JSP
Architecture, Building Blocks.
Kush Asrani , Krsna Chandarana, Manisha Chauhan, Soham Das
Index
Server
specialized computer system or software application designed to manage and provide resources, services, or data to other computers, known as clients, over a network.
- Handles requests from clients (e.g., web browsers).
- Processes data and sends responses back to clients.

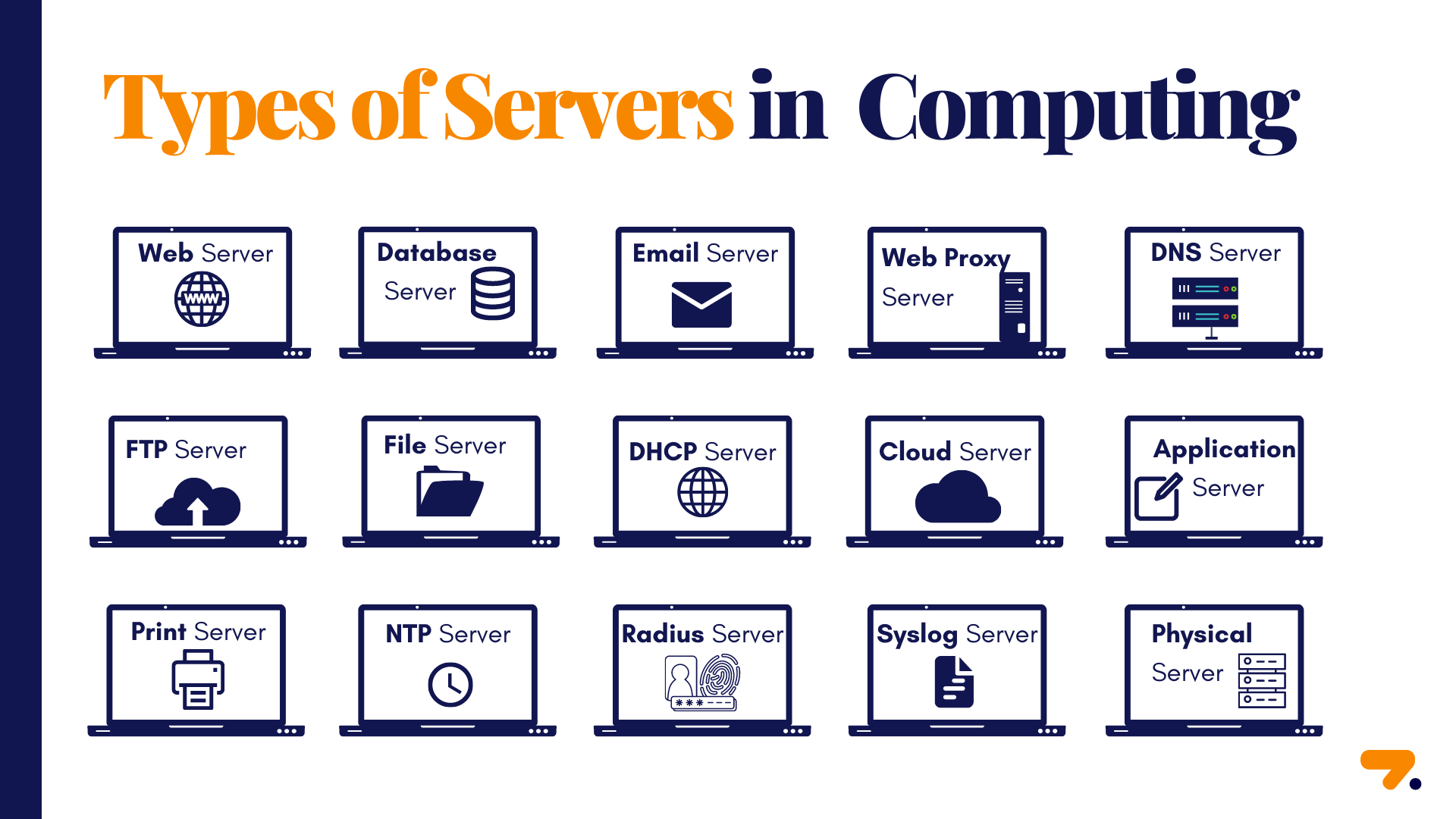

types of server
- Web Server
- Application Server
A JSP application typically runs on an application server, which processes JSP files and generates dynamic content.
