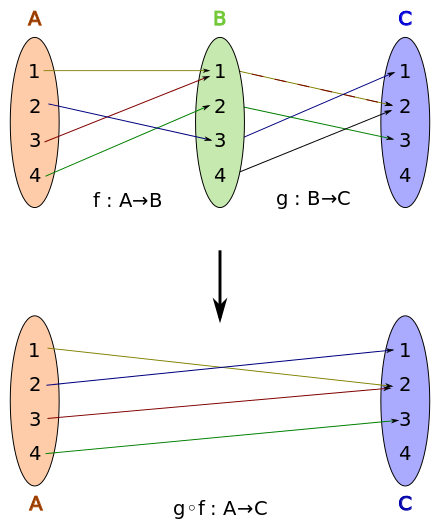
管線:函式的組合
r = h( g ( f ( x ) ) )
r = compose( h, g , f ) (x)
r = compose( h, g , f ) (x)



x
r
f
g
h
# 通用語法
request = generate_request()
response = get_response(request)
body = parse_body(response, "html")
html = render(body)html = compose(
render,
parse_body(:"html"),
get_response,
generate_request
)()
管線:函式的組合
r = pipe( f, g , h ) (x)
r = compose( h, g , f ) (x)



x
r
f
g
h
# 通用語法
request = generate_request()
response = get_response(request)
body = parse_body(response, "html")
html = render(body)html = compose(
render,
parse_body(:"html"),
get_response,
generate_request
)()
html = pipe(
generate_request,
get_response,
parse_body(:"html"),
render,
)()
let result = pipe(
x => x + 1,
x => x * 10,
x => x / 2
)(2)


x
r
f
g
h
所以 result 是...?
回到緣起:你 pipe 了嗎?
# Elixir 語法
html =
generate_request()
|> get_response()
|> parse_body(:html)
|> render()html = pipe(
generate_request
get_response,
parse_body(:"html"),
render,
)()
管線:Pipe的實作
// Let's give a try
function pipe() {
...
}input: f, g, h,...?
output: result
別忘了還有 initial value: x
let result = pipe(
x => x + 1,
x => x * 10,
x => x / 2
)(2)箭頭函式
lambda ...
const add = (a,b) => a + b
// 等於
const add = function(a,b) {
return a + b
}箭頭函式
lambda ...
const lambda = (param1,param2,...) => expression
// 或是
const lambda = (param1,param2,...) => {
statement1
statement2
return finalResult
}Curry ?
你可以只透過部分的參數呼叫一個 function,它會回傳一個 function 去處理剩下的參數。
你可以一次性的呼叫 curry function,也可以每次只傳遞每次只傳遞一個參數。


Show me the code
var add = function(x) {
return function(y) {
return x + y;
};
};
var increment = add(1);
var addTen = add(10);
increment(2); // 3
addTen(2); // 12
var result = add(1)(2); // 3你可以只透過部分的參數呼叫一個 function,它會回傳一個 function 去處理剩下的參數。
你可以一次性的呼叫 curry function,也可以每次只傳遞每次只傳遞一個參數。
管線:Pipe的實作
function pipe(f,g,h) {
return function(x){
return h(g(f(x)))
}
}const pipe = (f,g,h) => (x) => h(g(f(x)))能再更通用 (general) 一點嗎?
管線:Pipe的實作
const pipe =
(...fns) =>
(x) =>
fns.reduce((acc,fn)=>fn(acc),x)There you are
驗證一組社會安全碼是否合法
// Let's give a try
function isValidSsn() {
...
}SSN 是美國聯邦政府發給本國公民、永久居民、臨時居民的一組 9 位數字號碼
[social security number](美國身分證號)

ref - Functional Programming in JavaScript ( Luis Atencio )
驗證一組社會安全碼是否合法
[social security number](美國身分證號)

