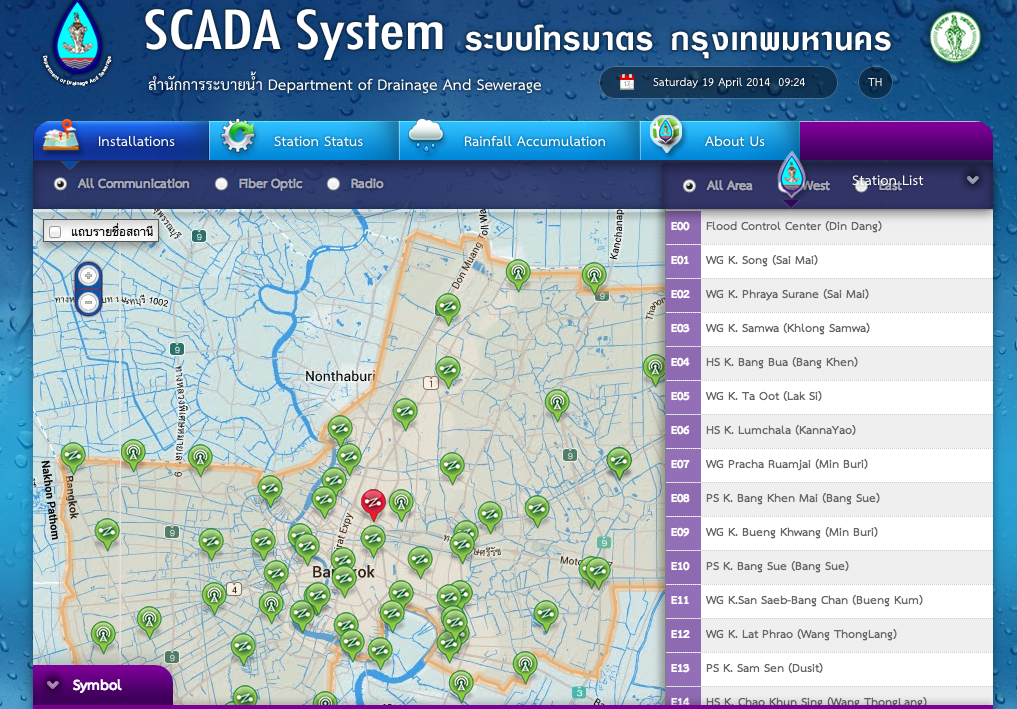
SCADA
Supervisory
Control and Data Acquisition
Problem statement
There are many systems used for decades, these are collectively called Distributed Control Systems (DCS). Systems are effective only in a closed area like a factory complex. There is also example like nuclear fusion facilities where the operations are remote controlled due to safety considerations.
Main concept

A large scale control system
Centralized systems
Open-loop control systems

Hardware Architecture
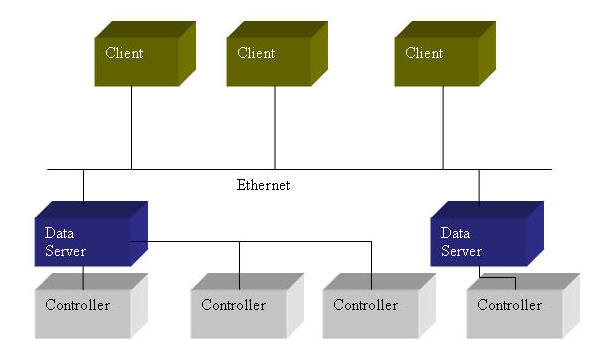
Supervisory
System
responsible for gathering data and sending commands to the
process with the field equipment .
Remote Terminal Units
responsible for
converting electrical signals to digital data and send to the supervisory
system.

Programmable Logic Controller
PLCs is connected to the data servers either directly or via networks

Software Architecture
The products are multi-tasking and are based upon a
real- time database (RTDB) located in one or more servers to handle particular tasks.