- Serves static content (HTML, images) and forwards requests for dynamic content to application servers.
- Hosts websites and serves web pages to clients (browsers) via HTTP/HTTPS.
web
- Manages and executes dynamic applications, providing business logic and data processing.
- small scale
- full stack
APplication



web server
apache HTTP
different servers
small scale application server for JSP and Servlets
APACHE TOMCAT
full stack application server
JBOSS
CGI (Common Gateway Interface)
- Introduced in early 1990s (1993).
- One of the earliest technologies
- Allows web servers to execute external programs for dynamic content.
- In response to client requests, commonly for processing form data.
- Performance issues due to new processes for each request.
evolution from Cgi to jsp
Servlets
- Introduced in 1997.
- Server-side technology for handling requests efficiently and generate dynamic responses.
- Supports state management and multiple requests in a single instance.
- Unlike CGI, servlets remain in memory, allowing them to handle multiple requests more efficiently.
- They are integral to Java EE applications, acting as the backbone for server-side processing.
evolution from Cgi to jsp
JSP (JavaServer Pages)
- Released in 1999 (Java EE 1.2).
- Embeds Java code directly into HTML for dynamic content.
- Promotes separation of presentation and business logic.
- The progression from client-side to server-side processing enhances performance, scalability, and usability in web applications.
evolution from Cgi to jsp
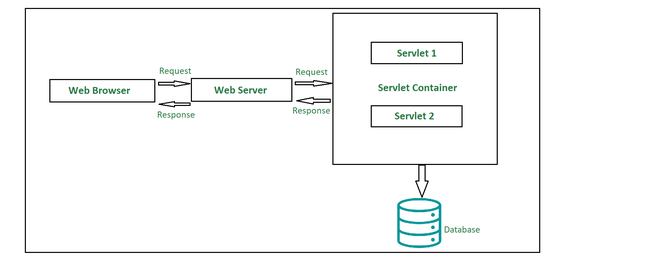
- Servlet is a java program that runs inside JVM on the web server. It is used for developing dynamic web applications.
- Servlet programs are handled by separate threads that can run concurrently more efficiently.
- Servlets provide a component-based, platform-independent method for building Web-based applications, without the performance limitations of CGI programs.
- Servlet only uses Java as programming language
servlet
-
concurrent requests to the server are handled by threads,
how servlet works
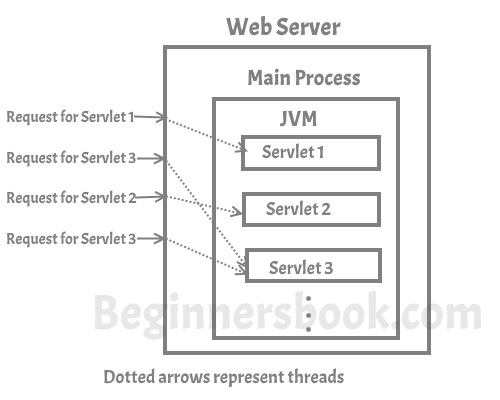
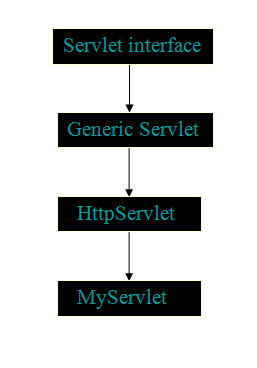
- Generic Servlet
A generic servlet is a protocol independent Servlet that should always override the service() method to handle the client request.