'123-12-1234' -> true
' 123-12-1234 ' -> true
首、末可能有空白
驗證一組社會安全碼是否合法
[social security number](美國身分證號)
'123-12-1234' -> true
' 123-12-1234 ' -> true
首、末可能有空白
已知工具包


function isValidSsn(str) {
const validLength = 9;
const trimmedString = str.replace(/^\s*|\s*$/g, "");
const normalizedString = trimmedString.replace(/\-/g, "");
if (normalizedString.length === validLength) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}cleanInput
isValidSsn
checkLengthSsn
cleanInput
isValidSsn
trim
normalize
checkLengthSsn
validLength -> 9
ref - Functional Programming in JavaScript ( Luis Atencio )
Top Down 拆解任務
const pipe = (fn1, fn2) => (x) => fn2(fn1(x));
const trim = (str) => str.replace(/^\s*|\s*$/g, "");
const normalize = (str) => str.replace(/\-/g, "");
const cleanInput = pipe(trim, normalize);
const checkValidLength = (validLength) => (str) => str.length === validLength;
const checkLengthSsn = checkValidLength(9);
const isValidSsn = pipe(cleanInput, checkLengthSsn);
isValidSsn funtional programming
cleanInput
isValidSsn
trim
normalize
checkLengthSsn
validLength -> 9
module3
module1
module5
module6
module2
module4
Top Down 拆解任務
組
合
功
能
拆
解
任
務
你已見過的FP
Input:[1,2,3,4,5] 陣列
Output: '135' 字串
let input = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
let isOdd = x => x % 2 !== 0
let toString = x => x.toString()
let accumulator = (a, b)=> a + b
let output = input.filter(isOdd)
.map(toString)
.reduce(accumulator)
一段 SQL
SELECT Customer, SUM(Price) FROM orders
GROUP BY Customer;只需關心要從哪裡、拿到什麼資料 (What)
不在乎資料庫是怎麼取得資料 (How)
類 SQL, 函數即數據
SELECT p.firstname, p.birthYear From Person p
WHERE p.birthYear > 1900 and p.country IS NOT 'US'
GROUP BY p.firstname, p.birthYearLodash/FP
_.mixin({ 'select': _.pluck,
'from': _.chain,
'where': _.filter,
'groupBy': _.sortByOrder
})
_.from(persons)
.where(p => p.birthYear > 1900 && p.address.country !== 'US')
.groupBy(['firstname', 'birthYear'])
.select('firstname', 'birthYear')
.value()ref - Functional Programming in JavaScript ( Luis Atencio )
製造水管的條件是什麼?
function pipe(f,g,h) {
return function(x){
return h(g(f(x)))
}
}const pipe = (f,g,h) => (x) => h(g(f(x)))


f
g
h
製造水管的條件是什麼?
function pipe(f,g,h) {
return function(x){
return h(g(f(x)))
}
}const pipe = (f,g,h) => (x) => h(g(f(x)))


f
g
h
function 可被作為參數傳入
製造水管的條件是什麼?
function pipe(f,g,h) {
return function(x){
return h(g(f(x)))
}
}const pipe = (f,g,h) => (x) => h(g(f(x)))


f
g
h
function 可為結果傳出
製造水管的條件是什麼?
function pipe(f,g,h) {
return function(x){
return h(g(f(x)))
}
}const pipe = (f,g,h) => (x) => h(g(f(x)))


f
g
h
function 可被儲存為變數
製造水管的條件是什麼?
function 可被儲存為變數
function 可為結果傳出
function 可被作為參數傳入
一等公民:function
如同其他的值(e.g number, string, boolean,...)
如何不讓你的水管漏水?