Communication Architecture
Internal Communication
Server-client and server-server communication is in general on publish-subscribe and event-driven basis and uses a TCP/IP protocol.
Access to Devices
The data servers poll the controllers at a user define
polling rate. The
controllers pass the requested parameters to the data servers.
Interface Architecture
The provision of OPC client functionality for SCADA to access devices in an open and standard manner is developing
Scalability Architecture
Scalability is understood as the possibility to extend the SCADA based control system by adding more process variables, more specialized servers or more clients
Redundancy Architecture
The products often have built in software redundancy at a server level, which is normally transparent to the user
Service Provided
A telemetry systemconnect PLCs and RTUs with control centers, data
warehouses, and the enterprise
A data acquisition server
a software service whichuses industrial protocols to connect software
services with field devices such as RTUs and PLCs
A human–machine interface or HMI
it is the equipment or device which presents processed data to a human operator




A Historian
a software service, which accumulates time-stamped data, Boolean events, and Boolean alarms in a database, can be queried or used to populate graphic trends in the HMI
A supervisory (computer) system
gathering (acquiring) data on the process and sending commands (control) to the process
Strength
Derived Control functions
SCADA will allow you to issue derived controls (automated responses) to specific combinations of sensor inputs, and it will also give you the freedom to design the exact response you need.
Reliability
the costs of system failure are extremely high. A failed part can be replaced without interrupting the process. A failing part can be quickly identified and its functionality automatically taken over by backup hardware.
Backup master support
Support several backup masters, located at different sites.
If main SCADA master fails, a backup master at a different site can resume.
Support for a variety of protocols and devices
Support a variety of open-source protocols
to prevent system becoming obsolete even if vendor goes out of business.
Automatic pager and email alarm notification
- SCADA master will automatically send a page or email directly to on-call technicians if there is a problem at your site.
Many data presentation options
- Display alarms in a language you can understand.
- It also give you a complete description of every alarm, and how you can correct the problem
Weakness
Open
system
- Open systems risk
with real and cyberspace attacks by terrorists.
- Unauthorized
access to the control the software
- The control
protocol lacks any form of cryptographic security. Meaning that they are
allowing an attacker to control a SCADA device by sending commands over a
network.
Application
specific
Most SCADA systems and each component is made to its specific application.
Wireless sensor networking
The current SCADA systems are not enabled to be integrated with wireless networking systems.
Extensible
Current SCADA systems are found lacking is extensibility. There is limitation of RTUs ability to take proactive measures to prevent accidents.
Predecessor Technology
GENERATION I : “Monolithic”
No network
Use mainframe computers > independent systems
Redundancy > since a back-up mainframe system was connected at the bus level
GENERATION II : “Distributed”
LAN > shared information in real time
The network protocols used were still mostly proprietary

GENERATION III : “Networked”
WAN
Open system (Open standards and protocols)
Internet Protocol (IP) is used for communication between the master station and communications equipment

Main Customer and Market
Power industry
monitor the power flow, power line voltage, circuit breaker status, and electrical processes
Manufacturing companies
monitor inventory & reduces inventory costs
Food Production
control temperature & movement of liquid and solid ingredients and mixtures
Electric and Gas Utilities
control the movement of electricity and gas
Competing Technologies
1. Distributed Control Systems (DCS)
Data Distribution Service (DDS) is a data-centric publish/subscribe for real-time communications.

Similarity
System used to control and monitor
Difference
DCS is implemented in closed-loop control.
Doesn't cover large area (no third party communication)
2. Building Automation System (BAS)
Building Automation System (BAS) is designed to monitor and control the mechanical, security, fire and flood safety, lighting (especially emergency lighting), HVAC and humidity control and ventilation systems in a building.
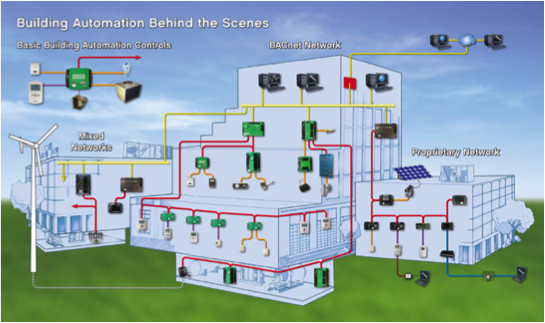
Similarity
system used to control and monitor(close relationship)
Difference
more specific in usage ex. control climate, humidity
3. Direct Digital Control (DDC)
Automatic control of a condition or process by a computer. Data bus is used for communication.

Similarity
system used to control and monitor
Difference
used in small area because of using LAN
Member
SECTION 1
Sukritta Harnmetta 5488034
Nattha Apiraknanchai 5488060
Suttichai Kitoanon 5488063
Krisanat Khlayprasit 5488257
Yanin Rotprasitporn 5488262
THANK YOU