- HTTP Servlet
HTTP Servlet doesn’t override the service() method. Instead it overrides the doGet() method or doPost() method or both. The doGet() method is used for getting the information from server while the doPost() method is used for sending information to the server.
Types of Servlet
To create Java Servlets, we need to use Servlet API which contains all the necessary interfaces and classes. Servlet API has 2 packages namely
- javax.servlet
used for serving protocol-less requests. It contains the interfaces and classes that every servlet must implements and extends respectively.
- javax.servlet.http
used for the development of servlets that use the HTTP protocol.
servlet api
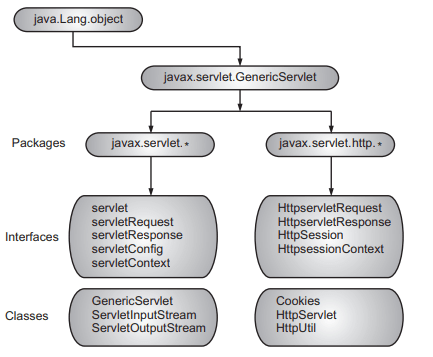
- The javax.servlet package is the core of the servlet API.
- It includes the basic servlet interface which all servlets must implement in one form or another and an abstract GenericServlet class for developing basic servlets
-
HttpServlet: A class that provides methods for handling HTTP requests (like
doGet()anddoPost()). - HttpServletRequest: An interface that provides methods to read data from the request (like parameters, headers).
- HttpServletResponse: An interface that allows the Servlet to send data back to the client.
api of servlet
1
Loading and Instantiation
2
init() method is executed.
3
service() method processes requests.
4
destroy() method cleans up resources.
Lifecycle of servlet
Text
servlet example
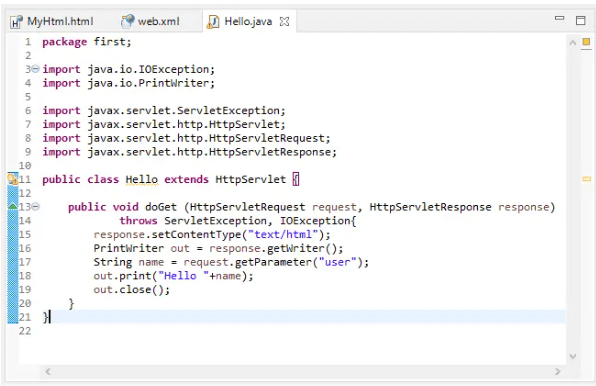
servlet example
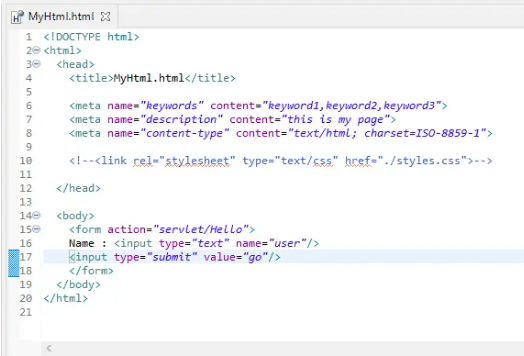
JavaServer Pages is a server-side technology used to create dynamically generated web pages based on HTML, XML or other document types.
JSP allows developers to insert Java code into their pages, simplifying the process of creating complex web applications.
