Why Nations Fail Illustrated
Lecture5
Origins of Inclusive Institutions #1: Why England, not Spain?
November 6, 2018
Masayuki Kudamatsu
Chapter 4 & pp. 208-212

Today's Road Map
Black Death and
the divergence of Western and Eastern Europe
Rise of Atlantic trade
and the divergence of England and Spain
Critical junctures
and the divergence of institutions
Term paper preparation #1

Today's Road Map
Black Death and
the divergence of Western and Eastern Europe
Rise of Atlantic trade
and the divergence of England and Spain
Critical junctures
and the divergence of institutions
Term paper preparation #1
Black Death: 1346-1353
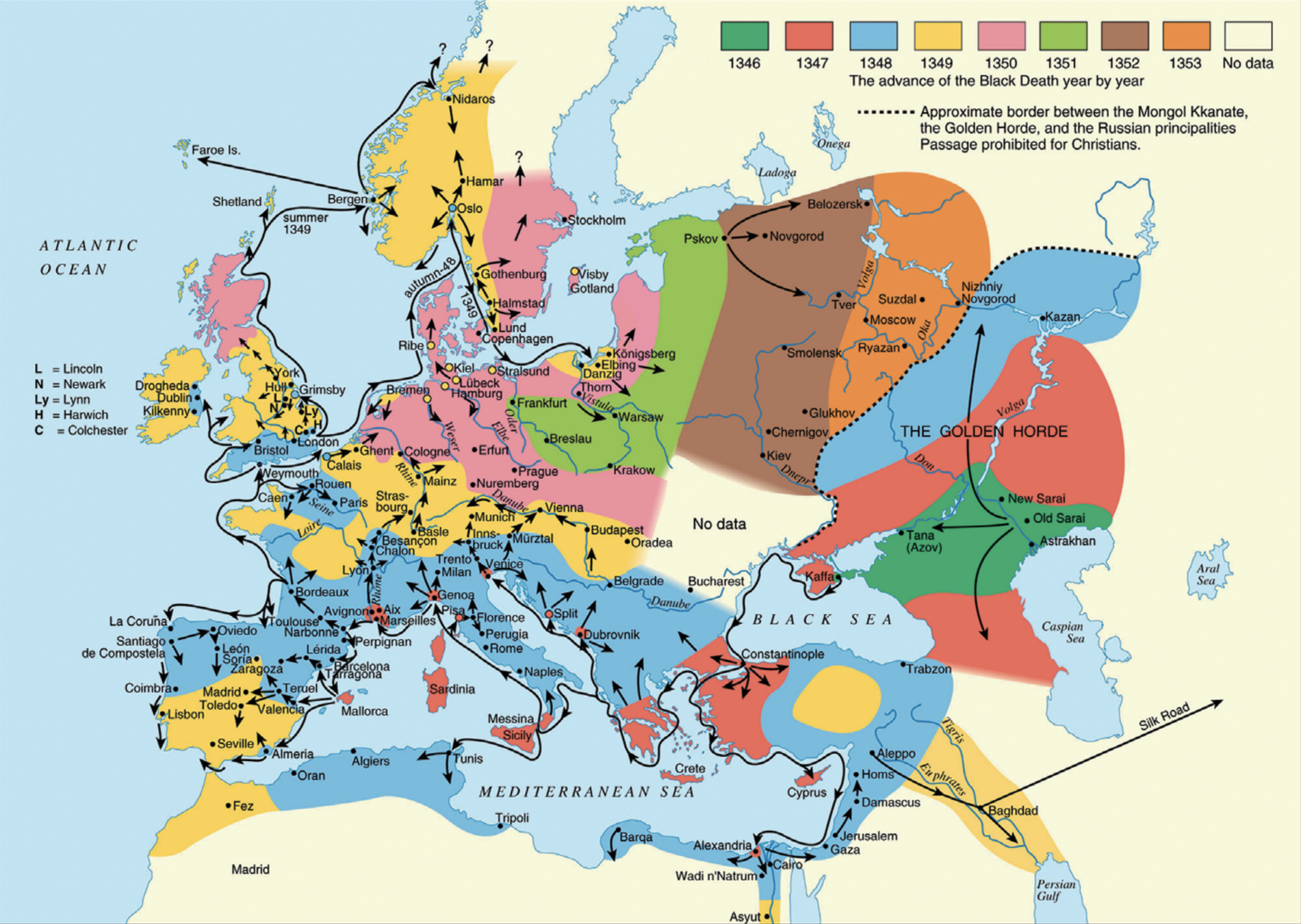
Source: Figure 1 of Cesana, Benedictow, and Bianucci (2017)
Wiped out about half of the population in Europe
Economic institutions in 14th-century Europe
King
Lords
Peasants
(Serfs)
Land
Military services
Unpaid labor,
Fines, Taxes
Land
Peasants need permission from lords to move out
cf. Ethiopia's gult system (Lecture 4)
Feudalism
Feudalism is a form of forced labor
| economic institutions | ||
|---|---|---|
| Secure for everyone |
Property rights | Insecure for majority of people |
| Free | Occupational choice |
Forced labor |
| Free | Entry of new businesses | Prevented by monopolies |
| Unbiased | System of laws | Biased for the powerful/rich |
| Promoted | Public service provision | Discouraged |
Economic Institutions
Inclusive
Extractive
Property rights
Secure for everyone
