Engineering Feature Show
2025 Q1
New in Aiken
new in Aiken
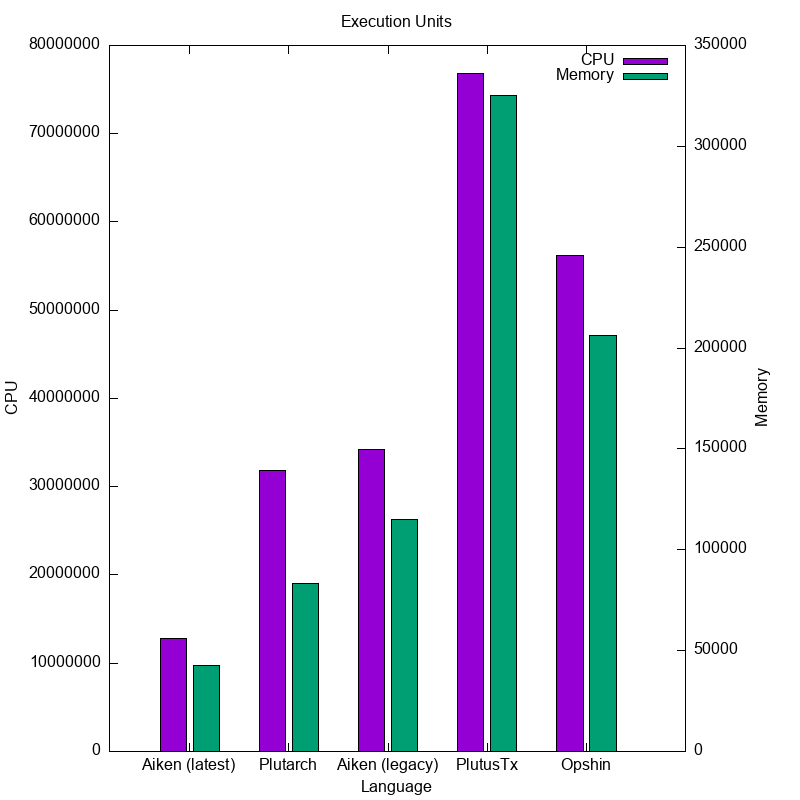
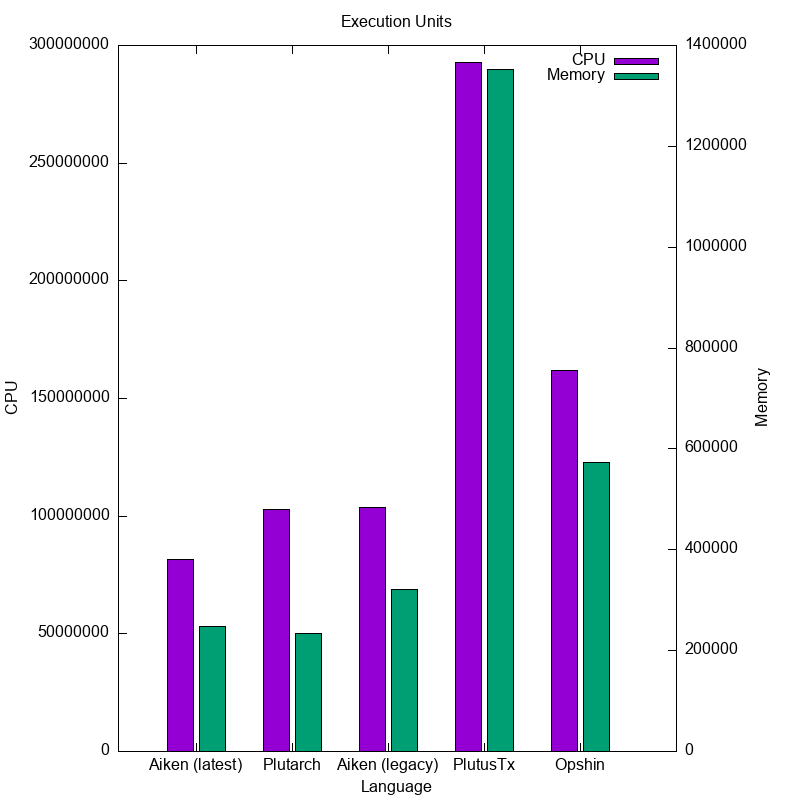