Once, you have a JSP capable web-server or application server, save your files as .jsp instead of.html and access the files from your browser.
jsp
-
JSP Page
-
Servlet
-
Web Container (like Tomcat)
-
HTTP Request & Response Objects
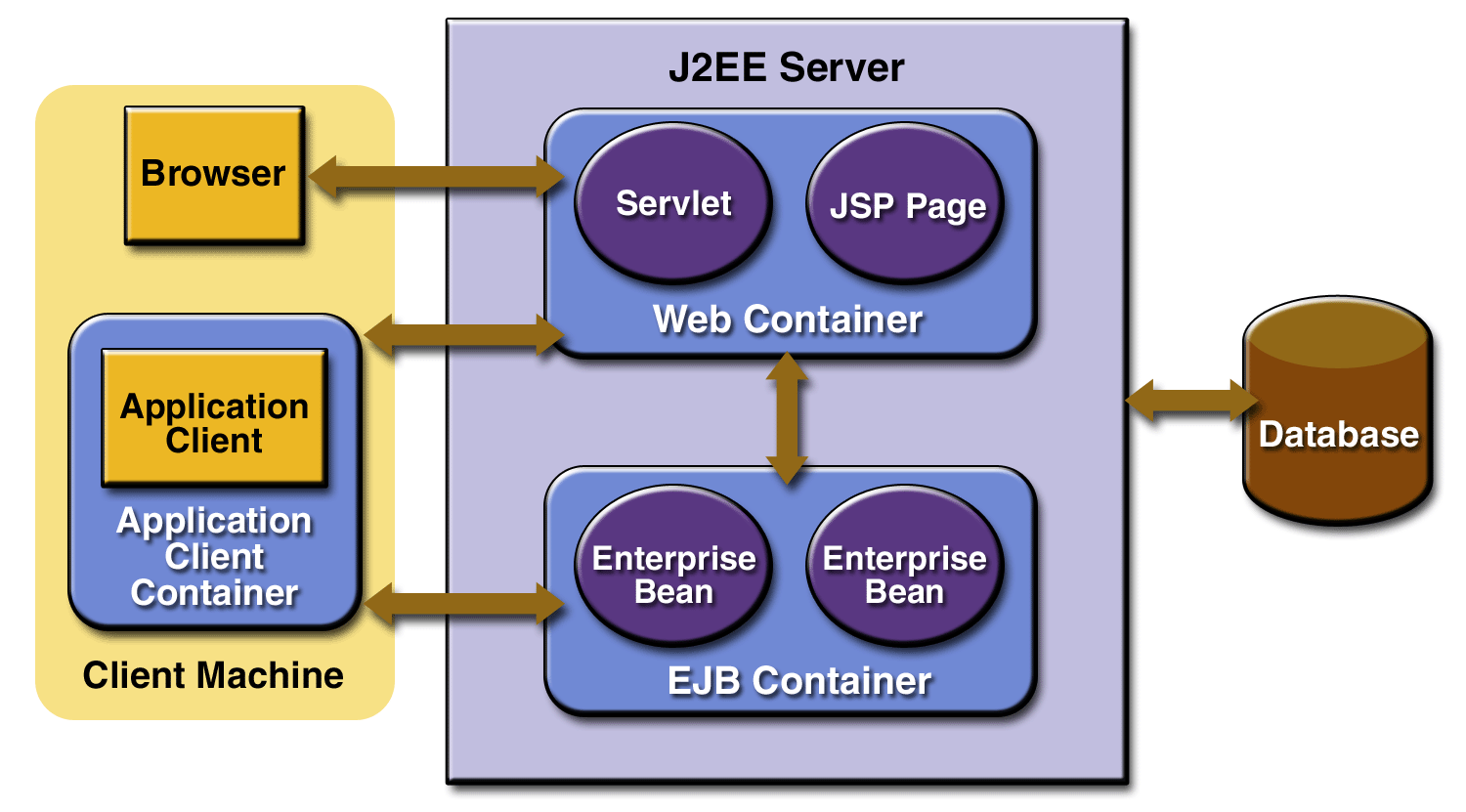
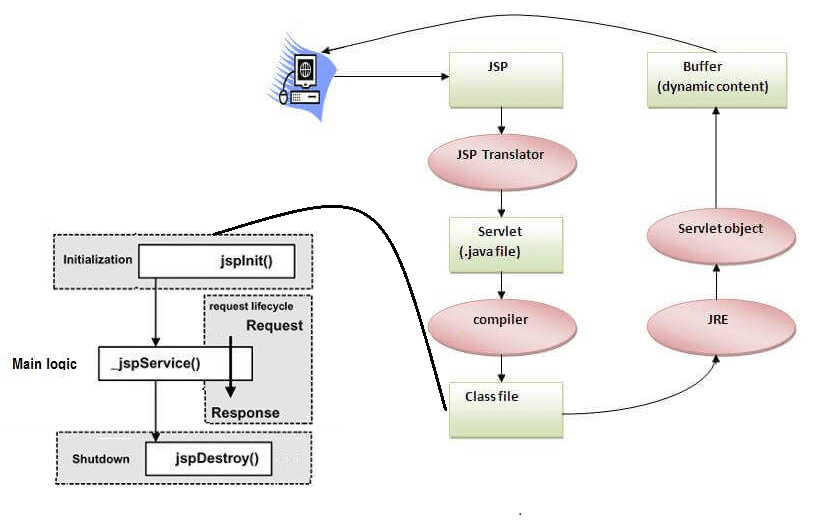
architecture of jsp
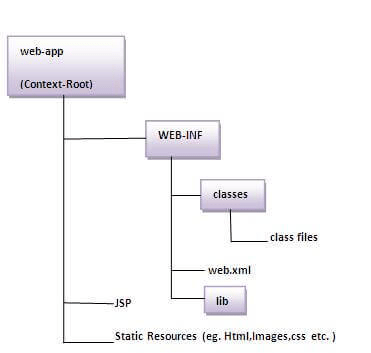
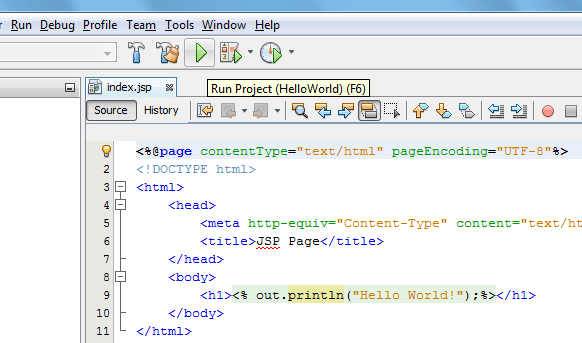
jsp page
A file containing HTML mixed with JSP tags (Java code).
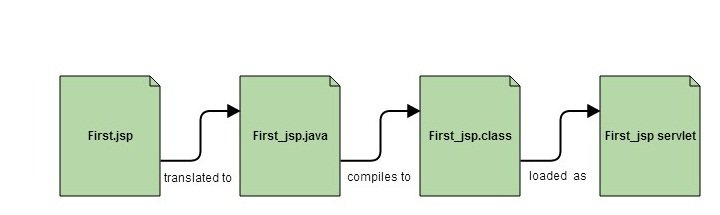
servlet
The JSP page is translated into a Servlet (Java class).
web container
Manages the lifecycle of JSPs and servlets, like translation, compilation, and execution.
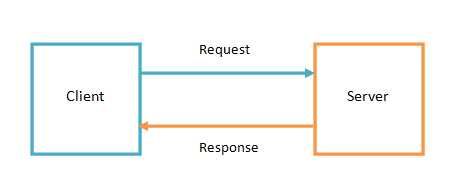
http objects
Communication between client (browser) and server, where requests are processed and responses are sent back.