Insecure for
majority of people
Occupational choice
Free
Forced labor
Entry of
new businesses
Free
Prevented by
monopolies
System of laws
Unbiased
Biased for
the powerful / rich
Public service provision
Provided
Limited
Feudalism is thus extractive econ. institutions
However, Western and Eastern Europe were not completely the same at that time
Rise of towns in Western Europe by 1300
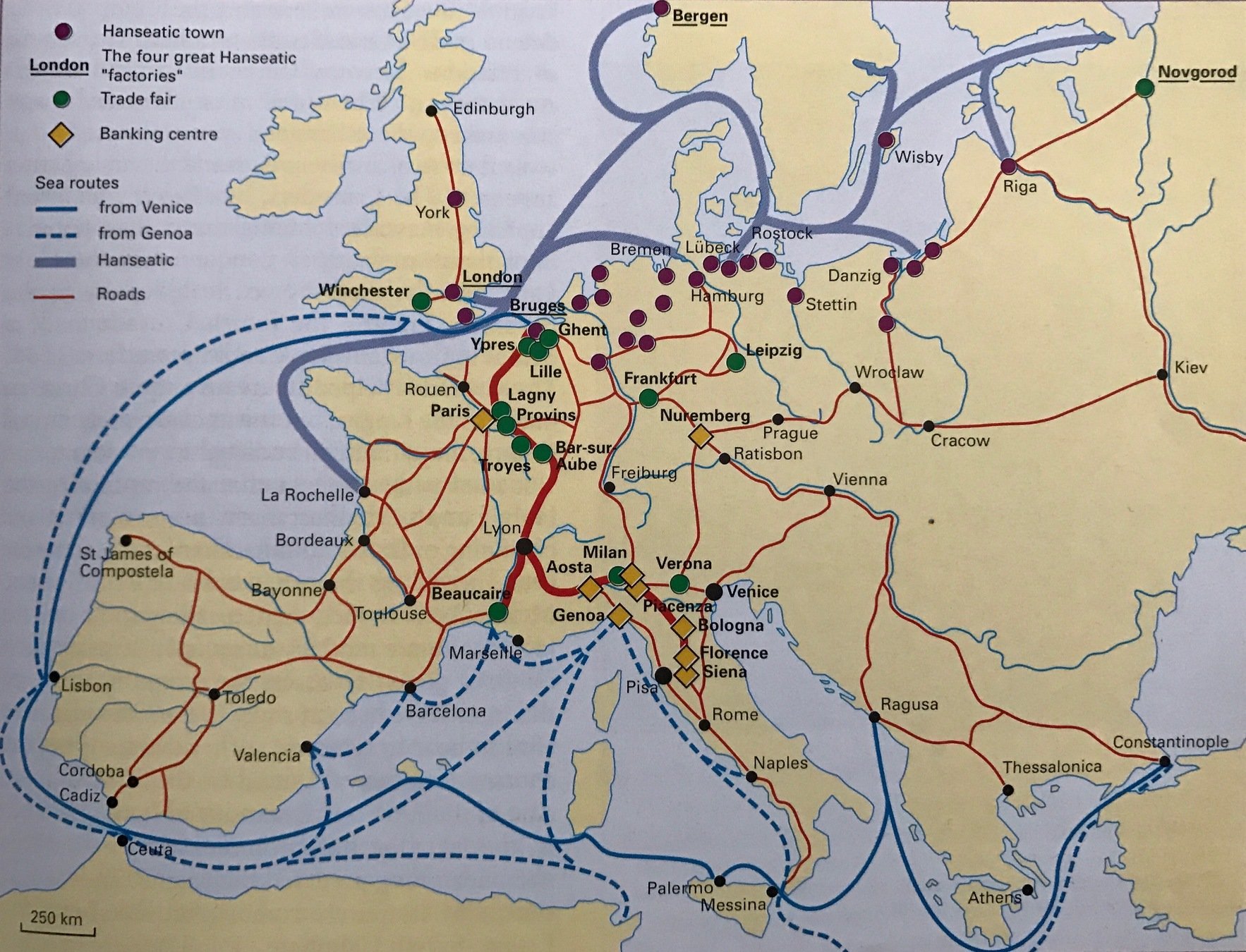
Source: Frederic Delouche ed. (2001) Illustrated History of Europe (2nd ed.) Cassell & Co, p. 147
Peasants in Western Europe could escape into these towns
Western Europe:
Rise of towns
Peasants have bargaining power
Eastern Europe:
Dominantly rural
Lords (relatively) powerful
Divergent path btw. Western/Eastern Europe
NOTE:
Chapter 4 of Why Nations Fail does not
(1) mention peasants' bargaining power
(2) explain why towns made a difference
This lecture note is based on Acemoglu and Wolitzky (2011), which is cited as the source for Chapter 4 (page 469)
Western Europe:
Rise of towns
Peasants have bargaining power
Eastern Europe:
Dominantly rural
Lords (relatively) powerful
Black Death
Peasants' demand for freedom prevailed
End of Feudalism
Divergent path btw. Western/Eastern Europe
Case of England
Statute of Laborers of 1351
Punish peasants for leaving employment w/o permission of lords
Peasants' Revolt of 1381
Rebels, led by Wat Tyler, captured most of London
The English state gave up enforcing Statute of Laborers