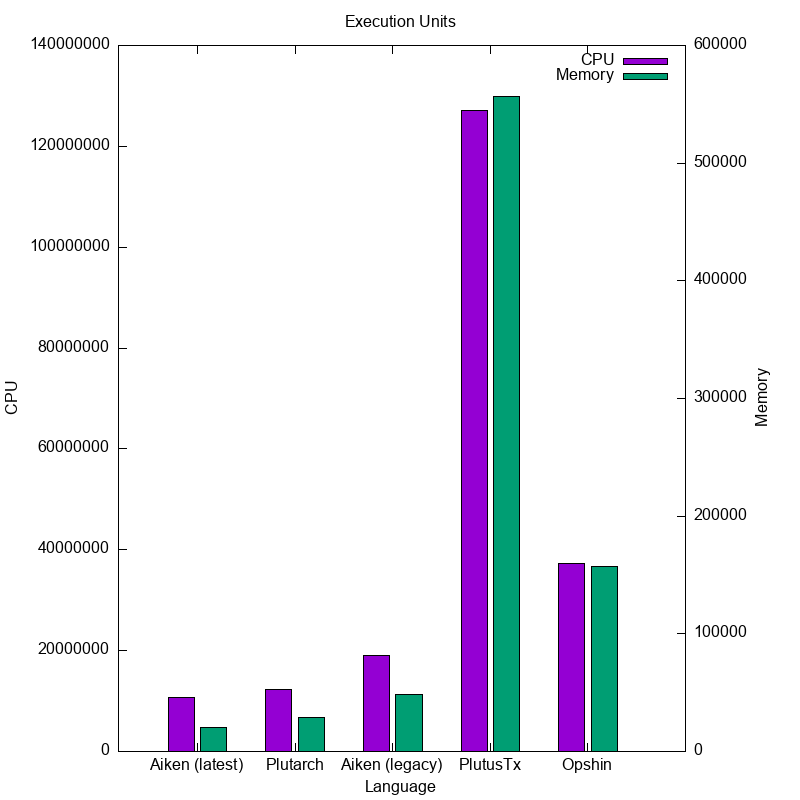
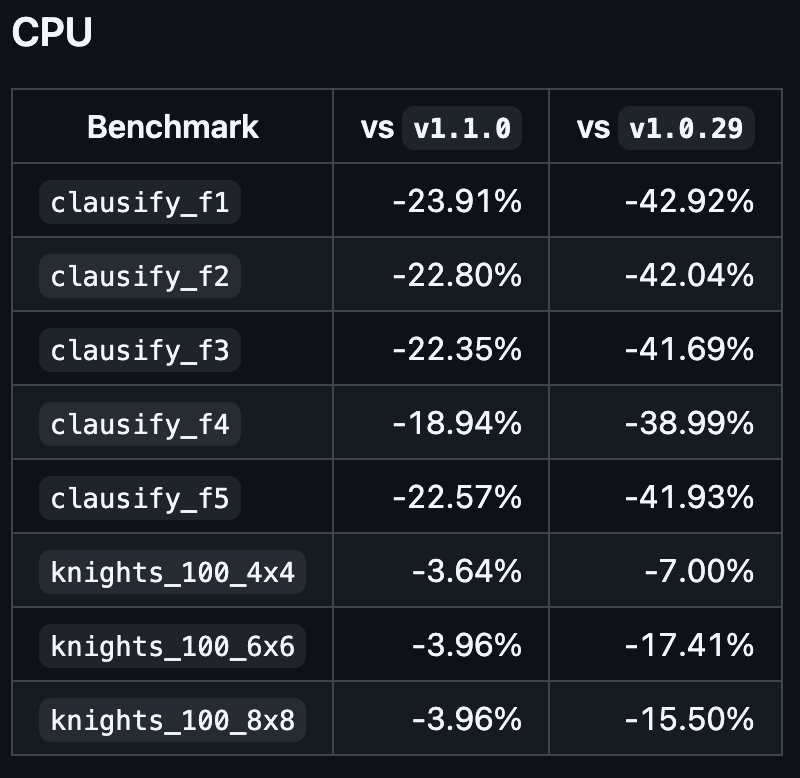
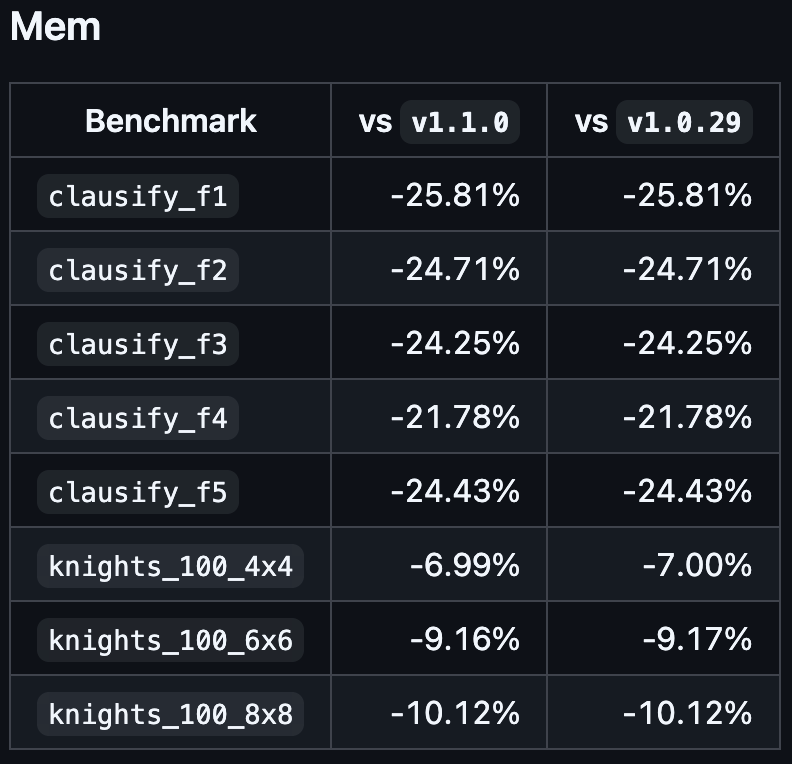
Faster Execution.