純函數

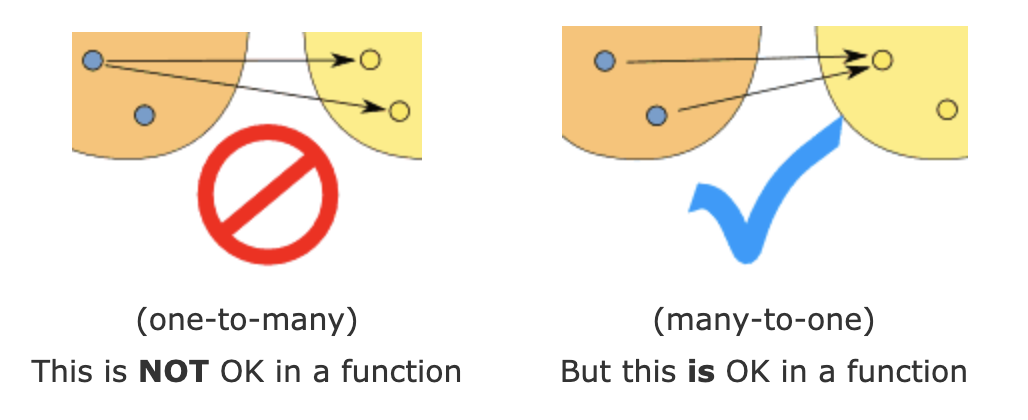
f(2) = 7 or 9
f(2) = 0
f(3) = 0
f(4) = 0
像數學一樣,想確保...
當同一個 input 傳入時,永遠回傳相同的 output
純函數
function 函式 要更接近數學上的 函數
function 職責,更明確、單一
不再只是 predure ,僅處理完一段任務,不一定回傳
function 必須回傳一個值
當同一個 input 傳入時,永遠回傳相同的 output
Immutable
const johnney = { firstName:'Johnney', lastName:'Feng', height:175 , weight:67 }
calculateBMI(johnney) // return 21.88
do something later ...
calculateBMI(johnney) // return 21.88
function calculateBMI (person) {
const heightInMeter = person.height/100
const BMI = person.weight / (heightInMeter*heightInMeter)
return BMI
}我們想要一種保證!
當同一個 input 傳入時,永遠回傳相同的 output
使用 johnney的人
不可以改變 johnney
純函數也不應該改變外面的狀態
引用透明
let discount = 0.8
function calculatePrice (amount, price) {
return amount*price*discount
}
calculatePrice(5,1000) // 4000
discount = 0.7
calculatePrice(5,1000) // 3500我們想要一種保證!
當同一個 input 傳入時,永遠回傳相同的 output
function calculatePrice (amount, price, discount) {
return amount*price*discount
}
calculatePrice(5,1000,0.8) // 4000
calculatePrice(5,1000,0.7) // 3500
// do something later
calculatePrice(5,1000,0.8) // 4000
calculatePrice(5,1000,0.7) // 3500函數的output只依賴input,引用透明就沒有副作用,也無需指定前後運行順序
F P 帶來什麼好處