Image source: luminarium.org
Western Europe:
Rise of towns
Peasants better-organized
Eastern Europe:
Dominantly rural
Lords (relatively) powerful
Black Death
Peasants' demand for freedom prevailed
End of Feudalism
Lords intensified forced labor
Second Serfdom
Divergent path btw. Western/Eastern Europe
Western Europe:
Rise of towns
Peasants better-organized
Eastern Europe:
Dominantly rural
Lords (relatively) powerful
Black Death
Peasants' demand for freedom prevailed
End of Feudalism
Lords intensified forced labor
Second Serfdom
Divergent path btw. Western/Eastern Europe
Rising demand for foods
in Western Europe after 1500
e.g.
Unpaid works in Second Serfdom
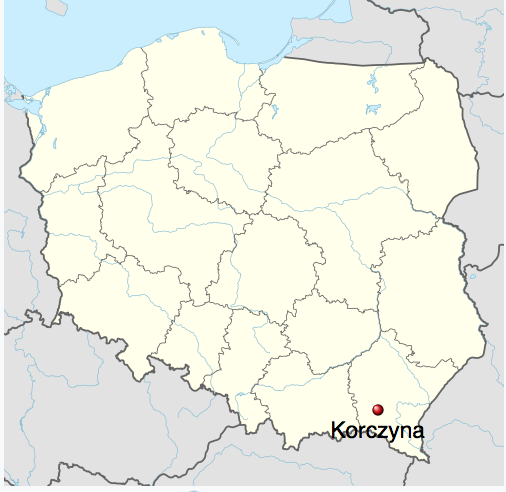
Korczyna in Poland
About 50% of works in 1600
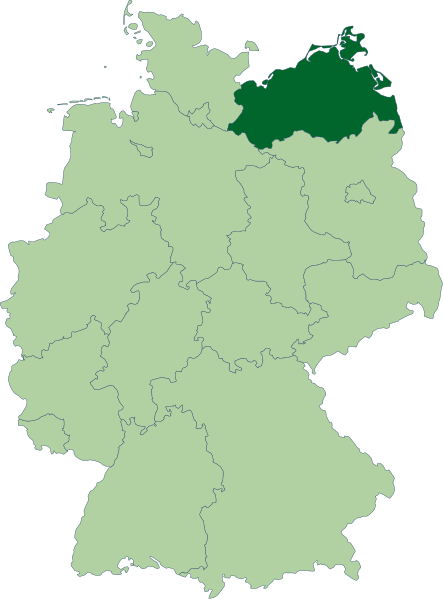
Mecklenburg in eastern Germany
1 day per week in 1550
3 days per week in 1600
Hungary
By legislation, 90% of rural population forced to work unpaid
1 day per week in 1514, 2 days in 1550, 3 days by 1600