- cpu: from -4% to -24%
- mem: from -7% to -26%
LP Mint :: Mint Two
Swap A for B
NFT Marketplace: buy one
new in Aiken
New builtins.
-
and_bytearray(padded: Bool, left: ByteArray, right: ByteArray) -> ByteArray -
or_bytearray(padding: Bool, left: ByteArray, right: ByteArray) -> ByteArray -
xor_bytearray(padding: Bool, left: ByteArray, right: ByteArray) -> ByteArray -
complement_bytearray(self: ByteArray) -> ByteArray -
rotate_bytearray(self: ByteArray, offset: Int) -> ByteArray -
shift_bytearray(self: ByteArray, offset: Int) -> ByteArray -
count_set_bits(self: ByteArray) -> Int -
find_first_set_bit(self: ByteArray) -> Int -
read_bit(self: ByteArray, index: Int) -> Bool -
write_bits(self: ByteArray, indices: List<Int>, value: Bool) -> ByteArray -
replicate_byte(length: Int, byte: Int) -> ByteArray -
ripemd_160(preimage: ByteArray) -> ByteArray -
unconstr_fields(data: Data) -> List<Data> -
unconstr_index(data: Data) -> Int
new in Aiken
Maths in docs.
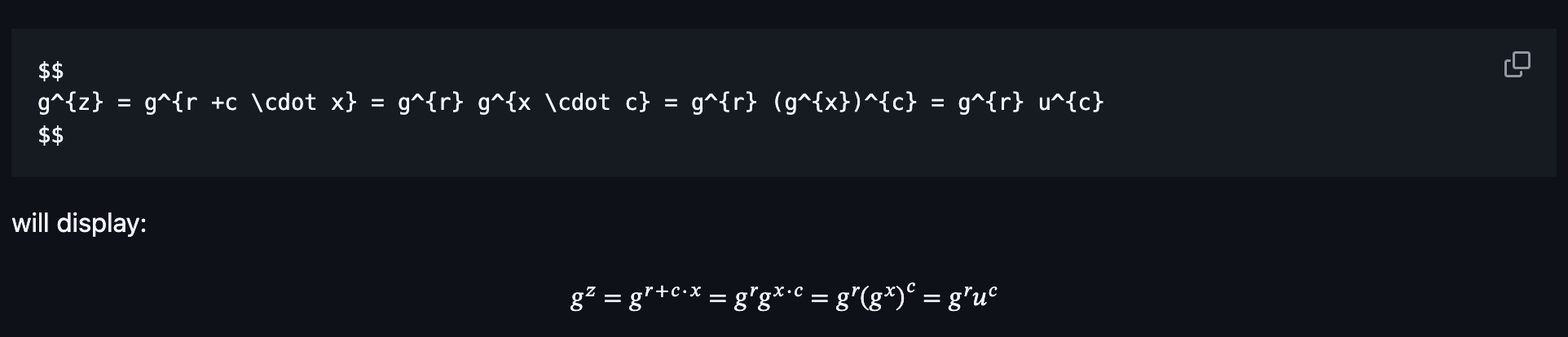

new in Aiken
Benchmarks.