const doubleMap = numbers => {
const doubled = [];
for (let i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++) {
doubled.push(numbers[i] * 2);
}
return doubled;
};const doubleMap = numbers => numbers.map(n => n * 2);
console.log(doubleMap([2, 3, 4])); // [4, 6, 8]var string = "hi there , I'm a web developer";
var removeSpace = "";
for (var i = 0; i < i.string.length; i++) {
if (string[i] === " ") removeSpace += "-";
else removeSpace += string[i];
}const removeSpaces = (string) => {
var removeSpace = "";
for (var i = 0; i < i.string.length; i++) {
if (string[i] === " ") removeSpace += "-";
else removeSpace += string[i];
}
return removeSpace;
};
const string = "Hi there, I'm a web developer ";
const result = removeSpaces(string);把底層實作裝入 function,也賦予了可讀性
換個角度想,我們是先基於要完成什麼任務,再去實作function
Imperative vs Declarative
const container = document.getElementById(‘container’);
const btn = document.createElement(‘button’);
btn.className = ‘btn red’;
btn.onclick = function(event) {
if (this.classList.contains(‘red’)) {
this.classList.remove(‘red’);
this.classList.add(‘blue’);
} else {
this.classList.remove(‘blue’);
this.classList.add(‘red’);
}
};
container.appendChild(btn);const Container = (props) => {
const [color, setColor] = useState('red')
const handleChange = () => {
setColor(prevColor => (
prevColor === 'red'? 'blue' : 'red')
)
}
return (
<div>
<button
className=`btn ${color}`
onClick={handleChange}
>
點我
</button>
</div>
)
}重視當下的值
及
接下來要怎麼操縱值
重視流程、結果
細節已成黑箱
放在 function 裡
How
What
Imperative vs Declarative
流程控制?
關注每個值當下的狀態、要控制這個值變成什麼
ref - Functional Programming in JavaScript ( Luis Atencio )
var loop = optC();
while(loop){
var condition = optA();
if(condition){
optB1();
} else {
optB2();
}
}
optD();optA
optB1
optB2
optC
optD
是
否
透過大量的 statement 來進行流程控管
透過 if else 操縱分支
透過 while 控制執行次數
一步一步命令電腦怎麼做
一連串的 statement 所組成的 procedure
流程控制?
常用的流程控制如 if/else, for loop, try/catch
let message = "";
if( age>=18 ){
message = "Let's drink and get drunk!"
} else {
message = "Go home, Kid!"
}
for ( let i = 0; i <= message.length; i++ ){
message = message + "!"
}message 在不同行、不同時間
結果可能不一樣
statement 之下
statement... 容易造成 stateful
// y = f(x) is pure function
1 + 1
f(2)
// do other thing...
1 + 1
f(2)
// do more things
1 + 1
f(2)expression 之下
在不同行、不同時間的結果仍一樣
function greeting(person){
return "Hi " + person
}
greeting('Ken')
// "Hi Ken"
greeting('Ken')
// "Hi Ken"
greeting('John')
// "Hi John"
greeting('Ken')
// "Hi Ken"Expression
o 算術: +, -, *, /
o 邏輯:&&, ||, !
o 比較:>=, <=, !=
...
運算式是任何一段可以取得一個值的程式碼 by MDN
Statement
o if else
o switch case
o for loop / while
o throw
o try catch
o var, let ,const
...
把細部操作丟進function 實作
opA().opB().opC().opD()


optA
optB
optC
ref - Functional Programming in JavaScript ( Luis Atencio )
optC
optD
optA
optB
執行 function
將一個一個任務裝進 function
每個 function 獨立運作,再把 function 組裝起來
使用的人不需要知道funtion 的實作,只要確信 相同 input 會得到對應 output 即可
數據、資料直接流過組合起來的 funtion
高階的抽象 使 分支、迭代,減少或消除
重流程、操作;輕數據
不是去關注 -> 每個值當下的狀態、要控制這個值變成什麼
而是去關注 -> 從比較高層次俯瞰整個流程要做什麼,
才能產出最終結果!
把每個任務封裝成 function
ref - Functional Programming in JavaScript ( Luis Atencio )
optC
optD
optA
optB
優點是
o More Readable, understandable
o 容易執行單元測試
o 因為要成為純函數,也必須引用透明
o 容易除錯,因為不斷將任務拆細,最小化 function
o 可執行平行運算
F P 帶來什麼壞處

- 寫 pure function 簡單,但要完全整併進系統,應用不簡單
-
Pure function 跟 I/O 操作,真 der 不好搭
-
因為不能竄改現有 data,你要先複製再修改 (immutable)
- 為了實現 immutable 及使用遞迴,有可能導致潛在效能問題(如 記憶體使用、速度...)
- 進階的數學術語 (如:monad, monoid, functor, ...) 讓 FP 看起來 hen 可怕
- 對大多數人而言,用遞迴思考感覺比較不自然
大師說過...