Today's Road Map
Black Death and
the divergence of Western and Eastern Europe
Rise of Atlantic trade
and the divergence of England and Spain
Critical junctures
and the divergence of institutions
Term paper preparation #1
Rise of Atlantic Trade in 16th century
"Discovery" of the Americas
by Christopher Columbus
in 1492
Massive trade opportunities opened up
Precious metals (gold, silver, etc.)
Plantation crops
Slaves

Landing of Columbus (12 October 1492), painted by John Vanderlyn
Image source: Wikimedia Commons
Political institutions in England vs Spain in 1500s
Both had an assembly of citizens
Parliament in England (Lecture 3)
Monarch needed to consult with them to raise new taxes
Monarch was (only slightly) weaker in England than in Spain
Scope of taxation: larger in England
Representation by parliament: broader in England
England:
(relatively) Strong
Parliament
Spain:
(relatively) Weak
Cortes
Rise of Atlantic Trade
Merchant class emerged
Monarch monopolized trade
Divergent path between England & Spain
702 exporters &
1283 importers
in London
by 1688 (p. 210)
Spanish monarch
financially
independent
from Cortes
England:
(relatively) Strong
Parliament
Spain:
(relatively) Weak
Parliament
Rise of Atlantic Trade
Merchant class emerged
Glorious Revolution of 1688
Crown monopolized trade
Absolutism persisted
Divergent path between England & Spain (cont.)
England:
(relatively) Strong
Parliament
Spain:
(relatively) Weak
Parliament
Rise of Atlantic Trade
Merchant class emerged
Glorious Revolution of 1688
Crown monopolized trade
Absolutism persisted
But this divergence could have been reversed
Invasion of Spanish Armada in 1588

English privateers challenged Spanish monopoly of Atlantic trade
The Spanish Crown
sent its Invincible Armada
to attack England
Image source: Wikimedia Commons
England:
(relatively) Strong
Parliament
Spain:
(relatively) Weak
Parliament
Rise of Atlantic Trade
Merchant class emerged
Glorious Revolution of 1688
Crown monopolized trade
Absolutism persisted
But this divergence could have been reversed
Spanish Armada in 1588
Defeat of Spanish Armada in 1588
Bad
weather
Last-minute appointment
of Spanish command-in-chief

English privateers challenged Spanish monopoly of Atlantic trade
The Spanish Crown
sent its Invincible Armada
to attack England
England defeated Spanish Armada, largely by chance
+
Image source: Wikimedia Commons
England:
(relatively) Strong
Parliament
Spain:
(relatively) Weak
Parliament
Rise of Atlantic Trade
Merchant class emerged
Glorious Revolution of 1688
Crown monopolized trade
Absolutism persisted
Defeat of Spanish Armada in 1588
Divergent path between England & Spain

Today's Road Map
Black Death and
the divergence of Western and Eastern Europe
Rise of Atlantic trade
and the divergence of England and Spain
Critical junctures
and the divergence of institutions
Term paper preparation #1
Society A:
(slightly) more inclusive
Society B:
(slightly) more extractive
Theory of institutional divergence (1/4)
No two societies create the same institutions
Society A:
(slightly) more inclusive
Society B:
(slightly) more extractive
Critical Juncture
Theory of institutional divergence (2/4)
Black Death in 14c
Rise of Atlantic trade in 15c
Industrial Revolution in late 18c
European colonization
Examples
Society A:
(slightly) more inclusive
Society B:
(slightly) more extractive
Critical Juncture
Theory of institutional divergence (3/4)
Power balance tilted for the ruled
Power balance tilted for the rulers
Society A:
(slightly) more inclusive
Society B:
(slightly) more extractive
Critical Juncture
Power balance tilted for the ruled
Inclusive institutions
Power balance tilted for the rulers
Extractive institutions
Theory of institutional divergence (4/4)