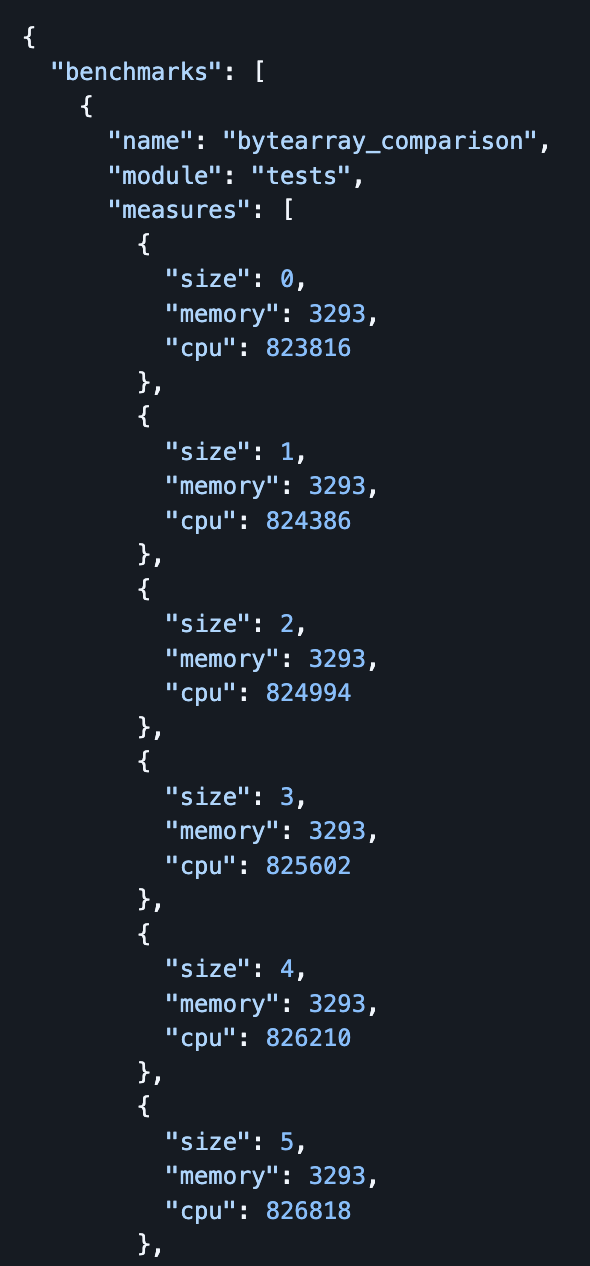

new in Aiken
Types as Namespaces
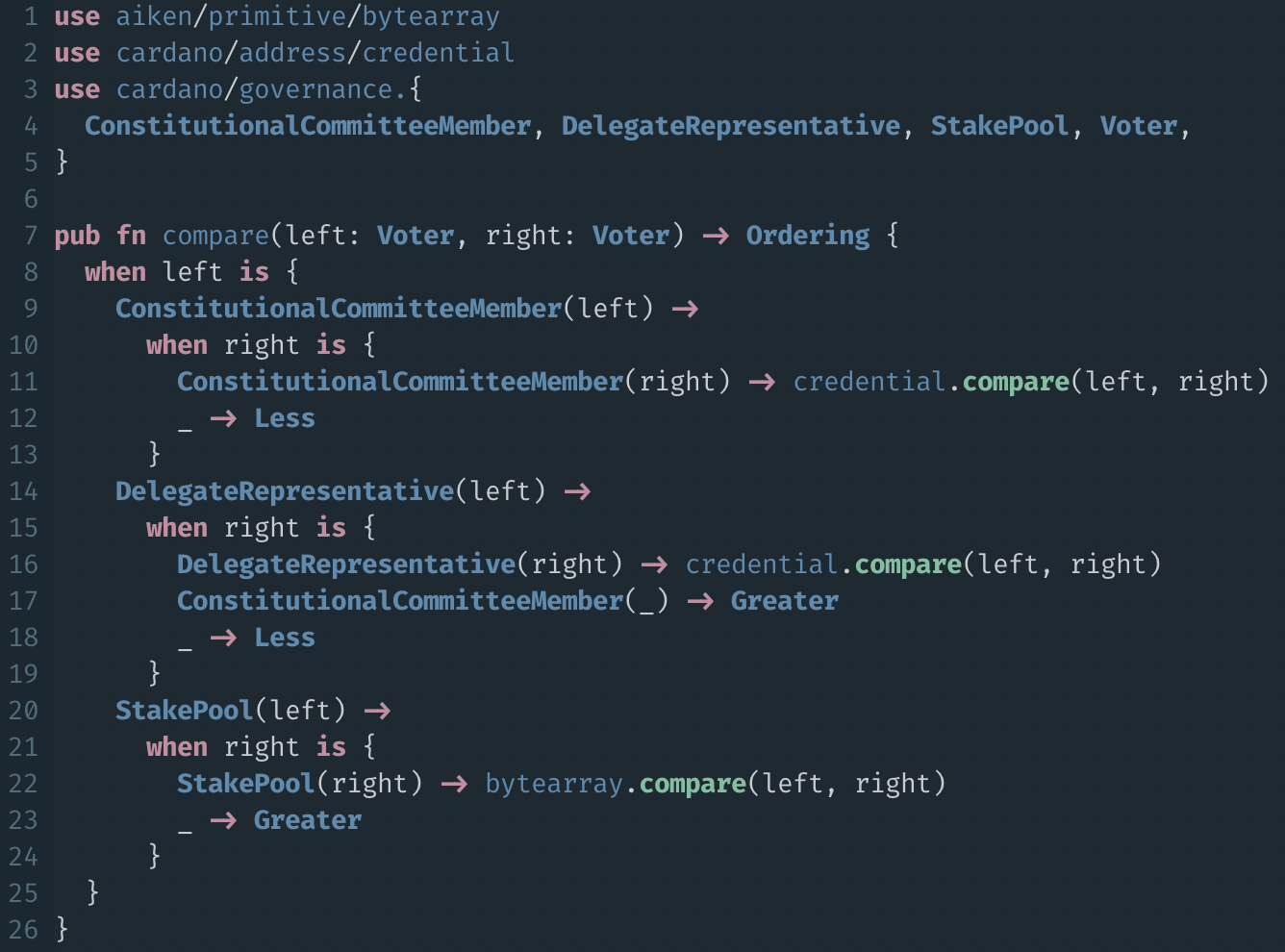