大師說過...
OOP v.s. FP
const ken = new Person('ken','chen',170,77)
calculateBMI(ken) // return 26.6
ken.run()
calculateBMI(ken) // return ???
const johnney = { firstName:'Johnney', lastName:'Feng', height:175 , weight:67 }
calculateBMI(johnney) // return 21.88
do something later ...
calculateBMI(johnney) // return 21.88憑藉著 Immutable 的保證
OOP v.s. FP
let ken = new Person('Ken','Chen','0987543345','Engineer')
ken.fullname // 'Ken Chen'
let getFullName = (person) => [person.firstname, person.lastname].join('')
getFullName(ken) // 'Ken Chen'
操控 Object,在 class contructor 之間定義屬性、方法
單純只將 Object 作為一種值, 透過函式運算,將值取出
OOP v.s. FP
ref - The Difference between Functional Programming and Object-Oriented Programming
現實是殘酷的...
你說不用 try catch ,如何預防程式錯誤?
你需要將不安全的值,包裹起來
Keyword: Functor, Monad
待續...
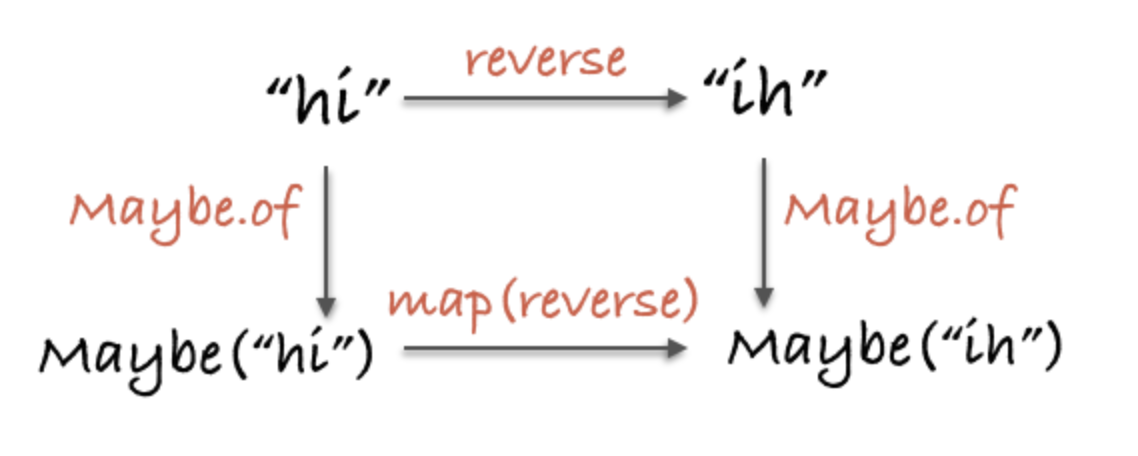