Today's Road Map
Black Death and
the divergence of Western and Eastern Europe
Rise of Atlantic trade
and the divergence of England and Spain
Critical junctures
and the divergence of institutions
Term paper preparation #1
Pick a country
And discuss whether
Theory of Why Nations Fail can
explain economic performances
of the country of your choice
Term Paper
Inclusive Economic Institutions
Economic Growth
Inclusive Political Institutions
Theory of Why Nations Fail
Extractive Economic Institutions
Economic Stagnation
Extractive Political Institutions
Inclusive Economic Institutions
Economic Growth
Inclusive Political Institutions
So you need to know that in the country of your choice...
Extractive Economic Institutions
Economic Stagnation
Extractive Political Institutions
Are political institutions
inclusive
or
extractive?
Inclusive Economic Institutions
Economic Growth
Inclusive Political Institutions
So you need to know that in the country of your choice...
Extractive Economic Institutions
Economic Stagnation
Extractive Political Institutions
Are economic institutions
inclusive
or
extractive?
Inclusive Economic Institutions
Economic Growth
Inclusive Political Institutions
So you need to know that in the country of your choice...
Extractive Economic Institutions
Economic Stagnation
Extractive Political Institutions
Is the economy
growing
or
stagnated?
Inclusive Economic Institutions
Economic Growth
Inclusive Political Institutions
If it turns out, for example, ...
Extractive Economic Institutions
Economic Stagnation
Extractive Political Institutions
The theory fails
Inclusive Economic Institutions
Economic Growth
Inclusive Political Institutions
If it turns out, for example, ...
Extractive Economic Institutions
Economic Stagnation
Extractive Political Institutions
The theory fails
Inclusive Economic Institutions
Economic Growth
Inclusive Political Institutions
Evidence is consistent with the theory if
Extractive Economic Institutions
Economic Stagnation
Extractive Political Institutions
It would be nicer if you find
evidence for causality
Inclusive Economic Institutions
Economic Growth
Inclusive Political Institutions
Evidence is consistent with the theory if
Extractive Economic Institutions
Economic Stagnation
Extractive Political Institutions
It would be nicer if you find
evidence for causality
So you need to find information on
Economic Institutions
Economic Performance
Political Institutions
So you need to find information on
Economic Institutions
Economic Performance
Political Institutions
Today we learn where to learn economic performance
Measure of economic performance
GDP per capita
Average annual income of a person living in the country
For detail, pick any introductory textbook on macroeconomics such as Jones (2017), Mankiw (2018), Acemoglu et al. (2018)
Data source for GDP per capita
Published by the World Bank
1. Click the link above

2. Click
3. Type "GDP per capita"

Which should you choose?
Then you'll see this:
You need to understand "current", "constant", and "PPP"
GDP in current $ (aka. nominal GDP)
"Current" doesn't take into account inflation
Economic growth typically comes with inflation
Ignoring inflation will overrepresent economic growth
100 yen in 1960 = 568.29 yen in 2018 (source: InflationTool.com)
e.g.
Some poor countries suffer from hyperinflation
e.g.
1,000,000% in Venezuela in 2018 (source: Reuters)
GDP in constant $ (aka. real GDP)
"Constant" does take into account inflation
GDP
(constant 2010 $)
GDP
(current $)
Inflation rate
since 2010
=
PPP (Short for "Purchasing Power Parity")
Used for international comparison
Foreign exchange rate
Many services (e.g. haircut) are not exported or imported
Investors speculate in the currency market
Japanese yen appreciates
whenever the world economy becomes uncertain
e.g.
price level difference across countries
PPP (cont.)
PPP is the "real" exchange rate
e.g.
Very simple version of PPP: the Big Mac index

Image source: The Economist
WDI's PPP is based on
cross-country price surveys by International Comparison Program

Then which indicator should you use?
Create a graph
Once you choose the indicator, click it.
Then click "DataBank" on the lower right.
Select "Country" and "Time". Click "Chart" on top right

WDI dates back to 1960 at most
Historical GDP data
provides the best estimates of historical GDP data
October 30
Chapter 4
November 6
Chapter 1
November 13
Chapter 10
United States
vs Mexico
from colonization
to early 20c
Weeks 5-7: Origins of inclusive institutions
Western
vs Eastern Europe
after Black Death
in 14c
Spain vs England
after Rise of Atlantic
Trade in 16c
Australia
French Revolution
and its spread to
Western Europe
Japan vs China
in 19c
Next week
Your to-do list until next class
Pick a country for your term paper
and post it on Prulu (if you haven't)
Read Chapter 1
and post questions on Prulu
1
2
3
Visualize the economic performance of the country of your choice