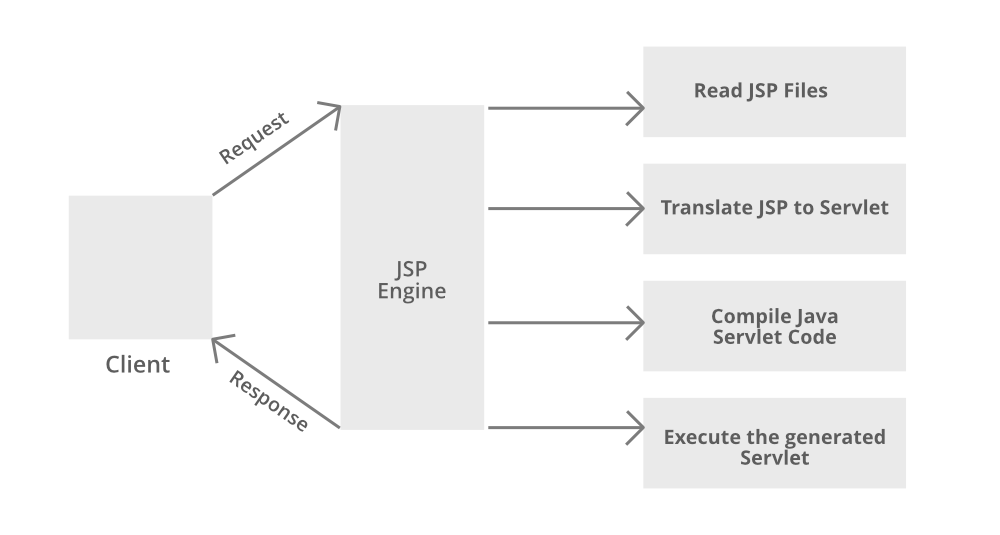
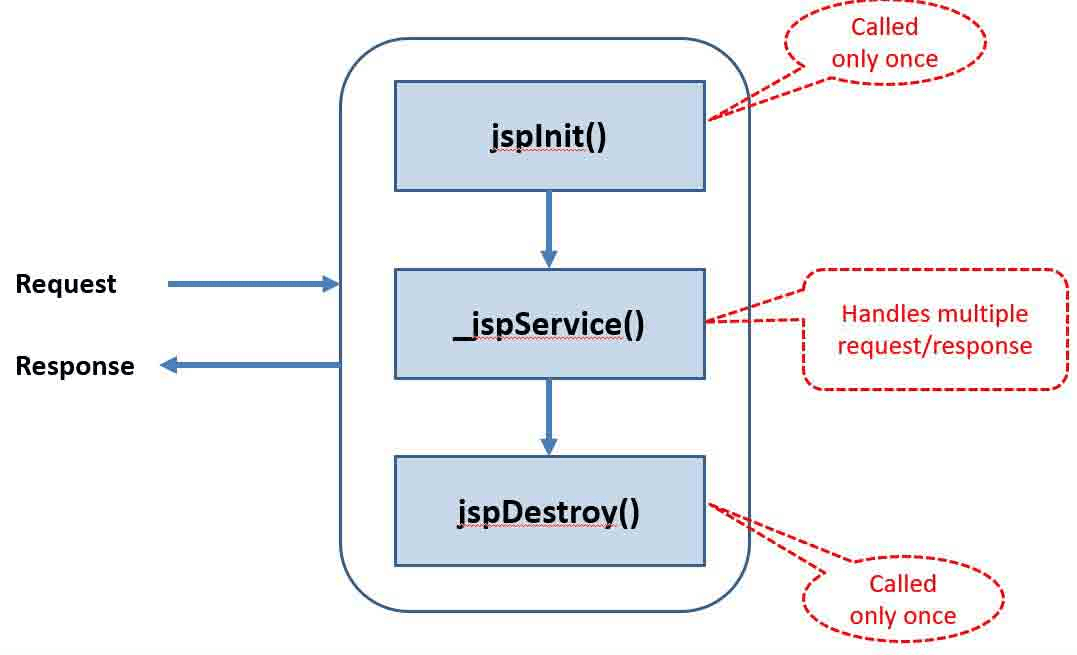
JSP lifecycle
The JSP Lifecycle consists of phases a JSP page goes through from creation to destruction.