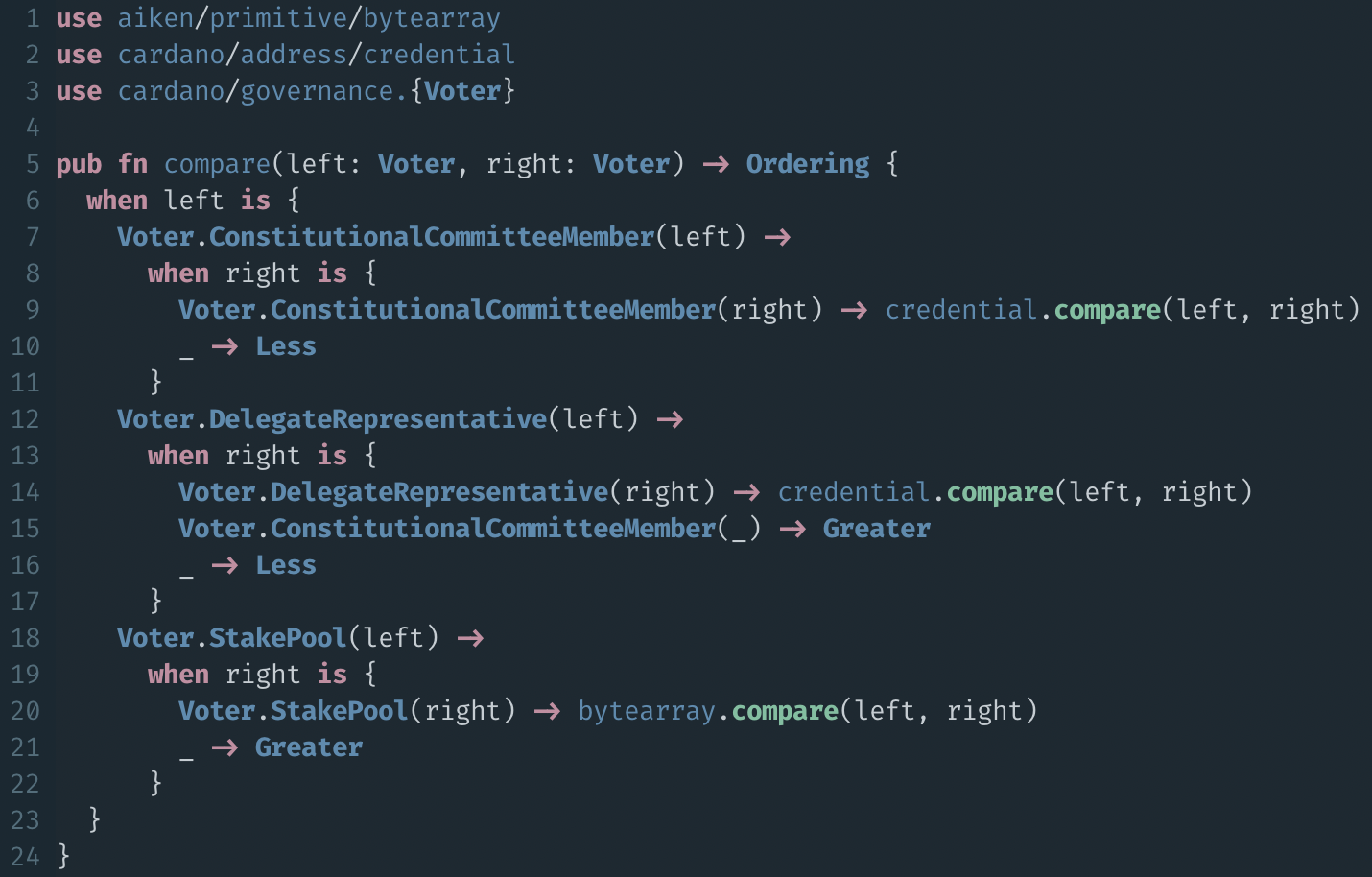
new in Aiken
Bug fixes & QoL improvements.