statement
現實是殘酷的...
待續...
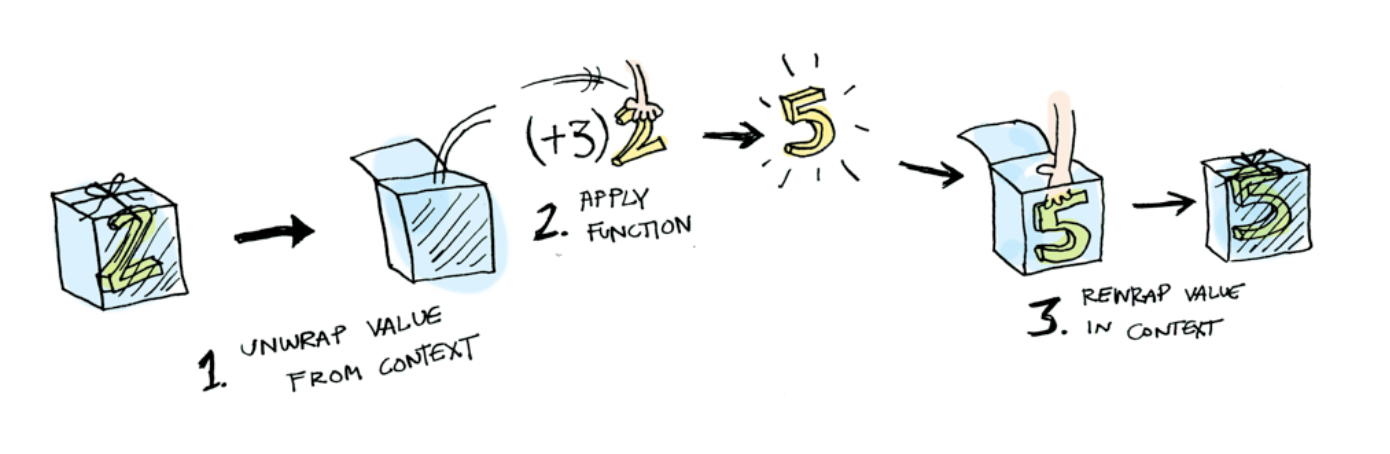
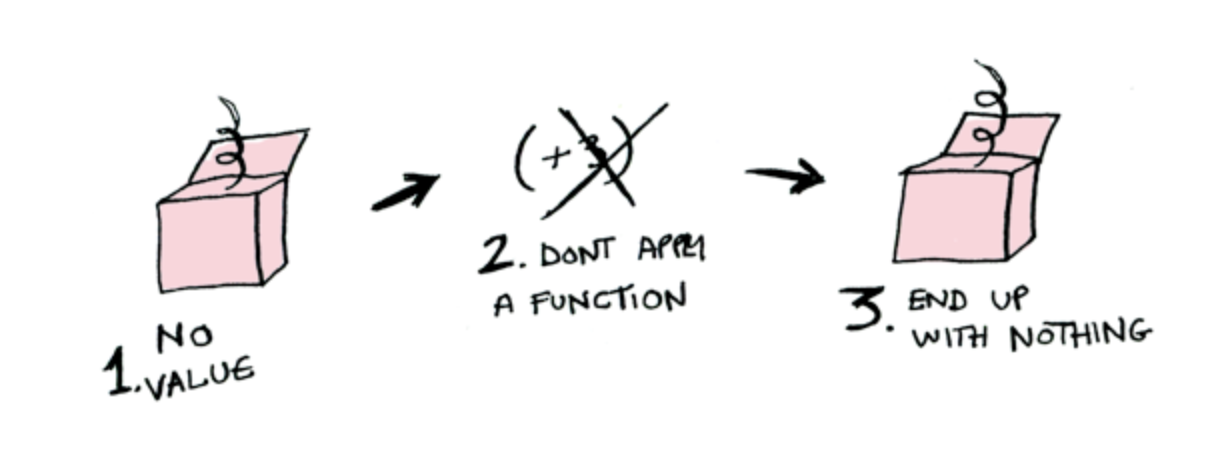
現實是殘酷的...
待續...
class Wrapper {
constructor(value){
this._value = value;
}
static of(a){
return new Wrapper(a)
}
map(f) {
return f(this._value)
}
}

現實是殘酷的...
待續...
class Maybe {
static of(a){
return new Just(a)
}
static just(a){
return new Just(a)
}
static nothing(){
return new Nothing()
}
static fromNullable(a){
return a != null ? just(a) : nothing()
} ...
}
class Just extends Maybe {
...
map(f){
return of(f(this.value))
}
}
class Nothing extends Maybe {
...
map(f){
return this
}
}
const something = Maybe.fromNullable(value).map(f)
Recap
o Pure function (也促進 fn 的單一職責)
o Immutable
o 引用透明
o 隔離 side effect
o 重視任務拆解 、串接的流程(往下拆更多fn)
o 輕數據的狀態及操作
and.....
你是有退路的
大多數的程式語言,都可以混用 FP, OOP 兩種風格
參考讀物
- Mostly-adequate-guide to Functional Programming 及其 中文
- Functional Programming in JavaScript ( Luis Atencio ) 簡中譯書
- Functional Programming in JS ( 2020 IT 鐵人邦 )