Key Stages:
1. Translation
2. Compilation
3. Initialization
4. Request Handling
5. Destruction
1
Translation Phase
JSP is translated into a Servlet.
2
Compilation Phase
Servlet is compiled into Java bytecode.
3
Initialization Phase
This is where any resource initialization is performed.
5
Destruction Phase
This is the process where the cleanup of resources begin.
4
Resource Handling Phase
The request from the client is processed.
jsp example
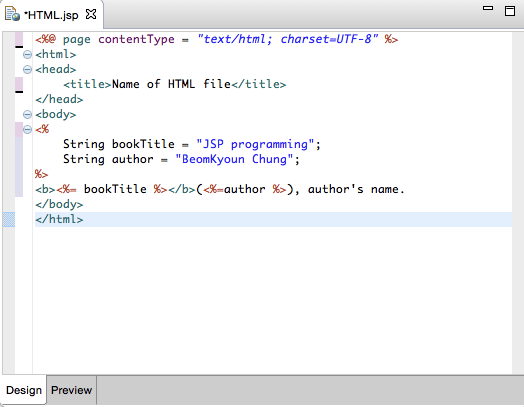
building blocks of jsp
JavaServer Pages (JSP) building blocks are the fundamental components that enable developers to create dynamic web content.
JSP has four main building blocks:
- directives that set page-wide attributes,
- declarations for variables and methods,
- scriptlets for embedding Java code,
- expressions for outputting data directly to the client.
These building blocks work together to allow developers to create dynamic, maintainable, and interactive web applications. Understanding each component is crucial for effective JSP development and ensures that applications are robust and scalable.
JSP Pages
containing HTML along with embedded Java code.
1
Directives
Provide global information about an entire JSP page
2
Scriptlets
Blocks of Java code embedded within a JSP page, enclosed in <% %> tags.
4
Comments
Help document code for developers.
3
Expressions
To output data directly to the client.
directive
Directive tags provide general information, overall properties about the JSP page to the JSP engine.
A directive tag always starts with <%@ and ends with %>.
There are 3 types of directives: page, include, and taglib.

<%@ page language=”java” %>
informs the JSP engine that Java will be used as scripting language in our JSP page
<%@ include file=”test.jsp” %>
tells the JSP engine to include the contents of another file (HTML, JSP, etc) into the current file.
declaration
Declarations declare and define variables and methods that can be used in the JSP page.
A declaration always starts with
<%! and ends with %>.

scriplet
Scriptlets are used to embed any Java code fragments in the JSP page.
For example: <% i++; %>
the value of i is incremented each time the page is requested.

expression
Expression tags are used as a shortcut to print values in the output HTML in a JSP page. Syntax is:
<%= variable %>
The variable denotes the variable value that is needed to be printed in the output HTML page.


Comments
Comments are used for documentation purposes but do not affect the output of the JSP page in any way. The syntax of a JSP comment is:
<%-- comment --%>

While both JSP and Servlets are used in Java web applications, JSP allows for easier page design by embedding Java code within HTML..
Servlets are Java classes that handle requests and responses, offering more control at the code level, but require more complex writing for web page creation.
why jsp over servlet
- Simplifies the development of dynamic web pages.
- Supports the separation of presentation and business logic.
- Easy integration with Java and other Java EE technologies.
- Tag libraries extend functionality.
advantages of jsp
apache tomcat
Apache Tomcat is a free and open-source implementation of the Jakarta Servlet, Jakarta Expression Language, and WebSocket technologies. It provides a "pure Java" HTTP web server environment in which Java code can also run. Thus it is a Java web application server, although not a full JEE application server.
It is a web container, which is a part of web server or application server that manages the execution of Servlets and JSP. It provides the environment required for components to run, including request handling, response generation, and lifecycle management.