- Fix
aiken blueprint policycomputing hashes as PlutusV1, instead of relying on the plutus version from the Blueprint. - Fixed a code gen crash when using records in when is expressions.
- Panic error when using
aiken uplc decodeon cbor encoded flat bytes. - Comment formatting in pipelines leading to confusion.
- Preserve holes discard name in function captures. See #1080.
- Disambiguate type-alias blueprint definition using module's name. See #1074.
- Fix blueprint schema definitions related to Pairs definitions, and generate them as data List.
- Fixed
UnknownTypeConstructorwrongly reported asUnknownVariable(then messing up with LSP quickfix suggestions). - Formatter was removing comments from function type annotation args.
- Parser wrongly merged two adjacent sequences together, effectively fusioning scopes.
- Fix hint when suggesting to use named fields, wrongly suggesting args in lexicographical order instead of definition order.
- Fix
aiken blueprint applywrongly overriding all validators handlers names & ABI to the mint's one. See #1099. - Prevent (type error) backpassing blocks with empty continuation. See #1111.
- Change default placeholder for trace to Void instead of todo.
- Disallow (parse error) dangling colon
:in traces. See #1113. - Additional code action to use constructors or identifiers from qualified imports is now offered on missing constructor or identifier.
-
eval_phase_twoand related functions now return an EvalResult. - New
-Sflag oncheckandbuildthat blocks the printing of warnings but it still shows the total warning count.
- Fix
aiken blueprint policycomputing hashes as PlutusV1, instead of relying on the plutus version from the Blueprint. - Fixed a code gen crash when using records in when is expressions.
- Panic error when using
aiken uplc decodeon cbor encoded flat bytes. - Comment formatting in pipelines leading to confusion.
- Preserve holes discard name in function captures. See #1080.
- Disambiguate type-alias blueprint definition using module's name. See #1074.
- Fix blueprint schema definitions related to Pairs definitions, and generate them as data List.
- Fixed
UnknownTypeConstructorwrongly reported asUnknownVariable(then messing up with LSP quickfix suggestions). - Formatter was removing comments from function type annotation args.
- Parser wrongly merged two adjacent sequences together, effectively fusioning scopes.
- Fix hint when suggesting to use named fields, wrongly suggesting args in lexicographical order instead of definition order.
- Fix
aiken blueprint applywrongly overriding all validators handlers names & ABI to the mint's one. See #1099. - Prevent (type error) backpassing blocks with empty continuation. See #1111.
- Change default placeholder for trace to Void instead of todo.
- Disallow (parse error) dangling colon
:in traces. See #1113. - Additional code action to use constructors or identifiers from qualified imports is now offered on missing constructor or identifier.
-
eval_phase_twoand related functions now return an EvalResult. - New
-Sflag oncheckandbuildthat blocks the printing of warnings but it still shows the total warning count.
Amaru
Terminology
| Node Type | Fetch data & submit txs from peers | Validate data (i.e. do not trust peers) | Participate in txs & block propagation | Can forge & produce blocks | Can validate historical data |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data | ✅ |
❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Proxy | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Relay | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Full | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
| Archive | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
The Haskell Node
Why build another node?
Good
Bad
Ugly
Exists
Reasonably stable
Designed end-to-end
Well-documented
Archive-capable
Controlled by one entity
Unmaintainable parts
Mixing responsibilities
Hard to radically extend
Heavy resource usage
Limited monitoring
Limited/pedantic interfaces
Developed end-to-end
Challenges
Amaru's challenges
Peer management
-
Random connections to arbitrary peers.
- May or may not send valid information
- May or may not abuse our own resources
- May or may not be a sibyl actor

-
Distributed system
- Messages (i.e. blocks) typically arrive out-of-order
- Information takes time to propagate
-
PoS & block legitimacy
- Requires intrinsic knowledge (stake distribution)
- Private leader-schedule
- Blocks are computationally cheap to forge
-
Distributed
-
Unknown peers
-
No extrinsic truth
Amaru's challenges
Peer management

-
Distributed
-
Unknown peers
-
No extrinsic truth
Amaru's challenges
Multiple realities
How people typically view "the blockchain"
How it actually is
up to 2160 levels
-
Stochastic settlement
- In practice, the probability of long-fork exponentially decreases with length, but increases with adversarial stake
- Attacks still feasible with <50% of the stake
-
Potentially as many chains as there are peers
- Must track all plausible forks
- Must remember who sent what (peer management)
-
Slot battles
- Induced by the private-leader schedule
- Cause regular small forks/rollbacks
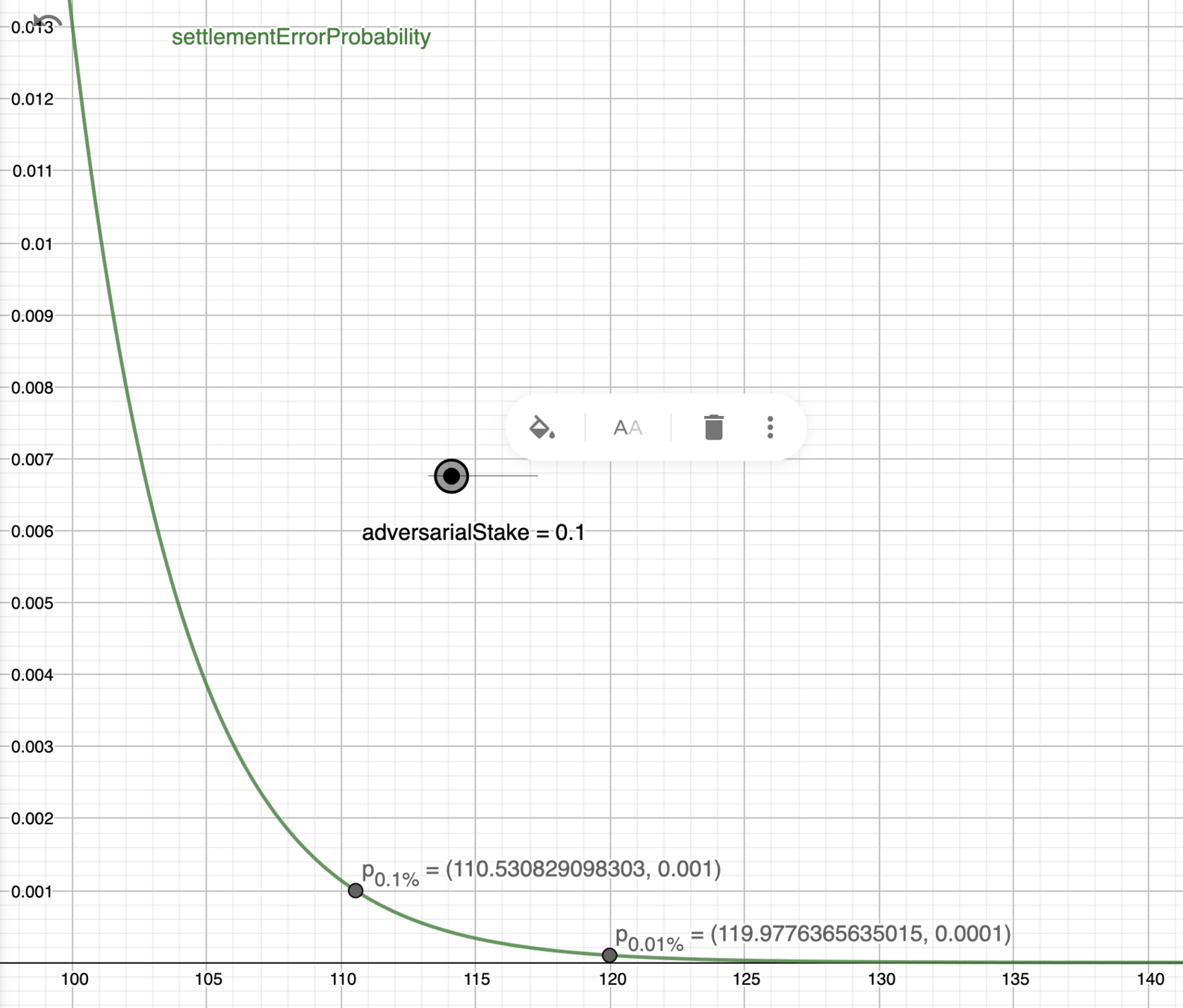
-
Private schedule
-
Stochastic
-
No single truth
Amaru's challenges
Multiple realities
How people typically view "the blockchain"
How it actually is
up to 2160 levels
-
Private schedule
-
Stochastic
-
No single truth
Amaru's challenges
Δ < 1s
-
Block propagation
-
Slow I/O
-
Binomial distribution
-
Block propagation must* reach 95% of network within 5s
- *For optimal network operation;
- Can still reach consensus otherwise but with degraded performances.
- Latency worldwide ~400-500ms
-
In practice, any block validation must be done within 1s
- Binomial distribution of blocks due to random leader schedule
- 1 block every 20s on average
- 50% of blocks between 1s and 14s
- Significant portion (5%) at 1s
- Binomial distribution of blocks due to random leader schedule
-
I/O is "slow", but required for persistence
- Trade-offs between RAM vs commodity storage
- Optimized for worse-case (Byzantine environment)
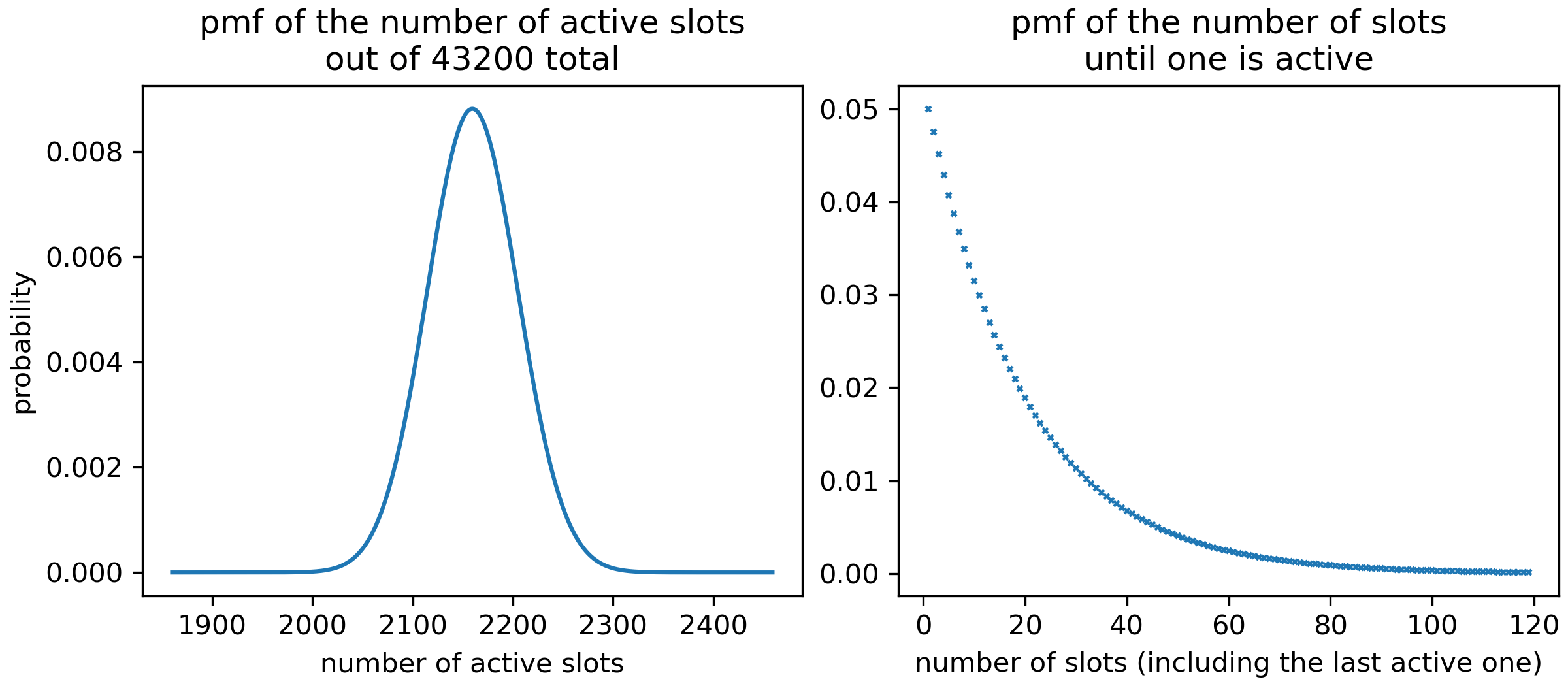

Amaru's challenges
Δ < 1s
-
Block propagation
-
Slow I/O
-
Binomial distribution

Amaru's challenges
Deferred computation
e
e+1
e+2
e+3
delegation
snapshot(e+1)
snapshot(e+2)
snapshot(e+3)
snapshot (e)
leader schedule
computed from e
computing rewards from:
- stake distr at e
- pool performances at e+2
distributing rewards
from e computed in e+3
Amaru's challenges
Deferred computation
-
Rewards are calculated using past stake distributions
- Need data from various epochs
- Mainnet: ~1.5M accounts, ~11M UTxO, ~3000 pools
- Paid directly into accounts, no on-chain materialization
- Influences leader-schedule
-
Randomness is obtained from past epochs (hence Ouroboros)
- VRF nonces made of randomness commitments collected during past epochs.
- Combined with other data from even earlier epochs.
-
Governance uses live stake distributions
- For both stake pools and DReps, live stake is used
- Computing stake distribution is long if stored on disk
- Storing stake distribution in memory increase resource usage
-
Rewards
-
Cyclic randomness
-
Governance

e
e+1
e+2
e+3
snapshot (e)
delegation
snapshot(e+1)
snapshot(e+2)
snapshot(e+3)
leader schedule
computed from e
computing rewards from:
- stake distr at e
- pool performances at e+2
distributing rewards
from e computed in e+3
Amaru's challenges
Deferred computation
-
Rewards
-
Cyclic randomness
-
Governance


